Neoplasms of the Musculoskeletal System - Clin Med
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What does this refer to
68-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for left leg pain.
His pain has been progressively worsening over the course of a month and is present at night.
Physical examination demonstrates impaired left lower extremity weakness limited by pain.
A radiograph of the left hip and femur demonstrates lytic lesions and intralesional calcifications.
Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
Chondrosarcoma is defined as a cancer of the cartilage
Central metaphyseal
Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
MC 40-75yo
M > F
3rd MC primary malignancy of bone
Epidemiology Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
Malignant cartilage forming tumor that does not produce osteoid
May arise from osteochondroma
MC bone location
Proximal femur
Pelvic bones
Proximal humerus
Ribs
Etiology Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
Pain that gets worse over time and with physical activity
Swelling, stiffness, and tenderness at the affected area
Back or thigh pain
Sciatica-like sx
Bladder sx
Unilateral edema
Clinical history Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
Tenderness to palpation at the site of involvement
Neurologic dysfunction if there are pelvic lesions close to the neurovascular bundle
Pearly white or light blue, often with focal calcification
May have small cysts or myxoid change
Clinical presentation/physical exam Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
Histopathology = Malignant chondrocytes in gelatinous cartilaginous matrix
Workup Chondrosarcoma
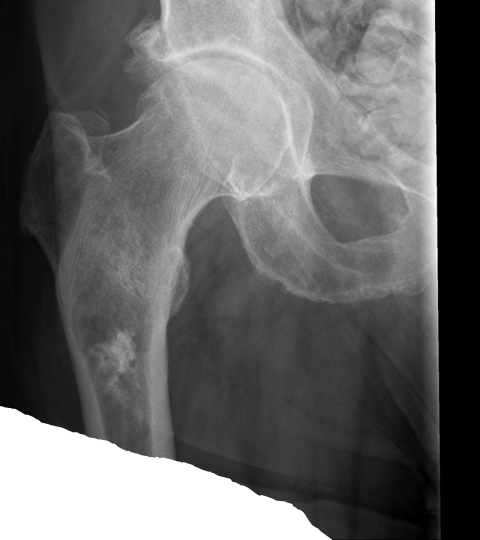
What does this refer to
Radiograph shows popcorn leisions!!!
Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
Consult/referral Orthopedic/Radiation Oncology
Surgical
Intralesional curettage (low grade)
Wide en bloc local excision (intermediate-high grade)
Clinical intervention Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
Morbidity/Complications
Pathologic fractures
Metastasis (low probability)
Referral to orthopedic oncology for best prognosis
Poor Prognostic Variables
More aggressive course
Axial and proximal extremity lesions
Advanced patient age
Inadequate surgical margins
Patients may have local recurrence or metastases up to 20 years later
5-year survival rate for adult bone cancer is 66%
Adults with chondrosarcoma have a 5-year survival rate of 80% compared to a 5-year survival rate of 54% for osteosarcoma.
If metastatic disease 5-yr survival rate is 55%
Prognosis Chondrosarcoma
What does this refer to
Bone is 3rd MC site for metastatic disease
Carcinomas that commonly spread to bone
Breast
Lung
Thyroid
Renal
Prostate
Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
Metastatic bone lesions MC > 40 yo
Most common sites of metastatic lesions
Axial skeleton _ vertebrae, pelvis, ribs
Proximal limb girdle
Proximal femur MC of fx secondary to metastatic bone lesions
Epidemiology Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
Metastatic bone destruction
Tumor induced activation of osteoclasts
Etiology Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
Pain
Bone due to destruction
Tumorigenic
Worse at night
Pathologic fx
Up to 30% of patients
Clinical history Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
Muscle weakness if malignant hypercalcemia
Physical exam Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to

Workup Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
Radiation therapy
Breast
Prostate
MM
Lymphoma
Operative
Arthroplasty with adjuvant radiation
Spinal neurologic decompression/stabilization
+ post-op radiation
Indicated with mets to spine
Clinical intervention Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
Bisphosphonate therapy
Dexamethasone
Spine mets
Clinical management Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
Metastatic hypercalcemia
confusion
polyuria & polydipsia
nausea/vomiting
Dehydration
Physical Exam
Muscle weakness
Complication Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
Survival rate
Thyroid – 48 months
Prostate – 40 months
Breast – 24 months
Kidney – varies
As little as 6 months
Lung – 6 months
Prognosis Metastatic Cancer to Bone
What does this refer to
A 12-year-old boy presents to the pediatric emergency department with pain in his right lower extremity.
He was recently playing in soccer, but he denies any trauma to the leg.
