Smartbook again
1/378
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
379 Terms
Osgood-Schlatter disease muscle
Quadricpes femoris
Reye syndrome liver biopsy show
Microvesicular steatosis
PE problem
V/Q mismatch
Autoimmune hepatitis liver biopsy
Portal and periporal lymphoplasmacytic cell infiltration, Anti-smooth muscle high
Anatomical feature last to disappear in lung
Cilia
Regeneration of alveolar ep lining a month later. what cells?
Type II pneumocytes
C7 nerve damage - increase, decrease or normal
Max inspiratory pressure and max epiratory p
Normal inspiratory (accessary inspiratory muscle and diaphram fine)
Decreased expiratory ( expiration muscles )
Acetaminophen overdose underlying mechanisms
Drug metabolite-induced mitochondrial dysfunction
Small particles in terminal bronchiole. what is responsible for clearing?
Ciliated cells
Coal dust worker, small, nodular opaciites in upper lobes, particle in respiratory bronchioles and alveolar duct? What responsible?
Phagocytosis - alveolar macrophages
Does Celiac disease have genetic component
Yes - DR2 and DR8
Chronic bronchitis most common cause
Tobacco smoking
Herpes simplex virus reactivation process? Mediated by?
Mediated by anterograde axonal transport
By kinesin
cause of Spina bifida occulta?
Failure of vertebral arch fusion
Anastrozole mechanism of action
Aromatase inhibitor - reduce synthesis of estrogen from androgen
Insulin increases glycolysis by?
Activating phosphofructokinase-2
Increase fructose 2,6-bisphosphate --> activate phosphofructokinase 1 -> convert fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Dobutamine causes increase in what
Increase HR, cardiac contractility --> increased myocardial oxygen consumption
Nutritional deficiency in vegan diet
Low vitamin B12, Vitamin D, calcium
Possible - iron, zinc * [low yield]
Neonate with rhinorrhea and maculopapular rash invovling palms/soles, limited prenatal care. Diagnosis?
Congenital syphilis
Pain on defecation, sharp severe subside in minutes. Tear in location?
Anal fissure - posterior midline distal to dentate line
Skin prick test 3 hours later wheal. Cause?
