Psych 101: Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/294
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:15 PM on 9/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
295 Terms
1
New cards
research cycle steps
theory → research questions → hypotheses → research design → data
2
New cards
operationalize
make quantifiable
3
New cards
directionality problem
unsure which variable is causing which
4
New cards
third variable problem
third variable is causing relationship
5
New cards
demand characteristics
aspects of procedure that influence participants to change behavior to fit how they think they are expected to behave
6
New cards
reliability
consistent
7
New cards
construct validity
accurately measures
8
New cards
proximate explanations
immediate causes, within lifetime
9
New cards
ultimate causes
long term → history of species
10
New cards
Darwin’s “three facts of life”
variation, competition, heredity
11
New cards
parental investment theory
NS favors “choosier” mate selection in sex w higher reproductive burden
12
New cards
implication of masculine features
more healthy (high t), but also more aggressive and less interest in parenting
13
New cards
what do women look for?
financial prospects, slightly older, athletic, masculine features, high levels of commitment
14
New cards
what do men look for?
younger (higher fertility), signs of ovulation, hourglass, sexual fidelity (b/c of parental uncertainty)
15
New cards
how do preferences align w/ gender?
align w/ gender over biological sex
16
New cards
the astonishing hypothesis
everything we are is just behavior of nerve cells
17
New cards
dualism (Rene Descartes)
mind/soul fundamentally distinct from body
18
New cards
what do neurons do?
communicate to process info
19
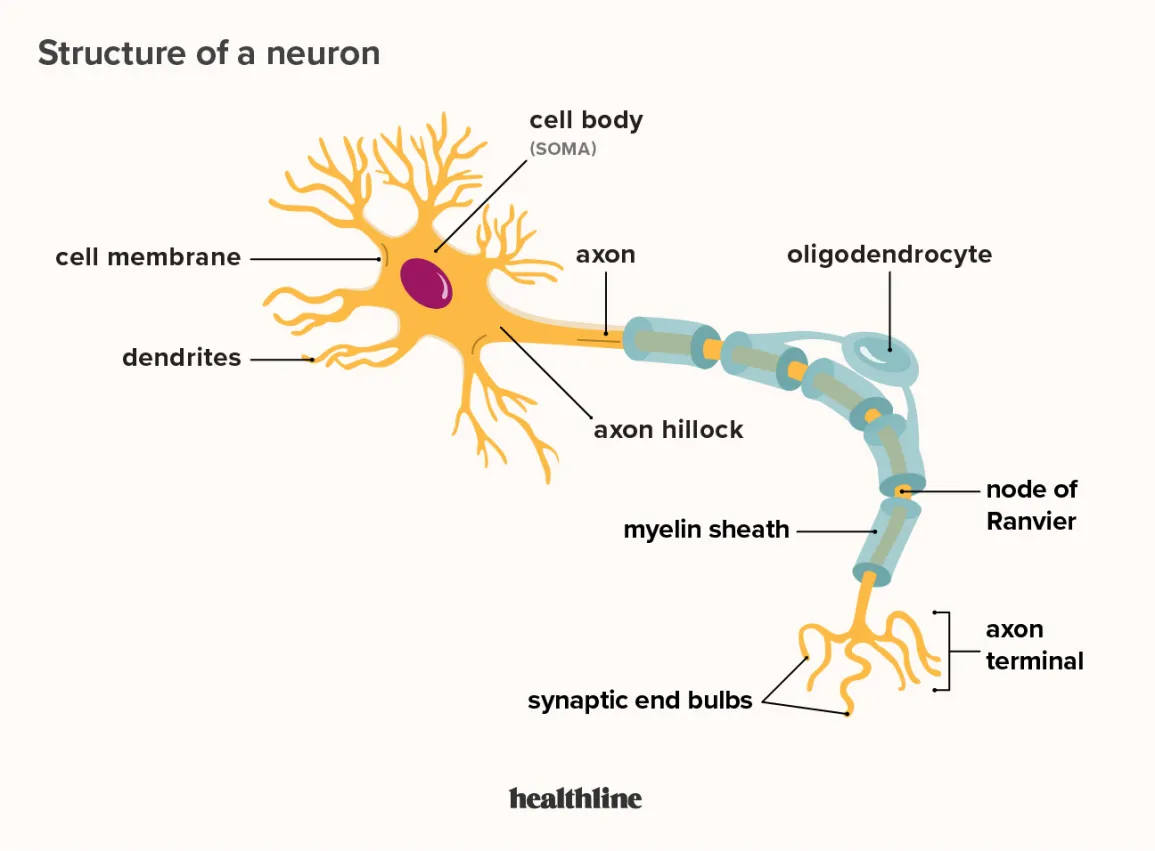
New cards
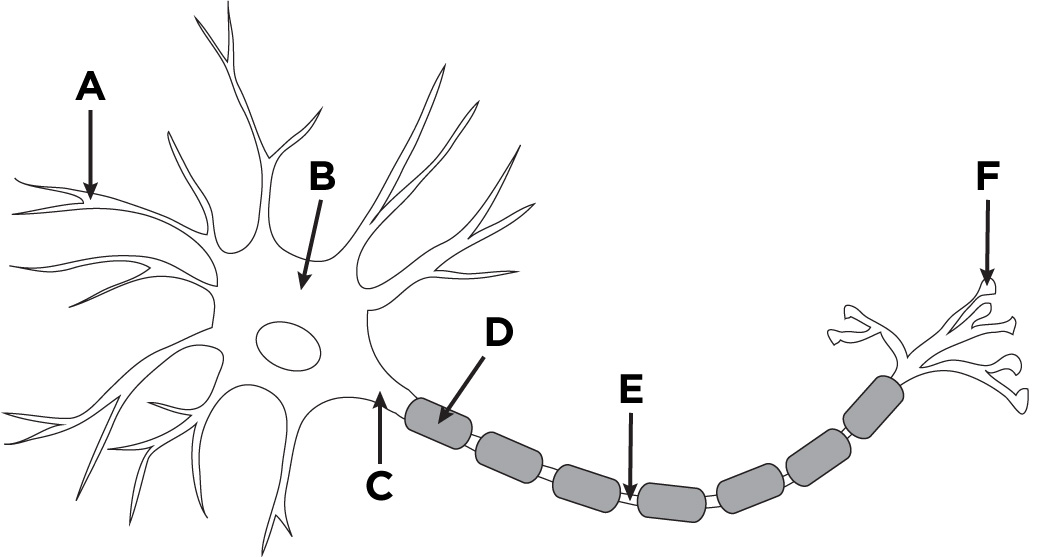
label parts of nerve
slay
20
New cards
glia function
structure and support; communicate with each other and with neurons
21
New cards
pre-synaptic neuron job
transmit
22
New cards
post-synaptic neuron function
recieve
23
New cards
synapse
gap between neurons
24
New cards
types of postsynaptic potentials