Physical examination is notable for mild swelling in the right mid-tibia and tenderness to palpation.
A radiograph of the leg demonstrate periosteal elevation and "onion skinning" concerning for malignancy.
Ewing sarcoma
What does this refer to
Cancerous tumor that grows in the bones or in the tissue around bones (soft tissue)
legs, pelvis, ribs, arms or spine
Includes
Ewing sarcoma
Askin tumor
Peripheral neuroectodermal tumors
Ewing sarcoma
What does this refer to
MC birth to age 20
M > F
9x > Caucasian v AA
Epidemiology Ewing sarcoma
What does this refer to
Genetic
t(11:22) translocation
Specific cause for the transformation hasn’t been identified
Etiology Ewing Sarcoma
What does this refer to
Patients usually present with pain
Patients often have a palpable mass
Back pain may indicate a paraspinal, retroperitoneal, or deep pelvic tumor
Systemic symptoms of fever and weight loss can also occur and often indicate metastatic disease
Clinical History Ewing Sarcoma
What does this refer to
Fever
Weight loss
Diaphysis of Long bones
Upper arm
Flat bones
Pelvis
Skull
Ribs
Palpable mass
Local tenderness
Joint swelling
Physical exam Ewing Sarcoma
What does this refer to
Physical exam Ewing Sarcoma
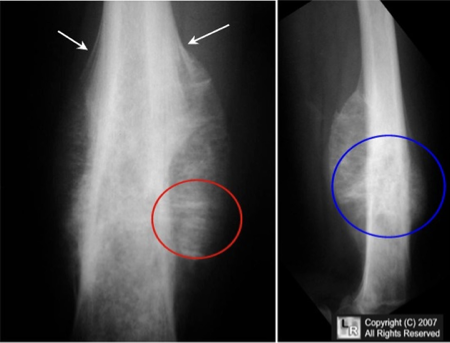
What does this refer to
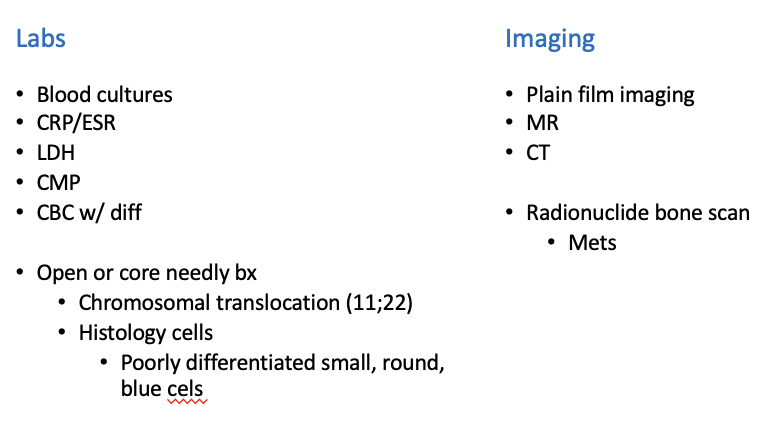
Workup Ewing Sarcoma
What does this refer to
Ewing sarcoma or another tumor is probable
Consultation with a pediatric oncologist BEFORE biopsy
Biopsy is required for definitive diagnosis
Histology
Small, round blue cell tumors
Differentiated or undifferentiated
Eval for Mets includes bilateral bone marrow biopsies
Biopsy Ewing Sarcoma
What does this refer to
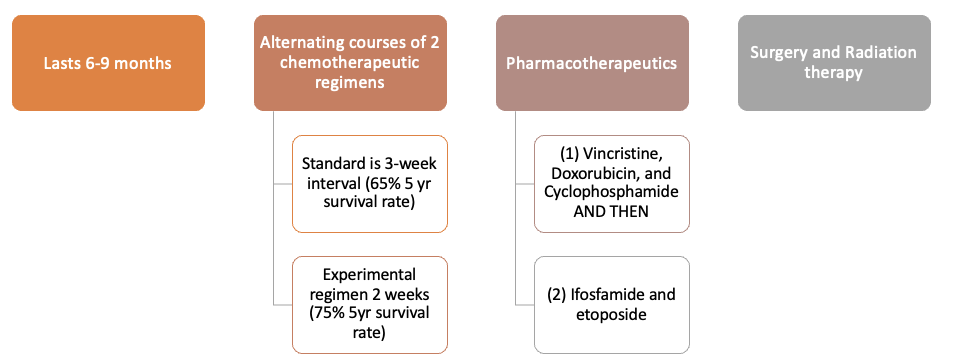
Clinical management Ewing Sarcoma
What does this refer to
Alopecia, nausea, vomiting, occasionally diarrhea
