Velocity, Torque, Voltage, Light
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
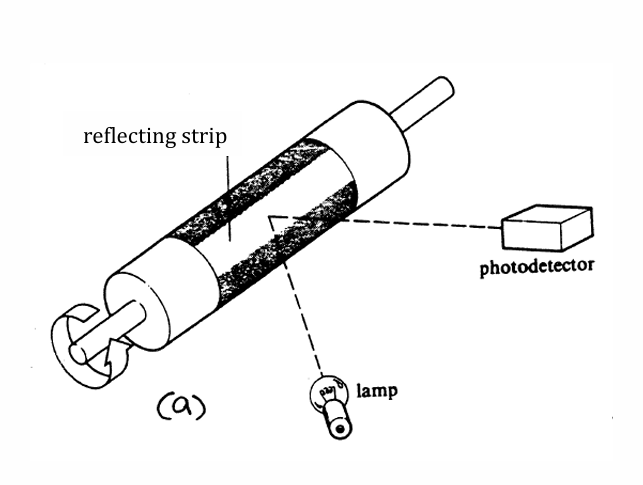
Working principle of velocity transducer with frequency output (photodetector)
shaft with reflective strip on non-reflective band rotates
detector detect light source when reflective part faces light source
2 types of angular velocity transducer
revolution counter- measure rate of rotation
tachogenerators- generate output proportional to angular velocity due to electromagnetic induction
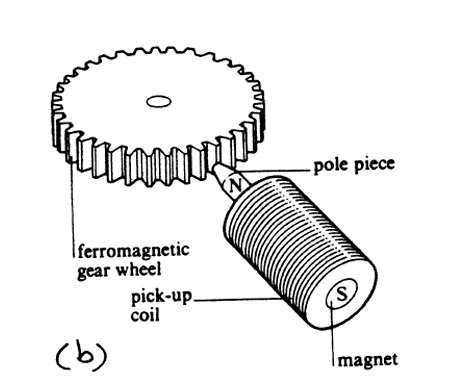
working principle of a variable reluctance tachometer
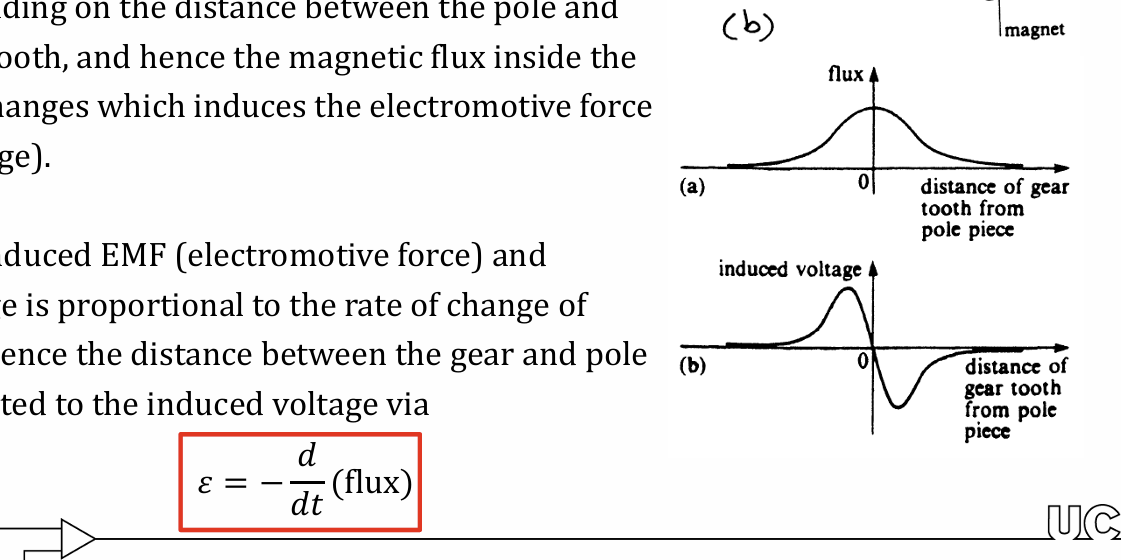
