Rickettsia
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/162
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 18
Last updated 1:18 AM on 6/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
Rickettsiales
The order ____________ is composed of two families:
* Anaplasmataceae
* Rickettsiaceae
* Anaplasmataceae
* Rickettsiaceae
3
New cards
anaplasmataceae
The order Rickettsiales is composed of two families:
* ______________
* Rickettsiaceae
* ______________
* Rickettsiaceae
4
New cards
rickettsiaceae
The order Rickettsiales is composed of two families:
* Anaplasmataceae
* _________________
* Anaplasmataceae
* _________________
5
New cards
small, pleomorphic, negative
Bacteria belonging to the order Rickettsiales are
* (SMALL/LARGE)
* (PLEOMORPHIC/UNIFORM)
* Gram-(POSITIVE/NEGATIVE)
* (SMALL/LARGE)
* (PLEOMORPHIC/UNIFORM)
* Gram-(POSITIVE/NEGATIVE)
6
New cards
true
(TRUE/FALSE): Rickettsia are obligate intracellular bacteria.
7
New cards
false
(TRUE/FALSE): Rickettsiales bacteria can be cultured on agar plates.
8
New cards
embryonated
Rickettsiales bacteria need to be cultured in
* yolk sac of _____________ eggs
* tissue culture cell lines
* yolk sac of _____________ eggs
* tissue culture cell lines
9
New cards
tissue culture
Rickettsiales bacteria need to be cultured in
* yolk sac of embryonated eggs
* __________ __________ cell lines
* yolk sac of embryonated eggs
* __________ __________ cell lines
10
New cards
true
(TRUE/FALSE): Rickettsiales bacteria can be stained with Romanowsky based stains.
11
New cards
erythrocytes, endothelial cells
When looking for Rickettsiales bacteria on microscopy, you’re looking for infected ____________ or __________ _______
12
New cards
viruses, bacteria
Rickettsiales characteristics make them a sort of “intermediate” between ___________(obligate intracellular organisms) and __________ (use oxygen, susceptible to antibacterial drugs, possess cell walls),
13
New cards
orientia
There are two genera in the family Rickettsiaceae
* ________
* Rickettsia
* ________
* Rickettsia
14
New cards
Rickettsia
There are two genera in the family Rickettsiaceae
* Orientia
* _________
* Orientia
* _________
15
New cards
bite, feces
Infection with Rickettsiaceae occurs through arthropod ______ or arthropod _______ inoculation/inhalation.
16
New cards
reservoirs, arthropod
Rodents and small mammals act as _______ for Rickettsiaceae, while ____________ hosts transmit infection.
17
New cards
spotted fever, typhus
Genus Rickettsia can be broken into two groups
* ________ _______ group
* _________ group
* ________ _______ group
* _________ group
18
New cards
Rickettsia
Genus ___________ can be broken into two groups
* Spotted Fever group
* Typhus group
* Spotted Fever group
* Typhus group
19
New cards
true
(TRUE/FALSE): All diseases caused by genus Rickettsia can infect humans.
20
New cards
Rocky mountain spotted fever
R. rickettsii causes (ROCKY MOUNTAIN SPOTTED FEVER/CAT FLEA TYPHUS-LIKE INFECTION/MURINE TYPHUS)
21
New cards
cat flea typhus-like infection
R. felis causes (ROCKY MOUNTAIN SPOTTED FEVER/CAT FLEA TYPHUS-LIKE INFECTION/MURINE TYPHUS)
22
New cards
murine typhus
R. typhi causes (ROCKY MOUNTAIN SPOTTED FEVER/CAT FLEA TYPHUS-LIKE INFECTION/MURINE TYPHUS)
23
New cards
f
Cat fleas transmit
a. R. rickettsii
b. R. felis
c. R. typhi
d. all of the above
e. a + b
f. b + c
g. a + c
a. R. rickettsii
b. R. felis
c. R. typhi
d. all of the above
e. a + b
f. b + c
g. a + c
24
New cards
c
Rat fleas transmit
a. R. rickettsii
b. R. felis
c. R. typhi
d. all of the above
e. a + b
f. b + c
g. a + c
a. R. rickettsii
b. R. felis
c. R. typhi
d. all of the above
e. a + b
f. b + c
g. a + c
25
New cards
a
Ticks transmit
a. R. rickettsii
b. R. felis
c. R. typhi
d. all of the above
e. a + b
f. b + c
g. a + c
a. R. rickettsii
b. R. felis
c. R. typhi
d. all of the above
e. a + b
f. b + c
g. a + c
26
New cards
rickettsii
R. ____________ is transmitted by Dermacentor andersoni and Dermacentor variabilis.
27
New cards
rickettsemia
In the sylvatic cycle, rodents and small mammals develop high ____________ - making them important reservoirs of Rickettsia.
