AP Bio - Unit 4 Review
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is bacterial quorum sensing?
Bacteria communicate by releasing and detecting signaling molecules to coordinate group behavior once a population threshold is reached.
How are plasmodesmata examples of direct contact between cells?
They are small channels between plant cells that allow molecules and ions to pass directly from one cell to another.
How is direct contact communication different than local regulation?
Direct = cells physically connected.
Local = signaling over a short distance through nearby cells (no physical contact).
How are neurotransmitters examples of local regulation?
They are chemical signals released from neurons that cross synapses to target nearby cells.
What is a hormone? How is it an example of long distance communication?
Hormones are chemical messengers released into the bloodstream to affect target cells far away (e.g., insulin).
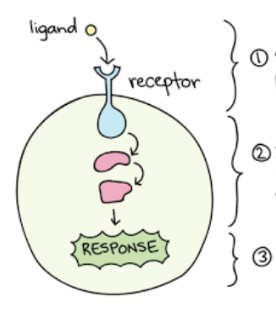
What is this diagram illustrating?
Cell Signaling Pathway
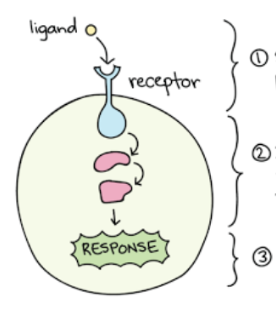
Identify step 1
Reception
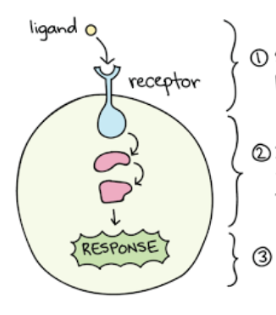
Identify step 2
Transduction
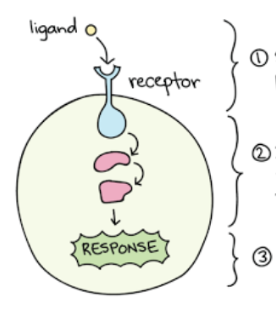
Identify step 3
Response
Compare an intercellular to an intracellular receptor.
Intercellular = on the cell membrane, receive external signals.
Intracellular = inside the cell, bind to small or nonpolar molecules like steroids.
What is a ligand?
A signaling molecule that binds to a receptor to trigger a response.
What are some common intercellular receptors? What occurs when the ligand binds to them?
Steroid or thyroid hormone receptors; when the ligand binds, the receptor activates and changes gene expression.
How is cAMP used in transduction?
Acts as a second messenger to amplify the signal and activate other proteins in the pathway.
Give an example of a response that may occur after transduction has taken place.
Activation of a gene, enzyme production, or change in cell metabolism.
How would a mutation in the receptor affect the signal transduction pathway?
The signal pathway may not activate or could send incorrect signals, disrupting normal cell responses.
Compare a positive to a negative feedback loop.
Positive = amplifies change.
Negative = reverses change to maintain balance.
Give 2 examples of a positive feedback loop.
Positive: Childbirth contractions, blood clotting.
Give 2 examples of a negative feedback loop.
Negative: Blood sugar regulation (insulin), body temperature control.
How are feedback loops used to maintain homeostasis?
Detecting changes and adjusting body processes to keep internal conditions stable.
What cells undergo mitosis and cytokinesis? Why?
Somatic (body) cells; to grow, repair tissues, or replace old cells.
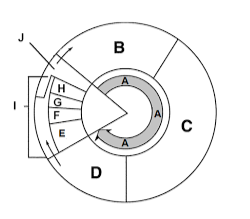
Label section a
Interphase
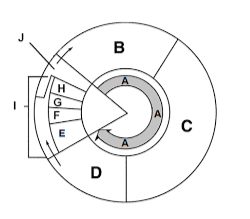
Label section b
G1
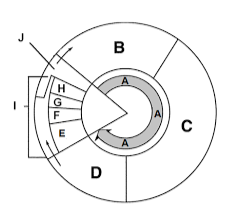
Label section c
S
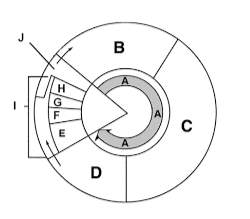
Label section d
G2
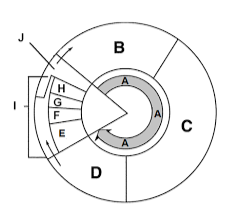
Label section e
Prophase
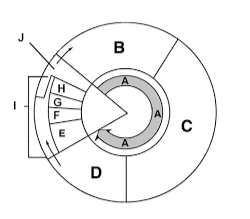
Label section f
Metaphase
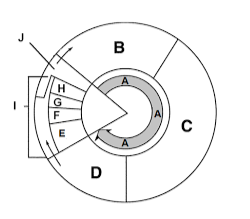
Label section g
Anaphase
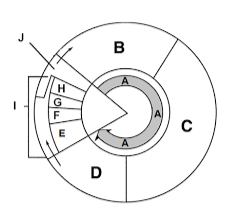
Label section h
Telophase
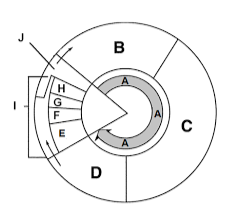
Label section i
Mitosis
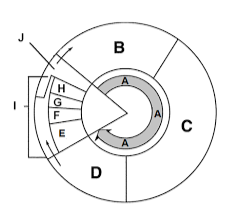
Label section j
Cytokinesis
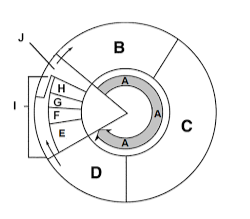
What happens in section B?
Cell growth
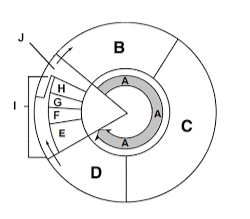
What happens in section C?
DNA Synthesis
What happens in section D?
Cell Growth
Why is cytokinesis important?
It divides the cytoplasm, creating two separate daughter cells.
How do cyclins and cyclin dependent kinases work to regulate the cell cycle?
Cyclins bind to CDKs to activate them; these complexes control progression through checkpoints.
What is the purpose of the checkpoints found at various stages of the cell cycle?
Ensure DNA is copied correctly, cell is large enough, and conditions are right before continuing.
Cancer is uncontrolled cell growth. How does this occur if there are checkpoints in the cell cycle system to regulate the growth?
Mutations disable checkpoints, allowing uncontrolled division even with damaged DNA.
What is apoptosis and why is this process important?
Programmed cell death; removes damaged or unnecessary cells to maintain health.
What happens during prophase?
Chromosomes condense, spindle forms, nuclear membrane breaks down.
What happens during metaphase?
Chromosomes line up along the cell’s equator.
What happens during anaphase?
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
What happens during telophase?
Nuclei reform around chromosomes, which begin to uncoil.