Anatomy 001 Objective Midterm 1
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
Describe the mucous membrane
Wet membrane that lines all body cavities that open to the exterior body surface, like digestive & respiratory tract
Describe the synovial membrane
lines the cavities of freely movable joints, secretes synovial fluid to lubricate joints
What is the 5th layer of the epidermis only found in the palms and soles of the feet?
stratum lucidum
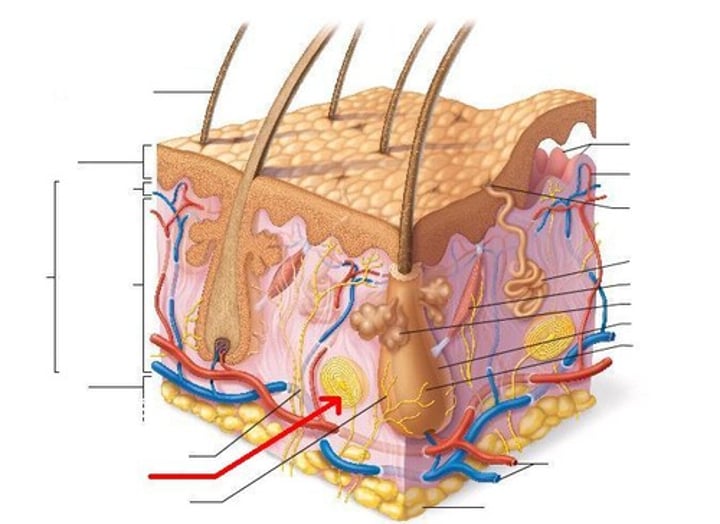