Ep damage from major basic protein
Gilbert syndrome levels
[ heaptocyte bilirubin storage, hepatocyte bilirubin excretion, bilirubin conjugation]
↓bilirubin conjugation
- hepatocyte bilirubin excretion
- hepatocyte bilirubin storage
Which receptors decrease insulin levels
A2 adrenergic
Somatostatin 2 (Gi)
14 yo boy chronic diarrhea, failure to gain weight, recurrent respiratory infeciton, previous sputum + Psuedomonas, younger bro died from resp infection. Diagnosis?
Cystic Fibrosis
Recurrent epigastric pain, vomiting chornic alch consumption, bilious vomiting, palpable epigastric mass. Vital and physical signs unremarkable. Diagnosis?
Pancreatic pseudocyst from chronic pancreatitis (leakage of pancreatic exocrine secretion from damaged duct)
Alcoholic, fever, tachy, jaundice, hepatomegaly, nausea, weight loss
Steatohepatitis
Increased glycerol 3-P formation
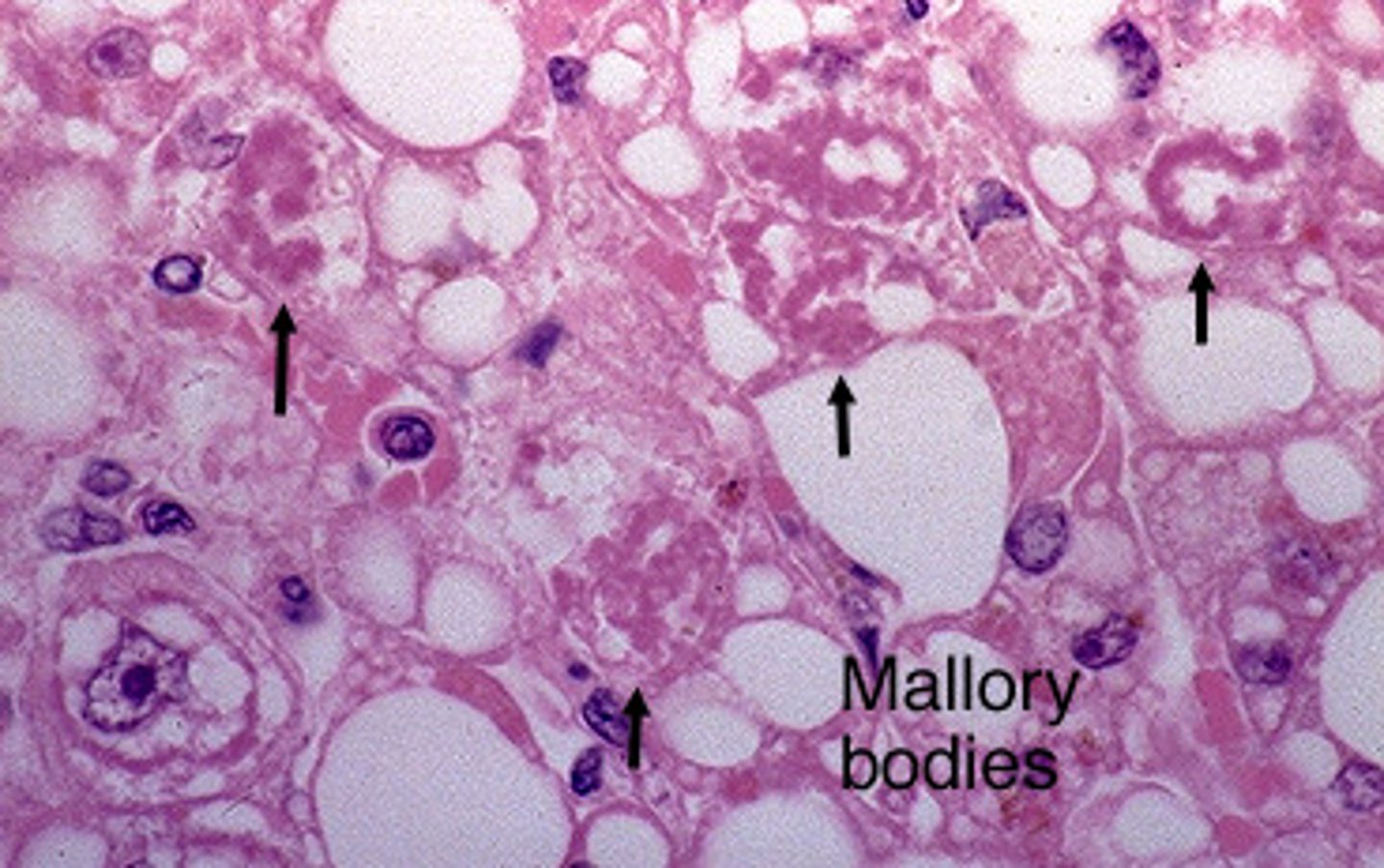
Mallory Body (shows balloon degenration)
What artery supplies upper esophageal sphincter
Inferior thyroid artery from thyrocervical trunk (cervical portion of esophagus and thoracic inlet)
Why does H. influenza grow better with Staph aureus on 5% blood sheep agar
H influenza requires both X factor (hematin) and V factor (NAD+) to support growth, staph aureus secrete V factor (NAD+)
Firm, violaceous nodules on patient's right upper arm after 10 years of breast cancer treatment and extensive axillary lymph dissection. Diagnosis?
Angiosarcoma [extensive lymph node dissection causing chronic lymphedema] A rare vascular tumor that can arise in areas of chronic lymphedema, often associated with prior radiation or surgical interventions.
How does angiosarcoma develop in patients with chronic lymphedema?
Combination of increased lymphatic proliferation (increase likelihood of malignant cells) and decreased number of lymph node (decrease ability to remove malignant cells)
Angiosarcoma develops in patients with chronic lymphedema due to prolonged exposure to inflammatory mediators and tissue hypoxia, which promote neoplastic transformation of lymphatic endothelial cells.
