A-Level Chemistry AQA Physical Chemistry
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Standard enthalpy of formation
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
Standard enthalpy of combustion
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely burnt in (excess) oxygen under standard condition
Enthalpy change
Heat energy change at constant pressure
Standard States
100kPa and 298K
Define electronegativity
A measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons in a covalent bond
Stages of TOF spectrometer
Ionisation: spray/impact
Acceleration
Drift
Detection
Ionisation (stage in mass spectrometry)
Electrospray: sample dissolved and pushed through nozzle. High voltage applied, particles gain H+
Electron impact: sample vaporised and electron gun fires electrons knocking off electron creating 1+ ions
Acceleration (stage in mass spectrometry)
Ions accelerated by electric field so all have the same KE
Ion Drift (stage in mass spectrometry)
Region of no electric field
Detection (stage in mass spectrometry)
Detector detects particles and mass spectrum produced. m/z
Metallic Bonding
The attraction between delocalised electrons and the positive metal ions in a lattice
Hydrogen Bonding
Strong type of intermolecular dipole-dipole attraction. Occurs between hydrogen and F, O or N. Creates a covalent bond Hydrogen bonding occurs due to difference in electronegativity leading to bond polarity and there is an attraction between ∂+ on one molecule and ∂− on another
Permanent dipole-dipole bonding
Difference in charge between atoms due to difference in electron density
Van der Waal Forces
Weak attractive forces between molecules resulting from the formation of temporary dipoles due to electron charge clouds moving
Covalent Bonding
A bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, with both nucleus' electrostatically attracted to electrons
Dative Bonding
Form of covalent bonding in which the electrons being shared are supplied by only one of the participating atoms . This type of bonding occurs when one of the atoms has a lone pair of electrons .
Mean bond enthalpy
The average value of the bond dissociation enthalpy for a given type of bond taken from a range of different compounds.
Activation Energy
The minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
Behaviour of ionic compounds
-Conduct electricity molten or dissolved in an aqueous solution as ions are free to move and carry their charge. Not possible solid, as in fixed position by ionic bonds
-High melting point due to giant ionic lattices, held together by strong electrostatic force requiring lots of energy to overcome
-Dissolve in water due to the -ve part of the polar H2O molecule attracting the +ve part of the ionic compound whilst the +ve part of the polar H2O molecule attracting the -ve part of the ionic compound. Ions in the compound get pulled away from the lattice so dissolves
Creating a standard solution
Work out moles needed
Measure mass of solid on boat, find precise mass by re-weighing boat after pouring mass in beaker with distilled water and stirring
Pour solution into volumetric flask to make up to volume
Rinse beaker and rod, add this to flask
Add stopper then shake upside down
Titration process
Determine if unknown concentration solution is acid or base, using litmus paper. Use a measured volume of the unknown concentration solution. Add one or two drops of indicator solution. Put standard solution into burette. Add this by drop by drop unknown concentration solution, swirling after each addition. When the colour in the flask with unknown solution changes, stop adding drops, and record the volume of the known concentration solution added
Ionic bonding
The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a lattice
% yield
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
% atom economy
mass of desired product / total mass of reactants x 100
Catalyst
Chemical agents that selectively speed up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction
Exothermic
Releases heat
Makes bonds
-ve
Endothermic
Absorbs heat
Breaks bonds
+ve
Explain how VDWFs arise between molecules
Within a covalent bond, the electrons move randomly resulting in temporary dipoles leaving one delta +ve, the other delta -ve. This induces a dipole in another molecule
Explain the structure of a metal
Ordered rows +ve metal ions surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons with strong electrostatic force of attraction between them
Oxidising Agent
Electron acceptor, is reduced
Reducing Agent
Electron donator, is oxidised
Define relative atomic mass
The weighted mean mass of an atom of an element relative to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Define rate of reaction
The change in concentration of a reactant or a product in a given time.
Define 1st ionisation energy
The energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions
Define 2nd ionisation energy
The energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions to form 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions
Define Hess' Law
The total enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the route taken.
What is an isotope?
Atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
Do isotopes have the same chemical properties?
Yes, because they have the same configuration of electrons but not same physical as different masses
Rate equation
Rate = k[A]^m[B]^n. units for k mol^-1dm^-3s^-1
Orders of reaction
Zero order: changes in concentration has no effect on rate
First order: changes in concentration has a proportional change on rate
Second order: changes in concentration hs a squared proportional change on rate
Overall order is m + n
What is a rate constant?
