NPB 100 Chapter 1 Test Bank
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
An action potential is a(n) _______ change in the electrical potential across the nerve cell membrane.
a. single
b. all-or-nothing
c. permanent
d. random
e. unidirectional
b. all-or-nothing
A neuron that innervates (i.e., makes synaptic contact with) a large number of other neurons
a. represents convergent neural signaling.
b. represents divergent neural signaling.
c. represents massive neural integration.
d. must fire at very high frequencies to be useful.
e. can fire only at very low frequencies.
b. represents divergent neural signaling.
A transgenic mouse animal model is created that expresses both the Cre recombinase gene, under control of a promoter for a gene expressed only in muscle fibers, and an androgen receptor with loxP sites around exon 2. How will expression of the androgen receptor protein be altered in the transgenic mouse?
a. The mouse will not express androgen receptor in muscle fibers.
b. The mouse will not express androgen receptor anywhere in the body.
c. The mouse will express increased levels of androgen receptor in muscle fibers.
d. The mouse will express increased levels of androgen receptor everywhere in the body.
e. The mouse will not express androgen receptor in the nervous system.
a. The mouse will not express androgen receptor in muscle fibers.
Compared with projection neurons, axons of local circuit neurons (interneurons)
a. are longer.
b. are shorter.
c. have more synapses.
d. have more branches.
e. reach more postsynaptic neurons.
b. are shorter.
