DPT 604: Hematologic System
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
transportation, regulation and protection
3 key functions of blood
oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, waste products
key components that blood transports
pH, body temperature and fluid balance
what does blood help regulate?
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells responsible for oxygen transport.
leukocytes
White blood cells involved in immune response and fighting infections
thrombocytes or platelets
blood cell type responsible for assisting with clotting
hematopoiesis
formation of blood cells
bone marrow
where are blood cells made?
spoon nail
this nail deformity can be an indication of iron deficiency and anemia
little to no trauma, lasting longer than normal, present in stool or emesis
when does bleeding/bruising become a concern?
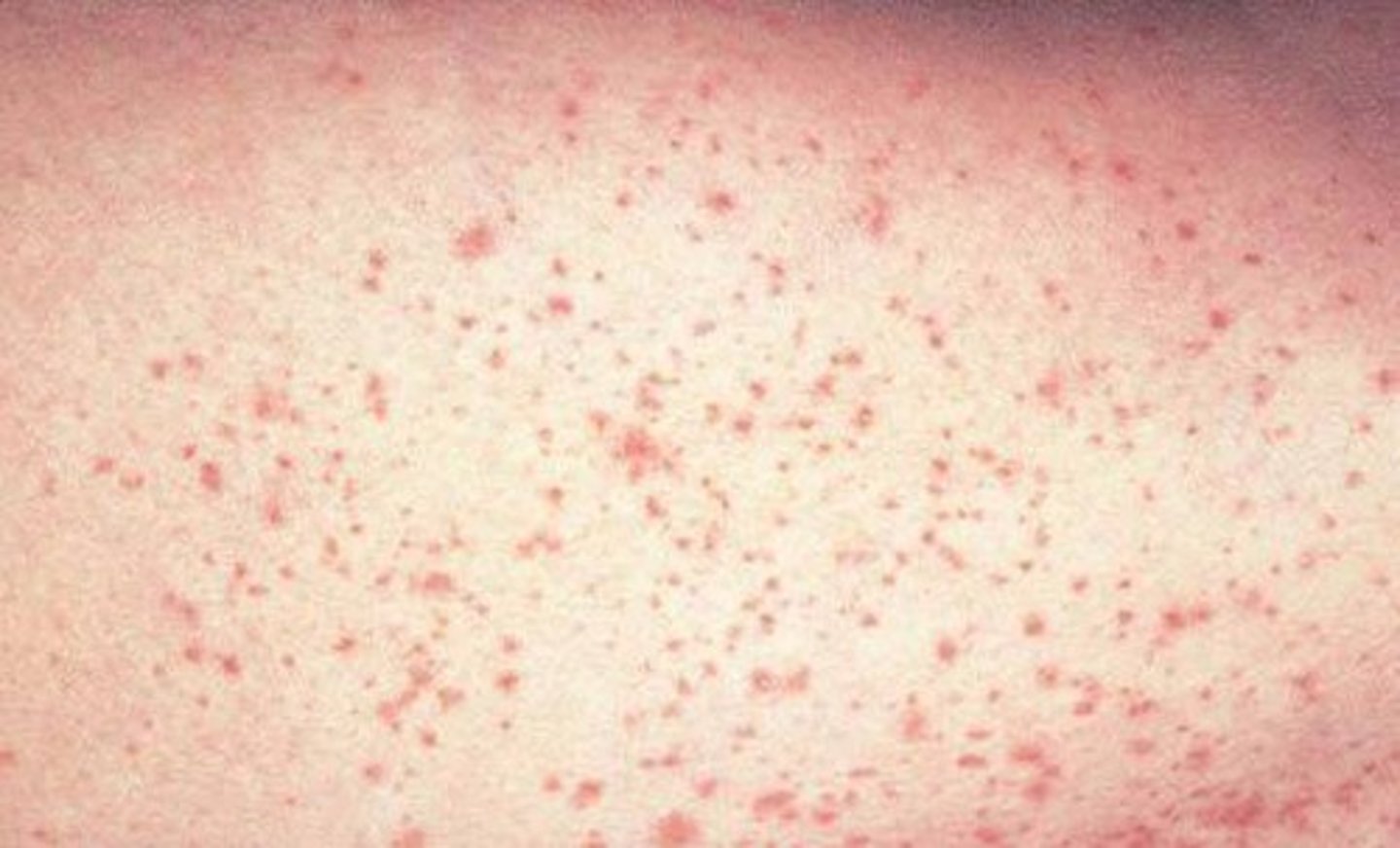
petechiae
smallest, flat, pin-point red/purple spot
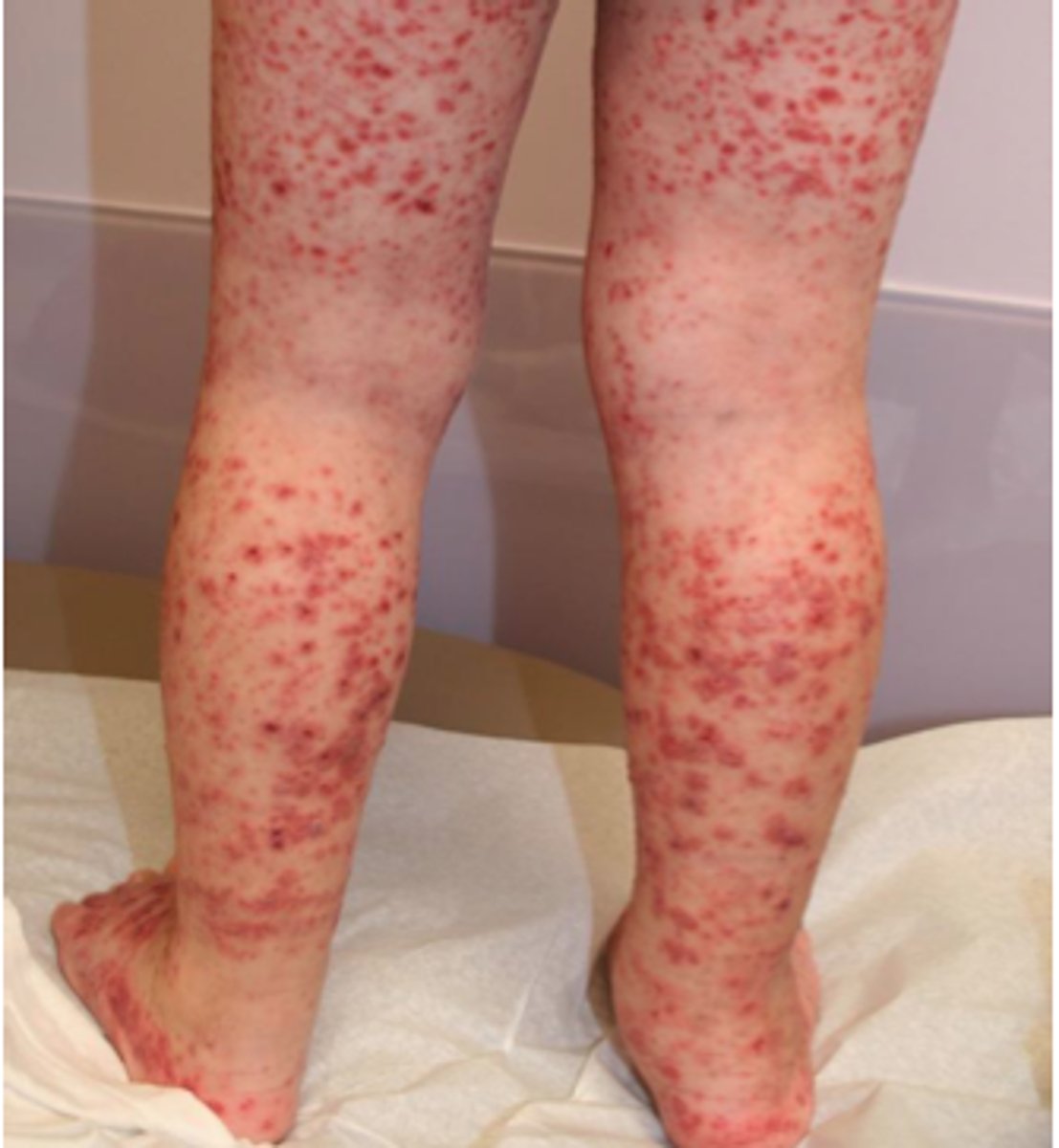
purpura
larger flat spots
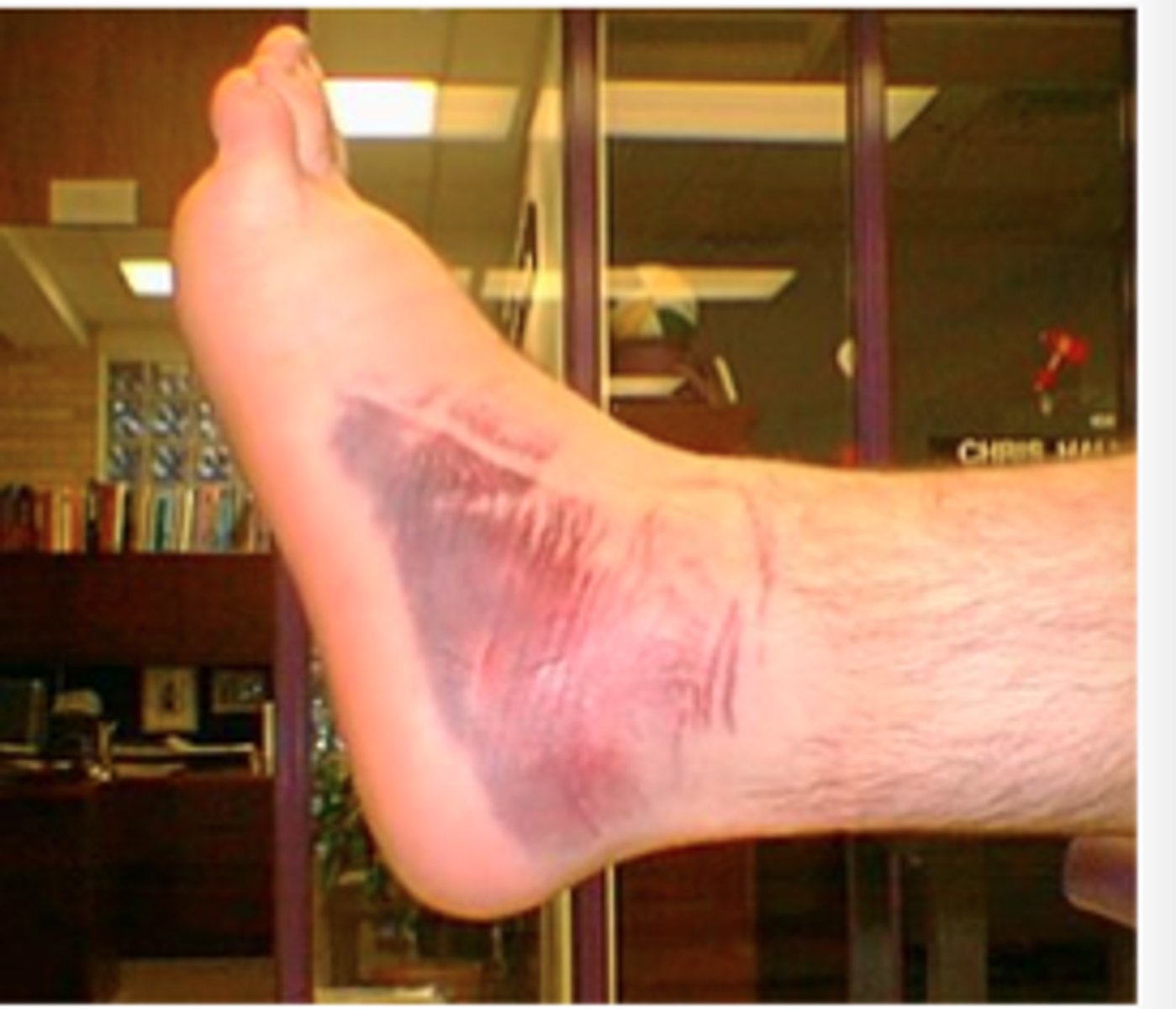
ecchymoses
AKA bruise or contusion; flat area of discolored skin
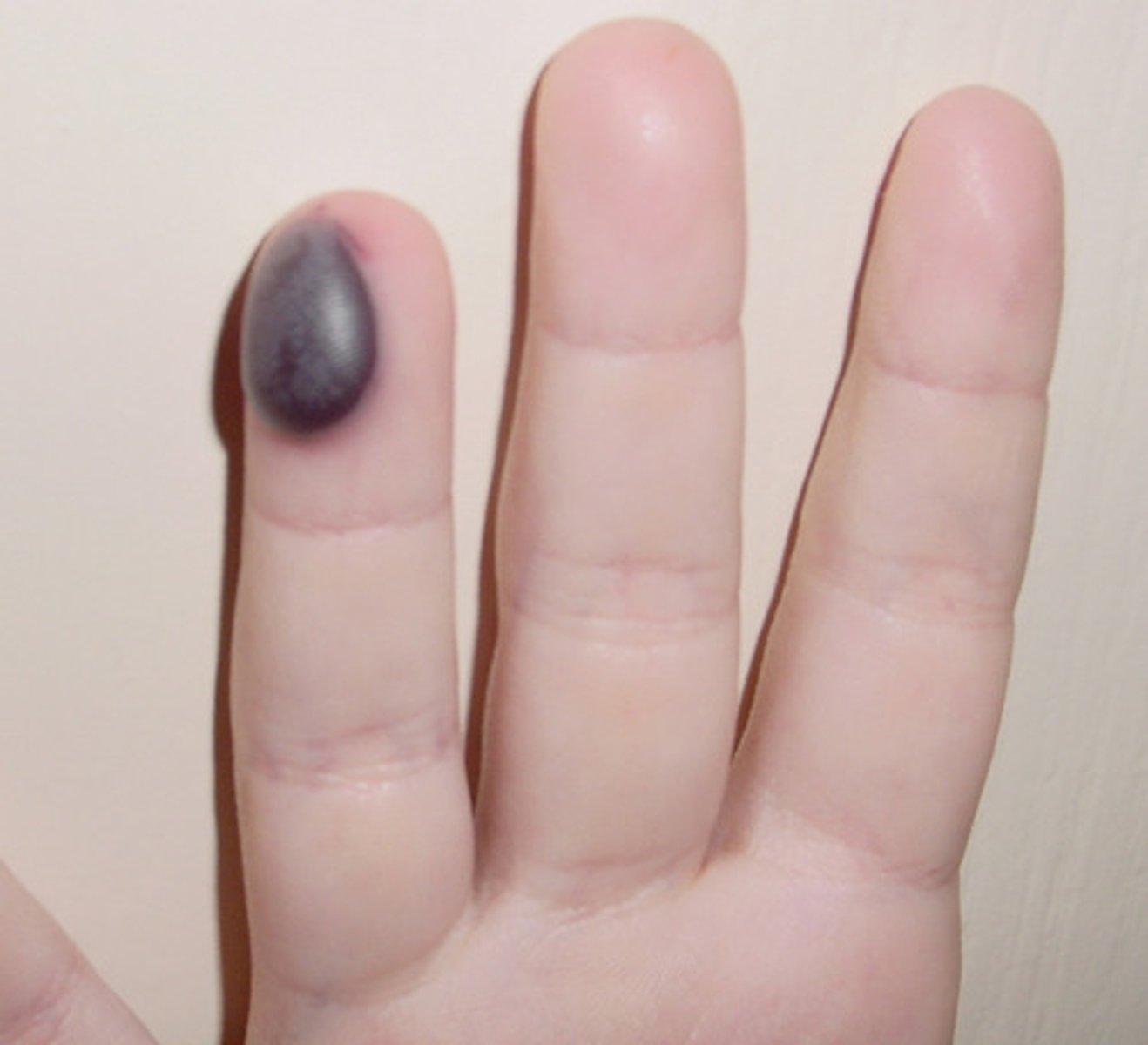
hematoma
large, localized collection of blood (often clotted) outside vessels; usually raised and palpable. can be painful
thrombus
solid mass of clotted blood within a blood vessel or heart chamber
embolus
mass of solid, liquid or gas that travels to lodge at distant site
congestion