Is a reflection of the probability that a reaction will occur relates the rate of the reaction to the concentration of reactants. Fixed at a particular temperature, so will change if temperature does. The larger the k value, the faster the reaction. Increasing temperature, increases k
Iodine clock reaction
Reaction for observing concentration effects.
Monitor rate of reaction by disappearance of bisulfite by adding more IO3- than HSO3- at the start of reaction. When the bisulfite is all used up there will be some iodate left.
Can detect the appearance of iodine w/ aid of start indicator, formas a blue complex w/ iodine. The time it takes for blue color to suddenly appear indicates when all the bisulfite is used up.
H2O2 + 2I- +2H+ -> 2H2O + I2 2S2O32- + I2 -> S4O62- + 2I-
How can rate be measured in experiments?
-Change in pH in a reaction
-Amount of mass lost
-Volume of gas produced
-Colour change (using colorimeter)- calibration curve
Which step is the rate determining step?
Slowest step
Arrehnius equation
k = Ae^(-Ea/RT)
What happens when Ae gets smaller in k = Ae^(-Ea/RT)?
k gets bigger, so rate of reaction increases
Define the term overall order of reaction
The sum of powers to which the concentrations are raised in the rate equation
Mole fraction equation
Number of moles of a gas / total number of moles of all gases
Partial pressure of gas equation
Mole fraction of gas x total pressure of the mixture
What affects Kp value?
Temperature
What affect does increasing temperature have on the rate constant?
Means particles have more kinetic energy, so have more energy or energy equal to activation energy required. So more successful collisions, increasing rate of reaction thus increasing rate constant
What is a half cell?
One half of an electrochemical cell.
Which direction do electrons flow to in an electrochemical cell?
From most reactive to least. Meaning most reactive is oxidised, and least reactive is reduced. The most negative value ion gets oxidised
Why is the electrode made out of platinum?
As it is inert but electrically conductive
Define standard electrode potential
The voltage measured under standard conditions when a half cell is connected to a standard hydrogen electrode.
Standard conditions for electrode potential
-Solutions must have concentrations of 1.00 mol dm^-3
-Temperature must be 298K
-Pressure must be 100kPa
What is the electrochemical series?
A list of electrode potentials in order of decreasing or increasing potential.
Standard cell potential equation
E°cell = E°cathode+ve(reduced) - E°anode-ve(oxidised)
What makes an electrode reaction feasible?
If the E°cell is positive
What is an electrolyte?
A liquid containing free-moving ions which conducts electricity
Fuel cells advantages
High efficiency - get more energy out of the same amount of fuel than less efficient devices
Only by-product is water (no CO2 produced)
Don't need to be recharged - they will work as long as the fuel is supplied
Fuel cells disadvantages
Hydrogen is flammable and must be stored very carefully
Energy is required to produce the reactants of hydrogen and oxygen
The energy often comes from fossil fuels so some CO2 emissions
Fuel cell equation
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
State the substances and conditions needed in a standard hydrogen electrode
H2(g) AND 100kPa
1 mol dm−3 AND HCl/HNO3/H+
Pt electrode AND temperature of 298 K
What is the purpose of a salt bridge?
Completes the circuit and allows ions to flow without the solutions mixing.
Define entropy
A measure of the disorder of a system. More disordered the particles are the higher the entropy is.
Define enthalpy of hydration
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions becomes aqueous ions.
When is the oxidation state of oxygen different?
When it is in a peroxide it is then-1, not -2
Define homogeneous reaction
A reaction in which all of the reactants and products are in the same physical phase
How does adding a catalyst affect the rate of reaction?