Draw a diagram of a myotatic spinal reflex. Show the afferent and efferent neurons and the interneuron (local circuit neuron).
.
Draw a simple diagram of a neuron and label its components. In what ways are neurons specialized for communication? How do these specialized features distinguish neurons from other types of cells?
.
Glia are at least as numerous as neurons in the brain, yet neurons are the predominant focus of neuroscience textbooks. Why?
Neurons generate and conduct electrical and chemical signals, while glia primarily play a supporting role
Neuroethology is the field devoted to studying complex behavior
a. through specifically designed behavioral tasks.
b. in the native environment.
c. in a laboratory.
d. during a limited number of trials.
e. using invasive methods.
b. in the native environment.
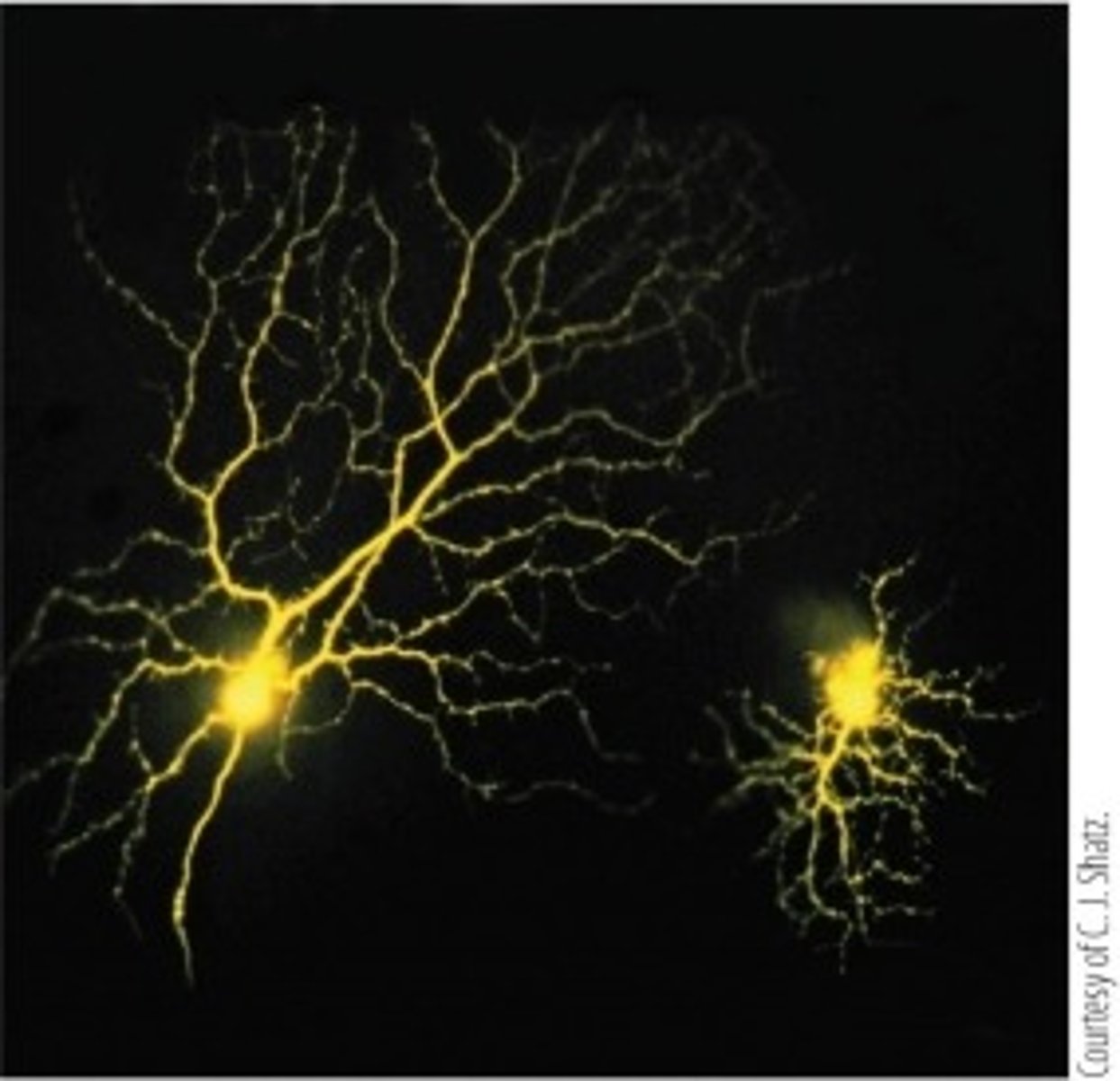
Refer to the figure. Which method was used to visualize the retinal neurons shown?
a. Cresyl violet staining
b. Intracellular injection of a fluorescent dye
c. Intracellular injection of an enzyme
d. Silver impregnation (the Golgi method)
e. Nissl stain
b. Intracellular injection of a fluorescent dye
The figure shows patterns of action potentials (vertical lines) in neurons that form the neural circuits for the knee-jerk reflex. Which pattern represents the activity of a flexor motor neuron?
a. Top
b. Second from the top
c. Third from the top
d. Bottom
e. None of the above
d. Bottom
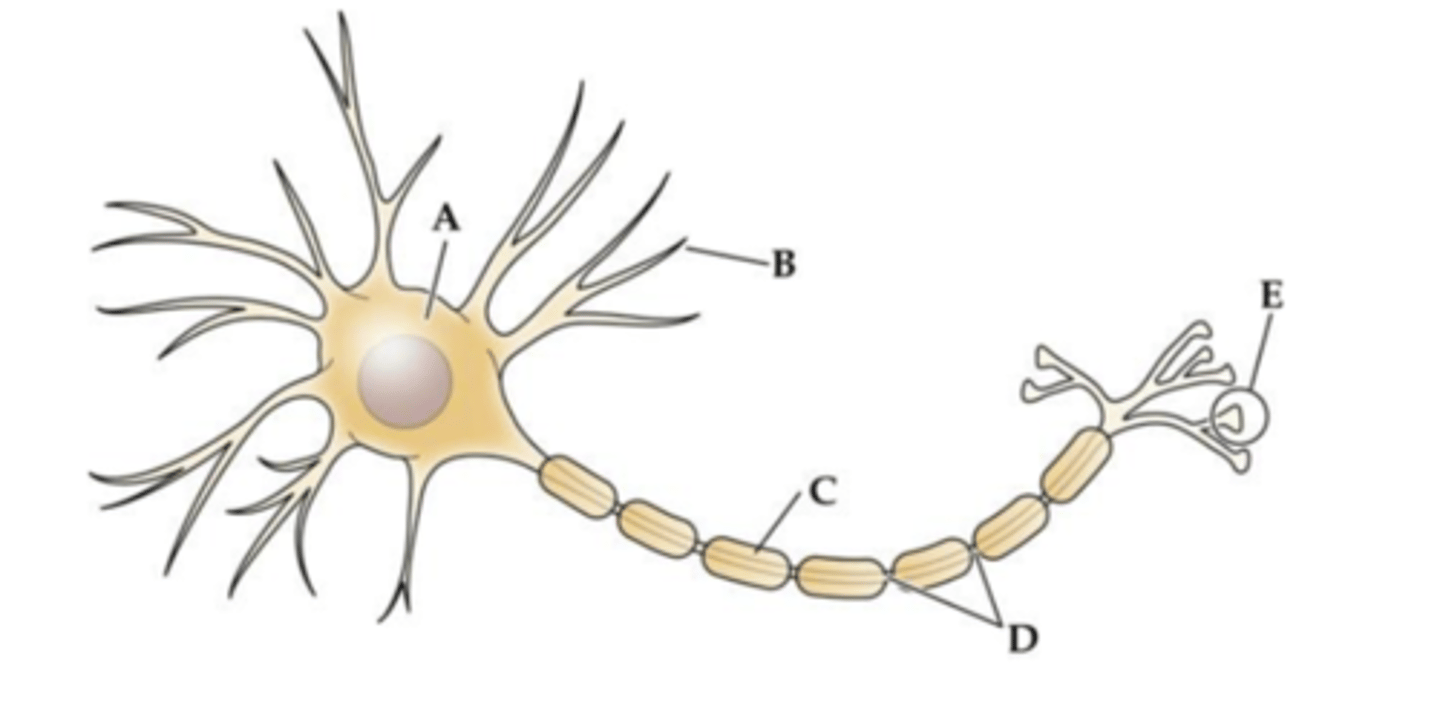
Structure _______ is the main target for incoming signals received from the axons of other cells.