accumulation of blood within blood vessels of organs or tissues
infarction
region of necrosis caused by reduction of arterial perfusion
edema
accumulation of fluid in interstitial tissues or body cavities
lymphedema
accumulation of lymph fluid in interstitial space
lymphadoenopathy
disease of lymph nodes
splenomegaly
enlargement of the spleen
shock
circulatory system unable to maintain adequate pressure to perfuse organs
etiology and pathophysiology of anemia
RBC cannot transport the sufficient amount of oxygen to meet the need of the body; lack of iron, lack of RBC. can be due to loss of too much blood or abnormal cell shape/function
symptoms of anemia
paleness/yellowing of skin
fatigue/dizziness
Changed stool color
SOB
Weak mm
Low BP
Decreased exercise tolerance
Severe: fainting, chest pain, angina, MI
diagnosis and treatment for anemia
Dx: CBC
Tx: diet, iron supplements, transfusion if severe. It all depends on cause
etiology and pathophysiology of polycythemias
The increased RBC increase blood viscosity and blood volume
Primary: polycythemia vera (neoplastic disease of bone marrow)
Secondary: due to underlying medical conditions/external factors (altitude change, smoking)
Increase # of RBC
signs and symptoms of polycythemias
SOB
Fatigue
Blurred vision
Fullness in head
Weight loss
Bruising
etiology and pathophysiology of Hemochromatosis
Genetic condition (mutation)
Body cannot break down iron in blood, iron overload