Increases the amount of particles able to react, by producing an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy required
Reason for a salt bridge
Completes the circuit
Allows free ions to transfer over
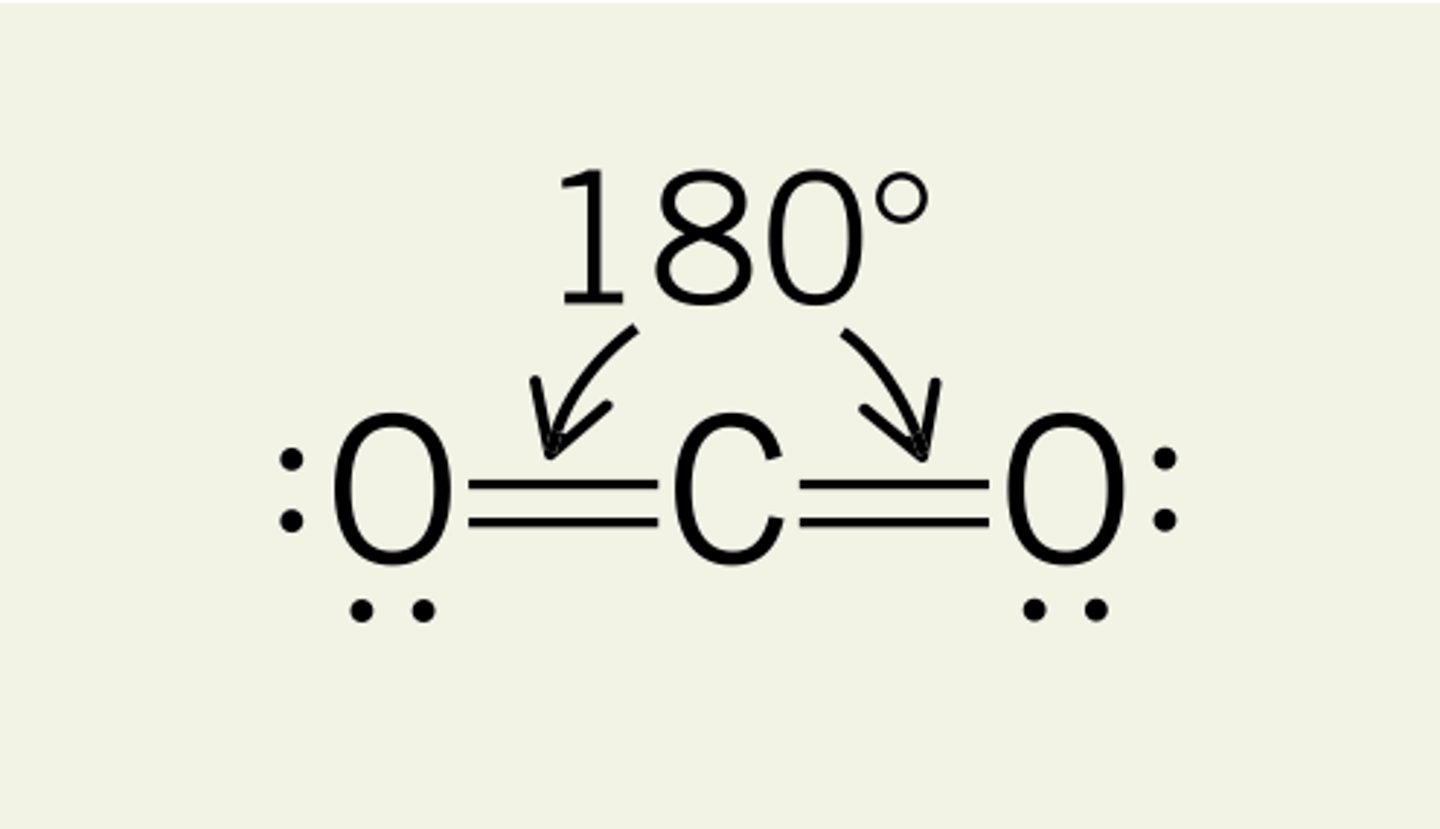
Linear shape
2 BP, 0 LP
180 degrees
V-shaped (bent)
2 BP, 2 LP
104.5 degrees

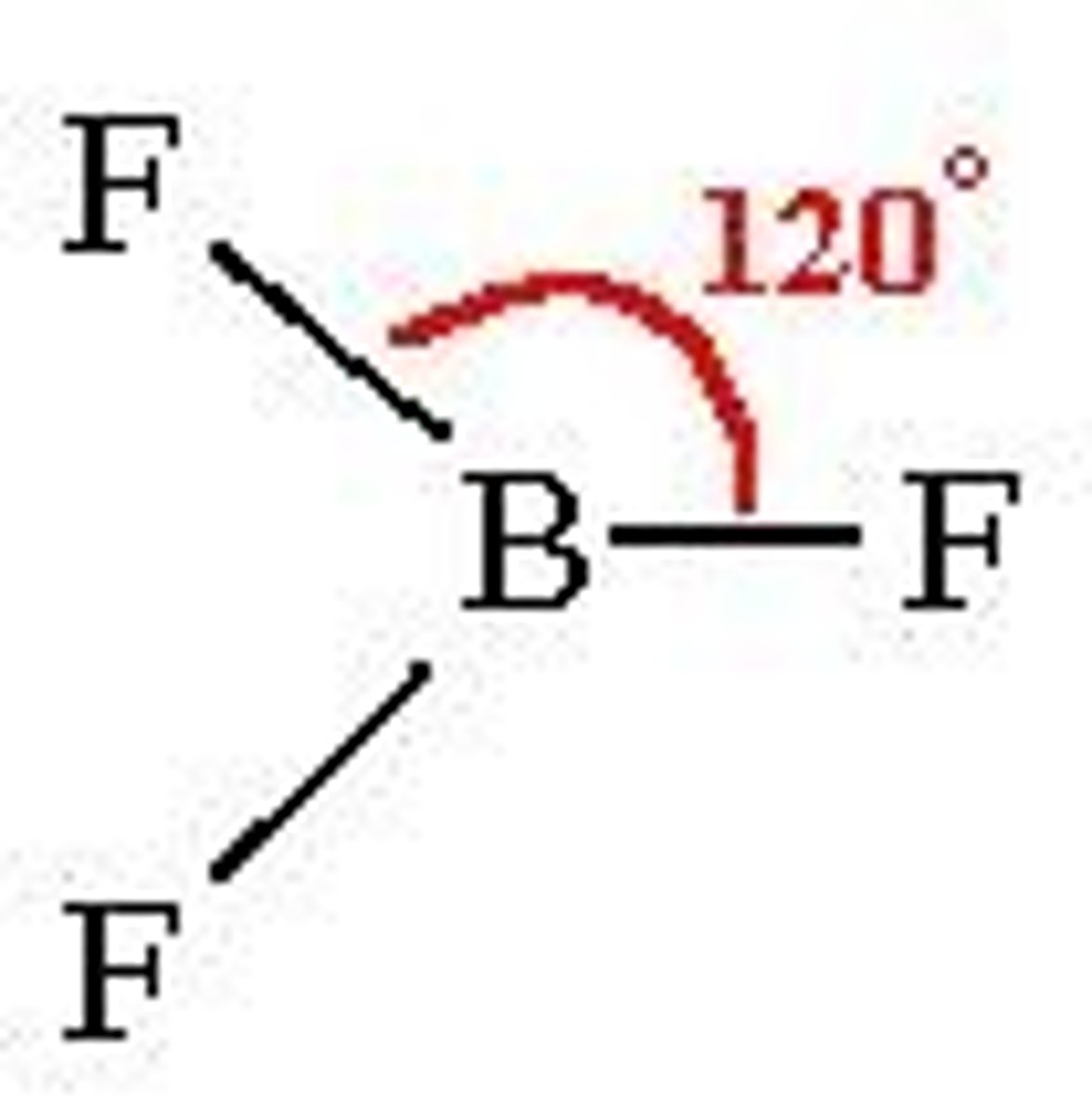
Trigonal planar shape
3 BP, 0 LP
120 degrees
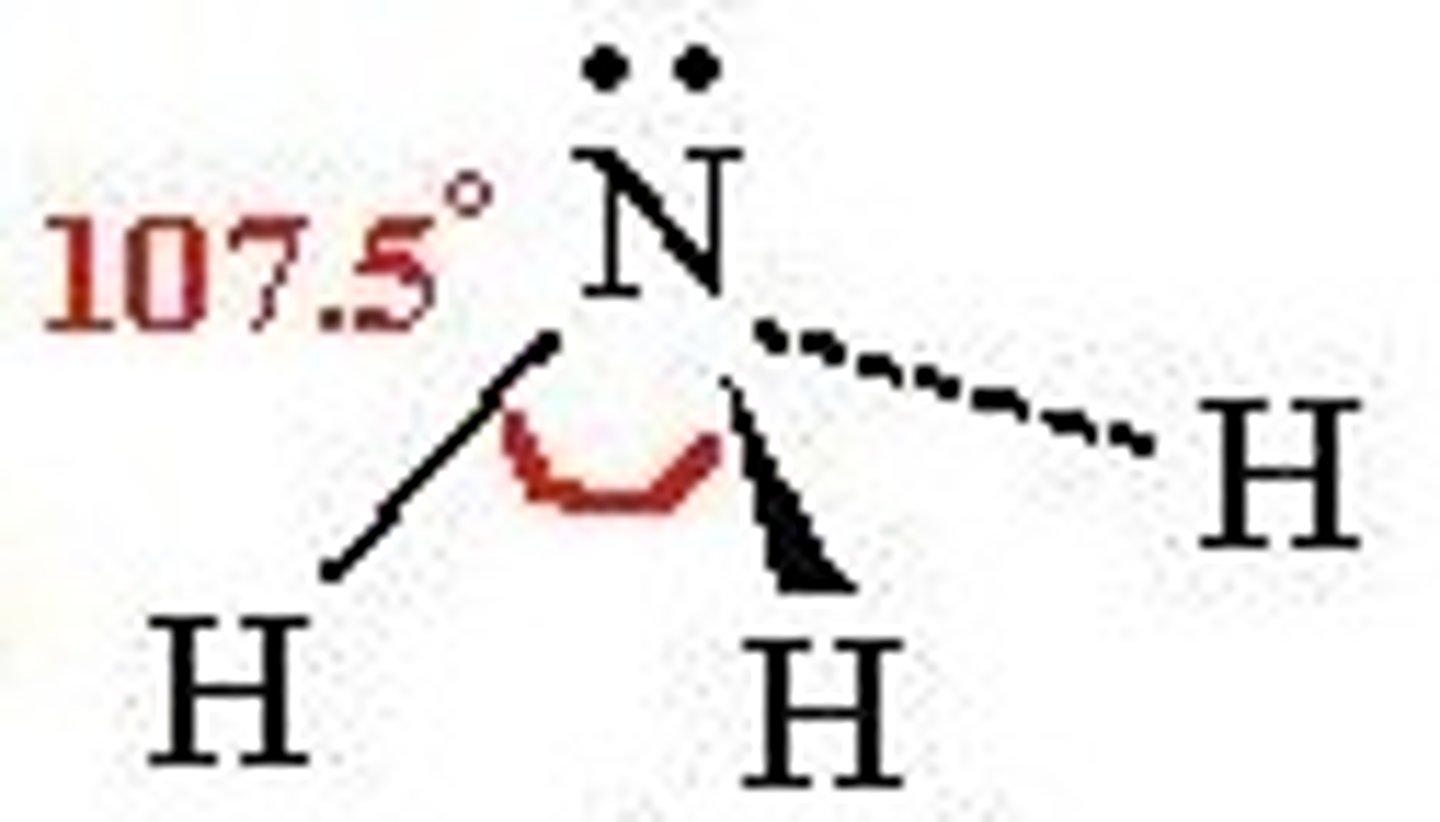
Pyramidal shape
3 BP, 1 LP
107 degrees
Tetrahedral shape
4 BP, 0 LP
109.5 degrees

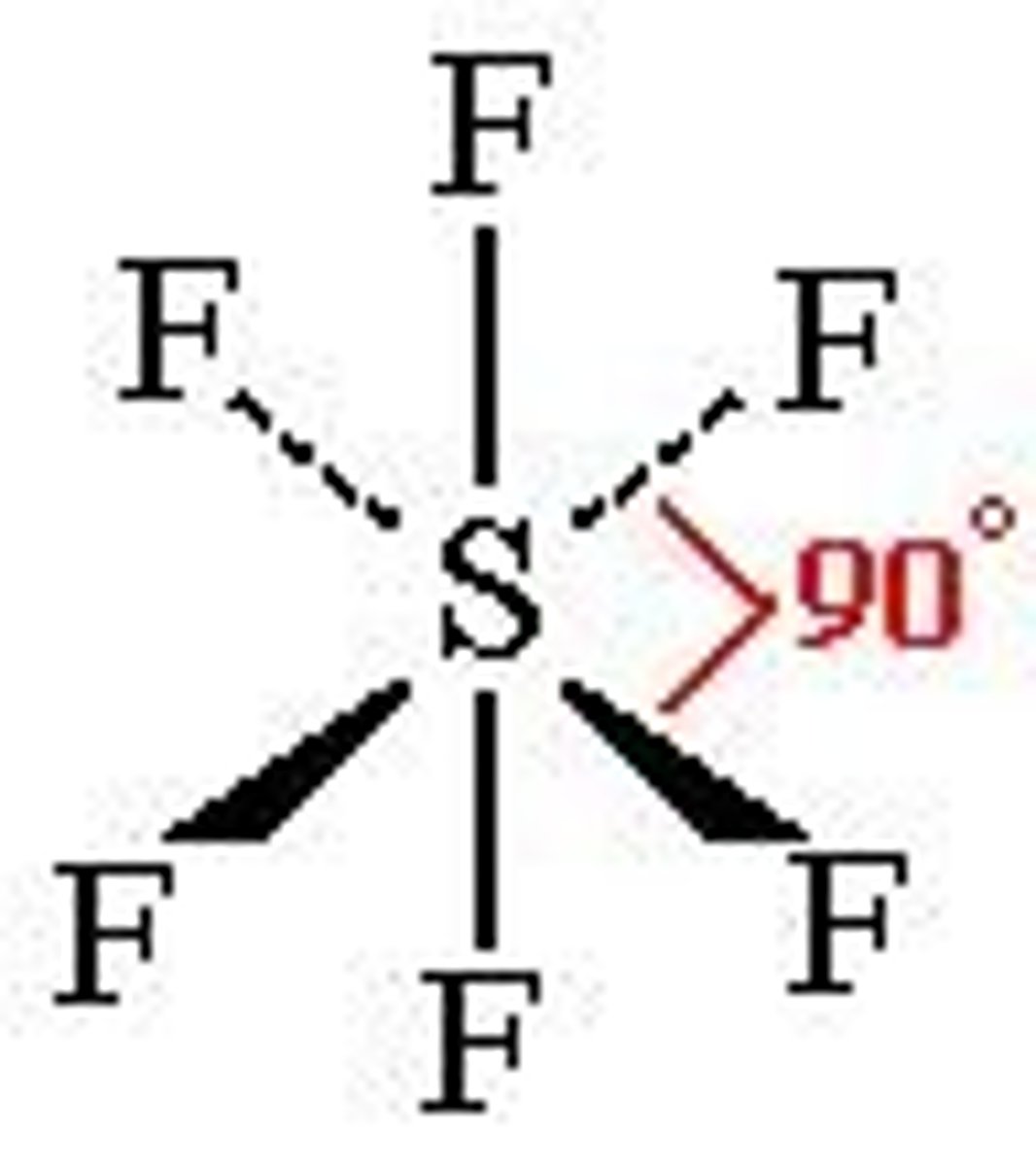
Trigonal bipyramidal shape
5 BP, 0 LP
120 and 90 degrees

Octahedral shape
6 BP, 0 LP
90 degrees
How to predict shape of molecule?
1) Identiy central atom
2) Find number of electrons in outer shell