EPSPs, ISPS
25
New cards
excitatory signals (EPSPs)
tug the cell to depolarize
26
New cards
inhibitory signals (ISPSs)
tug cell to become more negative (hyperpolarize)
27
New cards
what causes action potential?
excitatory inputs outnumber inhibitory ones enough, positive charge reaches threshold of -55mV
28
New cards
what happens when an action potential is fired?
positive ions flow in and diffuse, trigger action potential to start nearby, and it flows down the axon
29
New cards
what is the function of myelin?
insulation
30
New cards
what are the nodes of ranvier?
ion channels concentrated
31
New cards
how does insulation affect action potential
makes it much faster (saltatory conduction) - jumps from node to node
32
New cards
what are neurotransmitters?
endogenous chemical messengers
33
New cards
what are the four steps of transmission?
1\.) neurotransmitters packaged into vesicles, 2.) vesicles released 3.) neurotransmitters attach to receptors 4.) whatever isn’t taken up goes into re-uptake channels
34
New cards
what are the four major neurotransmitter types?
acetylcholine (muscles) amines (catecholamines like dopamine and norepinephrine in addition to serotonin) peptides (opiods) amino acids (glutamate EXCITATORY gaba INHIBITORY)
35
New cards
what are the two types of psychoactive drugs?
agonists and antagonists
36
New cards
what do agonists do?
amplify natural effect of NTs
37
New cards
what do antagonists do?
mute natural effects of NTs
38
New cards
what are four ways to be an agonist?
1\.) induce increased synthesis of neurotransmitter 2.) increase release of existing neurotransmitter 3.) mimic neurotransmitter at post synaptic receptor 4.) reduce action of re-uptake channels
39
New cards
what are three ways to be an antagonist?
1\.) interfere with release of neurotransmitter 2.) block receptor site 3.) cause leakage of vesicles
40
New cards
what are the four types of psychoactive drugs?
stimulants, depressants, opiates, psychedelics
41
New cards
cognitive psychology
relates to the brain
42
New cards
affective science
The study of emotions, moods, and feelings, as well as their influence on behavior and mental processes.