28
New cards
sylvatic
In the __________ cycle, rodents and small mammals develop high rickettsemia - making them important reservoirs of Rickettsia.
29
New cards
humans
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever affects a range of hosts
* Small mammals/rodents
* sylvatic cycle
* Dogs and __________
* domestic cycle
* Small mammals/rodents
* sylvatic cycle
* Dogs and __________
* domestic cycle
30
New cards
dogs
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever affects a range of hosts
* Small mammals/rodents
* sylvatic cycle
* ________ and humans
* domestic cycle
* Small mammals/rodents
* sylvatic cycle
* ________ and humans
* domestic cycle
31
New cards
rickettsia rickettsii
This map shows the range of ticks that carry ___________ ____________, the agent of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever.
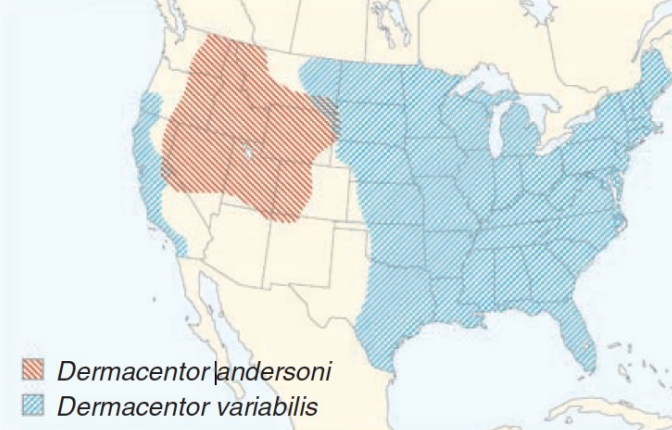
32
New cards
Rocky mountain spotted fever
This map shows the range of ticks that carry Rickettsia rickettsii, the agent of:
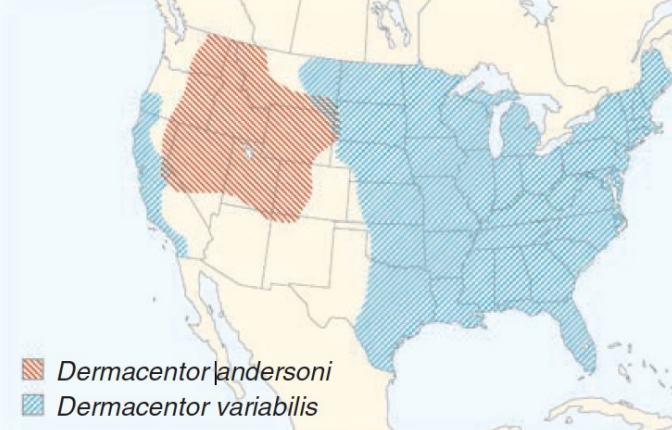
33
New cards
rocky mountain spotted fever
Pathogenicity of ______ _______ ______ ______
1. endothelial cell damage
2. vasculitis
3. platelet activation
4. thrombocytopenia
5. DIC
6. necrosis
1. endothelial cell damage
2. vasculitis
3. platelet activation
4. thrombocytopenia
5. DIC
6. necrosis
34
New cards
endothelial, vasculitis
Pathogenicity of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
1. __________ cell damage
2. __________
3. platelet activation
4. thrombocytopenia
5. DIC
6. necrosis
1. __________ cell damage
2. __________
3. platelet activation
4. thrombocytopenia
5. DIC
6. necrosis
35
New cards
platelet, thrombocytopenia
Pathogenicity of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
1. endothelial cell damage
2. vasculitis
3. _________ activation
4. _________________
5. DIC
6. necrosis
1. endothelial cell damage
2. vasculitis
3. _________ activation
4. _________________
5. DIC
6. necrosis
36
New cards
DIC
Pathogenicity of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
1. endothelial cell damage
2. vasculitis
3. platelet activation
4. thrombocytopenia
5. ____
6. necrosis
1. endothelial cell damage
2. vasculitis
3. platelet activation
4. thrombocytopenia
5. ____
6. necrosis
37
New cards
necrosis
Pathogenicity of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
1. endothelial cell damage
2. vasculitis
3. platelet activation
4. thrombocytopenia
5. DIC
6. _________
1. endothelial cell damage
2. vasculitis
3. platelet activation
4. thrombocytopenia
5. DIC
6. _________
38
New cards
rickettsia ricketsii
This flow chart outlines progression of disease caused by what bacteria?
