Topic 5
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Critical Period For Circulatory System Development
Day 20-50 Post Fertilisation
In what week does the Circulatory System begin development
Week 3
In what week is there a functional heartbeat
Week 4
Describe the maternal blood flow to and from the placenta
Blood flows from uterine arteries → maternal sinuses → uterine vein
How does gas exchange occur between mother and fetus
Across capillary walls in chorionic villi - foetal & maternal blood do not mix
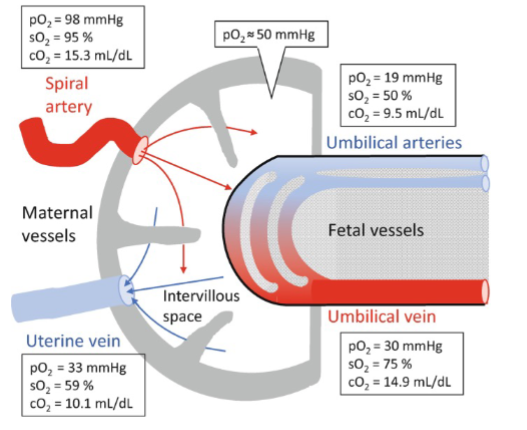
Foetal vein & artery direction of blood flow
Foetal vein: carries oxygenated blood toward the fetus from the placenta (via the umbilical vein).
Foetal artery: carries deoxygenated blood away from the fetus to the placenta (via the umbilical arteries).
What is the function of the ductus venosus
It links the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava, bypassing the liver - Allows Blood to Bypass Foetal Liver
How is blood flow through ductus venosus regulated
Flow Regulated by Sphincter
50-80% of Blood flow can Avoid Hepatic Sinuses
Why is the ductus venosus bypass important for the heart
It prevents cardiac overload during high venous return (e.g. uterine contractions).