Adult with Single, soft, rubbery, asymptomic, cutaneous nodule durign second and third decade of life. Diagnosis?
neurofibroma
A new inhaled anesthetic has a large arteriovenous (A-V) concentration gradient shortly after inhalation begins. What does this indicate about:
peripheral solubility
onset of action
arrival to brain
indicates high peripheral tissue solubility (likely lipid solubility)
a slow onset of action
The large A-V gradient means the anesthetic is being avidly taken up by peripheral tissues
delaying its arrival to the brain
thus slowing the onset of anesthesia.
what causes postpartum thyroiditis
autoimmune destruction of thyroid follicles, lymphocytic infiltration of thyroid tissue, leading to transient primary hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism.
loss of testosterones effects
lean body weight
subcutaneous fat
bone density
prostate glandular volume
decreased lean body weight
increased subcutaneous fat
decreased bone density
decrease prostate glandular volume
tissues supplied by what artery would be most liekly affected by compression of splenic artery
short gastric
(remember left gastroepiploic has anastomes)
why would you add acetazolamide to treatment regimen when you give patient other loop diruetics ?
metabolic alkalosis
headache, difficulty with vision. acute hemorrahge in left temporal lobe, compression of anteiror medial temporal lobe against tenorium cerebelli. diagnosis? what nerve affected?
uncal herniation
Oculomotor
Of the following, which will appear earliest in alcohol withdrawl?
nystagmus
tremulousness
seizures
visual hallucinations
tremulousness
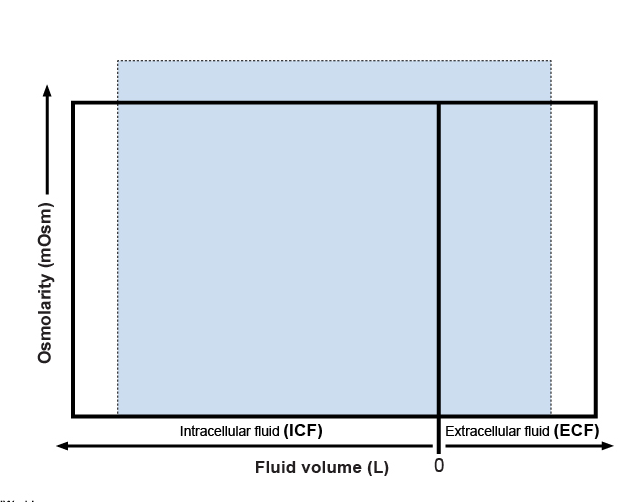
what most likely cause these findings?
central diabetes insipidus [decrease vsopressin secretion → excessive free water excretion —> hyperosmotic volume contraction
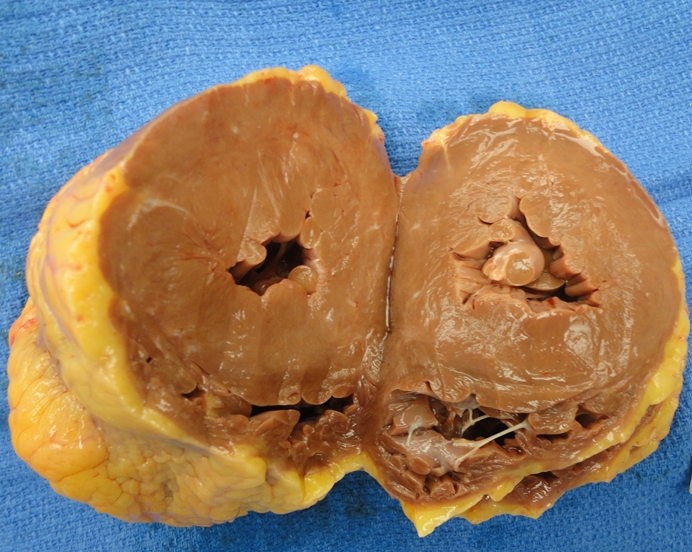
emergency SOB, palpitation, pulmonary edema, afib with rapid ventricular response. Histology= thick myocardial fibers with large hyperchromatic nuclei and mild intersitiial fibrosis. autopsy shown. Diagnosis?