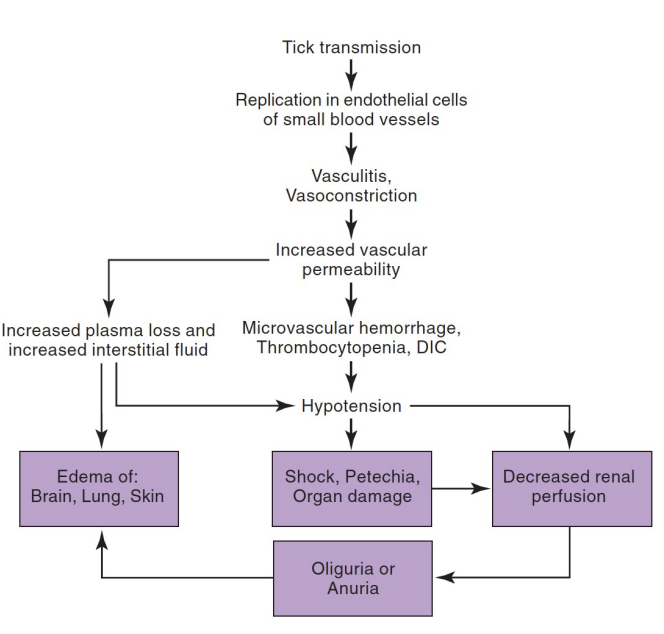
39
New cards
rocky mountain spotted fever
A 4-year-old MN Brittany presents to your clinic in Idaho after a week-long hunting trip. He has a fever, depression, anorexia, SQ edema, petechiated mucosa, and myalgia. Owner reports removing a few ticks from his head and neck.
Your top differentials are canine ehrlichiosis and what other tick-borne disease?
Your top differentials are canine ehrlichiosis and what other tick-borne disease?
40
New cards
Dermacentor andersoni
A 4-year-old MN Brittany presents to your clinic in Idaho after a week-long hunting trip. He has a fever, depression, anorexia, SQ edema, petechiated mucosa, and myalgia. Owner reports removing a few ticks from his head and neck.
The patient is diagnosed with Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. What species of tick are you suspicious of as the vector?
The patient is diagnosed with Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. What species of tick are you suspicious of as the vector?
41
New cards
Dermacentor variabilis
A 3-year-old F Rhodesian Ridgeback presents to your clinic in North Carolina after a week-long hunting trip. She has a fever, depression, anorexia, SQ edema, petechiated mucosa, and myalgia. Owner reports removing a few ticks from her head and neck.
The patient is diagnosed with Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. What species of tick are you suspicious of as the vector?
The patient is diagnosed with Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. What species of tick are you suspicious of as the vector?
42
New cards
Ctenocephalides felis
Cat flea typhus-like illness is caused by R. felis. The vector is believed to be ________________ ____________.
43
New cards
typhus-like illness
Cat Flea ____________ __________ involves two cycles:
* Opossums and fleas
* sylvatic cycle
* Cats and fleas
* domestic cycle
* Opossums and fleas
* sylvatic cycle
* Cats and fleas
* domestic cycle
44
New cards
opossums, cats
Cat Flea Typhus-like illness involves two cycles:
* __________ and fleas
* sylvatic cycle
* _______ and fleas
* domestic cycle
* __________ and fleas
* sylvatic cycle
* _______ and fleas
* domestic cycle
45
New cards
non-specific
People affected by Cat Flea Typhus-like illness often have ____________ signs such as cutaneous flea bite reactions, fever, hyperesthesia, and myalgia, but also develop a more diagnostic maculopapular rash.
46
New cards
maculopapular rash
People affected by Cat Flea Typhus-like illness often have non-specific signs such as cutaneous flea bite reactions, fever, hyperesthesia, and myalgia, but also develop a more diagnostic _____________ ________.
47
New cards
typhi
R. _______ is spread by cat and rat fleas. Exposure occurs after inoculation of infected flea feces into a flea bite wound.
