Chapter 3 Addendum (Done)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Required Rate of Return
The required rate of return (RRR) is the minimum return an investor will accept for owning a company's stock, as compensation for a given level of risk associated with holding the stock. The RRR is also used in corporate finance to analyze the profitability of potential investment projects.
The RRR is also known as the hurdle rate, which like RRR, denotes the appropriate compensation needed for the level of risk present. Riskier projects usually have higher hurdle rates, or RRRs, than those that are less risky.
The required rate of return is the minimum return an investor will accept for owning a company's stock, to compensate them for a given level of risk.
To accurately calculate the RRR and improve its utility, the investor must also consider his or her cost of capital, the return available from other competing investments, and inflation.
The RRR is a subjective minimum rate of return; this means that a retiree will have a lower risk tolerance and therefore accept a smaller return than an investor who recently graduated college and may have a higher appetite for risk.
Required Rate of Return
The required rate of return (RRR) is the minimum return an investor will accept for owning a company's stock, as compensation for a given level of risk associated with holding the stock. The RRR is also used in corporate finance to analyze the profitability of potential investment projects.
hurdle rate
The RRR is also known as the __________, which like RRR, denotes the appropriate compensation needed for the level of risk present. Riskier projects usually have higher hurdle rates, or RRRs, than those that are less risky.
minimum return
The required rate of return is the __________ an investor will accept for owning a company's stock, to compensate them for a given level of risk.
cost of capital
To accurately calculate the RRR and improve its utility, the investor must also consider his or her _________, the return available from other competing investments, and inflation.
subjective minimum rate of return
The RRR is a _____________________; this means that a retiree will have a lower risk tolerance and therefore accept a smaller return than an investor who recently graduated college and may have a higher appetite for risk.
Expected Rate of Return
The expected return is the profit or loss an investor can anticipate receiving on an investment.
Expected returns cannot be guaranteed.
weighted average
The expected return for a portfolio with multiple investments is the ______________ of the expected return of each investment.
Expected Return Formula
Σ (Returni x Probabilityi)
Using CAPM to Calculate Expected Rate of Return

PV of Cashflows
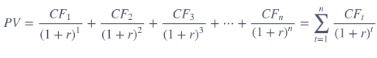
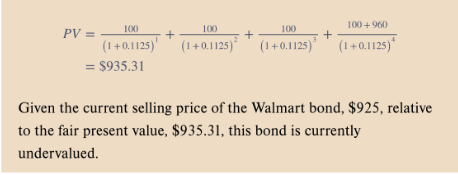
Suppose a Walmart bond you purchased two years ago for $890 is now selling for $925.
The bond paid $100 per year in coupon interest on the last day of each year (with the last payment made today). You intend to hold the bond for four more years and project that you will be able to sell it at the end of year 4 for $960. You also project that the bond will continue paying $100 coupon payments per year. Given the risk associated with the bond, its required rate of return over the next four years is 11.25% per year.
Is the bond undervalued or overvalued?
Relationship between Required Rate of Return and Expected Rate of Return

E(r) ≥ r or P ≤ PV
The projected cash flows received on the security are greater than or equal to those required to compensate for the risk incurred from investing in the security. Thus, buy this security.
E(r) < r or P > PV
The projected cash flows received on the security are less than is required to compensate for the risk incurred from investing in the security. Thus, do not buy this security.
Duration
The price sensitivity of a bond can be directly measured by a concept called duration.
(Modified) Duration also produces an accurate measure of the price sensitivity of a bond to small changes in interest rates.
The duration measure is a less accurate measure of price sensitivity to larger changes in interest rates.
(Macaulay) Duration is defined as the weighted-average time to maturity on a financial security using the relative present values of the cash flows as weights.
duration
The price sensitivity of a bond can be directly measured by a concept called _________.
small changes in interest rates
(Modified) Duration also produces an accurate measure of the price sensitivity of a bond to ______________.
larger changes in interest rates
The duration measure is a less accurate measure of price sensitivity to _________________.
relative present values of the cash flows as weights
(Macaulay) Duration is defined as the weighted-average time to maturity on a financial security using the _______________________________.
Duration (part 2)
On a time-value of money basis, duration measures the weighted average of when cash flows are received on a security.
In addition to being a measure of the average life of an asset or liability, duration also has economic meaning as the sensitivity, or elasticity, of that asset or liability’s value to small interest rate changes (either required rate of return or yield to maturity).
Duration describes the percentage change in price, or present value, of a security for a given small change in interest rates.
For investors and portfolio managers, duration is a tool that can be used to estimate the change in the value of a portfolio of securities for a given change in interest rates.
weighted average
On a time-value of money basis, duration measures the __________ of when cash flows are received on a security.
elasticity
In addition to being a measure of the average life of an asset or liability, duration also has economic meaning as the sensitivity, or _________, of that asset or liability’s value to small interest rate changes (either required rate of return or yield to maturity).
percentage change in price
Duration describes the ________________, or present value, of a security for a given small change in interest rates.
estimate the change
For investors and portfolio managers, duration is a tool that can be used to _________________ in the value of a portfolio of securities for a given change in interest rates.
***Features of Duration***
The higher the coupon (or promised interest payment on a security), the shorter its duration.
The higher the rate of return on a security, the shorter its duration.
Duration increases with maturity at a decreasing rate.