A
B
C
D
E
B
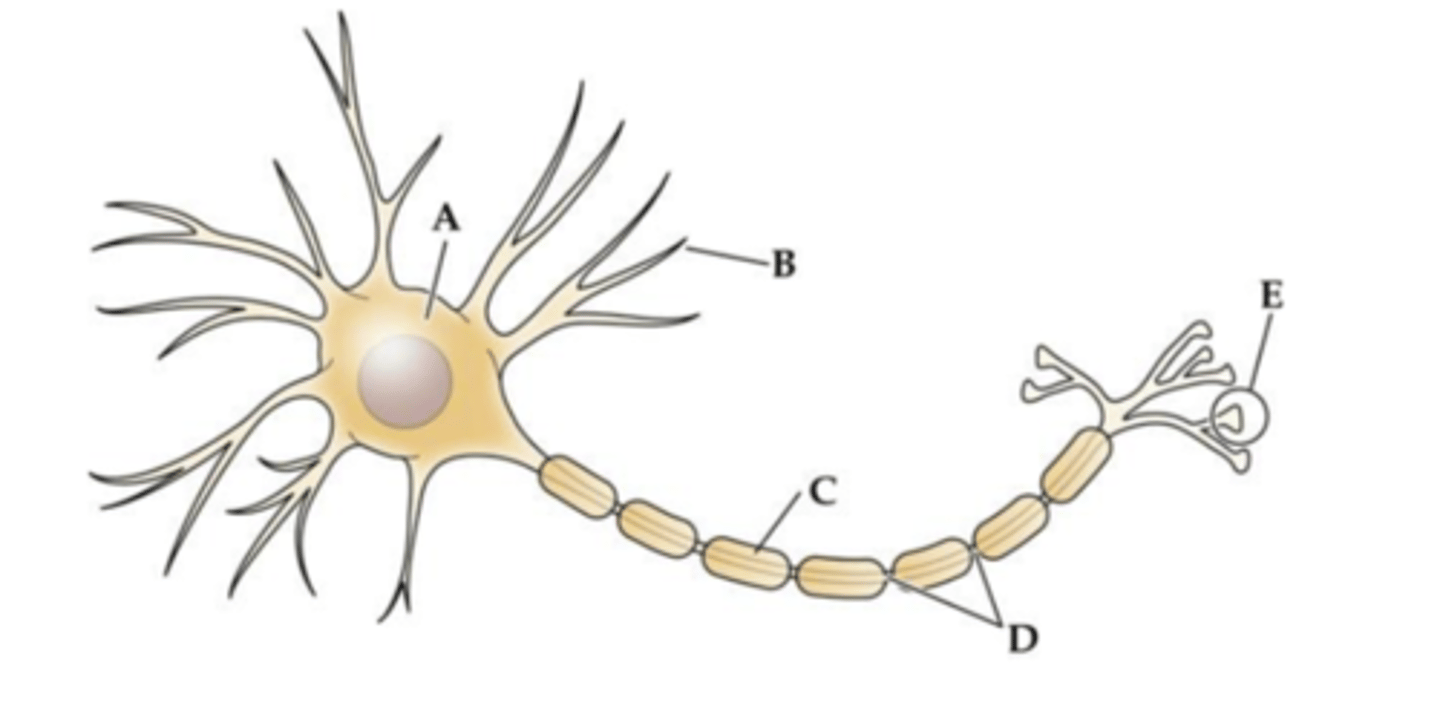
Which cell type forms the structure labeled C?
a. Oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system
b. Schwann cells in the central nervous system
c. Astrocytes in the peripheral nervous system
d. Microglia in the peripheral nervous system
e. Oligodendrocytes in the peripheral nervous system
a. Oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system
The brain imaging technique that makes use of a narrow X-ray beam is called
a. MRI.
b. fMRI.
c. PET.
d. SPECT.
e. CT.
e. CT.