hypertensive heart disease (uniform thickened)
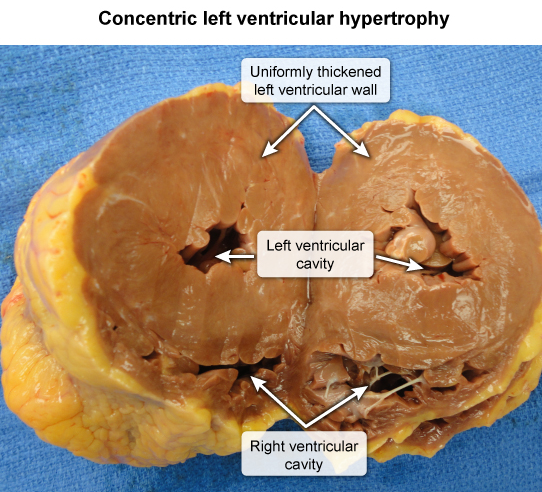
How to differentiate between hypertensive heart disease vs. hypertorphic caridomyopahty?
hypertrophic - uniform thickening of LV walls with reduction in LV cavity size
hypertorphic cardiomyopahty - localized thickening of LV walls predominantly affecting interventricular septum
osteoporosis bone structure changes
trabecular thinning with fewer interconnections
best initial treatment for gout
NSAID (COX inhibitor)
how can high-dose IL 2 therapy used for advanced renal cell carcinoma and metastatic melanoma lead to long-lasting remission?
enhanced activity of natural killer cells
why do patients on warfarin who take antibiotics (eg - metronidazole, marolides, fluroquiolones for gram - organisms) develop supratherapeutic INR
alter gut flora → disruption of vitamin K producing intestinal flora [remember supratherapeutic means higher INR]
if you take cytochrom P450 inducer (ex- phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin) with warfarin, what will happen to INR?
subtherapeutic INR (decreased INR)
what is the most direct cause of fibrous cap formation of atheorma (atheroscloersis)?
medial smooth muscle cells (synthesize extracellular matrix protein → form fibrous cap)
what organ is least susceptible to infarction after occlusion from left atria?
liver (dual/collateral blood supply, hepatic artery and portal vein)
stepped on old nail, pain near site, imaging shows gas in tissues, extensive tissue necorsis. gram positive rod. organism? mechanism of action?
clostridium perfingens → splits host phospholipid
pentad for acquired thormbotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TPP)
1) severe thrombocytopenia
2) microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
3) neurologic manifestations
4) renal insufficiency
5) fever
pathophysiology of TTP
↓ ADAMTS13 → uncleaved vWF multimers → platlet trapping and activation
Mucosal Lymphocyte Trafficking - "Common Mucosal System"
Lymphocytes activated in one mucosa (e.g., lung) can travel to other mucosae (e.g., vagina) and provide IgA protection.
Acyclovir - Activation Enzyme
Viral Thymidine Kinase (TK)
Acyclovir - Drug Class
Guanosine Analog, Viral DNA Polymerase Inhibitor
Hydatidiform Mole - Fetal Tissue: Complete vs. Partial
Complete: Absent; Partial: Present (but abnormal)
baby with cardiac defect (tetralogy of fallot), abnormal facies (clef palate, wide eyes), thymic aplasia, cleft palate and hypocalcemia. diagnosis and mechanism?
DiGeorge - 22q11.2 microdeletion
Mannitol
Drug Class and MOA?
osmotic diuretic
MOA: draws water from tissue (brain) into blood stream, recedue cerebral edema/ICP
Mannitol Side effect respiratory
pulmonary edema (rapid increase in intravascular volume)
Atrial fibrillation - effect on preload in Aortic stenosis
sudden decrease in left ventricular preload (loss of atrial kick)
Carotid Sinus Massage - Effect on Baroreceptor Firing Rate
INCREASED firing rate (stimulates baroreceptors, they sense increased pressure)
how does carotid sinus massage decrease heart rate?
via vagal nerve stimulation, prolonged AV node refractory period
Monoclonal Antibody (mAb) Therapy - Primary Immune Mechanism
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) primary effector cell Type
Natural Killer Cells
Monoclonal Antibody DRUG" (e.g., Trastuzumab) - Type of Immunoglobulin
IgG (therapeutic, specific target, Antibody Dependnet Cellular Cytotoxicity) - NOT IgM
Fever + Fatigue + Early Diastolic Murmur (AR) + subungal Splinter Hemorrhages + Leukocytosis + Elevated ESR + gram positive cocci
strep viridians —> subacute bacterial endocarditis
which bacteria Synthesizes DEXTRANS from sucrose
strep viridians
Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction - Primary Mechanism
Drug-induced bacterial cell wall disintegration releases bacterial components (lipoproteins, cytokines) -> Systemic inflammatory response.
Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction vs. Penicillin Allergy (type 1) timing
Hours (2-12 hours) after treatment initiation vs. minutes to 1 hour
Thoracodorsal Nerve - Primary Function
Motor to Latissimus Dorsi Muscle (shoulder adduction, extension, internal rotation)
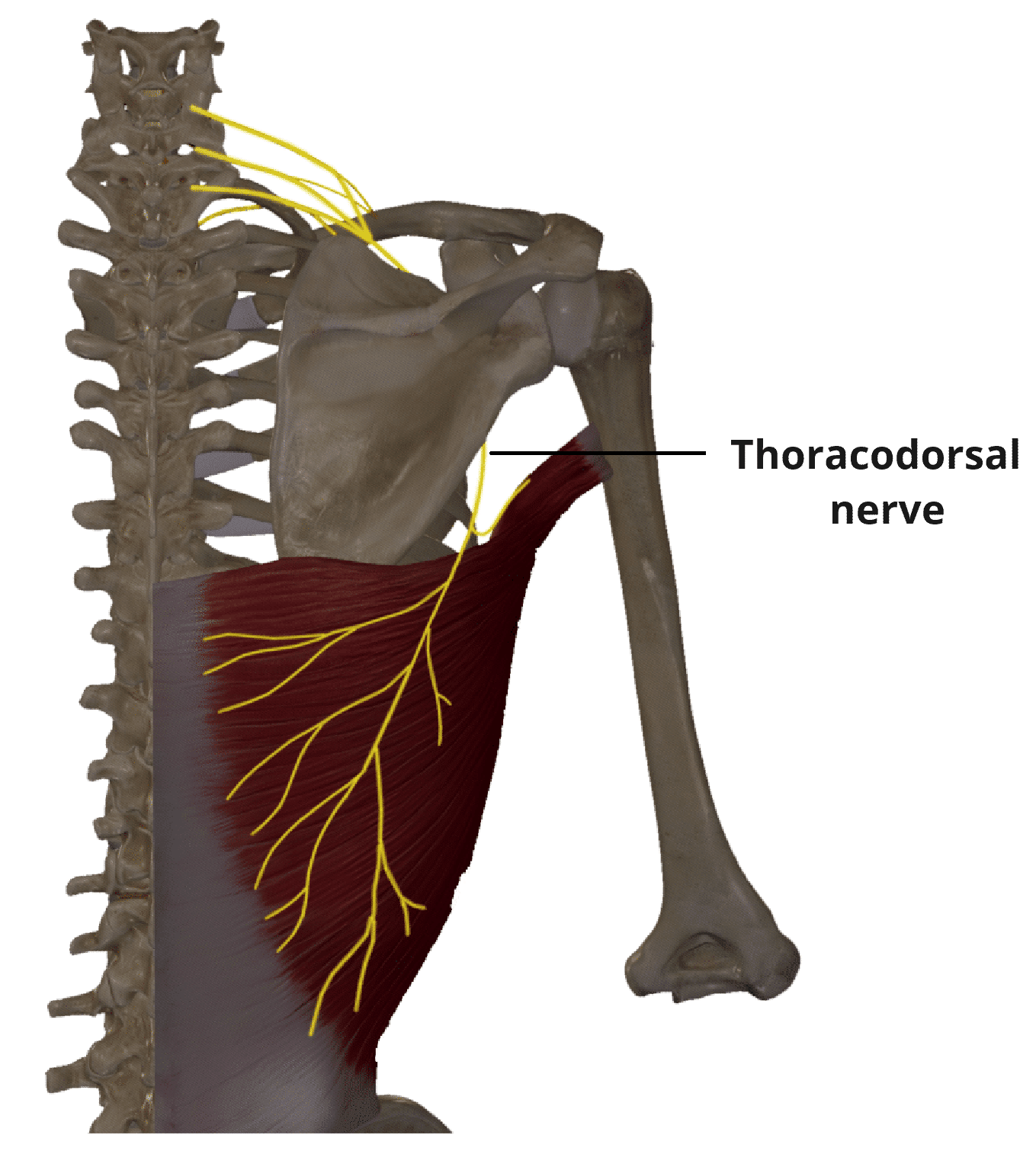
Post-mastectomy, medial upper arm burning pain and sensory loss near axilla, normal shoulder ROM. what nerve injury
INTERCOSTOBRACHIAL NERVE INJURY (sensory only)
Diabetic Cataracts - Primary Metabolic Pathway
Glucose -> aldose reductase —> Sorbitol (Polyol Pathway)
Galactosemia Cataracts - Primary Metabolic Pathway
galactose -> aldose reductase —> Galactitol (Polyol Pathway)
Hyperthyroidism - Bone Loss Mechanism
Increased Osteoclast Stimulation -> Increased Bone Resorption - NOT primarily decreased mineralization
Proximal Fibula Fracture - Nerve at Risk (Most Common)
Common Peroneal Nerve (Common Fibular Nerve)
Superficial Peroneal Nerve - Sensory Territory
Dorsum of the Foot (major area), Distal Anterior/Lateral Lower Leg
Deep Peroneal Nerve - Sensory Territory
Webspace between 1st and 2nd Toes (small area)
Common Peroneal Nerve Injury - Motor Deficit (Classic)
Foot Drop (Dorsiflexion weakness), impaired Eversion
Abrupt-onset, Severe, "Tearing" or "Ripping" Chest Pain, Radiating to Back. Diagnosis?
Aortic Dissection
Aortic Dissection - Key Physical Exam Finding
Blood Pressure Differential between Arms (or pulses)
post-neck surgery (tongue cancer, lymph nodes), increasing shortness of breath, large LEFT PLEURAL EFFUSION. what structure injured?
thoracic duct
Sarcoidosis - Cytokine Profile (Key Set)
Th1 cytokines:
IL-2 - T cell growth factor, prolif
IFN-γ - macrophage activation and granuloma
TNF-alpha
(less primary than IL-2, IFN-γ for defining Th1 response in sarcoidosis immunology questions)
Th1 Response - Primary Immune Function
Cell-mediated immunity, Intracellular pathogen defense, Granuloma formation