Increased iron absorption of the small intestine
signs and symptoms of Hemochromatosis
Skin bronzing, joint pain (iron fist sign), weakness, fatigue, abdominal pain
diagnosis and treatment for Hemochromatosis
Dx: blood test/genetic screening
Tx: therapeutic phlebotomy
etiology and pathophysiology of Thrombocytopenia
Inadequate production of bone marrow
Increased platelet destruction
Splenic sequestration
Causes: medications/supplements, cancer, bone marrow issues, alcohol use
Low platelet count
signs and symptoms of Thrombocytopenia
Bleeding
Easy bruising
Mennoragia
diagnosis and treatment for Thrombocytopenia
Dx: CBC
Tx: treat underlying cause, platelet transfusion
etiology and pathophysiology of Thrombocytosis
High platelet count
Primary & secondary
signs and symptoms of Thrombocytosis
clotting/thrombosis
Asymptomatic until higher
diagnosis and treatment of Thrombocytosis
Dx: CBC
Tx: treat underlying cause, platelet transfusion
etiology and pathophysiology of Leukopenia
Infections, autoimmune disorders, bone marrow failure/suppression, diseases, medications
Low WBC count
signs and symptoms of Leukopenia
⬆️infection risk, fever, fatigue, mouth ulcers
diagnosis and treatment of Leukopenia
Dx: CBC w/ differential, eval leukocyte count. Maybe bone marrow biopsy
Tx: depends on underlying cause
etiology and pathophysiology of Leukocytosis
Inflammation, infection, severe stress/pain, steroids
Increased WBC count
signs and symptoms of Leukocytosis