pick-up coil surrounds permanent magnet that is placed close to ferromagnetic gear wheel mounted on sensing shaft
reluctance of magnetic circuit varies due to changes in distance of pole to gear tooth
reluctance: resistance to change in magnetic flux (high reluctance at greater distance)
magnetic flux in coil changes which induce electromotive force as they are proportional
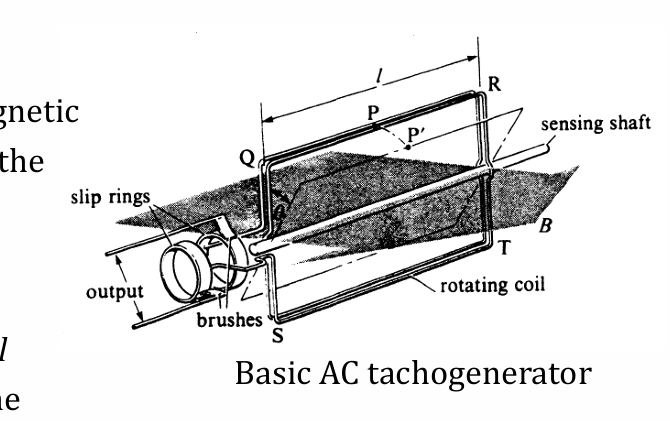
working principle of tachogenerator
transducer use energy of rotation of sensing shaft to generate electric output via electromagnetic induction
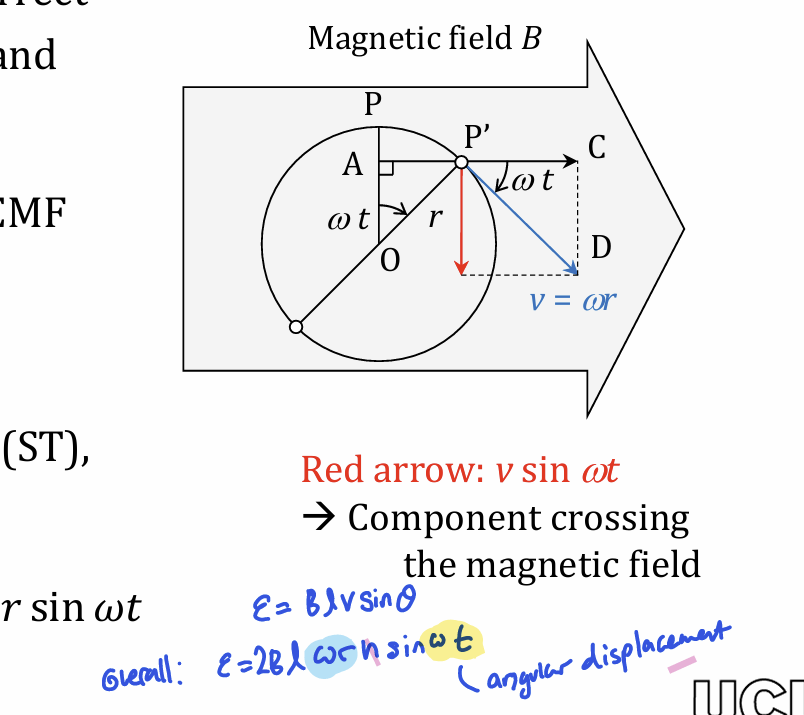
when conductor is moving perpendicular to field, emf is maximum as theta=90 and voltage=Blv
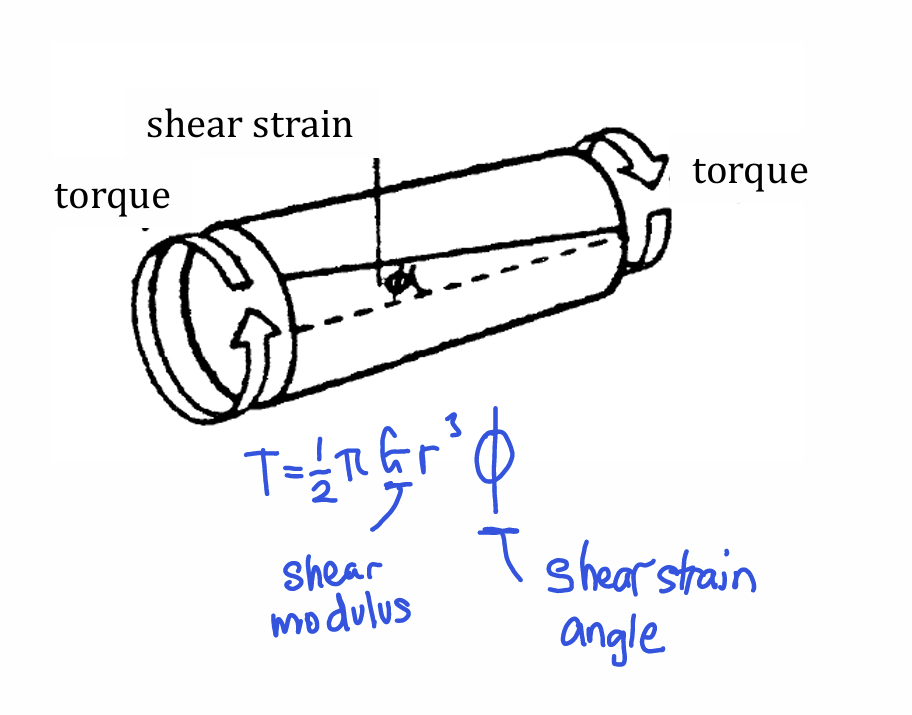