48
New cards
inoculation
R. typhi is spread by cat and rat fleas. Exposure occurs after ___________ of infected flea feces into a flea bite wound.
49
New cards
flea bite
R. typhi is spread by cat and rat fleas. Exposure occurs after inoculation of infected flea feces into a ______ _____ wound.
50
New cards
eschar
People affected by Murine typhus can be identified by the presence of __________ and lymphadenomegaly.
51
New cards
eschar
Stages of __________ - an important and early clinical feature of some rickettsial diseases.
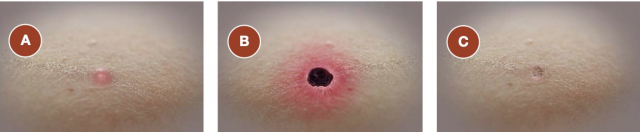
52
New cards
Murine typhus
An owner brings her 6-year-old MN DSH into your clinic in southern Texas. She’s concerned about how itchy her cat has been lately. During the consult you note a lesion on her arm (pictured). What zoonotic bacterial infection are you concerned about?
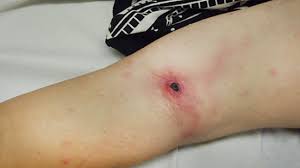
53
New cards
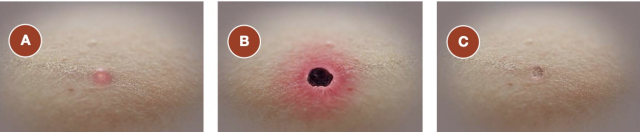
Ctenocephalides felis
An owner brings her 2-year-old FS Bengal into your southern California clinic. She’s concerned about how itchy her cat has been lately. During the consult you note a lesion on her arm (pictured). What insect vector are you looking for?
54
New cards
cutaneous
Primary clinical signs of rickettsia are often __________ in human infections
55
New cards
serology
Rickettsial disease diagnosis
* clinical signs
* history of flea/tick exposure
* __________
* ELISA
* IFI
* Agglutination
* culture and isolation
* requires BSL 3 lab
* PCR
* may be negative on host
* useful on reservoirs and vectors
* clinical signs
* history of flea/tick exposure
* __________
* ELISA
* IFI
* Agglutination
* culture and isolation
* requires BSL 3 lab
* PCR
* may be negative on host
* useful on reservoirs and vectors
56
New cards
3
Rickettsial disease diagnosis
* clinical signs
* history of flea/tick exposure
* serology
* culture and isolation
* requires BSL __ lab
* PCR
* may be negative on host
* useful on reservoirs and vectors
* clinical signs
* history of flea/tick exposure
* serology
* culture and isolation
* requires BSL __ lab
* PCR
* may be negative on host
* useful on reservoirs and vectors
57
New cards
host, reservoirs
Rickettsial disease diagnosis
* clinical signs
* history of flea/tick exposure
* serology
* culture and isolation
* requires BSL 3 lab
* PCR
* may be negative on _______
* useful on __________ and vectors
* clinical signs
* history of flea/tick exposure
* serology
* culture and isolation
* requires BSL 3 lab
* PCR
* may be negative on _______
* useful on __________ and vectors
58
New cards
true
(TRUE/FALSE): Antibiotics are effective in treating Rickettsial diseases.
59
New cards
vector
Prevention of Rickettsial diseases mostly involves ________ control
60
New cards
serology
__________ is often used in diagnosis of Rickettsial diseases, but there is often cross-reactivity between species of the typhus group and SFG.
61
New cards
Rickettsiaceae, Anaplasmataceae
_____________ parasitize endothelial cells while ________________ parasitize leukocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets in addition to endothelial cells.
62
New cards
endothelial
Both Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae parasitize __________ cells.
63
New cards
Anaplasmataceae
Obligate intracellular aerobes lacking a glycolytic pathway and cell wall.
64
New cards
glycolytic, cell wall
Anaplasmataceae are obligate intracellular aerobes lacking a _____________ pathway and _______ ______.
65
New cards
hematopoietic
Anaplasmataceae inhabit ___________ cells of mammalian hosts.