Often asymptomatic; fever, infection signs, inflammation,
diagnosis and treatment of Leukocytosis
Dx: CBC w/ differential, eval leukocyte count. Maybe bone marrow biopsy
Tx: depends on underlying cause
etiology and pathophysiology of Leukemias
Originate in blood forming tissue
Risk factors: radiation exposure, chemical exposure, genetic disorders, family hx
Abnormal proliferation of WBC
Acute: accumulation of immature cells; aggressive, higher death rate
Chronic: prolonged course; accumulation of more mature
signs and symptoms of leukemias
Anemia
bleeding/bruising
Bone pain
diagnosis and treatment of leukemias
Dx: CBC, blood smear, bone marrow biopsy
Tx: varies by type: chemo, HCT
etiology and pathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma
Cancer originating in plasma cells in the bone marrow
Idiopathic
Risk factors: old age, chemical exposures, genetic mutations
B-lymphocytes differentiated
Malignant cells invade bone marrow
signs and symptoms of Multiple Myeloma
CRAB
Calcium increase (confusion, constipation, weakness)
Renal failure
Anemia
Bone lesion
diagnosis and treatment of Multiple Myeloma
Dx: CBC and bone marrow biopsy
Tx: chemo, targeted therapy, stem cell transplant, corticosteroids, radiations for bone lesions
etiology and pathophysiology of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms/Disorders
Excess of certain type of blood cell
Too many cells in the body
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML); too many WBC