Foramen Ovale function
Links Right Atrium with Left Atrium
Avoids Oxygen Rich Blood Going to Pulmonary Circulation
More Direct Route To Ascending Aorta → Up to the Brain
What does the ductus arteriosus connect
The pulmonary artery to the descending aorta
Ductus arteriosus purpose
To bypass the non-functioning fetal lungs. Only ~10% of fetal blood passes through the lungs (for their growth & development)
Describe pathway of foetal circulation around body
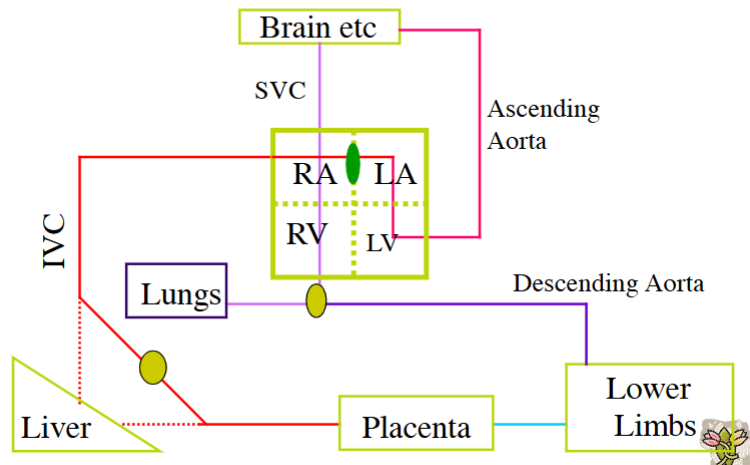
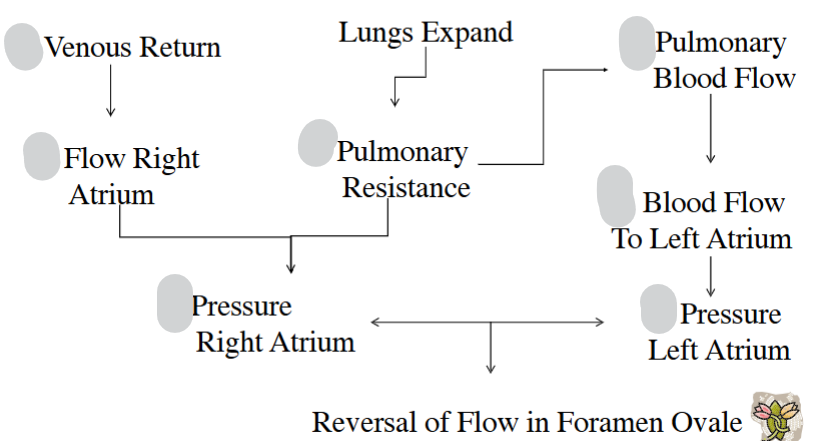
Up/Down arrow for each of these at birth
Causes foramen ovale to close
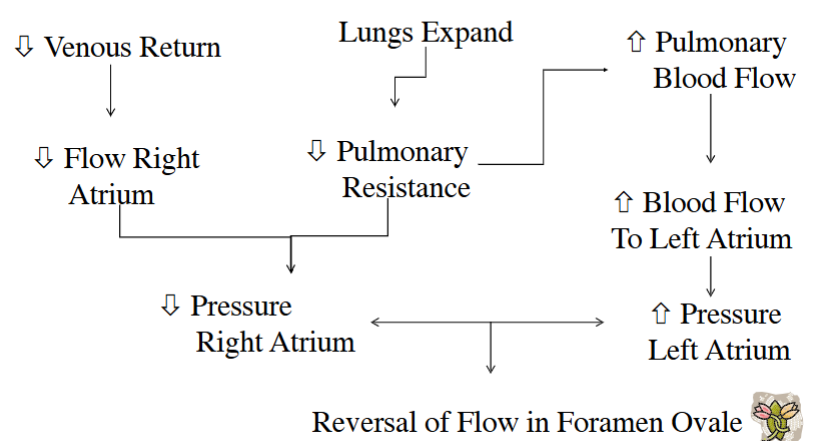
Most Common Atrial Septal Defect
Patent Foramen Ovale
What is the clinical significance of a patent foramen ovale
None, as pressure in the left heart exceeds the right, keeping it closed
Clinical significance of patent foramen ovale occurring with other defects
Cyanosis of Skin and Mucus Membrane (due to right-to-left shunting)
What triggers ductus arteriosus closure
Increased oxygen tension (PO₂) and decreased prostaglandin E₂ levels (constriction)
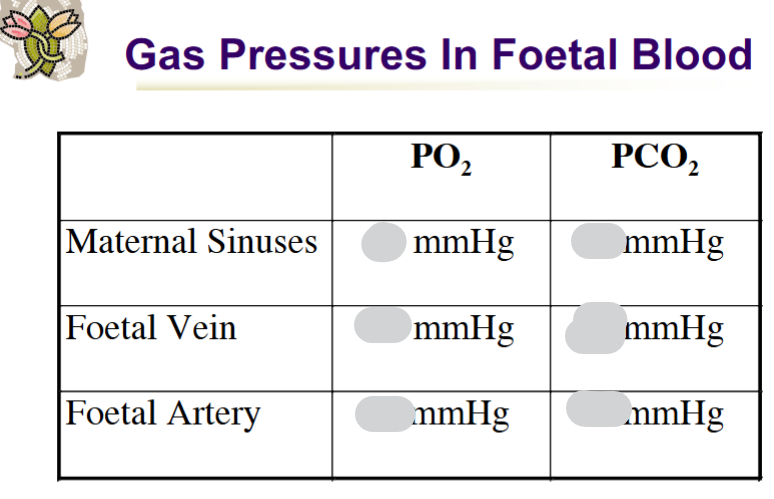
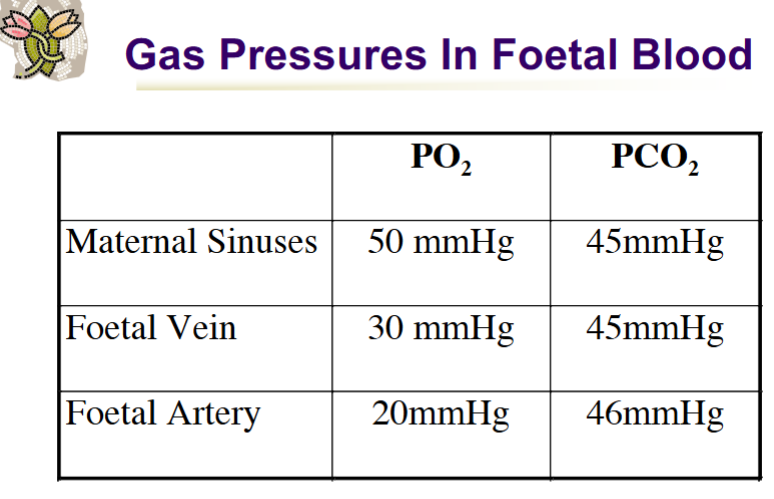