43
New cards
social psychology
Study of how individuals' thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by others and the social environment
44
New cards
developmental psychology
Study of how individuals grow, change, and develop across their lifespan
45
New cards
David Hume’s Principle of Association
Our mind naturally connects ideas and experiences based on three principles - resemblance, contiguity, and cause and effect. This association of ideas forms the basis of how we perceive, think, and remember things.
46
New cards
what are three evolutionary principles that are important to remember for psych?
\-evolution is slower than environment, natural selection is impartial, evolution is only a piece of the puzzle
47
New cards
naturalistic fallacy
just because something is the product of natural selection doesn’t mean it’s good
48
New cards
oliver sacks
Renowned neurologist and author who explored the fascinating world of the human brain. Known for his captivating case studies and compassionate storytelling, he shed light on rare neurological conditions. His works, like "The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat," brought awareness to the complexities of the mind, inspiring both scientists and the general public alike.
49
New cards
agnosia
inability to recognize sensory stimuli
50
New cards
prosopagnosia
inability to recognize familiar faces (fusiform gyrus damage)
51
New cards
leisons
accidental or intentional, can be imprecise
52
New cards
single-cell electrophysiology
measure electrical activity of neurons
53
New cards
electrical stimulation
activate or deactivate different areas of the brain
54
New cards
stereotaxic instrument
make leisons
55
New cards
hubel and wiesel
research on cats using single-cell electrophysiology
56
New cards
Wilder penfield