Polycythemia: too many RBC
Essential thrombocythemia (ET): too many platelets
Primary myelofibrosis (MF): fibrosis/scar tissue of bone marrow
signs and symptoms of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms/Disorders
Increased thrombosis/hemorrhage
Fatigue
Weight loss
Itching
Bone pain
diagnosis and treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms/Disorders
Dx: biopsy
Tx: oral medication, chemo, HCT
etiology and pathophysiology of Von Willebrand Disease (vWD)
Autosomal inheritance
Deficiency/dysfunction of von willebrand factor (vWF)
signs and symptoms of Von Willebrand Disease (vWD)
Easy bruising
mucocutaneous bleeding
Heavy periods
Excessive bleeding
diagnosis and treatment of Von Willebrand Disease (vWD)
Dx: CBC, coagulation factors, genetic testing
Tx: factor replacement therapy, antifibrinolytics
etiology and pathophysiology of Hemophilia
X linked inheritance; mainly affects males
Deficiency in clotting factors
signs and symptoms of Hemophilia
Easy bruising
mucocutaneous bleeding
Heavy periods
Excessive bleeding
Hematoma*
Hemoarthrosis*
Bleeding in deep muscles*
Bleeding into internal organs*
*unique to hemophilia
diagnosis and treatment of Hemophilia
Dx: CBC, coagulation factors, genetic testing
Tx: factor replacement therapy, gene therapy, antifibrinolytics
etiology and pathophysiology of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Acquired syndrome with widespread coagulation/clotting