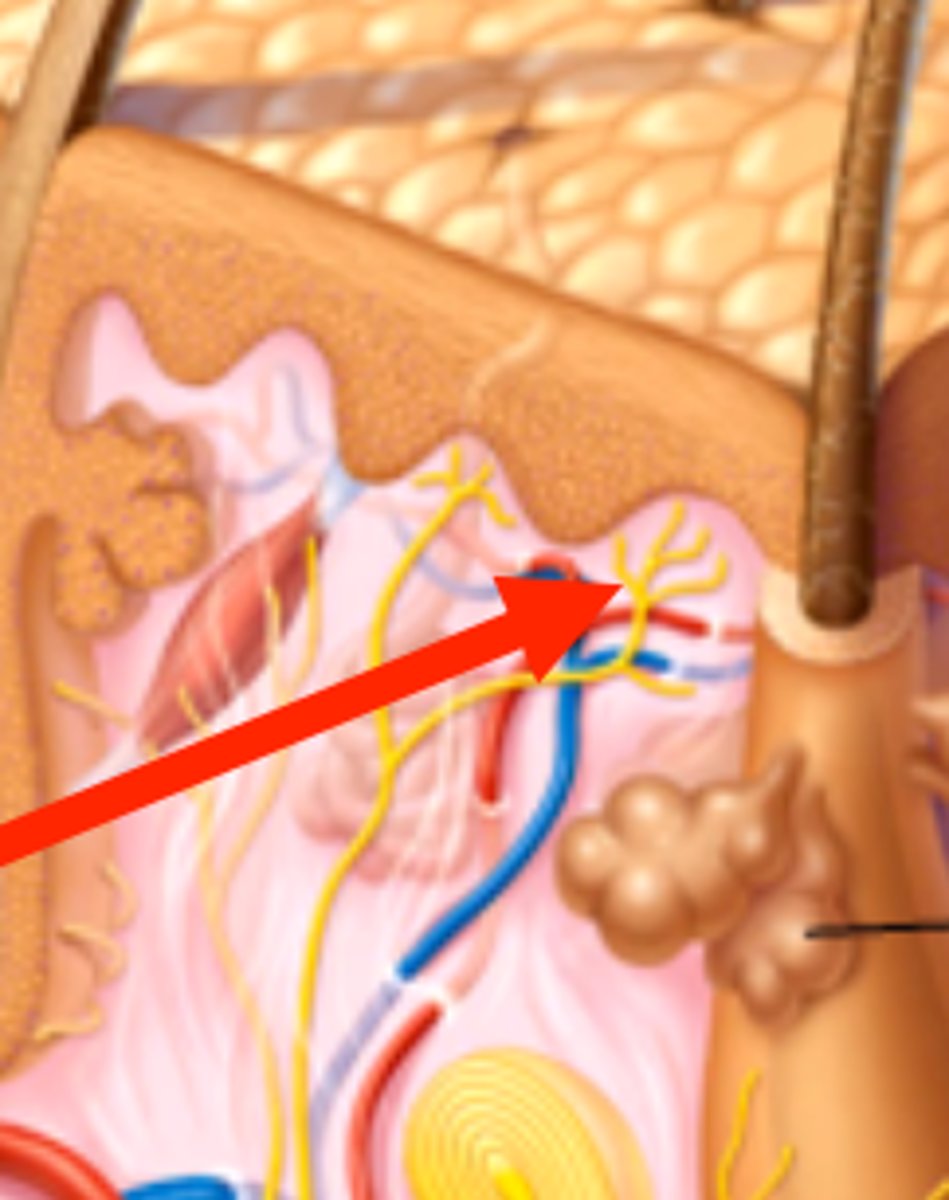
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
pacinian corpuscle
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
Meissner's corpuscles
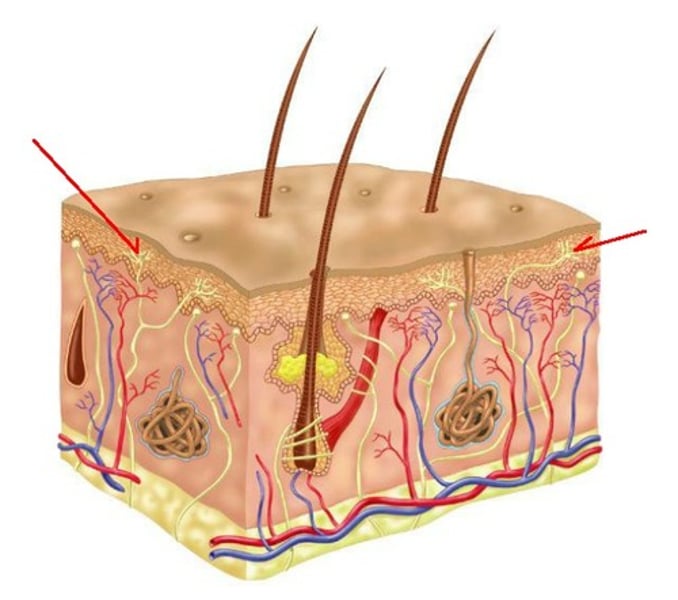
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
dermal papillae
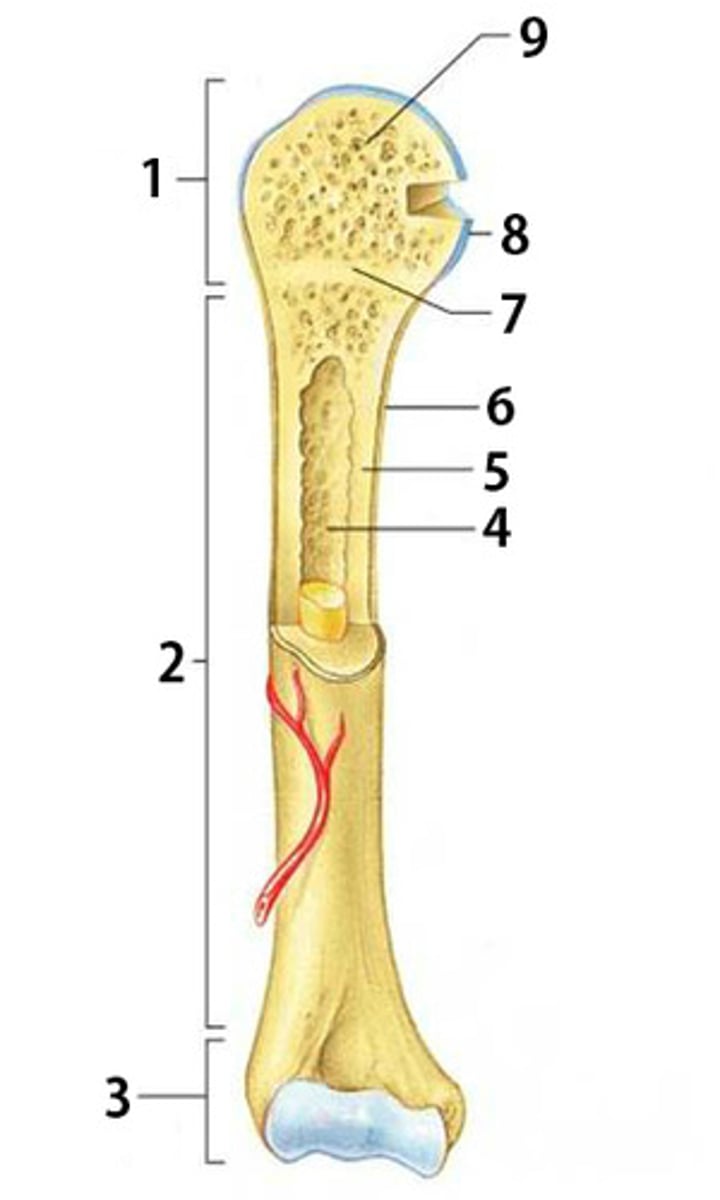
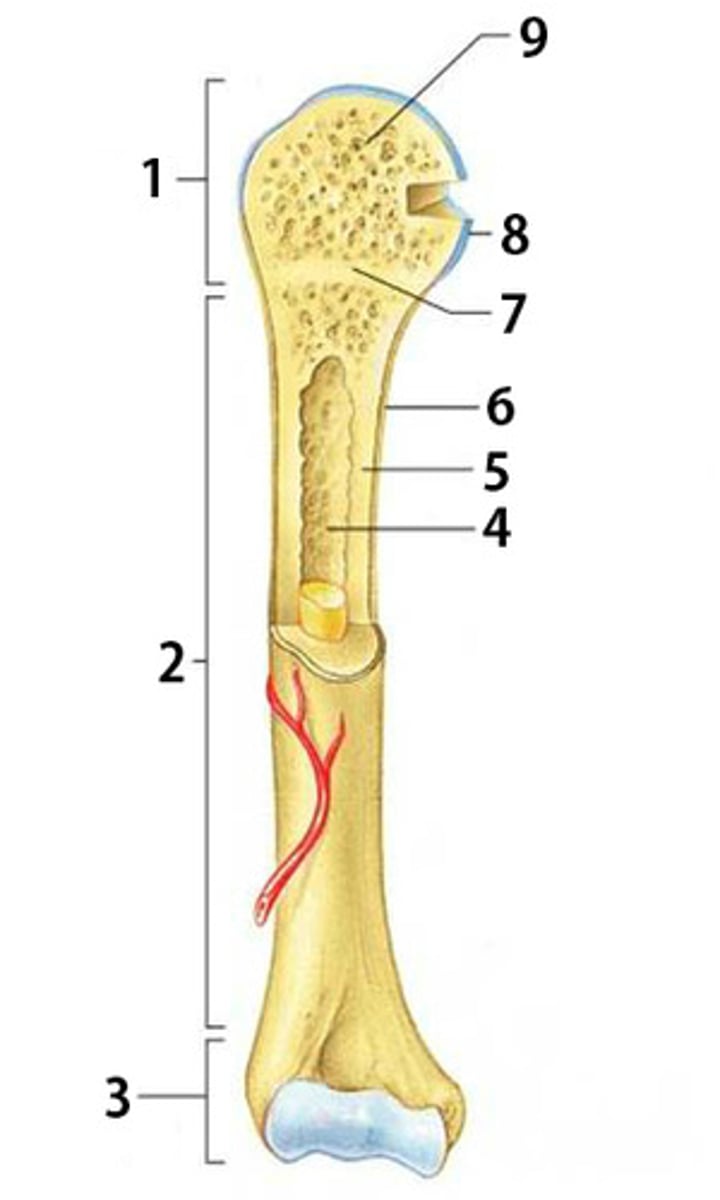
What is part 2 of the long bone pictured called?
diaphysis
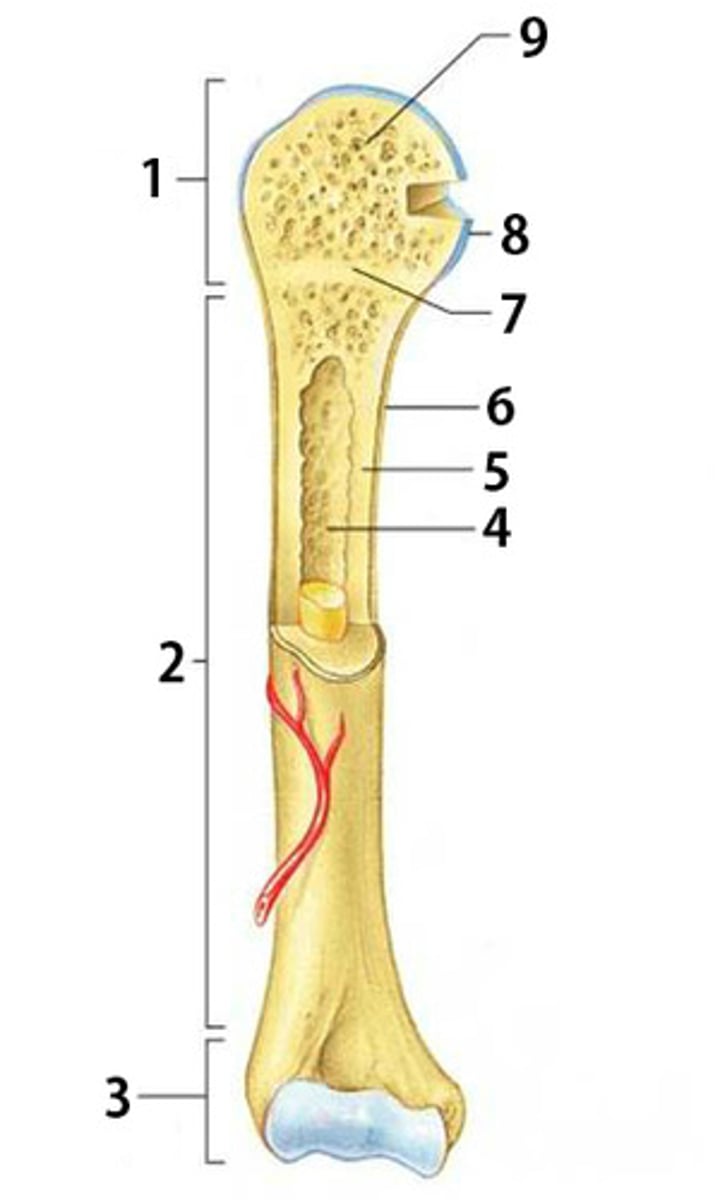
What is part 6 of the long bone pictured called?
