Mass Transport (Animals)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
give the pathway a red blood cell taken when travelling in the human circulatory system from a kidney to the lungs
renal vein
vena cava to right atrium
right ventricle to pulmonary artery
define mass transport
the bulk movement of gases or liquids in one direction
why is mass transport important in animals (3)
helps bring substances quickly from one exchange site to another
help maintain the diffusion gradients at exchange sites between cells and their fluid surroundings
ensures effective cell activity by keeping the immediate fluid environment of cells within a suitable metabolic range
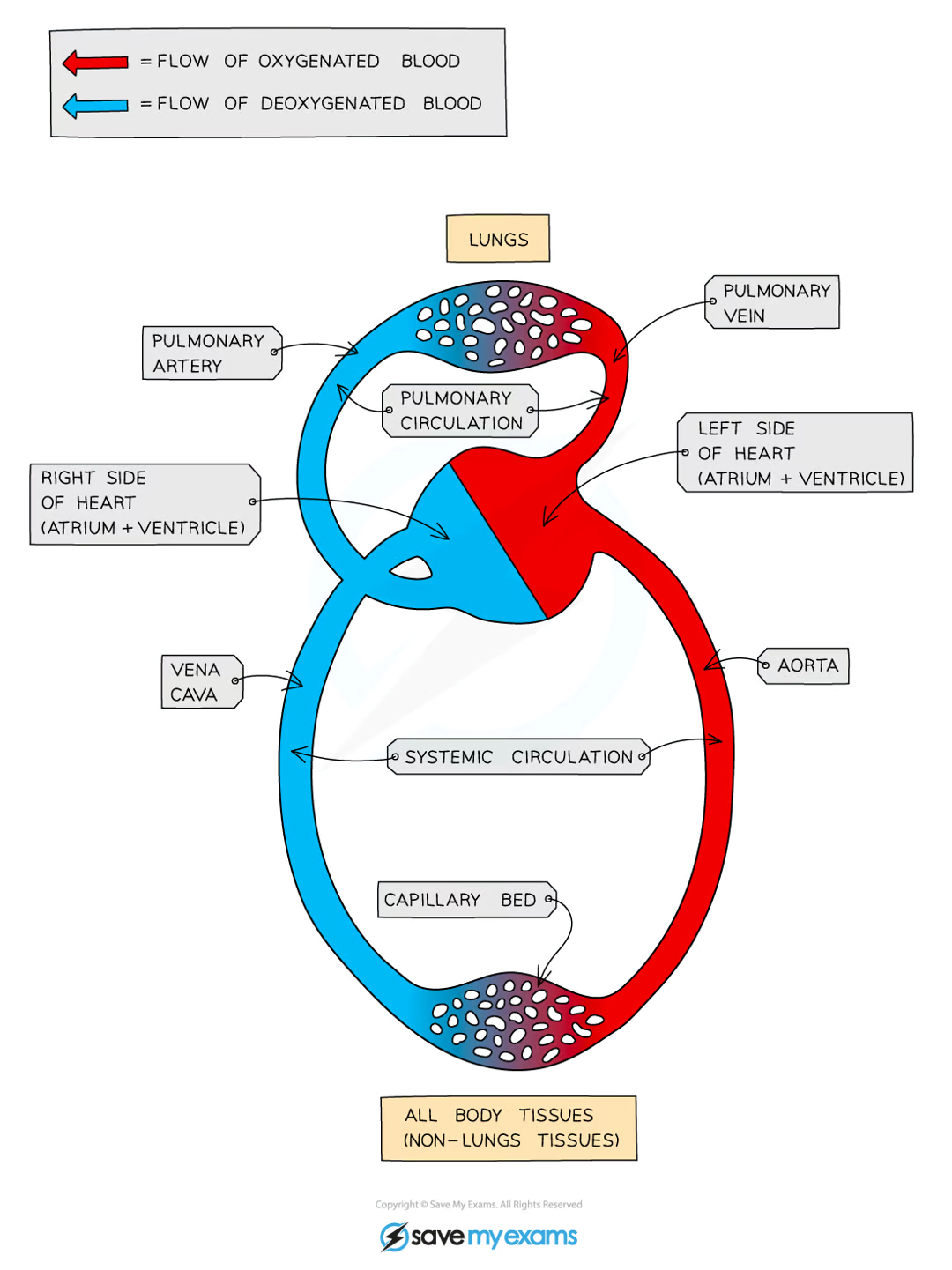
draw and label the circulatory system in animals (8)
explain how the structure of the RBC makes them efficient for carrying oxygen (4)
have haemoglobin which oxygen binds to
are biconcave so give high SA:V ratio
do not contain nucleus so provide more space inside the cell for haemoglobin so that they can transport as much oxygen as possible
existence of Fe2+ in the haemoglobin allows oxygen to reversibly bind to it
explain co operative binding in hemoglobin
binding of the first oxygen molecule results in a confrontational change in the structure of the hemoglobin
making it easier for each successive oxygen molecule to bind
define affinity of oxygen
the ease with which each haemoglobin binds and dissociates with oxygen
explain the shape of the curve on an oxygen dissociation graph (7)
due to shape of haemoglobin molecule, it is difficult for the first oxygen molecule to bind to it
therefore the binding for the first oxygen occurs slowly
therefore there is a shallow curve at the bottom left
however after the first oxygen, it is easier for the other oxygens to bind due to cooperative binding
explaining the steeper part of the curve in the middle of the graph
it takes longer for the fourth oxygen molecule to bind due to the shortage of remaining binding sites
explaining the levelling off
define Bohr shift (1)
changes in the oxygen dissociation curve as a result of CO2 levels
explain why the Bohr shift happens (4)
when partial pressure of CO2 is high, haemoglobin affinity for oxygen is reduced
because CO2 lowers the pH of the blood by combining with water to form carbonic acid
which dissociates into hydrogen and hydrogen carbonate ions
meaning that at any partial pressure of oxygen, the percentage saturation of haemoglobin is lower at higher levels of CO2
draw an oxygen dissociation curve and label it
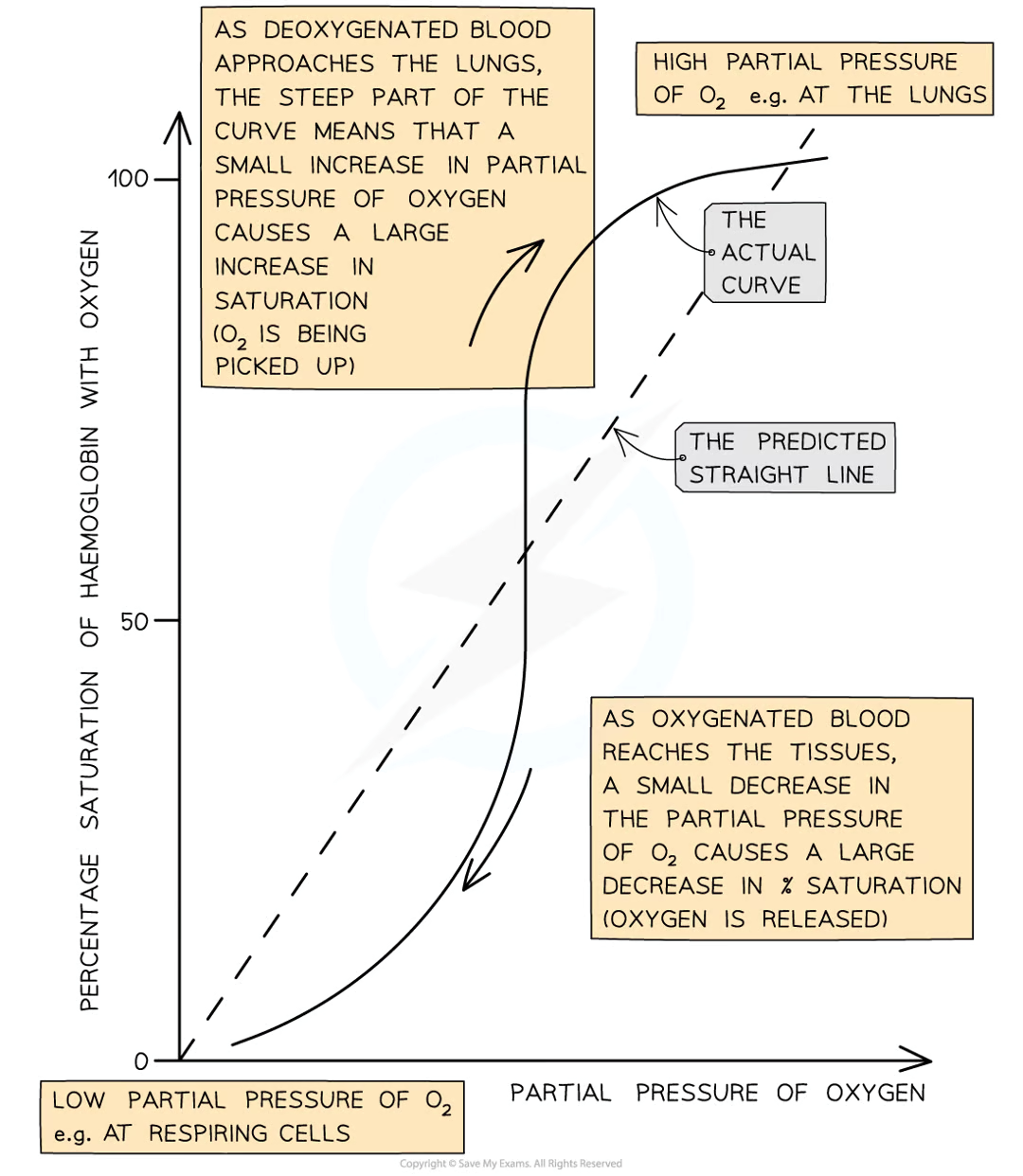
draw an oxygen dissociation curve and a new one with higher levels of CO2

define cardiac output
describes the volume of blood that is pumped by the heart per unit of time
how to recognise stroke volume on a graph
amount between highest point on curve and lowest point on curve
why are haemoglobins shapes in different animals