PO2 in Foetal Ductus arteriosus vs PO2 in neonatal ductus arteriosus in mmHg
PO2 in Foetal Ductus arteriosus = 15-20mmHg
PO2 in neonatal ductus arteriosus = >100 mmHg
What PO₂ level is critical for closure of ductus arteriosus
50 mmHg
What happens if ductus arteriosus remains patent
Increased Re-circulation & Cardiac Output
Decreased Cardiac and Respiratory Reserves
Patent ductus arteriosus prevalence
1in 5500
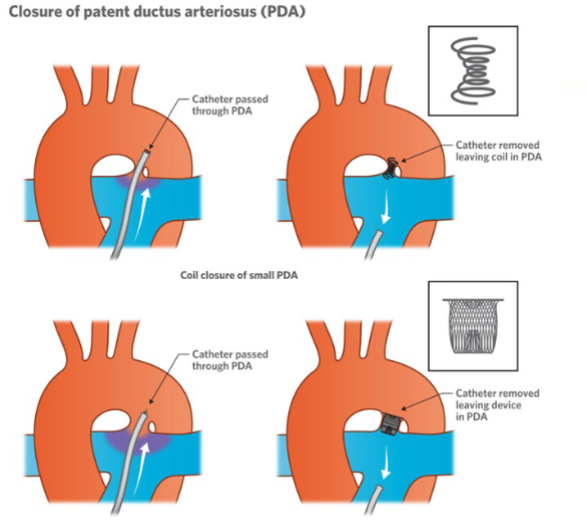
How is a Patent ductus arteriosus treated
When does the ductus venosus close
Within 1–3 hours of birth
What causes the closure of ductus venosus
Increased portal pressure (6–10 mmHg) forcing blood through the liver
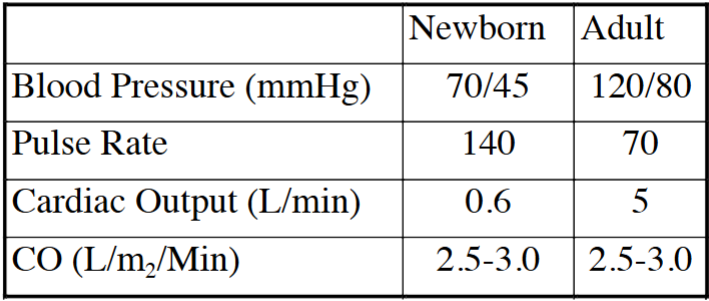
What happens to fetal respiratory movements during pregnancy
They decrease in the third trimester
Why do fetal respiratory movements decrease in the third trimester
To reduce swallowing of waste products and promote fetal growth
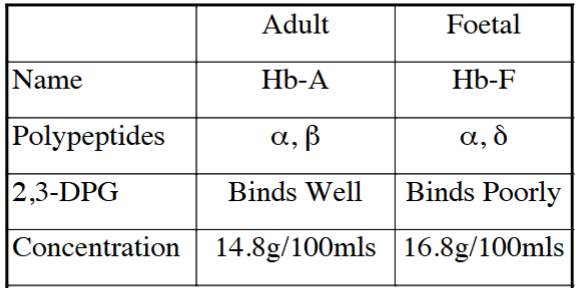
To allow the Foetus to Survive at Low PO2, the Oxygen Dissociation Curve Shifts to what side
LHS
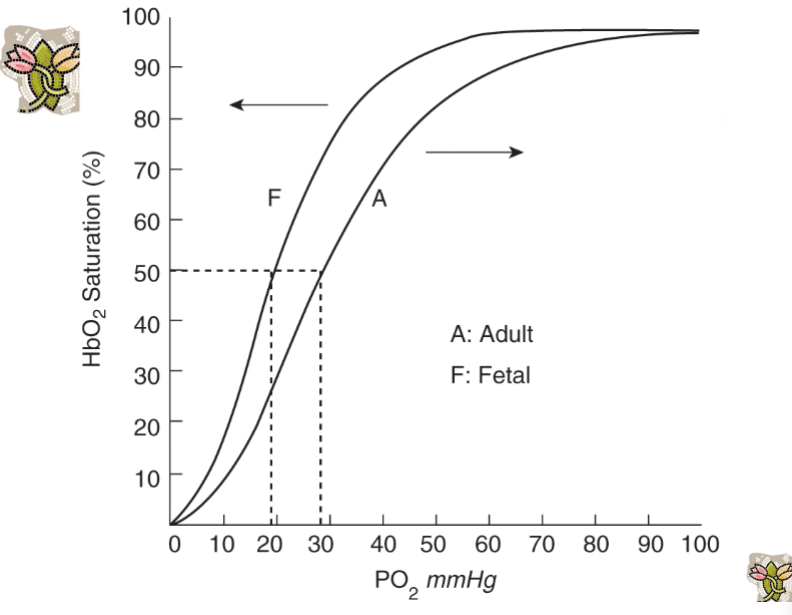
How is Hb-F helpful to allow the Foetus to Survive at Low PO2
At Any PO2 Hb-F binds 20-30% More O2 than Hb-A