Increased risk of infection from immune suppression
Change in mood/appetite
Monitor Nutritional and psychological status
Side Effects of chemotherapy
Organ damage
Infertility
Risk of secondary malignancy
Chemotherapy Complications Ewing Sarcoma
What does this refer to
Most significant factor to determine prognosis is presence or absence of metastatic disease
Primary tumor site also a factor
Distal extremities more favorable
Age younger than 15yr more favorable prognosis
Prognosis Ewing sarcoma
What does this refer to
Osteogenic bone tumor
MC bone Locations
Metaphysis of long bones
Distal femur
Proximal tibia
Distant Mets
MC lungs
Can also mets to same bone or different bone
Osteosarcoma
What does this refer to
More Common in Adolescents
Osteosarcoma is the 5th most common malignancy among adolescents 15-19
Bimodal distribution with 2nd peak in 50-60 yo
M > F
In children – MC site is LE
In adults – MC site is axial
In adults – greatest risk factor is Hx of Paget’s disease (benign bone lesion)
Epidemiology Osteosarcoma
What does this refer to
Bone pain is MC complaint (Long Bone)
Pathologic fx usually absent
Pain may result in a limp, loss of function
+/- swelling
Osteosarcoma
What does this refer to
Palpable mass
↓ ROM in affected bone/joint
Motion/activity increases pain
Physical exam Osteosarcoma
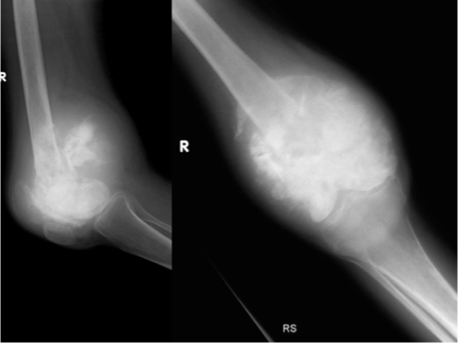
What does this refer to

Workup Osteosarcoma
What does this refer to
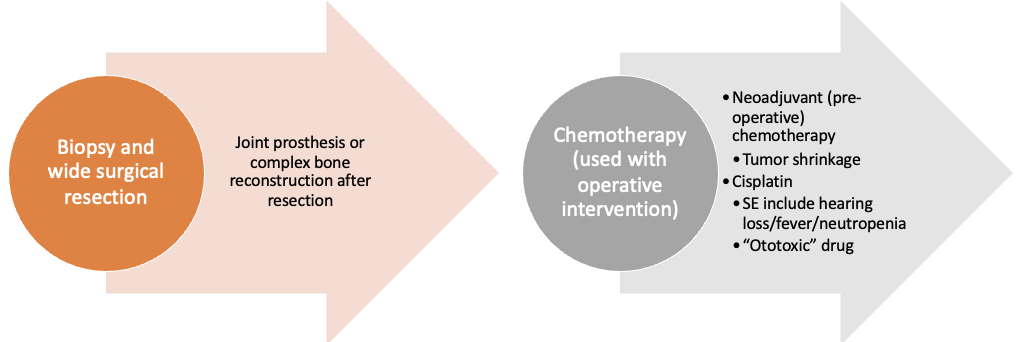
Clinical management Osteosarcoma
What does this refer to

Prognosis Osteosarcoma
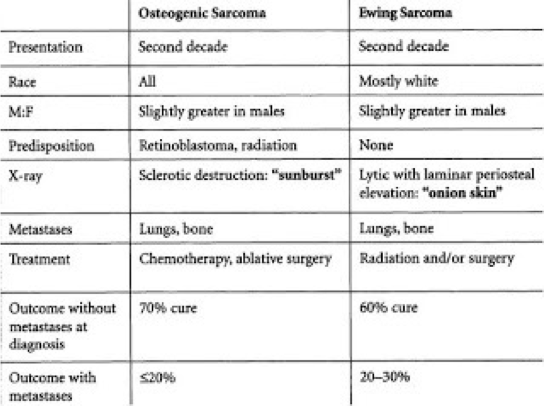
What does this refer to
Comparison Osteosarcoma – Ewing Sarcoma
What does this refer to
________ is a type of cancer that occurs in (lipocytes)fat cells
Muscles of the limbs or the abdomen
Rare cancer
Type of soft tissue sarcoma