Disruption of steady state
signs and symptoms of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Bleeding, organ dysfunction
diagnosis and treatment of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Dx: labs
Tx: treat underlying cause, supportive care
etiology and pathophysiology of Sickle Cell Disease
Inherited, geographic influence
Sickle shaped RBC that prevents the RBC from functioning properly
signs and symptoms of Sickle Cell Disease
Anemia
Fatigue
SOB
Infections
Slowed growth
Jaundice
Dark urine
Splenomegaly
Bone deformities
Pain episodes*
Swelling*
stroke*
Acute chest syndrome*
Organ damage*
*unique
diagnosis and treatment of Sickle Cell Disease
Dx: genetic testing, prenatal testing, CBC, hemoglobin tests, newborn screening
Tx: transfusions, HCT, gene therapy
etiology and pathophysiology of Thalassemias
Inherited disorder affecting the hemoglobin chain
Structurally impaired defective hemoglobin synthesis
signs and symptoms of Thalassemias
Anemia
Fatigue
SOB
Infections
Slowed growth
Jaundice
Dark urine
Splenomegaly
Bone deformities
diagnosis and treatment of Thalassemias
Dx: genetic testing, prenatal testing, CBC, hemoglobin tests, newborn screening
Tx: transfusions, HCT, gene therapy
hemoglobin
number 1 lab value for PTs to keep an eye on
general s/s of hematologic disorders
Fever
Chills
Pallor
Fatigue
Weakness
Chest pain
Palpitations
Dizziness
Dyspnea
Changes to nails
Tissue inflammation
Syncope
Spoon/clubbing nails