The in situ hybridization method is based on
a. labeling specific neuronal components with antibodies.
b. using nucleic acid probes to detect mRNAs that encode specific genes.
c. using nucleic acid probes to detect specific proteins.
d. injecting a fluorescent dye into a neuron.
e. formation of an insoluble colored product within cell bodies.
b. using nucleic acid probes to detect mRNAs that encode specific genes.
The neurons whose synaptic connections with glandular cells trigger stomach secretions are located in
a. the spinal cord.
b. the brain stem.
c. the ganglia located along the vertebral column.
d. front of the vertebral column.
e. the ganglia embedded in the wall of the stomach.
e. the ganglia embedded in the wall of the stomach.
The part of a synapse to which the contents of synaptic vesicles bind is called the
a. presynaptic terminal.
b. synaptic ending.
c. axon terminal.
d. terminal bouton.
e. receptor.
e. receptor.
What are the main types of glial cells, and what is the main function of each?
Astrocytes maintain an optimal environment for neural signaling;
microglia respond to injury within the nervous system;
oligodendrocytes and Schwann cell produce myelin in the CNS and the PNS, respectively
Which cell produces myelin in the nerves of the peripheral nervous system?
a. Astrocyte
b. Neuron
c. Schwann cell
d. Microglia
e. Neural progenitor cell
c. Schwann cell
Which feature distinguishes the four model organisms (mouse, zebrafish, fruit fly, and nematode) from other animals that have been intensively studied by neuroscientists?
a. Ease of genetic analysis and manipulation
b. Nervous system of substantial complexity
c. Extensive and interesting behavioral repertoire
d. Specific neural structures or behaviors of interest
e. Expression of behaviors is reflex-only (i.e., no complex behaviors)
a. Ease of genetic analysis and manipulation
Which function is a characteristic primarily of neurons only, and not glia?
a. Transmits action potentials
b. Supports electrical signals
c. Repairs the nervous system
d. Prevents regeneration of the nervous system
e. Produces myelin
a. Transmits action potentials
Which glial cell type serves as a resident immune cell in the central nervous system?
a. Glial stem cell
b. Astrocyte
c. Microglia
d. Oligodendrocyte
e. Schwann cell
c. Microglia
Which intracellular component facilitates the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis underlying synaptic communication?
a. Mitochondria
b. Endoplasmic reticulum
c. Cytoskeleton
d. Golgi apparatus
e. Nucleus
c. Cytoskeleton
Which of the following is not an established role for glial cells?
a. integrating information to assist neural computation
b. Maintaining the ionic milieu surrounding nerve cells
c. Hastening the propagation of neural impulses
d. Assisting synaptic transmission via neurotransmitter uptake
e. Providing scaffolds that assist neural development
a. integrating information to assist neural computation
Which part of DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA?
a. Exon
b. Intron
c. Promoter
d. Non-coding DNA
e. Regulatory DNA
a. Exon
Which statement accurately describes neural and glial cells?
a. In both types, mitochondria are concentrated in the cell body.
b. The endoplasmic reticulum is concentrated in axons.
c. Exocytosis and endocytosis are important for synaptic communication.
d. Glial cells and neurons rapidly transmit long-range electrical signals.
e. Neither cell type relies on cytoskeletal filaments.
c. Exocytosis and endocytosis are important for synaptic communication.
Which statement accurately describes the expression of genes in the nervous system?
a. Every gene in the human genome is expressed in the CNS.
b. Splice variants add diversity to brain function via beneficial mutations.
c. Most of the genes in the human genome are expressed in the CNS.
d. The genes that are expressed in the CNS are expressed equally in all neurons.
e. A small subset of the total human genome is expressed in the CNS.
c. Most of the genes in the human genome are expressed in the CNS.
Which statement best describes most neurons?
a. They receive information via axons.
b. They transmit information to other cells via dendrites.
c. They are polarized.
d. They conduct signals bidirectionally.
e. They transmit electrical signals via cytoplasmic continuity.
c. They are polarized.
Which statement best describes the function of a neuron with multiple, highly branched dendrites and one axon?
a. It passes information directly to multiple neurons.
b. It cannot integrate information from multiple neurons.
c. It receives information from only one other neuron.
d. It integrates information from many neurons.
e. The information it receives will not be relayed.
d. It integrates information from many neurons.