periosteum
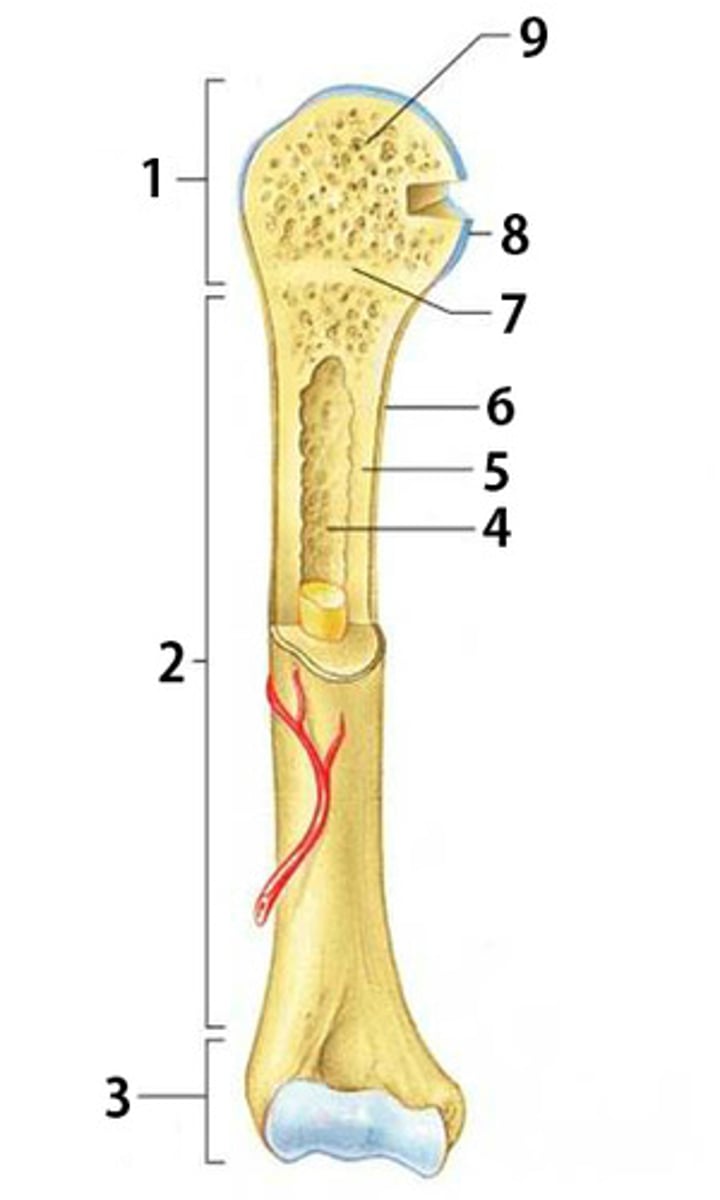
What is part 8 of the long bone pictured called?
articular cartilage
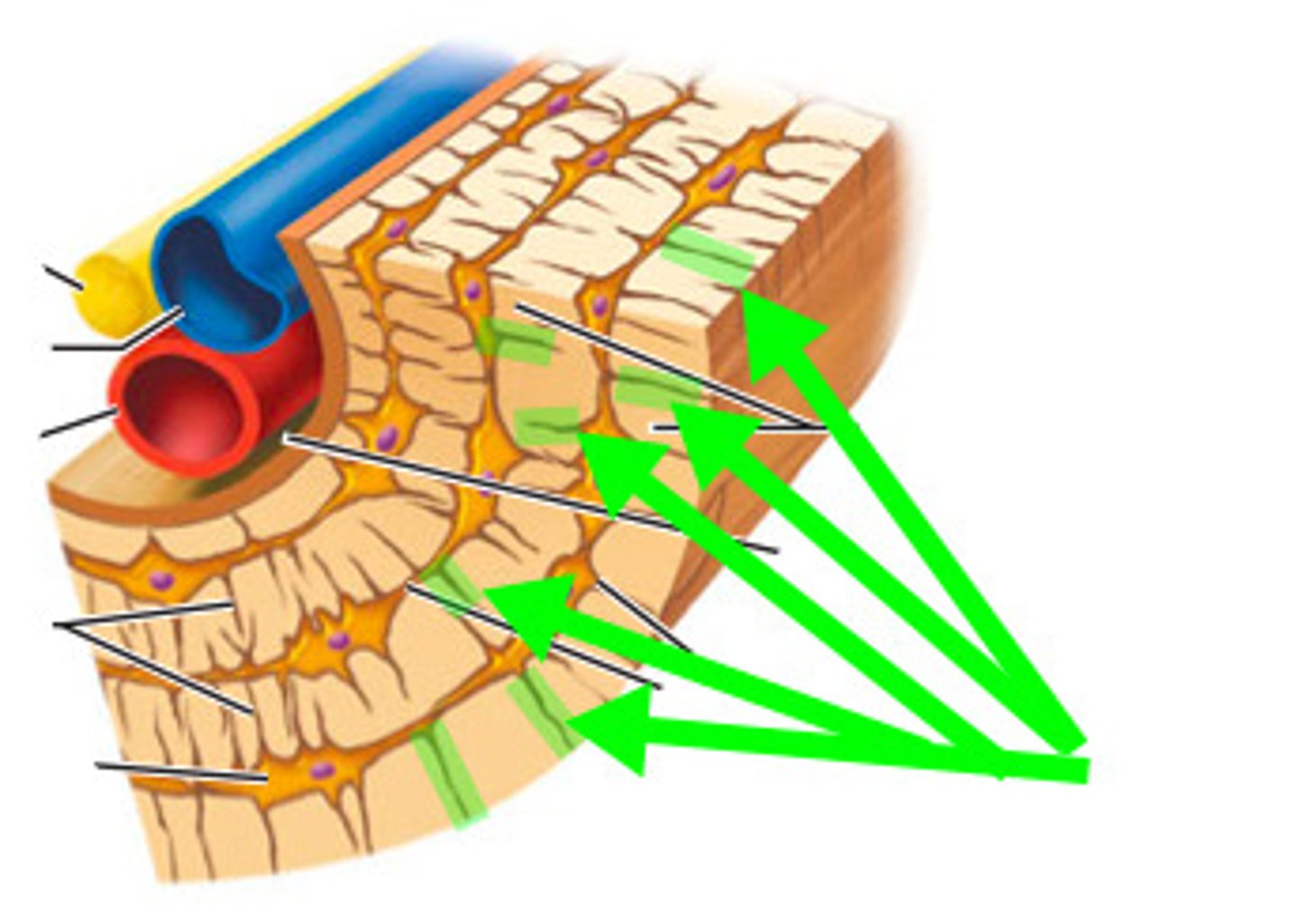
what is this called in compact bone?