How does the mother help to allow the Foetus to Survive at Low PO2
Increased oxygen given up by Mother
How does uterine blood flow change during pregnancy
It increases 20-fold to ~500 mL/min
What hormones regulate uterine blood flow change during pregnancy
Oestrogen (vasodilation), progesterone (venoconstriction), and placental hormones
What is the Bohr effect
The shift of the O₂ dissociation curve due to pH changes — alkalosis → LHS (more oxygen binds), acidosis → RHS (less oxygen binds)
Explain the double Bohr effect in the placenta
Foetal PCO2 = 46mmHg; Maternal PCO2 = 45mmHg
Foetal blood: CO₂ diffuses out → ↓ Foetal PCO₂ → ↑ pH → Hb binds more O₂.
Maternal blood: gains CO₂ → ↓ pH → Hb releases O₂.
This enhances O₂ transfer to the foetus
Foetal O2 Dissociation Curve Shifted to LHS
Maternal O2 Dissociation Curve Shifted to RHS
What triggers the first breath
Mild asphyxia (↑ PCO (hypercapnia)₂, ↓ O₂ (hypoxia)) stimulates central chemoreceptors
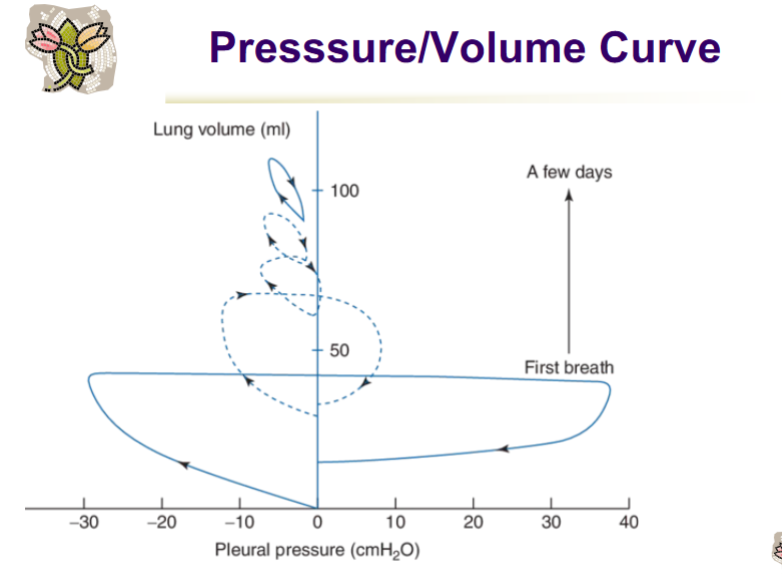
Explain
First Breath
The first inspiration is the most difficult — requires high transpulmonary pressure (~60–80 cmH₂O) to overcome:
Surface tension in fluid-filled alveoli,
Viscous resistance of the lung fluid,
Chest wall recoil (very compliant chest).