the partial pressure of oxygen in the air is lower at higher altitudes so species in those altitudes have haemoglobins that are adapted to these changes
draw an oxygen dissociation curve and a new one with higher altitude

define as closed circulatory system
blood is pumped around the body and is always contained within a network of blood vessels
define open circulatory system
blood is contained within blood vessels but is pumped directly into body cavities
define closed double circulatory system (3)
in one complete circuit of the body, blood passes through the heart twice
the right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange
blood then returns to left side of heart so that oxygenated blood can be pumped efficiently
define pulmonary circulatory system
the right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange
define systemic circulatory system
blood then returns to left side of heart so that oxygenated blood can be pumped efficiently
what is the function of the heart
muscle which pumps blood
what is the function of the arteries
blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart
what is the function of arterioles
small arteries which branch from larger arteries and connect to capillaries
what is the function of capillaries
pass directly past cells and tissues and perform gas exchange and exchange of substances
what is the function of venules
small veins which join capillaries to larger veins
what is the function of veins
blood vessels which carry blood towards the heart
name the main blood vessels (7)
pulmonary artery
pulmonary vein
coronary arteries
aorta
vena cava
renal artery
renal vein
what is the function of pulmonary artery
carries deoxygenated blood away from heart, towards the lungs
what is the function of pulmonary vein
carries oxygenated blood away from the lungs towards the heart
what is the function of coronary arteries
supply the heart with oxygenated blood
what is the function of aorta
carries oxygenated blood out of the heart and to the rest of the body
what is the function of vena cava
carries deoxygenated blood into the heart
what is the function of renal artery
supplies the kidneys with oxygenated blood
what is the function of renal vein
carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys, towards the heart
draw and label the heart (10)
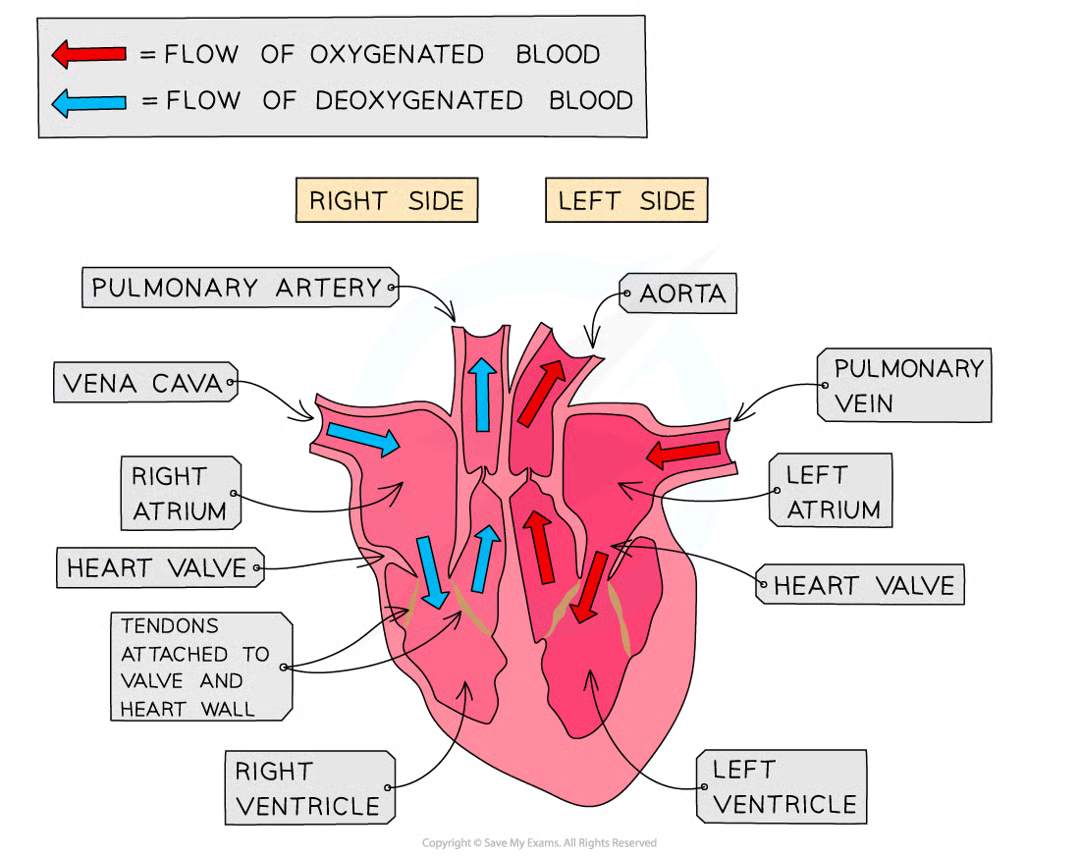
explain how the valves open and close (2)
open when the pressure of blood behind them is greater than the pressure in front of them
close when the pressure of blood in front of them is greater than the pressure behind them
define interatrial septum
portion of the septum which separates the left and right atria
define the interventricular septum
separates the left and right ventricles
define atrioventricular valve
separates the right atrium and right ventricle
define bicuspid valve
separates the left atrium and left ventricle