used electrical stimulation to figure out what different areas of the brain did
57
New cards
EEG
brain cap that detects electrical activity in brain
58
New cards
adrian owens
studied patients in vegetative state with EEG
59
New cards
FMRI
patterns of energy to infer areas of energy
60
New cards
subtraction method
process for isolating brain activity by comparing to a control condition
61
New cards
Nishimoto study of brain activity
showed people movies, AI were able to recreate using brain activity
62
New cards
TMS
change brain activity using a magnet
63
New cards
above
dorsal, superior
64
New cards
beneath
ventral, inferior
65
New cards
forward
rostral, anterior
66
New cards
backwards
posterior, caudal
67
New cards
medial
middle view
68
New cards
lateral
side view
69
New cards
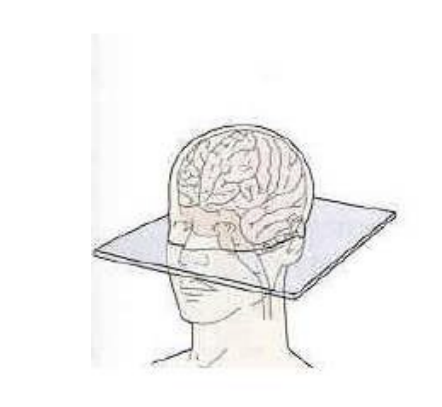
what type of slice is this
axial/horizontal
70
New cards
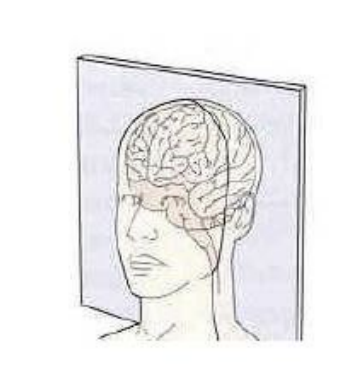
what type of slice is this
coronal
71
New cards
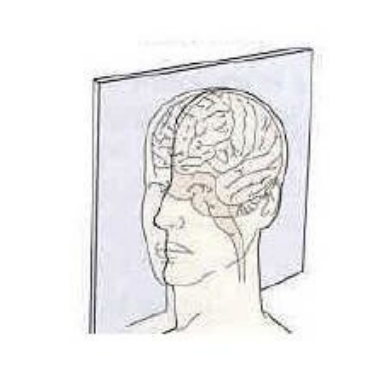
what type of slice is this
sagittal
72
New cards
midbrain
primitive systems for vision and hearing reflexes, reward, movement
73
New cards
pons
bridge across brain and connects to cerebellum, breathing, sleep, sensations up to brain
74
New cards
medulla
connects brain and spinal cord; basic life support: blood pressure, heart rate, coughing gagging, swallowing, vomiting
75
New cards
cerebellum
smooths out voluntary movement
76
New cards
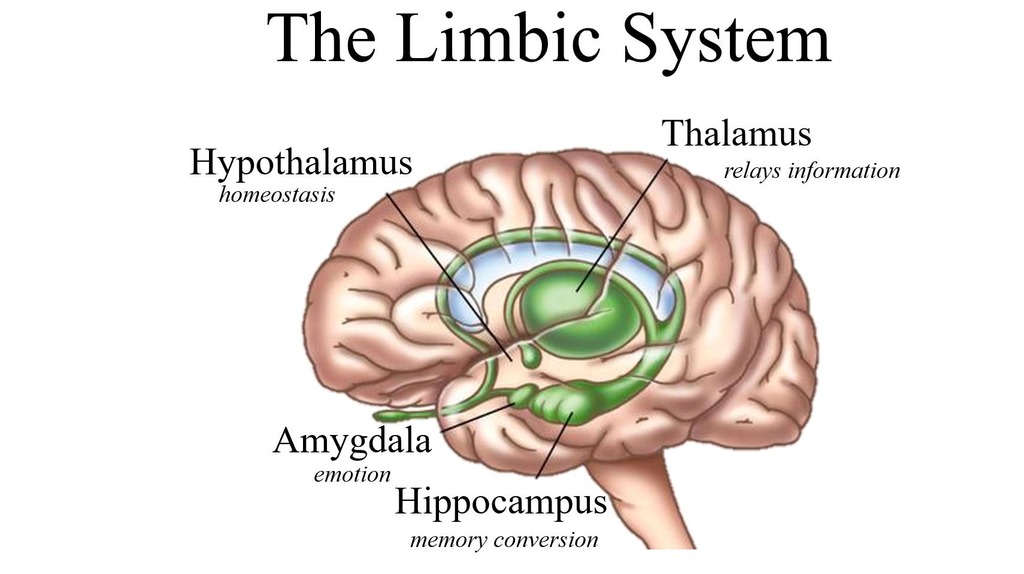
what makes up the limbic system?
hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus
77
New cards
thalamus
receives and routes all sensory info except smell
78
New cards
hypothalamus
four fs - fight, flee, feed, freak
79
New cards
amygdala
motivation & emotion, aggression, emotional memory - fear
80
New cards
hippocampus
stores new memories by interacting with temporal lobe