canaliculi
What makes up the axial skeleton?
skull
vertebral column
rib cage
Name the 8 facial bones; note most of them are paired for 14 bones total
maxilla
palatine
zygomatic
lacrimal
nasal
vomer
mandible
inferior nasal concha
what 2 types of bones make up the pectoral girdle?
scapula
clavicle
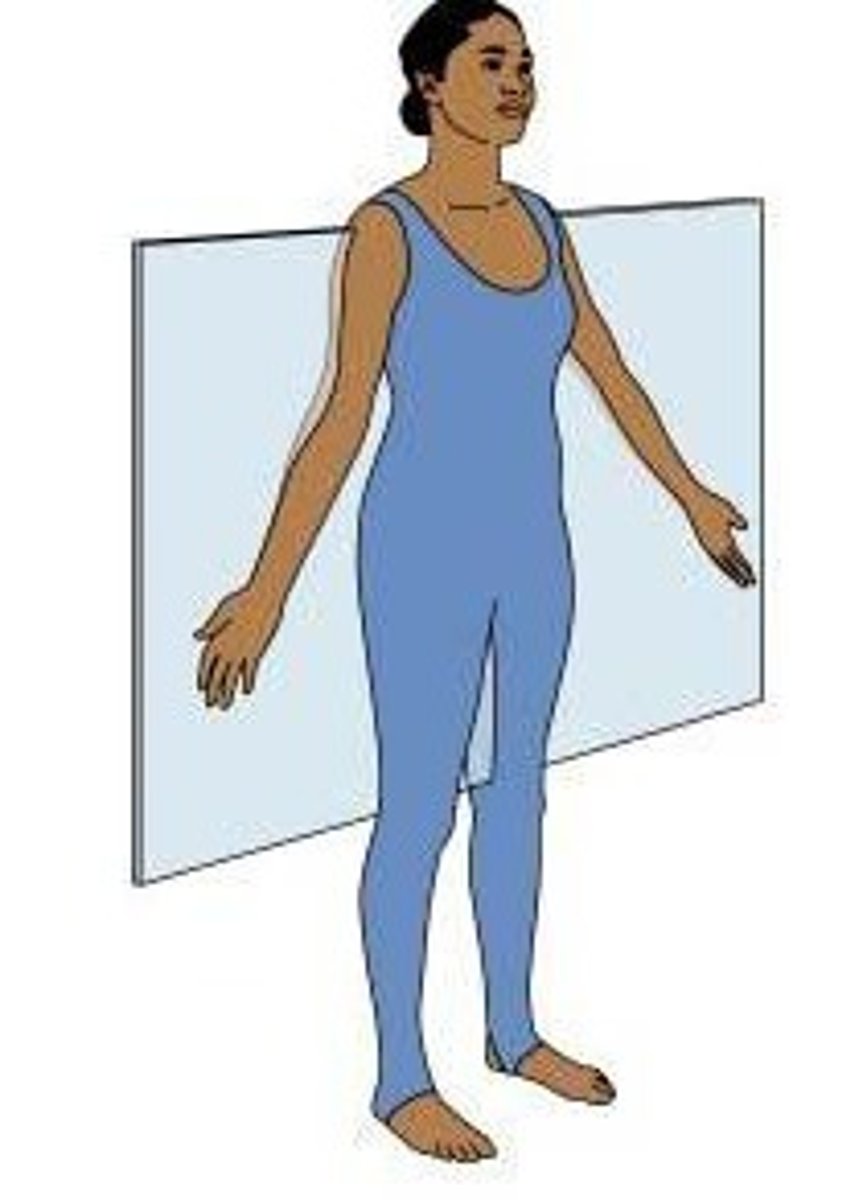
Describe anatomical position
Body erect; facing forward; palms facing forward with thumbs pointing out
Define Superior (as a directional term)
toward the head end or upper part of a structure; above
Define Inferior (as a directional term)
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure; below
Define anterior (as a directional term)
toward or at the front of the body; in front of
Define posterior (as a directional term)
toward or at the back of the body; behind
Define medial (as a directional term)
toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of
Define lateral (as a directional term)
away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
Define ipsilateral (as a directional term)
body parts on the same side
Define contralateral (as a directional term)
body parts on opposite sides
Define proximal (as a directional term)
closer to the origin of the body part
Define distal (as a directional term)
farther from the origin of the body part
Define superficial (as a directional term)
toward or at the body surface
Define deep (as a directional term)
away from the body surface; more internal
What is the dorsal cavity? What cavities does it contain?
-cavity located toward the back of the body
-contains cranial cavity and vertebral cavity
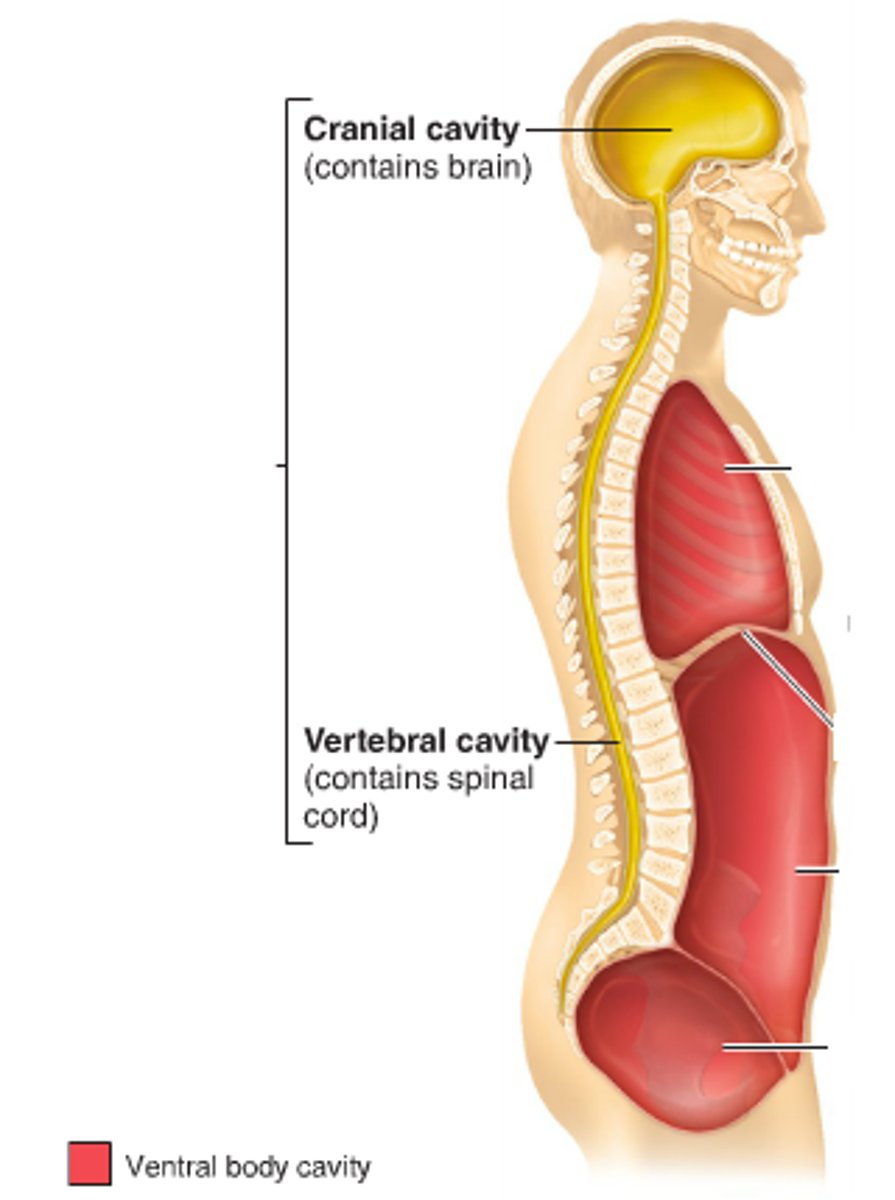
What organ does the cranial cavity contain?
