Chemistry unit 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What effects Effusion?
The mass of the molecule
What is the difference between effusion and diffusion?
Effusion is through a pin hole and diffusion is through an open space
When will gasses behave most ideally?
High temperature and low pressure
What is heat capacity?
the number of heat units needed to raise the temperature of a body by one degree.
what is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1oC
what is oxidation? (OIL RIG)
loss of electrons
what is reduction? (OIL RIG)
gain of electrons
How to calculate the oxidation number?
Look at the charge of a molecule and take use known from the periodic table.
Nuclear Charge is
the ability of protons in nucleus to attract negative electrons. (charge of protons)
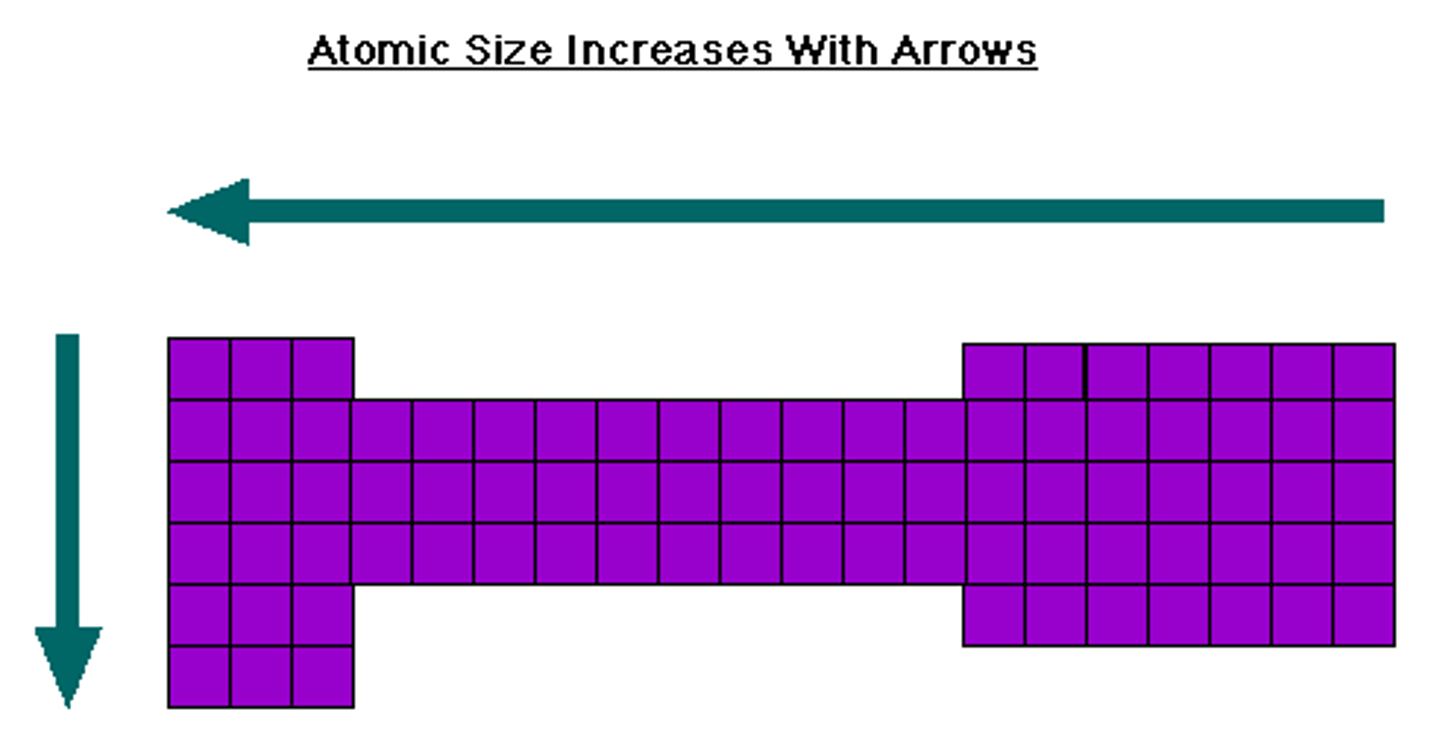
Atomic size
Decrease along the period and increases along the group
cation
A positively charged ion
anion
A negatively charged ion
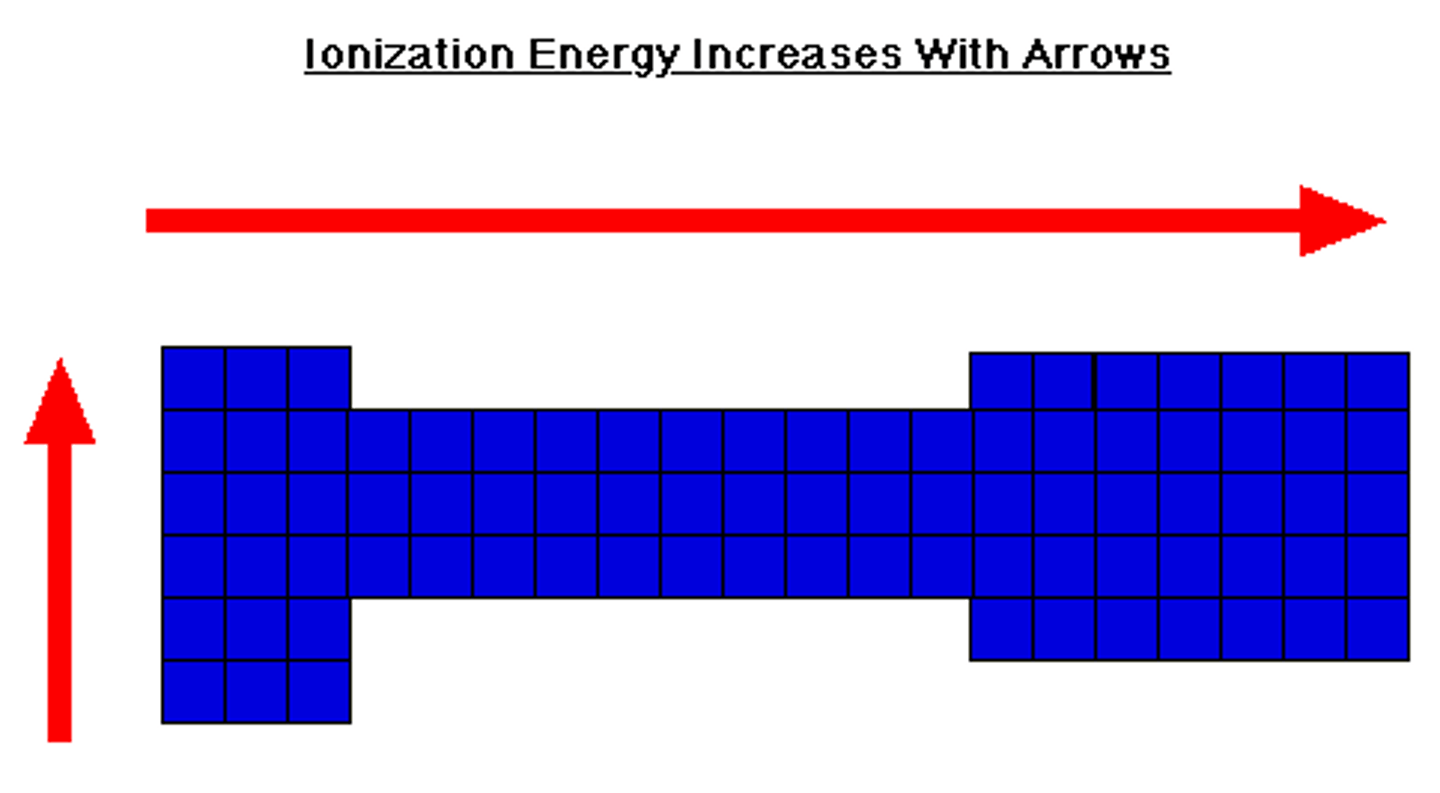
Ionization energy is
energy required to complete removal of 1 mol of electrons from 1 mol of gaseous atoms or iions
Ionization energy
decreases down group and increases across period
Larger atoms
hold electrons less tightly
smaller atoms
hold electrons tighter
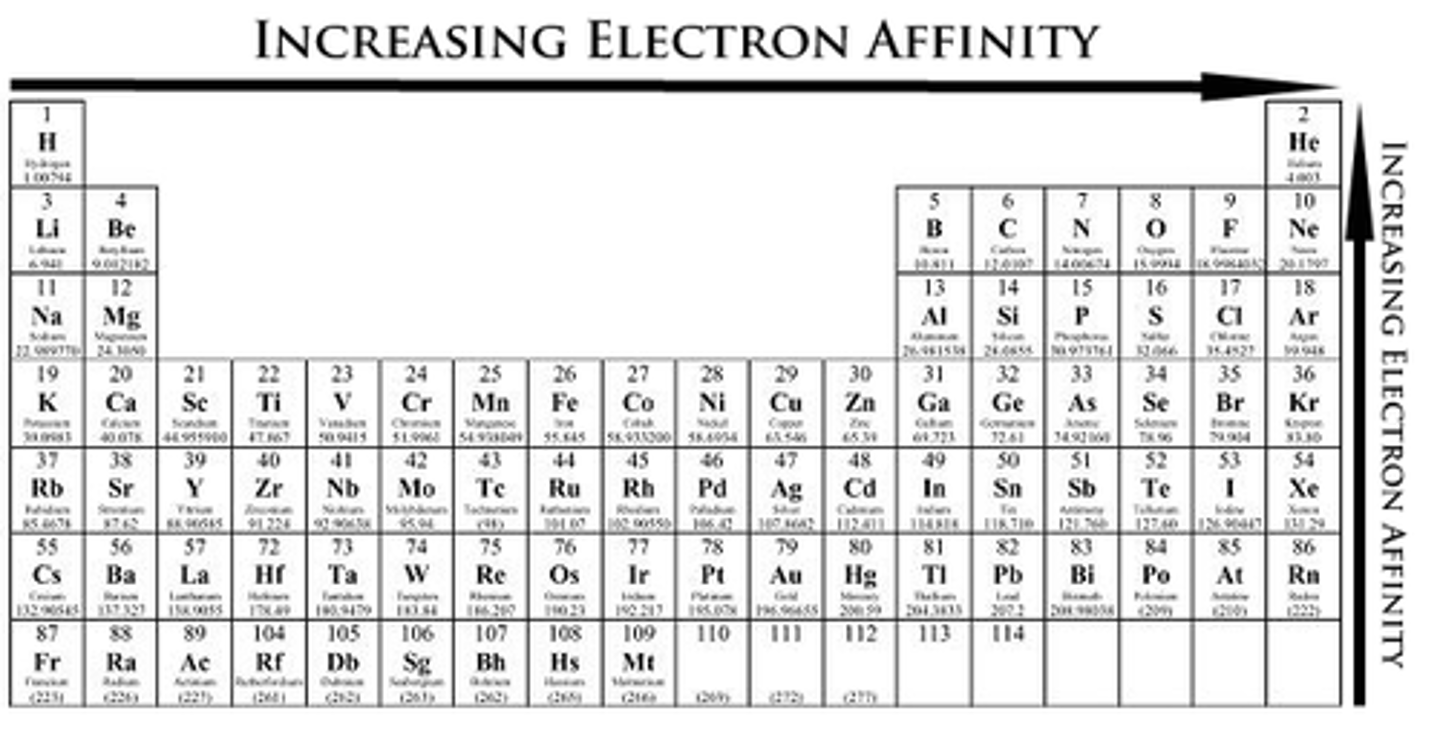
Electron Affinity is
the energy charge that occurs when 1 mole of electrons is added to 1 mol of gaseous atoms or ions.
Electron Affinity
Decreases down group and increases along period
Paramagnetism
attracted by a magnetic field
diamagnetism
not attracted (and is slightly repelled) by magnetic field.
Ionic bond
transfer of electrons and is usually observed when metal bonds to nonmental
covalent bonding
sharing of electrons, usually observed when a nonmetal bonds to a metal
Electronegativity is
the ability for an atom to pull electron toward it
Electronegativity
increased across the period and decreases down the group.