81
New cards
sulci
valleys of cerebral cortex
82
New cards
gyri
ridges of cerebral cortex
83
New cards
important sulci
central sulcus, lateral fissure
84
New cards
what are the five lobes of the cerebral cortex
frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, insular
85
New cards
frontal lobe
motor control, higher cognition, self control & personality, language
86
New cards
broca’s area
impairs ability to speak but not to understand speech
87
New cards
parietal lobe
body sensation, fine sensation, spatial awareness
88
New cards
contralateral neglect
damage to parietal lobe on right causes loss of ability to recognize anything on contralateral side of visual world
89
New cards
temporal
smell, hearing, memory, language
90
New cards
weirnicke’s aphasia
impaired ability to understand speech, but not to speak
91
New cards
occipital lobe
vision
92
New cards
insular lobe
taste, internal awareness of organs
93
New cards
caveats of studying the brain
function not totally localized, the brain changes
94
New cards
event-related potential
Electrical activity recorded from the brain in response to a specific event or stimulus. Used to study cognitive processes and sensory perception.
95
New cards
parvizi’s
stimulation of the fusiform gyrus causes faces to change shape
96
New cards
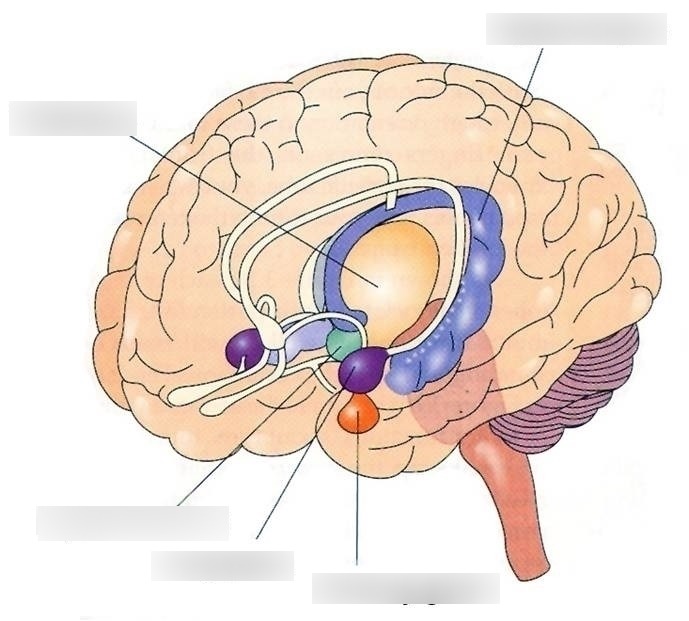
label the limbic system
slay
97
New cards
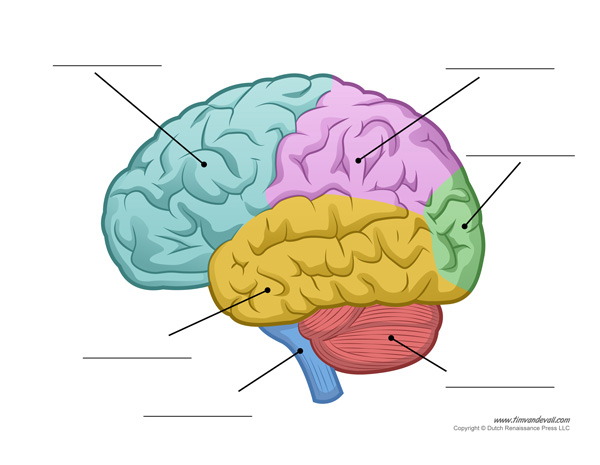
label the lobes of the brain
slay
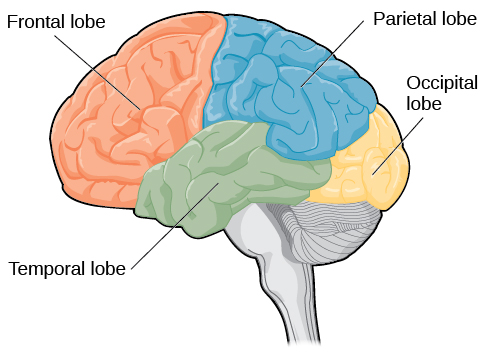
98
New cards
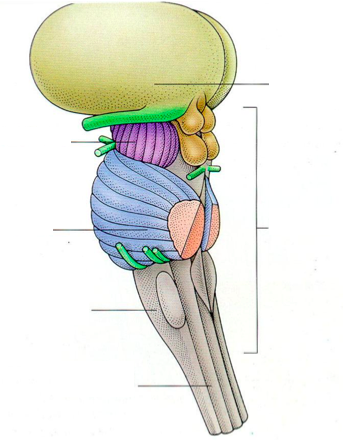
label the parts of the brain stem
slay
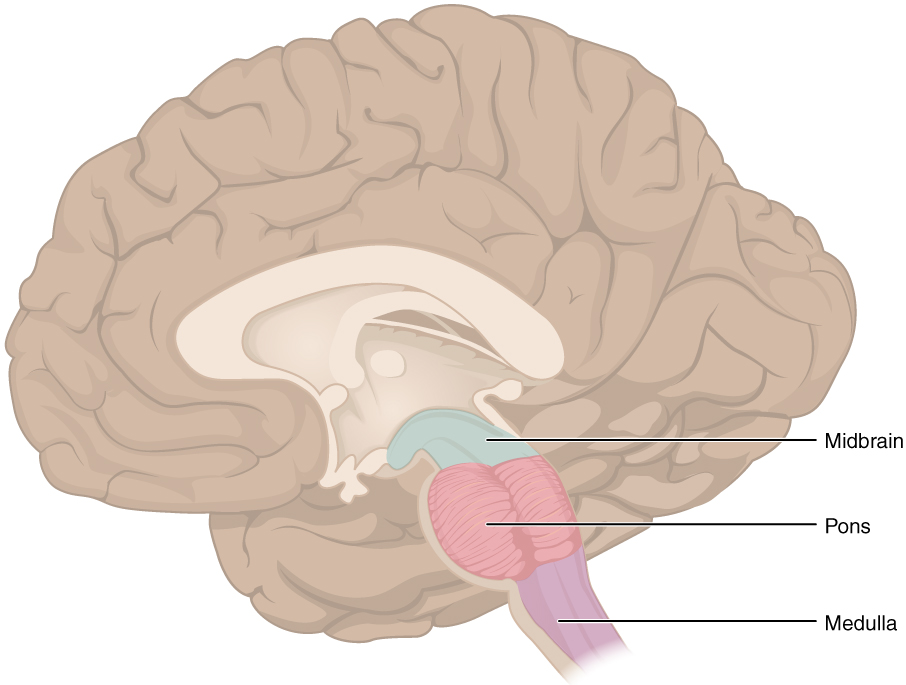
99
New cards
principle of association
tendency to see conjoined events as causal
100
New cards
overconfidence effect
think that you know best, even if research goes against what you think