brain
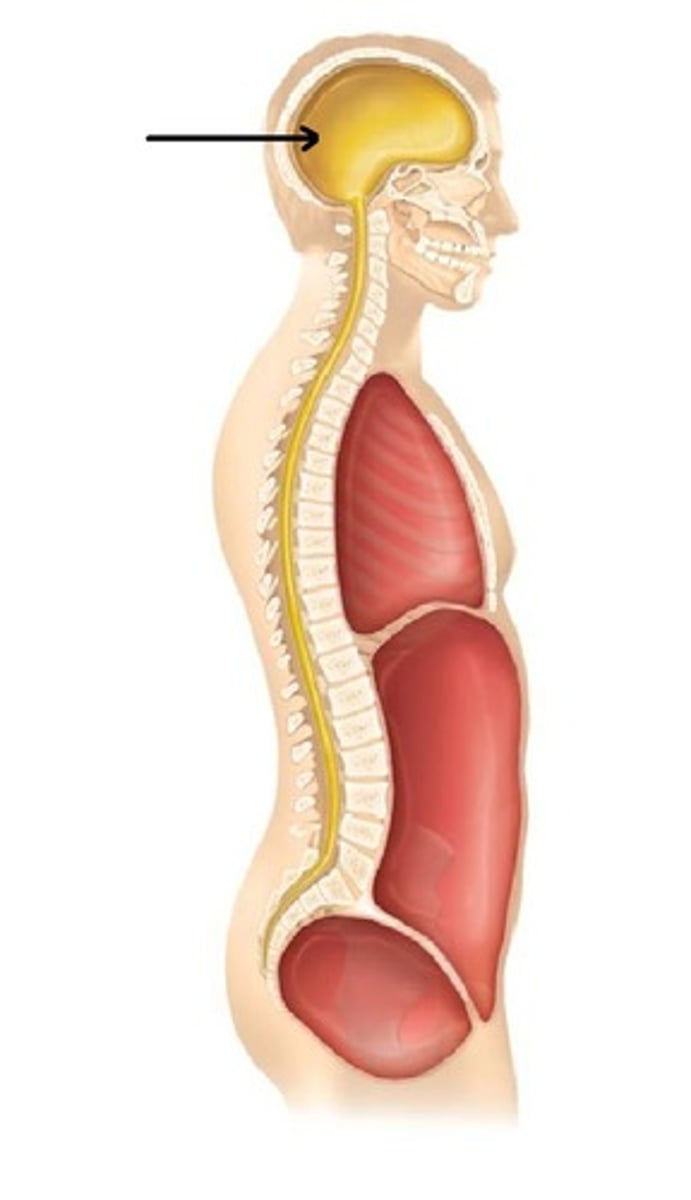
What organ does the vertebral cavity contain?
spinal cord
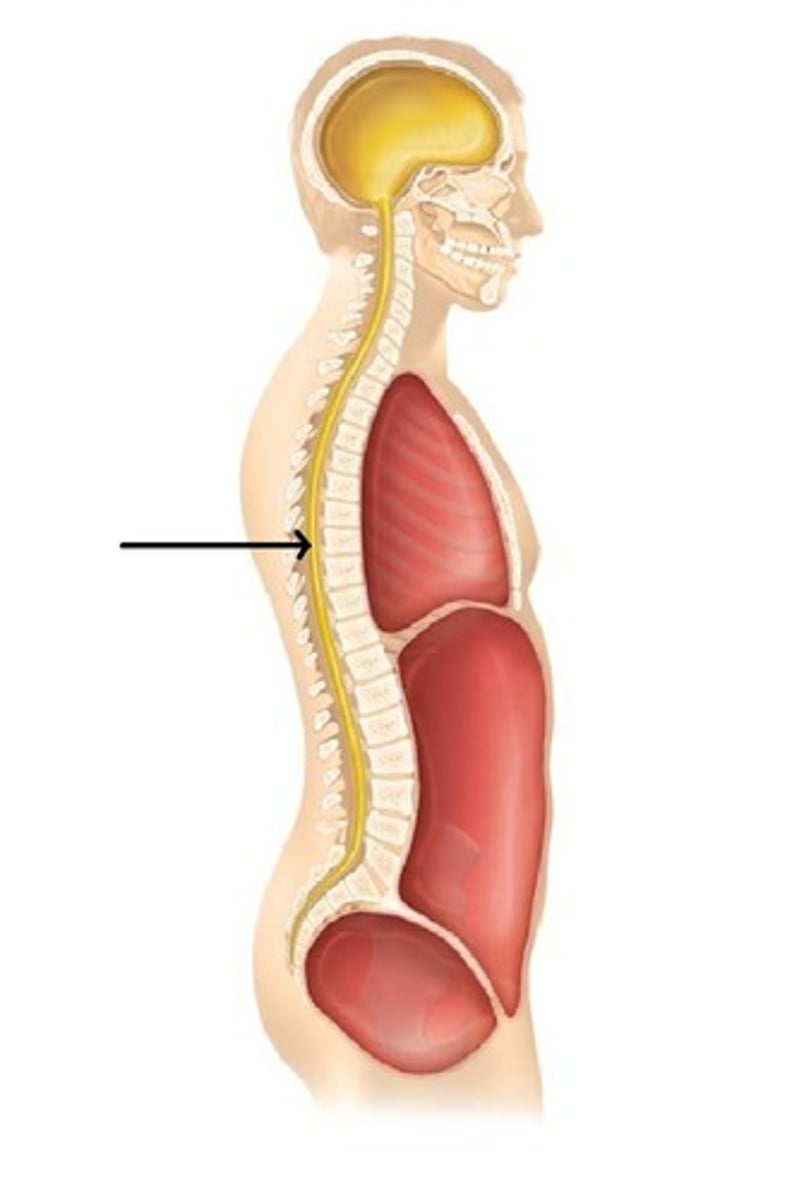
What is the ventral cavity? What cavities does it contain?
