Med Careers- Chapter 20
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
4 measured vital signs
temperature, pulse, blood pressure, and respiration
factors that may influence vital signs
anxiety, nervousness, drinking a hot/cold beverage, being in a hurry to get to an appointment, being in pain
4 anthromorphic measurements
height, weight, BMI, and infant head circumference
what is body temp and why is it measured
it is the internal temp of the body and it is measured to ensure that the body is healthy and has good regulation
5 factors that can affect body temp measurement
gender, age, stress, physical activity, and external factors
intermittent fever
-come and go
-fluctuates between elevated and normal temperatures
intermittent fever causes
viral infections and acute bacterial endocarditis
continuous fever
-stays above the normal range but fluctuates about 3 degrees or less
continuous fever causes
viral and bacterial infections
remittent fever
-fluctuate considerably
-never return to normal
remittent fever causes
pyogenic focal infections, tuberculosis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis
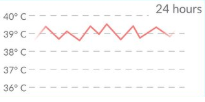
continuous
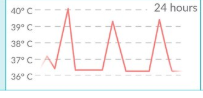
intermittent
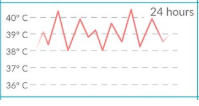
remittent
Temperature measurement sites
oral, axillary, rectal, ear, forehead
Celsius → Fahrenheit formula
(C x 1.8) + 32
Fahrenheit → Celsius formula
(F - 32)/ 1.8
avg TEMP adult AXILLARY
97.6 F
avg TEMP adult ORAL
98.6 F
avg TEMP adult TYMPANIC(ear membrane)
99.6 F
avg TEMP adult RECTAL
99.6 F
avg TEMP adult TEMPORAL ARTERY(forehead)
99.6 F
What is pulse and why is it important to measure
Pulse= number of times your heart beats per minute, important because it shows heart health
Pulse measurement sites
carotid artery
radial artery
brachial artery
dorsalis pedis artery
politeal artery
femoral artery
posterior tibial artery
pulse characteristics
rhythm, rate, volume
pulse vol. 3+
strong, full, bounding pulse, does not disappear w/ moderate pressure
pulse vol. 2+
normal pulse, disappears with moderate pressure
pulse vol. 1+
weak, thready pulse, not easily detected, disappears with light pressure
pulse rate
heartbeats felt as blood moves through the artery
rhythm
time between pulse beats
volume
strength of heart as it contracts
Newborn pulse rate
120-160
avg: 140
1-2 y/o pulse rate
80-140
avg: 120
3-6 y/o pulse rate
75-120
avg: 100
7-11 y/o pulse rate
75-110
avg: 95
adolescence-adulthood pulse rate
60-100
avg: 80
respiration and counting
inhalation and expiration
counted by measuring the number of breaths per minute (don’t mention you’re counting them!)
newborn respirations
30-50
avg: 40
1-3 y/o respirations
20-30
avg: 25
4-6 y/o respirations
18-26
avg: 22
7-11 y/o respirations
16-22
avg: 19
adolescence-adulthood respirations
12-20
avg: 16
blood pressure
the force of blood on the body wall as it is pumped throughout the body
factors affecting blood pressure
blood volume & viscosity, vessel elasticity, and the condition of heart muscle and arterial walls
Normal BP
<120-80 mm Hg
Elevated BP (hypertension)
systolic: 120-129
AND
diastolic: <80 mm Hg
Stage 1 (hypertension)
systolic: 130-139
OR
diastolic: 80-89 mm Hg
Stage 2 (hypertension)
systolic: >/= 140
OR
diastolic: >/= 90 mm Hg
Hypertensive Crisis (hypertension)
systolic: >180
AND/OR
diastolic: >120 mm Hg
Korotkoff stages: Phase I
-sound heard as cuff deflates
-tapping sound
-systolic pressure
Korotkoff stages: Phase II
-swishing sound
-blood flow becomes more turbulent
Korotkoff stages: Phase III
-sharp, rhythmic tapping
-blood flow continues to increase
Korotkoff stages: Phase IV
-soft, muffled tapping
-artery resists collapsing
Korotkoff stages: Phase V
-all sounds disappear
-artery is no longer compressed
-marks diastolic pressure
pulse oximetry
provides information on pulse rate and oxygen saturation of blood
NORMAL= 95% or higher
kilograms → lbs
Kg x 2.2
lbs → kilograms
lbs x .45