what are the two vessels bringing blood to the heart (2)
vena cava
pulmonary vein
what are the two vessels taking blood away from the heart (2)
artery
aorta
what is the function of coronary arteries
supply the cardiac muscle with deoxygenated blood , nutrients and remove waste products
explain why the atria walls and ventricle walls have different structures (4)
atria walls are thinner than ventricle walls as they do not need to generate as much pressure
but enough to force blood down into the ventricles through the AV valve
ventricle walls are thicker and more muscular
and they need increases pressure to push the blood out of the heart through the semilunar valves
explain the different in structure of left and right ventricle (4)
muscle of left ventricle is significantly thicker than right ventricle
blood pumped from right ventricle travels to lungs only whereas
blood pumped from left ventricle travels to rest of body
therefore blood leaving the right ventricle travels less distance than that leaving the left ventricle
define the term cardiac cycle
the series of events that take place in one heart beat
what is the term which describes the contraction of the heart
systole
what is the term which describes the relaxation of the heart
diastole
explain the volume and pressure changes in the cardiac cycle (3)
contraction of the heart muscle causes a decrease in volume
which increases again when the muscle relaxes
volume decrease leads to pressure increase
explain the atrial systole (6)
the walls of the atria contract
atria volume decreases
atria pressure increases above the ventricles
forcing the AV valves open
blood is forced into the ventricles which increases the ventricular pressure and chamber volume
ventricles are relaxed at this point as ventricular systole coincides with atrial diastole
explain the ventricular systole (6)
walls of the ventricles contract
ventricular volume decreases
ventricular pressure increases forcing the AV valves to close, preventing the backflow of blood
the pressure increase in ventricles above the aorta and pulmonary artery forces the semi-lunar valves open
so blood is forced into the arteries and out of the heart
during this, the atria are relaxing as atrial diastole coincides with ventricular systole
explain diastole (7)
ventricles and atria are both relaxed
the pressure in the ventricles drops below that in the aorta and pulmonary artery
forcing the SL valves to close
atria continues to fill with blood as it returns to the heart via pulmonary vein and vena cava
pressure in the atria rises above that in the ventricles forcing the AV valves open
blood flows passively into the ventricles
cycle begins again with atrial systole
explain atrial systole, ventricular diastole (2)
atria contract
pushing blood into the ventricles
explain atrial diastole, ventricular systole (3)
atria relax
ventricles contract
pushing blood out of the heart
explain cardiac diastole (2)