Working principle of strain gauge torque measurement+ equation of torque in terms of shear strain angle
measured by detecting angular displacement of sensing shaft
strain gauge detects strain on surface of shaft
to maximise strain, place gauge in 45 degree angle
place dummy gauge perpendicular to measuring gauge for temperature compensation
Definition and formula of shear sensitivity

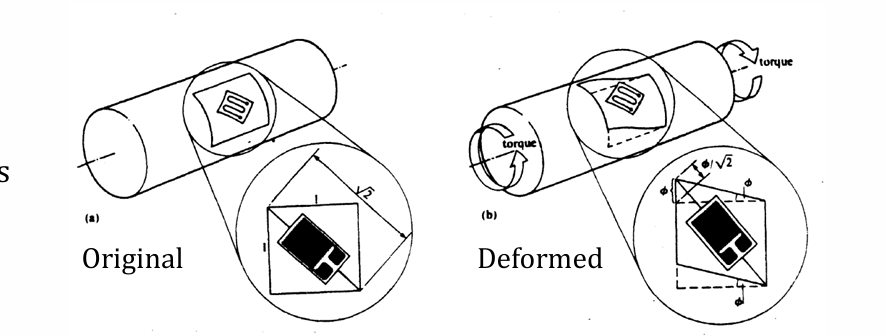
strain and shear strain angle relationship + gauge sensitivity when gauge is placed 45 degrees to axis of shaft
assume unit square area is small so that displacement=phi/2
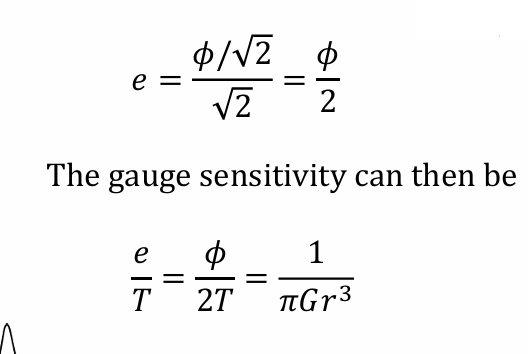
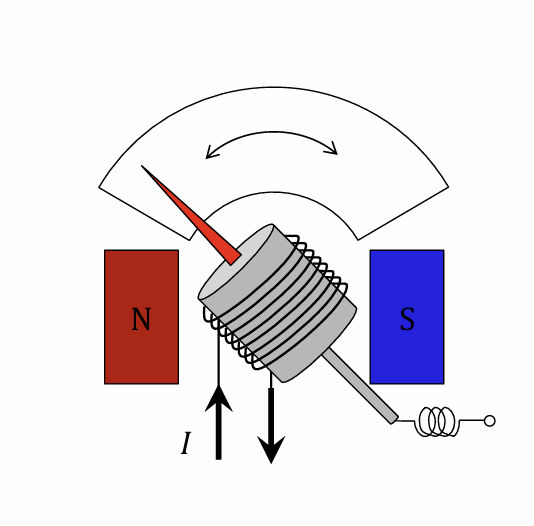