66
New cards
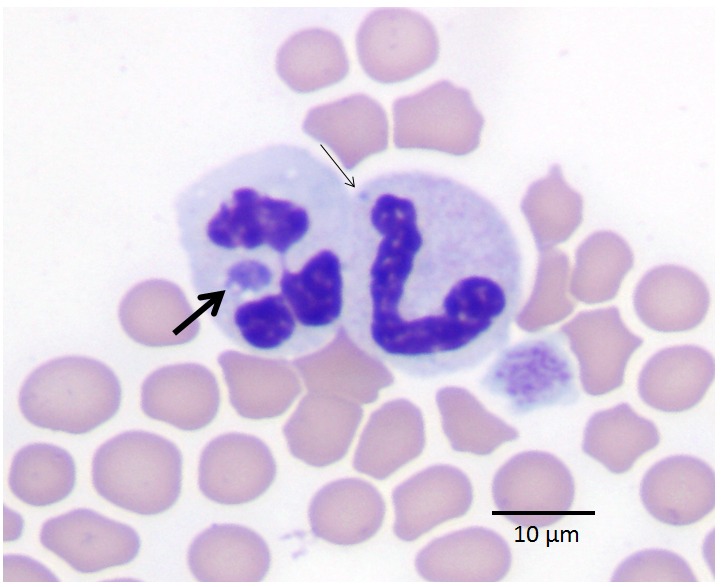
morula
The thick black line is pointing to a __________, a cluster of bacteria commonly seen in Anaplasmataceae infections.
67
New cards
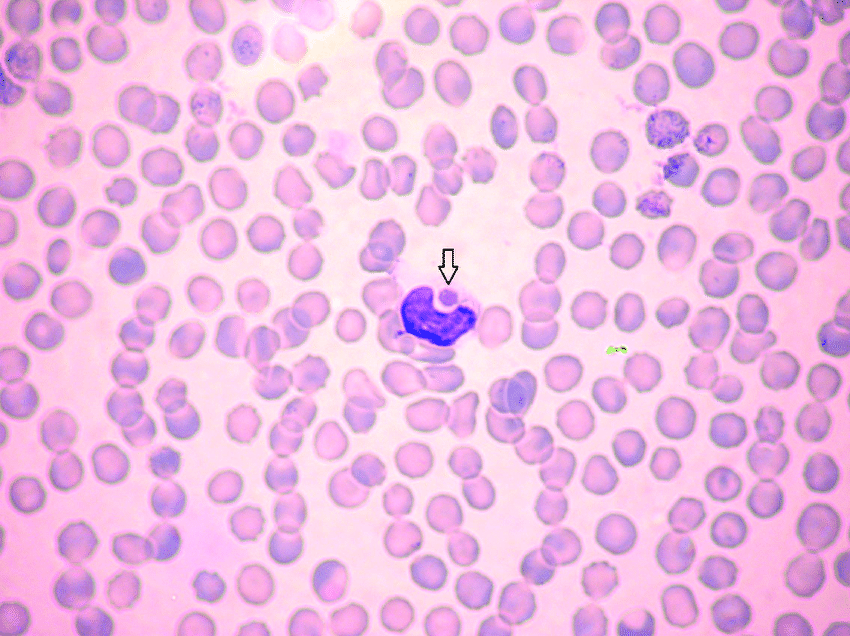
canine monocytic ehrlichiosis
A 5-year-old M medium-sized mixed-breed dog presents to your clinic in early June for nasal discharge. The owner removed a Brown Dog Tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) from him and is upset he hadn’t yet restarted flea/tick prevention.
The patient has a fever, generalized lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly. Bloodwork shows thrombocytopenia and the following is seen on peripheral blood smear.
What condition are you concerned for?
The patient has a fever, generalized lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly. Bloodwork shows thrombocytopenia and the following is seen on peripheral blood smear.
What condition are you concerned for?
68
New cards
anaplasma phagocytophilum
_____________ ______________ is the causative agent of granulocytic anaplasmosis that infects neutrophils (+/- eosinophils). It encapsulates a few species of bacteria formerly classified as separate - E. equi, E. phagocytophilia, and the HGE agent in humans.
69
New cards
granulocytic anaplasmosis
Anaplasma phagocytophilum is the causative agent of __________ ___________ that infects neutrophils (+/- eosinophils). It encapsulates a few species of bacteria formerly classified as separate - E. equi, E. phagocytophilia, and the HGE agent in humans.
70
New cards
migratory birds
Anaplasma phagocytophilum is known to be amplified by
71
New cards
phagocytophilum
A. _______________ is known to be amplified by migratory birds.
72
New cards
ixodes ticks
The vectors of Anaplasma phagocytophilum.
