The cardiac cycle
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
the cardiac cycle
encompasses all events which coordinate passage of blood through the heart during one single beat
includes electrical, mechanical and pressure changes in a process transitioning from a relaxed heart to a contracted heart
wiggers diagram components
electrophysiological events
pressure events
clinical findings
LV pressure events
mechanical events and blood flow
route of blood during the cardiac cycle
superior and inferior vena cava
right atrium
bicuspid valve
right ventricle
pulmonary valve
pulmonary trunk→ pulmonary arteries
lungs
pulmonary veins
left atrium
mitral valve
left ventricle
aortic valve
aorta
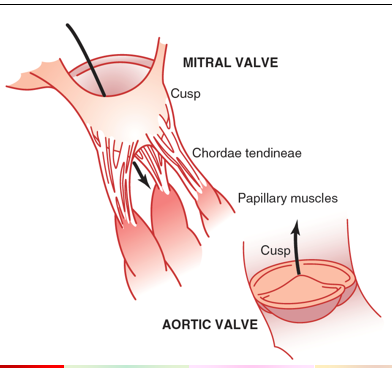
purpose of cardiac valves
prevent backflow of blood
how many leaflets do each valve have
mitral→ 2
tricuspid→ 3
aortic→ 3
pulmonary→ 3
valve anatomy
mechanical events occurring in the cardiac cycle
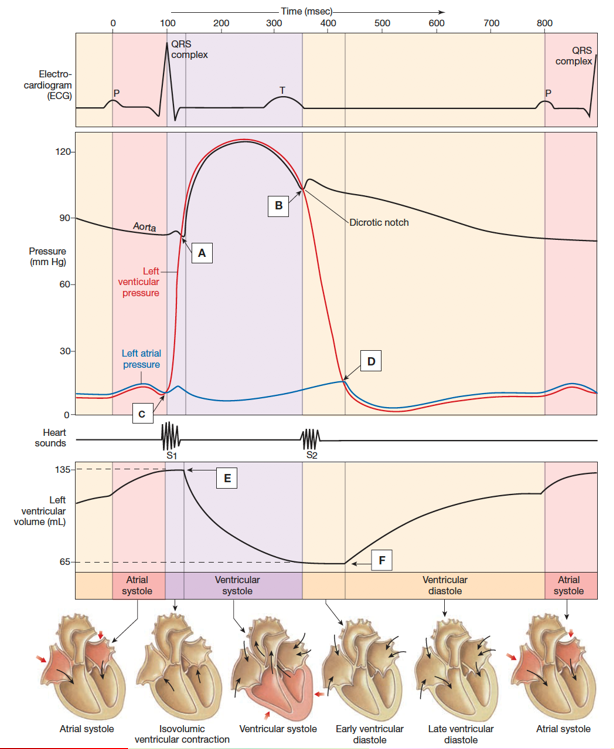
late diastole
atrial systole
isovolumic ventricular contraction
ventricular ejection
isovolumic ventricular relaxation
late diastole
both sets of chambers relaxed
ventricles filled passively
atrial systole
atrial contraction forces small amount of additional blood into ventricles
isovolumic ventricular contraction
first phase of ventricular contraction
pushes AV valves closed
does NOT create enough pressure to open semilunar valves
ventricular ejection
ventricular pressure rises and exceeds pressure in the arteries
semilunar valves open and blood is ejected
isovolumic ventricular relaxation
ventricles relax
pressure in ventricles falls
blood falls back into cusps of semilunar valves and snaps them closed
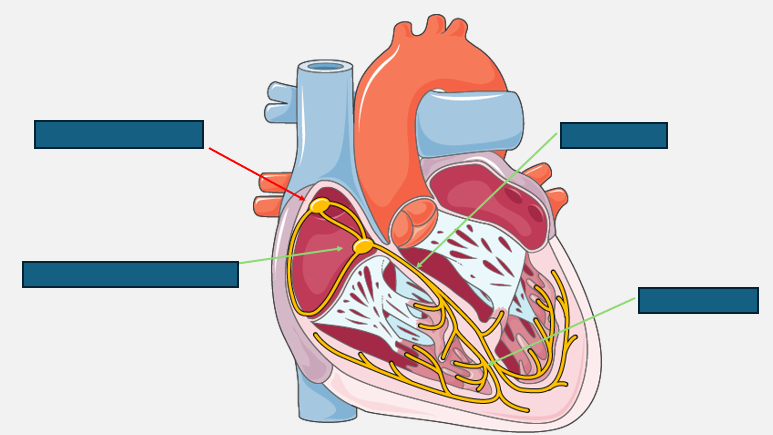
electrophysiological anatomy of the heart
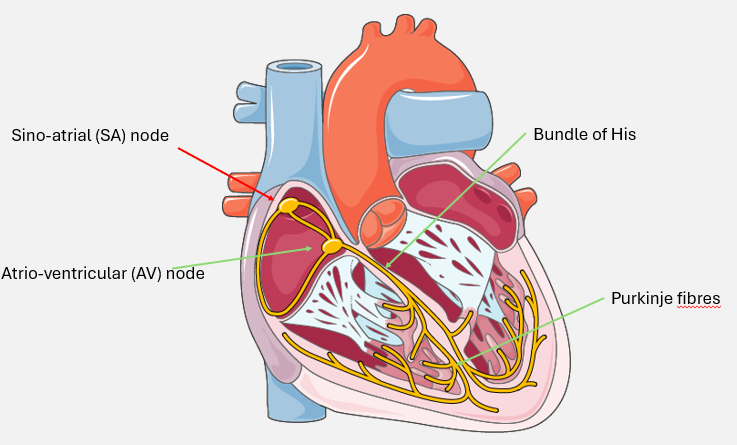
myogenic contraction of the heart
sino-atrial node initiates electrical depolarisation across both atria
atria have completed contraction and there is a short pause before AVN depolarises
AV nod depolarises and sends electrical activity down the bundle of His and Purkinje fibres→ ventricular depolarisation
ventricular depolarisation has completed
ventricular repolarisation phase→ prepares cell for next phase of depolarisation
ECG trace
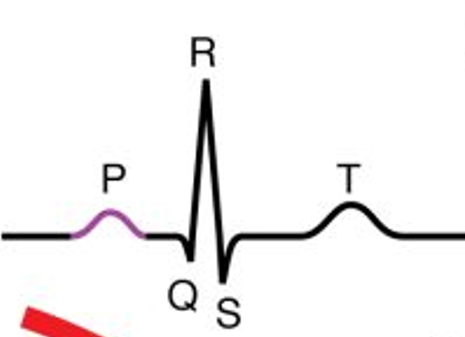
p-wave
generally positive deflection on ECG
smaller wave that QRS→ atria create smaller
PR interval
pause in electrical activity before ventricular depolarisation
delay caused by AV node
QRS complex
formed from direction of ventricular depolarisation goes down heart and back up ventricular walls
ST segment
demonstrates post-ventricular contraction
phase prior to repolarisation
T wave
ventricular repolarisation
usually demonstrated by positive deflection
heart sounds
lubb→ closure of antrioventricular valves
dupp→ closure of semilunar valves
murmurs
chnage in nature of normal heart sounds
not always pathological
e.g. valve stenosis (narrowing), regurgitation (leaky)
stroke volume
blood volume ejected from left ventricle during each heartbeat
cardiac output
total blood volume pumped from heart in 1 minute
stroke volume x heart rate
ejection fraction
percentage of blood pumped from LV that enters systemic circulation