Slow growing
Liposarcoma
What does this refer to
Most common soft tissue worldwide
Only 20% of soft tissue cancers in the US are a liposarcoma
Don’t confuse this with a lipoma
Average age of dx is 50 yo
No race of gender predilection
Epidemiology Liposarcoma
What does this refer to
Risk factors
Radiation therapy
Family cancer syndromes
Damage/trauma to the lymphatic system
Toxic chemical exposure
Etiology Liposarcoma
What does this refer to
Types of liposarcoma
Well differentiated & dedifferentiated liposarcoma
Myxoid and round cell liposarcoma
Pleomorphic liposarcoma
Pathology Liposarcoma
What does this refer to
History and physical exam findings depend on location of the tumor
Paresthesias
Varicose veins
Fatigue
Weight loss
N/V
When in the abdomen – dysphagia & regurgitation of food
Clinical history Liposarcoma
What does this refer to
Most are asx
Pain/tenderness
Edema
Functional loss
Deep mass in the lower extremity
Often non-tender
Physical exam Liposarcoma
What does this refer to

Workup Liposarcoma
What does this refer to
Surgical excision
Wide and deep
Adjuvant radiation (possibly with chemo) for high-grade lesions
Clinical intervention Liposarcoma
What does this refer to

Strong correlation with histology subtypes, tumor grade, location and status of surgical margins
Prognosis Liposarcoma
What does this refer to
Subtypes
Embryonal
MC infants/young children
Alveolar
MC Adolescents/young adults
Botryoid
MC infants/young children
Pleomorphic
MC patients 40-70 yo
Nodal metastasis often occurs with rhabdomyosarcoma
Bx of sentinel node should be part of the treatment
Bone marrow bx required for staging
Epidemiology Rhabdomyosarcoma
What does this refer to
Orbit: Proptosis or dysconjugate gaze
Paratesticular: Painless scrotal mass
Prostate: Bladder or bowel difficulties