Th2 Response - Primary Immune Function
Humoral immunity (antibody production, especially IgE), Extracellular parasite defense, Allergic reactions
pregnant woman with fever, vomit, dirreha (febril gastronetiertiis) and gram positive rods in blood stream. what bacteria"?
LIsteria monocytogenes
Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis
listerionolysin O: pore in phagosome memrbane
actin-based transcellular spread (hijack actin cellular motility)
most important opsonin
IgG and complement C3b * coating proteins
Normal Hemoglobin (HbA)
Structure
_____ Binding
_______ Dissociation Curve
Tetramer (α2β2), Cooperative Binding, Sigmoidal Oxygen Dissociation Curve
Monomeric Beta Subunits - Cooperativity?
No Cooperativity (tetramer disrupted)
Cooperativity and Curve Shape
Cooperativity -> Sigmoidal Curve; No Cooperativity -> Hyperbolic Curve
Monomeric Beta Subunits - Oxygen Affinity
Higher Oxygen Affinity (especially at low PO2) compared to HbA
Oxygen Dissociation Curve - Left Shift Indicates...
Increased Oxygen Affinity
HIV Entry Coreceptors - Primary Types
CCR5 and CXCR4
CCR5 Coreceptor - Cell Tropism Association (General)
Macrophages and T-cells
CXCR4 Coreceptor - Cell Tropism Association (General)
Primarily T-cells
gp120 V3 Loop - Role in Tropism
Determines Coreceptor Preference (CCR5 vs. CXCR4)
Maraviroc - Antiretroviral Class and Target
Entry Inhibitor, CCR5 Antagonist
V3 Loop Mutation Causing CCR5 Resistance - Drug Ineffective?
Maraviroc (CCR5 Antagonist) - Ineffective if virus is no longer CCR5-dependent for entry (especially into macrophages)
Painful, Heavy Menses (Dysmenorrhea & Menorrhagia), Regular Cycles, Endometrial Tissue in Myometrium. Diagnosis?
Adenomyosis
Irregular Bleeding, Pelvic Pain, Plasma Cells in Endometrium. Diagnosis?
Chronic Endometritis
Painful Menses (Dysmenorrhea), Pelvic Pain, Endometrial Tissue Outside Uterus. Diagnosis?
Endometriosis