A few mins → a few days
With each breath:
More alveoli are aerated,
Surfactant spreads over alveolar surfaces, reducing surface tension,
FRC is established.
The P–V curve moves upward and to the left, meaning:
Higher compliance (steeper slope),
Less pressure needed to achieve a given volume,
The lung can now maintain some air at end-expiration (FRC).
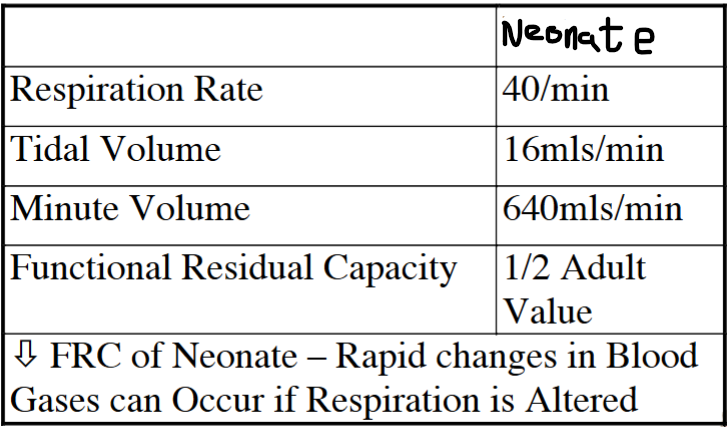
What is pulmonary surfactant
A phospholipid-protein mixture that reduces surface tension in alveoli
How does surface tension arise
Surface tension arises from the difference between the attractive forces on molecules at an air-liquid interface
Results in a tension on the surface film that resists expansion
WHy is surfactant important
Prevents alveolar collapse during exhalation and contributes to innate lung defence against pathogens
Where and when (gestation weeks) is it produced
By type II pneumocytes, between 24 - 34 weeks gestation
Surfactant main components
70–80% dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (phospholipid)
10% proteins (SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, SP-D)
10% neutral lipids (cholesterol)
What increases surfactant production
Cortisol, estrogen, prolactin, thyroid hormones (T₃/T₄), hypoxia, prostaglandins
What decreases or alters surfactant composition
Ozone (↓ SP-A), NO₂ (alters lipids), TNF-α (↓ production)
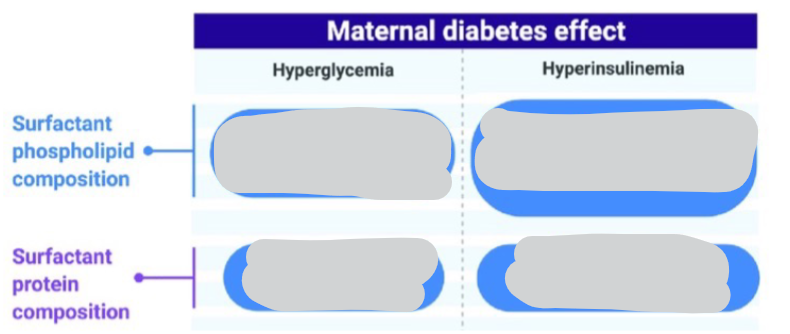
Effect of Insulin on Surfactant
Most prevalent cause of respiratory distress & death in premature newborns
Lack of surfactant
Is surfactant amphipathic / hydrophilic / hydrophobic
amphipathic (hydrophilic & hydrophobic)
What can be given to mothers at risk of early delivery to reduce risk of respiratory distress caused by a lack of surfactant
Cortisol increases surfactant