all chambers are relaxed
blood flows into the heart
name 5 factors that can influence heart rate (5)
drugs
caffeine
alcohol
sex
temperature
describe and explain the structure of arteries (7)
walls are relatively thick
as they must be able to withstand high pressures generated by contracting the heart
and maintain these pressures when the heart is relaxed
elastic fibres allow the artery wall
to expand around the blood surging through at high pressure when heart contracts
these fibres then recoil when the heart relaxes
alongside a narrow lumen maintains high blood pressure
describe and explain the structure of veins (4)
wall of vein is relatively thin as they receive blood that has passed through the capillary network
therefore it is at a low pressure
lumen is much larger than artery
contain valves that prevent backflow of blood
explain the structure and function of capillaries
have thin walls with gaps that are ‘leaky’
allowing substances to leave the blood to reach the body’s tissues
they can form networks called capillary beds
which are very important exchange surfaces within circulatory system
have small diameter lumen
which forces the blood to travel slowly which provides more opportunity for diffusion to occur
walls are one ednothelial cell thick to reduce the diffusion distance for O2 and CO2
how is tissue fluid formed (7)
as blood passes through capillaries, some plasma leaks out through the gaps in the walls of the capillaries to surround the cells of the body
when blood is at the end of the arteriole end of capillary, the hydrostatic pressure is great enough to push fluid out of the capillary
protein remain in the blood
the increases protein content creates a water potential between capillary and tissue fluid
at venule end of capillary, less fluid is pushed out of the capillary as hydrostatic pressure within the capillary is reduced
the water potential gradient remains the same at the arteriole end
so water begins to flow back into the capillary from the tissue fluid via osmosis
how does hypertension affect tissue fluid (2)
blood pressure is high then the pressure at the arteriole end is even greater
this pushes more fluid out of the capillary and fluid begins to accumulate around the tissues
define oedema
build up of tissue fluid in the body
how is lymph formed (6)
some tissue re enters the capillaries while some enters the lymph capillaries
which have closed ends and large pores that allow large molecules to pass through
larger molecules enter the lymphatic system
the liquid moves along the larger vessels of this system by compression caused by body movement
the lymph eventually re enters the bloodstream through the veins close to the heart
any plasma proteins that have escaped from the blood are returned via lymph capillaries
what does blood plasma consist of (5)
glucose
amino acids
mineral ions
oxygen
plasma proteins