-cavity located toward the front of the body
-contains abdominopelvic cavity and thoracic cavity
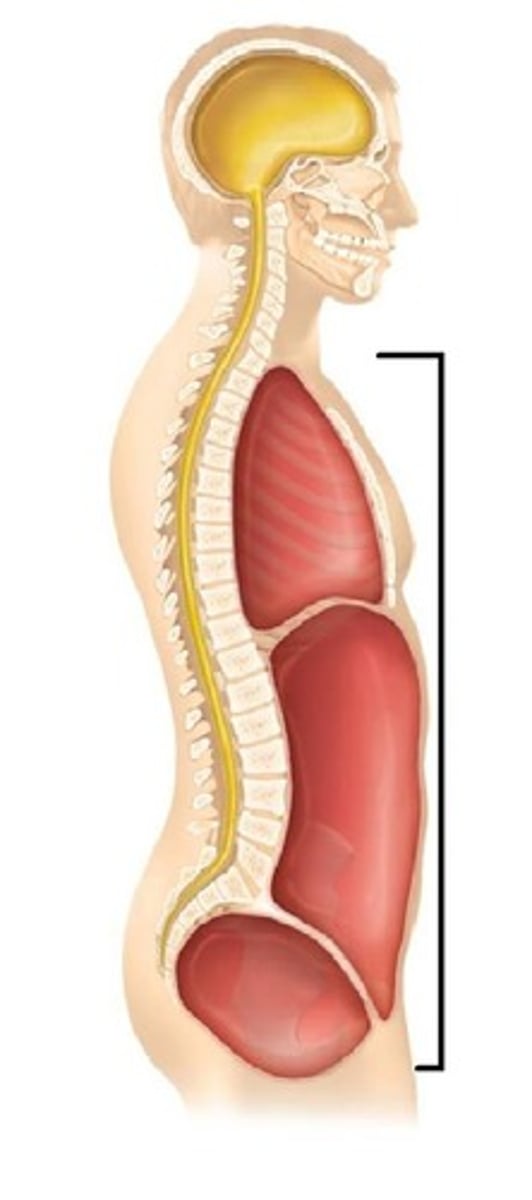
What cavities make up the abdominopelvic cavity?
abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
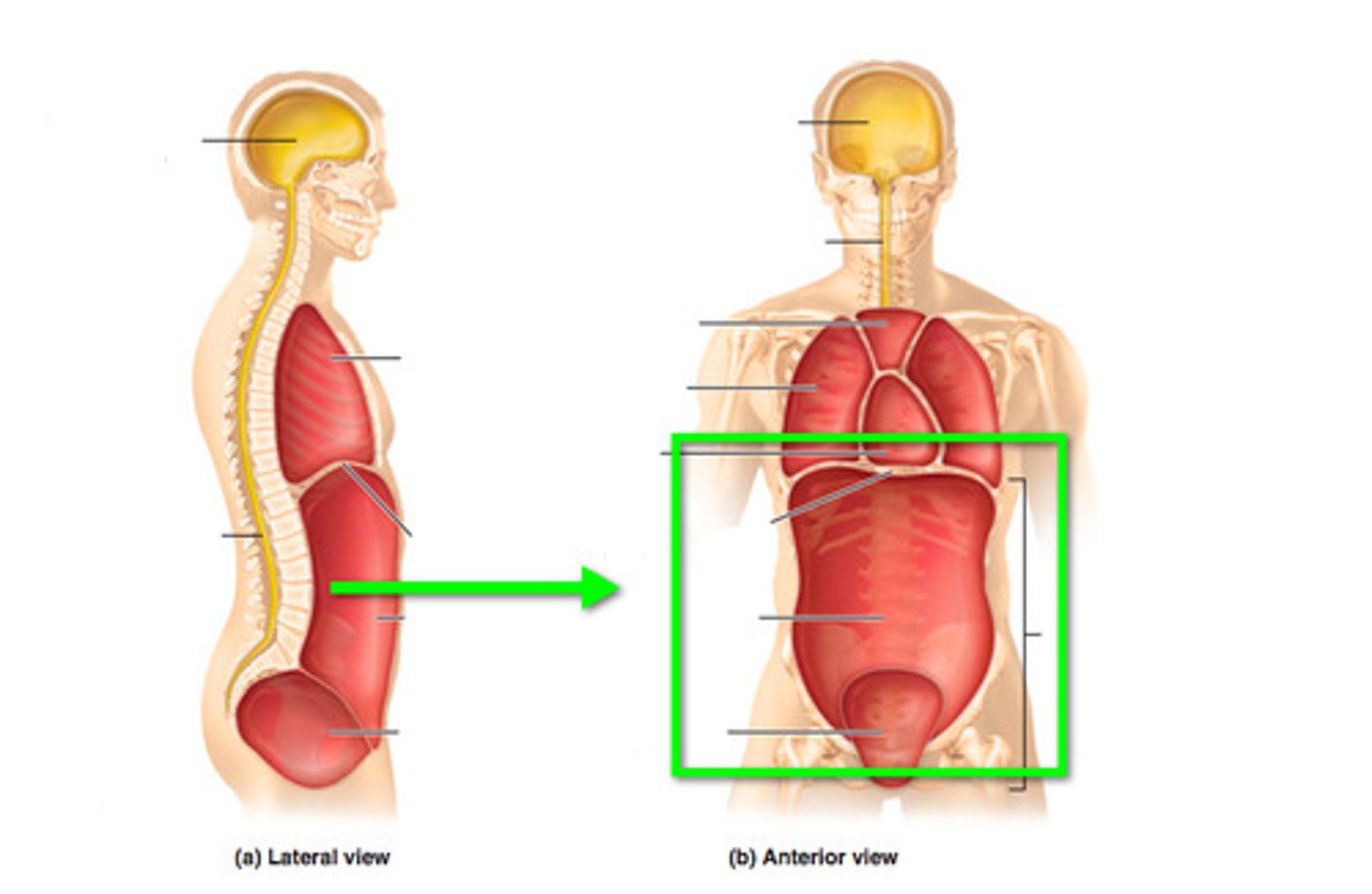
What organs does the abdominal cavity contain?
stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, pancreas, and most of the small and large intestines
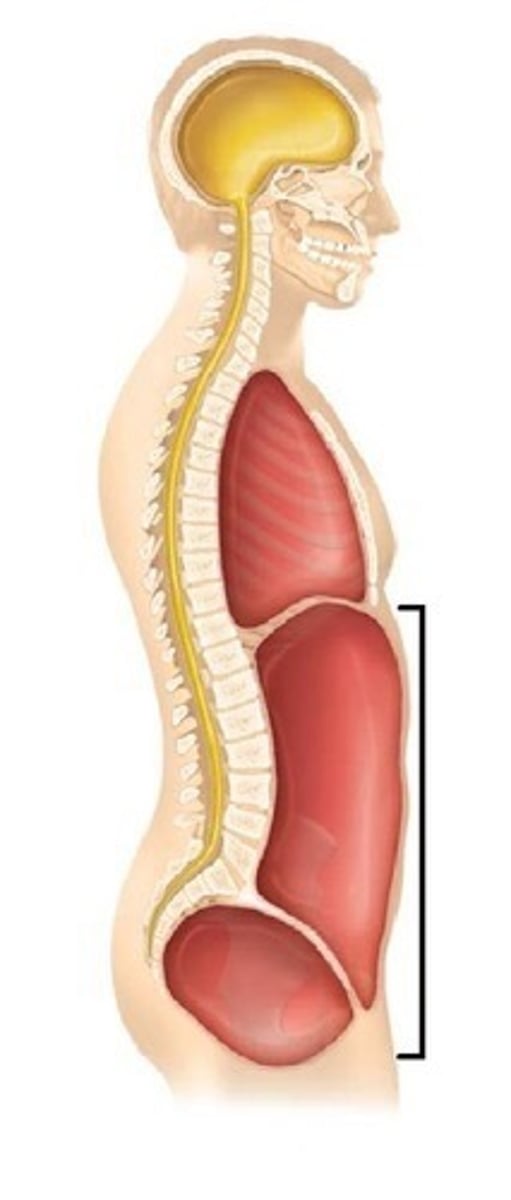
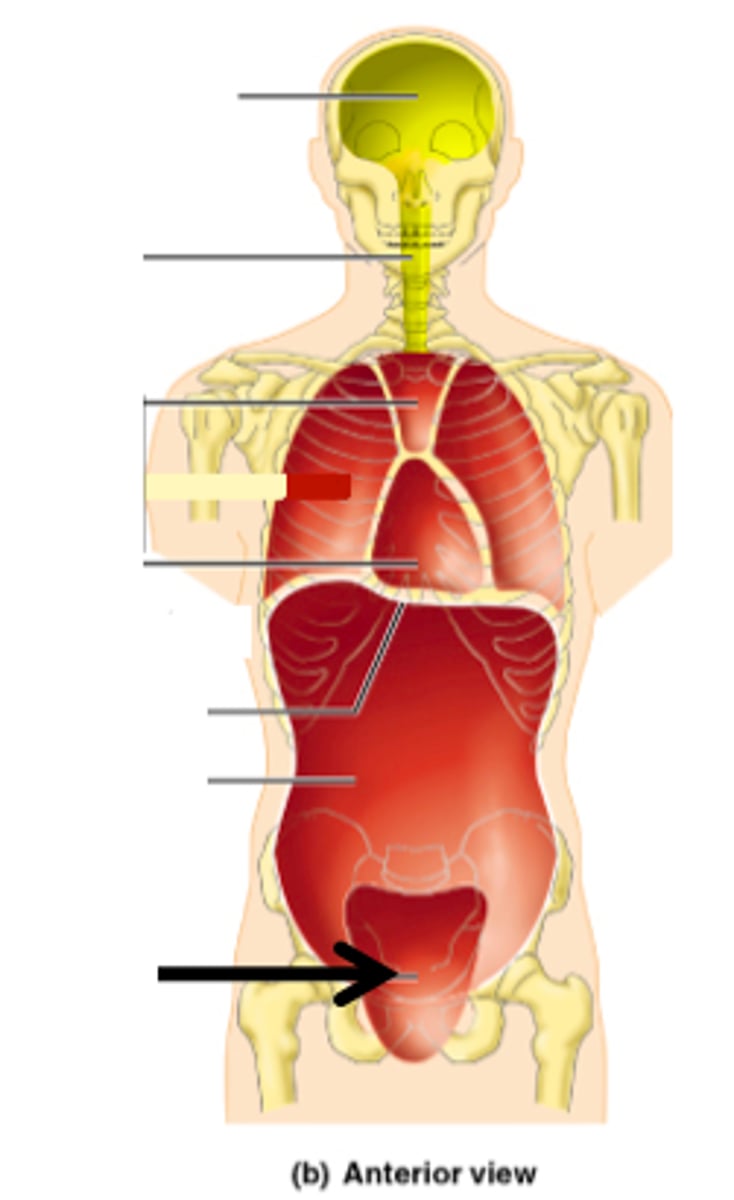
What organs does the pelvic cavity contain?
urinary bladder, reproductive organs, rectum
What cavities make up the thoracic cavity?
pleural cavity and pericardial cavity
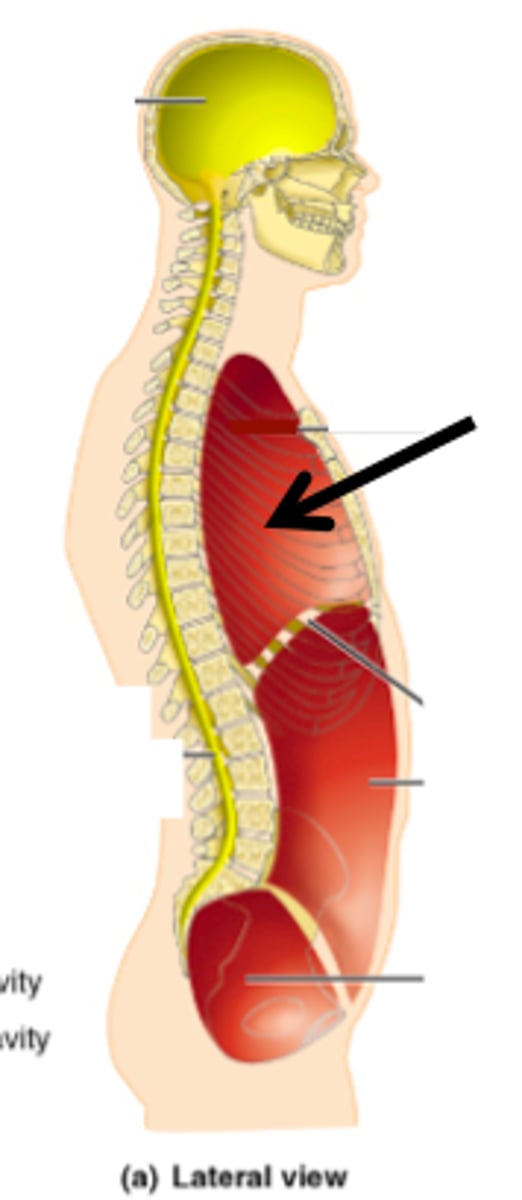
what organs are in the pleural cavity?