3) Add one to this number for every atom that the central atom is bonded to
4) Divide by 2 to find number of electron pairs
5) Compare amount of electron pairs, to amount bonded to find out lone pairs
Strength in electronegativity
Strongest: F, O, Cl, N, C, H
Graphite structure
Giant covalent lattice bonded in flat layers (hexagons) which are weakly attracted to each other by VDWFS
Each carbon is covalently bonded to 3 others, leaving a delocalised outer shell e- on each atom free to move along the layers
What happens when ice is heated to its melting point?
When heated molecules gain more energy and begin to vibrate
As reaching mp, molecules have enough energy to break H-bonds and move away randomly
Why is ice less dense than water?
Ices lattice has hydrogen bonds between the molecules, but these are held far apart creating spaces/gaps between the molecules, making it less dense than water
Trend in oxidising/reducing agent in electrode chemical series
LHS is reduced form, more positive means more likely to be reduced. Most positive Ecell is strongest oxidising agent
RHS is oxidised form, more negative means more likely to be oxidsed. Most negative Ecell is strongest reducing agent
Difference between 2 metal and 2 non-metal electrochemical cell practical
With 2 non-metals, the electrode must be a metal, such as platinum- therefore this must be included in cell notation at the end. But with the metals, each metal makes up its own electrode.
Define moles
Avogardo's number of molecules in 12g of 12C
Non-polar molecule shapes
Linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar
These molecules can have polar bonds, but due to the shape being symmetrical, the polar effect can be cancelled out
Define electron affinity
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of ions is formed from 1 mole of gaseous atoms
What does the perfect ionic model assume?
All ions are perfectly spherical
The ions display no covalent character
Attractions are purely electrostatic
When does covalent character occur?
When two joined ions have varying sizes or charges meaning the distribution of charge is not even
Measuring enthalpy of combustion
Weigh alcohol before and after combustion, measure volume of water in colorimeter, then burn alcohol to measure temperature change of water