define what is meant by cardiac cycle
the sequence of events that make up a single heartbeat
explain the cardiac cyle (5)
contraction of the muscles in the wall of the heart reduces the volume of the heart chamber
increasing the pressure of the blood within that chamber
when the pressure withing a chamber exceeds the next chambers, valves are forced open and blood moves through
then the muscle in the wall of the heart relax and recoil which increases the volume of the chamber
decreasing the pressure so that the valves close
what are the main risk factors for coronary heart disease (5)
genetic factors
age and sex
high blood pressure
smoking
high conc of low density lipoproteins
explain how water from tissue fluid is retuned to the circulatory system (4)
plasma proteins remain
creating water potential gradient
waver moves to the blood via osmosis
returns to blood by lymphatic system
explain how an arteriole can reduce the blood flow into capillaries (2)
muscle contracts
narrowing the lumen
what blood vessel carries blood at the lowest pressure
vena cava
describe the advantages of the Bohr effect during intense excercise (2)
increases dissociation of oxygen
for aerobic respiration at the tissues
name and explain how a physiological change would allow for the removal of the increase in the volume of carbon dioxide (2)
increases breathing rate
has similar pCO2 per breath but more breaths
describe and explain the effect of increasing CO2 concentration on the dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin (2)
increases oxygen dissociation
by decreasing blood pH
give four safety precautions that should be followed when dissecting a heart (4)
use a sharp scalpel
wash hands
disinfect bench
cover any cuts
explain the role of the heart in the formation of tissue fluid
contraction of ventricles produces high hydrostatic pressure
forcing water out of blood capillaries
explain how the binding of one molecule of oxygen to haemoglobin makes it easier for a second oxygen molecule to bind (2)
binding of first oxygen changes tertiary structure of haemoglobin
which uncovers another binding site
Why do mammals require a double circulatory system
To manage the pressure of blood flow
So it flows through lungs at a lower pressure
To prevent damage to the capillaries in alveoli
And reduces the speed of blood flow
Enabling more time for gas exchange
Blood is then pumped at a higher pressure from heat to body
To ensure that it reaches all the body cells
What are the unique properties of the cardiac muscles
myogenic
Therefore it can contract and relax without nervous hormonal stimulation
It never fatigues
as long as it has a constant supply of oxygen and glucose
Describe the structure of the arterioles
Muscle layer is Thicker than arteries
to help restrict blood flow into the capillaries
Elastic layer is Thinner than arteries
As pressure is lower
Walls are thinner
as pressure is lower
Has no valves