The higher the duration number, the more sensitive your bond investment will be to changes in interest rates.
shorter its duration
The higher the coupon (or promised interest payment on a security), the ___________.
shorter its duration
The higher the rate of return on a security, the _____________.
decreasing rate
Duration increases with maturity at a __________.
more sensitive
The higher the duration number, the _____________ your bond investment will be to changes in interest rates.
Features of Duration (part 2)
The higher the coupon payment, the shorter the duration of a bond.
This is due to the fact that the larger the coupon payment, the more quickly investors receive cash flows on a bond and the higher are the present value weights of those cash flows in the duration calculation.
On a time-value of money basis, the investor recoups their initial investment faster when coupon payments are higher.
shorter the duration
The higher the coupon payment, the _____________ of a bond.
quickly investors receive cash flows
This is due to the fact that the larger the coupon payment, the more _____________________ on a bond and the higher are the present value weights of those cash flows in the duration calculation.
faster
On a time-value of money basis, the investor recoups their initial investment___________ when coupon payments are higher.
Features of Duration (part 3)
Duration decreases as the rate of return on the bond increases.
This makes intuitive sense since the higher the rate of return, the higher the present value cost of waiting to receive the later cash flows.
Higher rates of return discount later cash flows more heavily, and the relative importance, or weights, of those later cash flows decline when compared to cash flows received earlier.
decreases
Duration _______ as the rate of return on the bond increases.
higher the present value
This makes intuitive sense since the higher the rate of return, the _______________ cost of waiting to receive the later cash flows.
more heavily
Higher rates of return discount later cash flows __________, and the relative importance, or weights, of those later cash flows decline when compared to cash flows received earlier.
Stock Duration
The duration of a stock is the average of the times until its cash flows are received, weighted by their present values.
The most popular model of duration uses dividends as the cash flows. In vernacular, the duration of a stock is how long we need to receive dividends to be repaid the purchase price of the stock. If a stock doesn't pay dividends, other methods using distributable cash flows, may be utilized.
The duration of an equity is a noisy analogue of the Macaulay duration of a bond, due to the variability and unpredictability of dividend payments. The duration of a stock or the stock market is implied rather than deterministic.
weighted by their present values
The duration of a stock is the average of the times until its cash flows are received, ___________________.
dividends
The most popular model of duration uses __________ as the cash flows. In vernacular, the __________ of a stock is how long we need to receive __________ to be repaid the purchase price of the stock. If a stock doesn't pay __________ , other methods using distributable cash flows, may be utilized.
implied
The duration of an equity is a noisy analogue of the Macaulay duration of a bond, due to the variability and unpredictability of dividend payments. The duration of a stock or the stock market is ______ rather than deterministic.
Stock Duration (part 2)
Duration of the U.S. stock market as a whole, and most individual stocks within it, is many years to a few decades. A nominal value, assumed in many analyses, would be 20-30 years, analogous to long term bonds. Higher price/earnings and other multiples imply longer duration.
Duration is a measure of the price sensitivity of a stock to changes in the long-term interest rate, i.e., the longer the duration, the more sensitive the stock is to interest rates.
In U.S. stock markets, an SEC rule adoption in 1982 (rule 10b-18) that allowed discretionary stock buybacks has distorted the calculation of duration based on dividends since at least the early 1990s.
The rule change had no ascertainable impact on duration, but duration now needs to account for all cash distributions including buybacks.
Higher price/earnings and other multiples imply longer duration.
Duration of the U.S. stock market as a whole, and most individual stocks within it, is many years to a few decades. A nominal value, assumed in many analyses, would be 20-30 years, analogous to long term bonds.
sensitivity
Duration is a measure of the price __________ of a stock to changes in the long-term interest rate, i.e., the longer the duration, the more __________ the stock is to interest rates.
discretionary stock buybacks
In U.S. stock markets, an SEC rule adoption in 1982 (rule 10b-18) that allowed ______________ has distorted the calculation of duration based on dividends since at least the early 1990s.
all cash distributions including buybacks
The rule change had no ascertainable impact on duration, but duration now needs to account for ________________________..
Stock Duration (part 3)
Suppose a stock costing $100 pays a 4% dividend, grows at a terminal rate of 6.5% and has a discount rate of 7.9%.
The price/dividend first estimate of 25 years is easily calculated. If we assume an additional 33% duration to account for the discounted value of future dividend payments, that yields a duration of 33.3 years.
Present value of the dividend payment in year one is $4, year two $4*1.065*.921=$3.92, year three $3.85, etc. There is an infinite series, such that each year's dividend payment has a present value of .9809 of the previous year's payment, starting with $4. The present value of the stock in perpetuity (i.e. the sum of present values of all dividend payments) is $209.04.
To recover the price paid of $100 must take some time considerably less than till the end of time. That time is between 33 and 34 years: the present value of dividends paid through the 34th year (but not the 33rd) will exceed $100. That is very close to the rule of thumb estimate above.
Stock Duration (part 4)
However, what may be gained in mathematical precision is lost by the compounding of uncertainties, particularly about growth, over the term of 34 years: they make any numbers we may calculate with conjectural.
It may be more appropriate to derive an empirical estimate of duration and encapsulate it in a rule of thumb that's reasonable most of the time.
reasonable most of the time
It may be more appropriate to derive an empirical estimate of duration and encapsulate it in a rule of thumb that's __________________________.