Uterus, cervix, bladder: Menorrhagia or metrorrhagia
Vagina: Protruding polypoid mass (botryoid, meaning a grapelike cluster)
Extremity: Painless mass
Parameningeal (ear, mastoid, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, infratemporal fossa, pterygopalatine fossa): Upper respiratory symptoms or pain
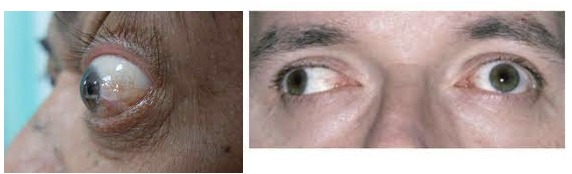
Clinical history Rhabdomyosarcoma
What does this refer to
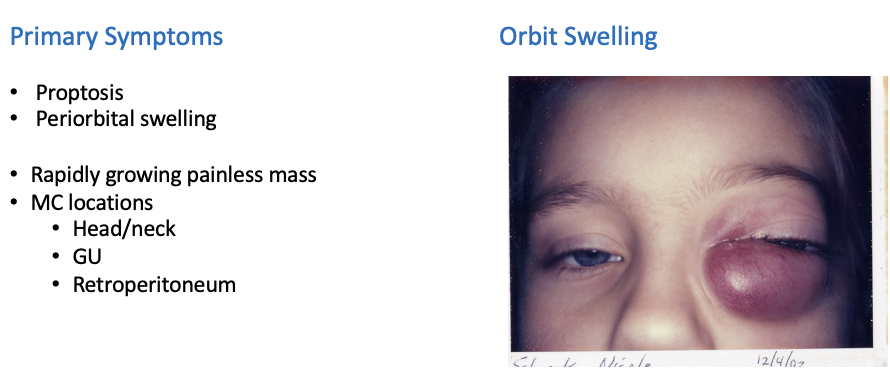
Rhabdomyosarcoma Head and Neck
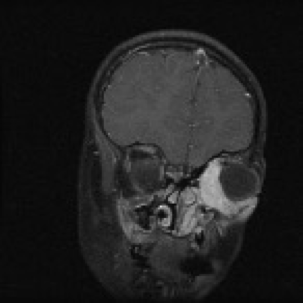
What does this refer to
Cranial Nerve Palsies
Hearing Loss
Chronic aural or sinus drainage
Image shows PARAMENINGEAL
Physical exam Rhabdomyosarcoma – Head and Neck
What does this refer to
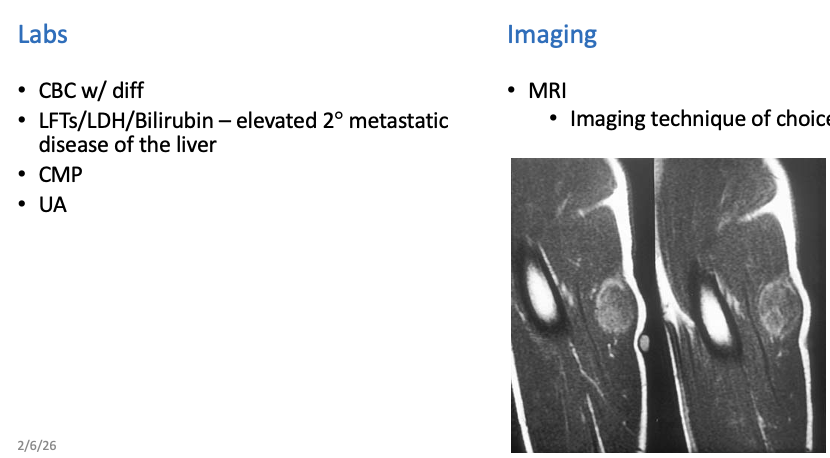
Workup Rhabdomyosarcoma
What does this refer to
Localized disease, overall 5-year survival rates have improved to more than 80% with the combined use of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy
Prognosis Rhabdomyosarcoma
What does this refer to
___________ are tumors that effect the cartilage inside the bones
MC benign bone neoplasm of the hand, but can effect other areas
Enchondroma – Benign Bone Tumor
What does this refer to
Typically asymptomatic unless accompanied with injury such as a fracture
Symptoms
Pain
Changes in growth
Abnormal exam
Affected area may enlarge
Clinical history/physical exam Enchondroma
What does this refer to
Bone infarct
Chondrosarcoma
Differential diagnosis Enchondroma
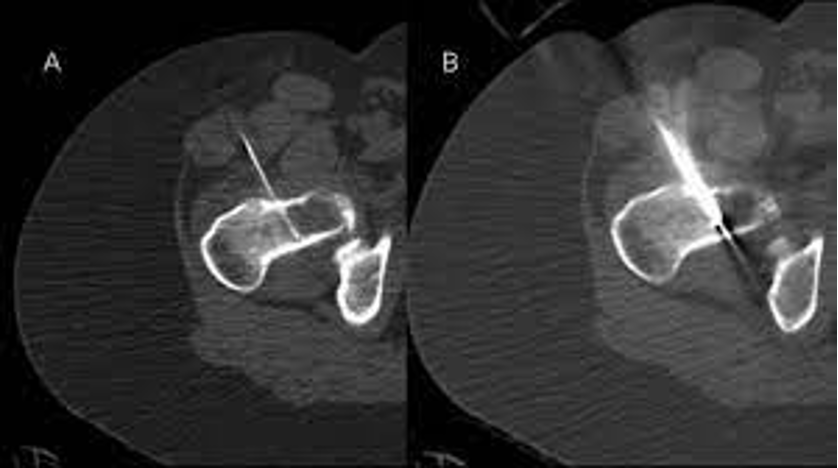
What does this refer to
Core needle bx
From areas of bone scalloping or lysis
Histology
Blue-gray lobulated hyaline cartilage with scattered calcifications
Workup Enchondroma
What does this refer to
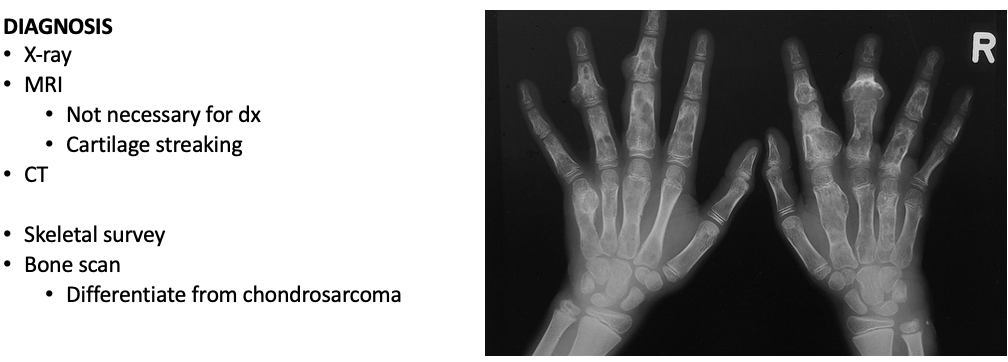
Workup Enchondroma
What does this refer to

Clinical management Enchondroma