73
New cards
neutrophils
Anaplasma phagocytophilum impairs phagocytosis and bactericidal activities of _____________.
74
New cards
granulocytic
Clinical signs of ______________ anaplasmosis include fever and lethargy in both humans and domestic species, with additional signs of musculoskeletal pain and headache in humans.
75
New cards
musculoskeletal pain
Clinical signs of granulocytic anaplasmosis include fever and lethargy in both humans and domestic species, with additional signs of ___________ _________ and headache in humans.
76
New cards
granulocytic anaplasmosis
Differential diagnoses for a dog presenting with fever and lethargy after a bite from an Ixodes tick
* __________ ____________
* Lyme disease
* __________ ____________
* Lyme disease
77
New cards
Lyme disease
Differential diagnoses for a dog presenting with fever and lethargy after a bite from an Ixodes tick
* Granulocytic anaplasmosis
* _______ _________
* Granulocytic anaplasmosis
* _______ _________
78
New cards
True
(TRUE/FALSE): Granulocytic anaplasmosis can be self-limiting in humans and dogs.
79
New cards
DIC
Horses infected with granulocytic anaplasmosis can die rapidly due to ______.
80
New cards
Horses
_______ infected with Anaplasma phagocytophilum can suffer
* mild or subclinical limb edema
* ataxia
* DIC
* mild or subclinical limb edema
* ataxia
* DIC
81
New cards
edema, ataxia
Horses infected with Anaplasma phagocytophilum can suffer
* mild or subclinical limb ______
* _______
* DIC
* mild or subclinical limb ______
* _______
* DIC
82
New cards
Anaplasma platys
Causative agent of Canine Cyclic Thrombocytopenia. Transmitted by Rhipicephalus sanguineus.
83
New cards
Rhipicephalus sanguineus
Anaplasma platys causes Canine Cyclic Thrombocytopenia. It is transmitted by
84
New cards
true
(TRUE/FALSE): Dogs affected by canine cyclic thrombocytopenia are often asymptomatic.
85
New cards
platelets
Anaplasma platys enters _________, resulting in the formation of a morula.
86
New cards
1-2
Parasitemias and subsequent thrombocytopenic episodes caused by A. platys recur at ______ *(range)* week intervals
87
New cards
platys
Although many dogs infected with A. _____ are asymptomatic, acute infections can manifest as fever, petechia, and ecchymosis.
88
New cards
petechia
Although many dogs infected with A. platys are asymptomatic, acute infections can manifest as fever, ________, and ecchymosis.
89
New cards
ecchymosis
Although many dogs infected with A. platys are asymptomatic, acute infections can manifest as fever, petechia, and ____________.
90
New cards
anaplasma marginale
Causative agent of Bovine anaplasmosis. Transmitted by ticks, flies, and blood-contaminated fomites
91
New cards
false
(TRUE/FALSE): Bovine anaplasmosis is associated with age immunity.
92
New cards
true
(TRUE/FALSE): Bovine anaplasmosis is associated with reverse age immunity.
93
New cards
50
Mortality rate in naïve adult cattle infected with Bovine Anaplasmosis can reach ___%
94
New cards
adult
Mortality rate in naïve _________ cattle infected with Bovine Anaplasmosis can reach 50%
95
New cards
bovine anaplasmosis
Control measures for _________ ____________ are aimed at
* testing and removing carrier animals
* minimizing stress
* vaccination
* testing and removing carrier animals
* minimizing stress
* vaccination
96
New cards
carrier
Control measures for Bovine Anaplasmosis are aimed at
* testing and removing ________ animals
* minimizing stress
* vaccination
* testing and removing ________ animals
* minimizing stress
* vaccination
97
New cards
stress
Control measures for Bovine Anaplasmosis are aimed at
* testing and removing carrier animals
* minimizing ___________
* vaccination
* testing and removing carrier animals
* minimizing ___________
* vaccination
98
New cards
vaccination
Control measures for Bovine Anaplasmosis are aimed at
* testing and removing carrier animals
* minimizing stress
* ____________
* testing and removing carrier animals
* minimizing stress
* ____________
99
New cards
endemic
In areas where Anaplasma marginale is __________, some livestock management involve infecting all young animals so they are resistant to infection later in life.
100
New cards
Ehrlichia canis
_________ _______ is spread via Rhipicephalus sanguineus (the brown dog tick). Replication occurs in vacuoles which offer protection from the immune system.