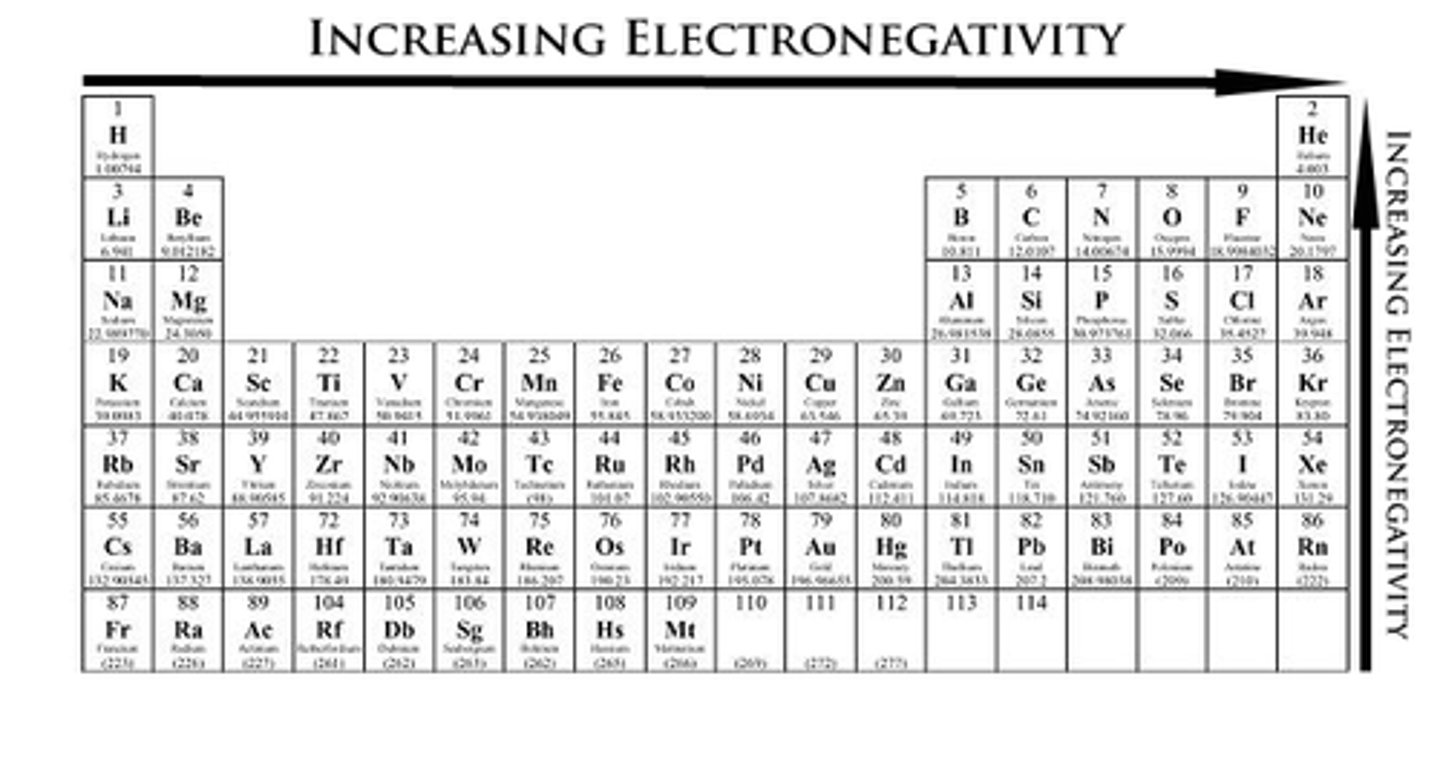
What is the most electronegative element?
Fluorine (F)
Bond order
the number of shared electron pairs between two atoms
Bond energy
energy needed to overcome attraction between nuclei and shared electrons
Bond order: Shorter bond =
stronger strength
Bond energy: Stronger bond=
higher bond energy
Higher bond order results in
shorter bond length and higher bond energy
In LDD, what element goes in the center?
The least electronegative
How to calculate bond order
sum of bond types/number of bonds
Formal charge
charge of atom if all electrons were shared equally
How to calculate formal charge?
#valence electrons-(#unshared electrons+1/2# of shared valence electrons)
change in heat of reaction =
sum of change heat of reactant bonds broken (heat of reactants) + sum of change in heat of product bonds formed (heat of products)
Shape of molecule with 2 electron clouds
linear (180 degree)
Shape of molecule with 3 electron clouds
Triangular planar (120 degree)
Shape of molecule with 4 electron clouds
tetrahedral (109.5 degrees)
Shape of electron with 5 electron clouds
triagonal bipyramid
shape of six electron clouds
octohedral
Electrolytes
substance that produces a solution that conducts electricity when it is dissolved in water
What is Dilution?
process of adding water to a concentrated solution to achieve the molarity desired for a particulate solution
How to Calculate dilution
M1V1=M2V2
What is neutralization?
acid + base = salt + water
What is the Gas Law equation?
PV=nRT
Density of Gas equation
d=PM/RT
Moles of gas
mass/Molar Mass
Boil Law
Pressure is proportionate to 1/v
Volume is proportionate to moles
Volume is proportionate to temperature
What is 1 atm in mmHg?
760mmHg
combine gas law
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
What is 0 degrees C in K?
273K
Partial Pressure is
the total pressure in a mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases.
Partial Pressure equaiton
Pa=Xa*Ptot
Higher temperature=
Higher speed
Lower temperature=
lower speed
Endothermic reaction
heat is ABSORBED from environment
Exothermic reaction
heat is RELEASED into environment
Energy=
Heat+Work
Enthalpy=
E+PV or P/\ V
Higher specific heat means
it takes more heat to change the temperature.