AP Human Test 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
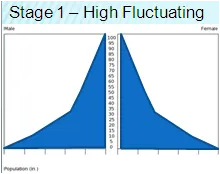
Stage 1 (name, example, br, dr)
Name: High Fluctuating
Current Example: Amazon, Basin tribes
Birthrate: High
Deathrate: High
Natural Increase: Stable or slow
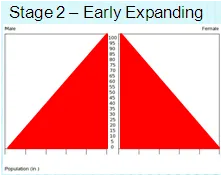
Stage 2 (name, example, br, dr)
Name: Early Expanding
Current Example: Ethiopia
Birthrate: High
Deathrate: RAPIDLY FALLS
Natural Increase: Very big increase
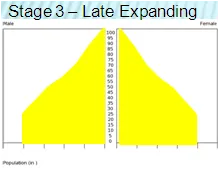
Stage 3 (name, example, br, dr)
Name: Late Expanding
Current Example: India, Brazil
Birthrate: falling
Deathrate: falling slowly
Natural Increase: increase at a slower rate
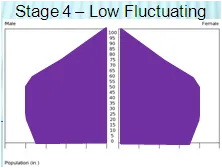
Stage 4 (name, example, br, dr)
Name: Low fluctuating
Current Example: UK, USA
Birthrate: low
Deathrate: low
Natural Increase: stable or slow increase
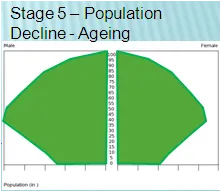
Stage 5 (name, example, br, dr)
Name: Decline
Current Example: Russia, Germany, Japan
Birthrate: Very low
Deathrate: low
Natural Increase: slow decrease
Population Distribution
Spread of people across the earth
pattern of human settlement
Does not change
Population density
Measure of Average population per square mile
Does increase
Why does population density / population distribution matter?
Set boundaries for electrical districts and housing
Ecumene
A term geographers use that means inhabited land
Who was Thomas Malthus
English economist
Anglican, very anti catholic
Worried that British population was rising to fast, especially among the poor
Malthusian Catastrophe
The idea that the human population will grow more then the ability to produce food bc humans grow exponentially while food grows linearly. Not True!!
What did Thomas Malthus want to be done?
Preventive checks: Birth Control, Abstinence, Moral Education (cut birth rates)
Negative checks: Famine, Disease
What did Thomas Malthus’s negative check ideas lead to?
Stop giving assistance to the poor
Irish Potato Famine and British did nothing to help
Social Darwinism - Herbert spencer thought Europeans were “fittest” and “most evolved” which lead to racism, white supremacy, an excuse/reason for colonialism
Eugenics - The practice of improving the human species by selectivity mating people with “desirable” traits.
Neo-Malthusianism
Paul Ehrlich wrote a book call “population bomb” about this theory
Concerns over resource depletion by over consumption
Sounds like….. Environmental Determinism
A theory extended from Thomas Mauthus’s theory but more modern
What is the biggest factor in why people move today?
Economics
Key facts about Physical factors
Early survival depended on food, water, and shelter
As population increases, population density increases
Most people live in midlatitudes - more moderate climates and better soil
Low-lying areas typically have better soil and are close to the ocean
Close to the ocean = good living
People today can move more easily
People move near things that make there life easier
Arithmetic density formula
Regions population / total area of a region
Note: Does not tell you how distributed they are in the area
Physiological density
Dividing regions population/amount of arable land
A high physiological density indicates that many people rely on a limited amount of arable land
Agricultural density
Number of farmers / arable land
Developed countries = more farmers, developing countries = more farmers
Tells you how developed a country is
Compare Bangladesh to the Netherlands
What does population density and distribution imply?
Businesses earn more when located near a large costumer base
Manufacturing plants are closer to large labor force
Urban districts are usually smaller then rural but this is changing in America
Ex: People want to live in America because of the economic opportunities therefore there are more people living in cities.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum number of individuals of a species (humans) that an environment can sustainably support without degrading the ecosystem.
Population composition
People with the same ethnic group cluster in particular regions
Age shapes public policy
Many children = schools
Many old people = old people homes
Gender of a population is effected by war, migration, mining collages
What do population pyramids tell us?
Gender, age, and precent of population in each group
Impacts of war on population
Affects people of all ages but more specifically men between 18-40
Men and women are separated therefore there is a decline in birth rates, this is called a birth deflect
Once war ends there is normally a baby boom
Baby Boom, Bust, Echo
Boom: A big spike in population
Bust: little decline until the boomers reach child-bearing age
Echo: spike again bc the baby boomers are having kids
Dependency Ratio
Comparing the working to the non working (working:nonworking)
Population pyramid data is used to estimate the dependency ratio
Population Pyramids: Stage 1
High Fluncating
No
Pronatalist vs Antinatalist
Pronatalist: Supports high birth rates and population growth
Aninatalist: Does not support high birth rates / population growth
Stage 1 Pyramid
Stage 2 pyramid
Stage 3 pyramid
Stage 4 Pyramid
Stage 5 Pyramid