Working principle of analogue voltmeter/ammeter
use of electromotive forces
working principle of digital voltmeter
unknown amplified voltage applied to input terminal
passed to a successive approximation analog-to-digital converter(ADC)
convert continuous analog voltage signal to discrete digital code
code sent to microprocessor which determines actual voltage and convert to inputted scale and unit
microprocessor sent to digital display
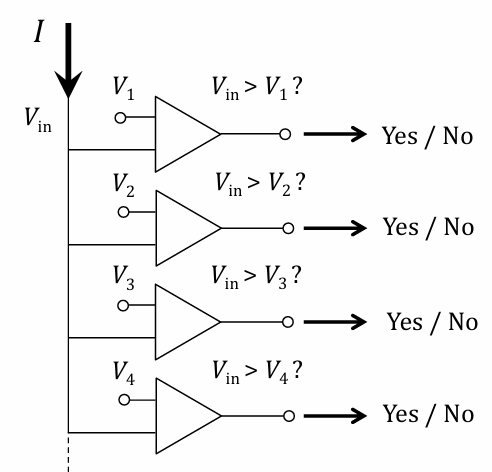
working principle of successive approximation ADC
compare input to reference voltage → if reference voltage<input, reference voltage increase by half and repeated
reference voltage adjusted at smaller increments until it matches input voltage
Advantages of DVM over analogue voltmeter
eliminate observational error by operator
no parallax or approximation error
quick reading
output can be stored on memory device
low power
compact and cheap and accurate
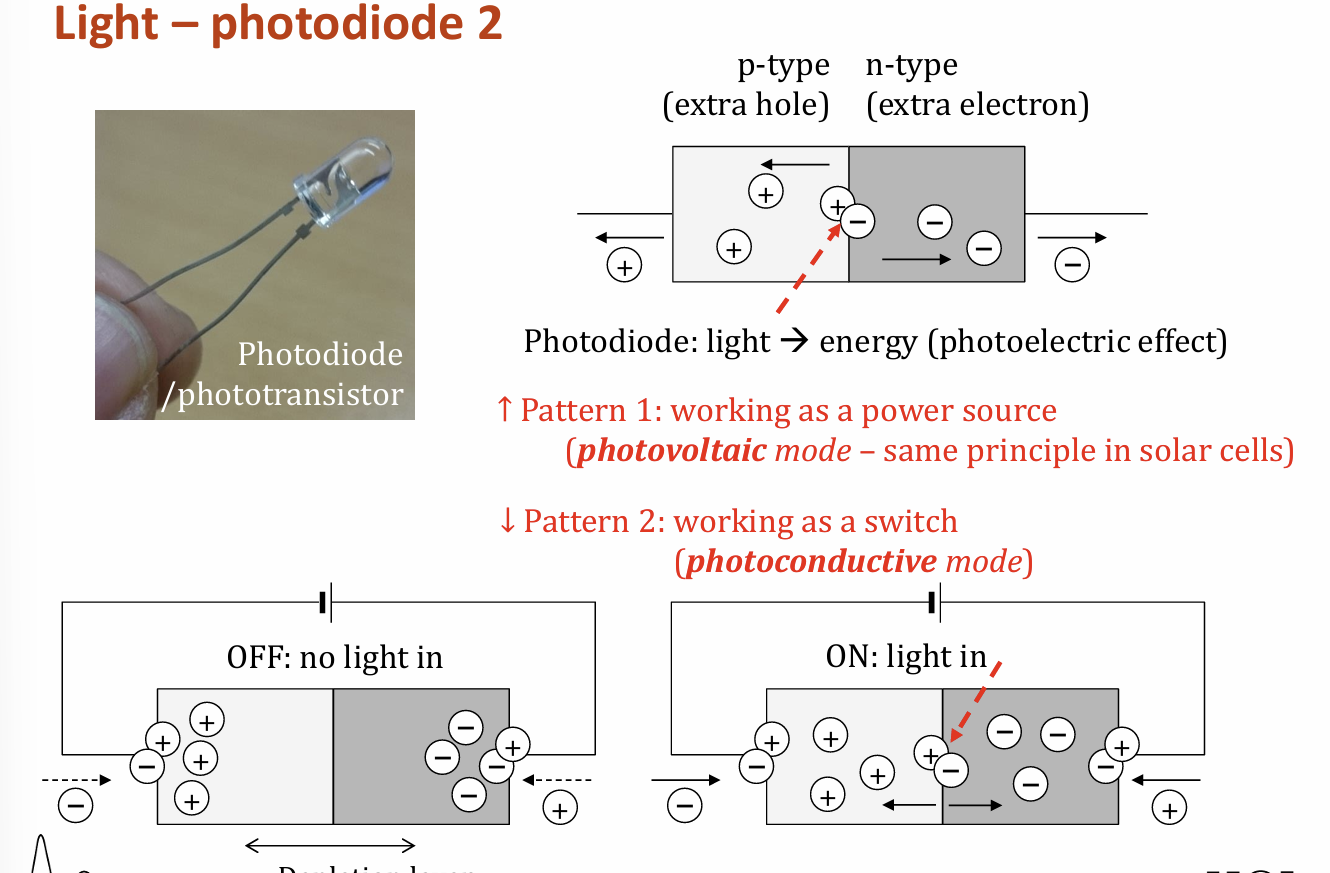
working principle of photodiode
when light of sufficient energy strike photodiode, it creates electron hole pair in semiconductor called photoelectric effect
current is produced
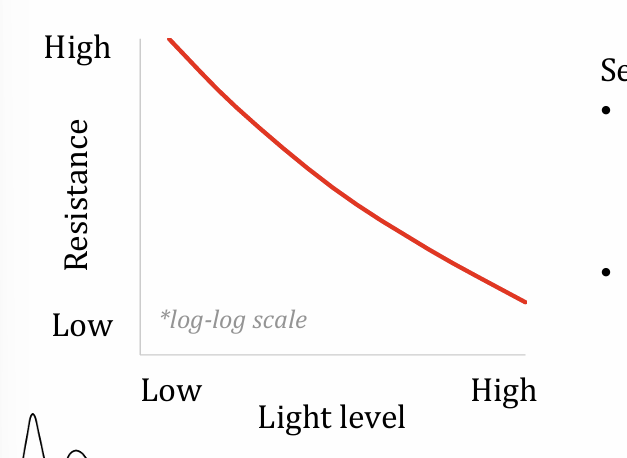
working principle of LDR
light energy excite electron from valence band to conductive band (E=hv)
reduces resistivity
semiconductor require lower excitation energy than metals