lungs
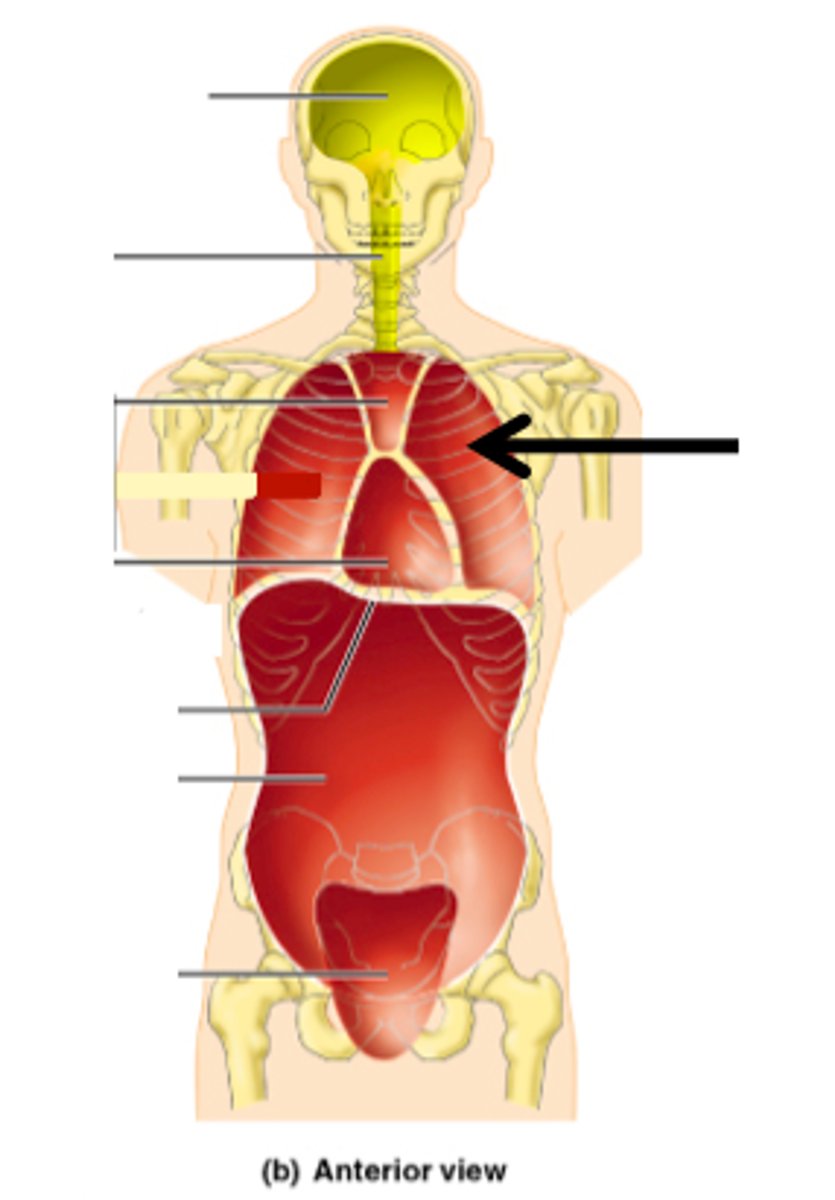
What organs are in the pericardial cavity?
heart
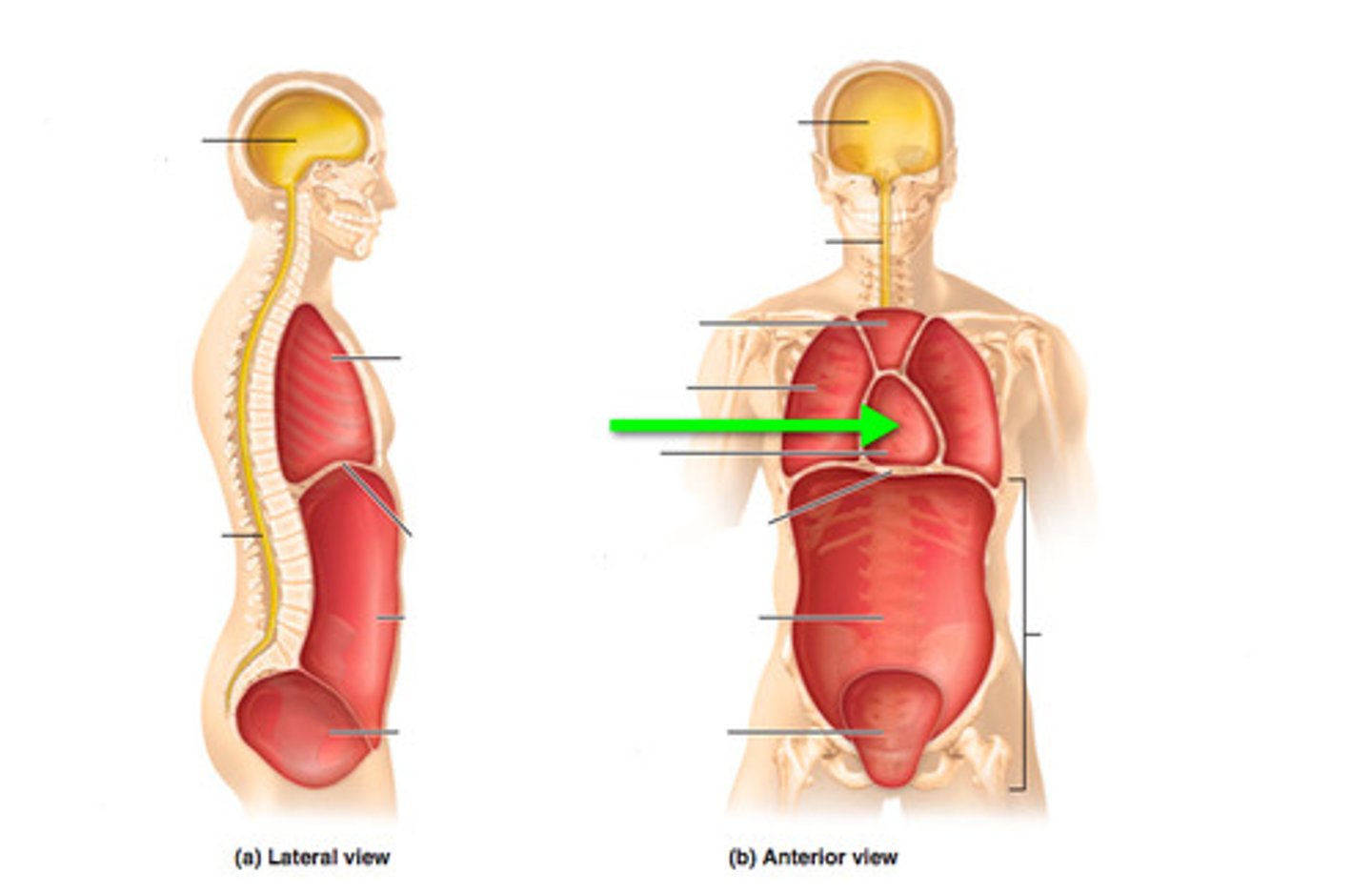
What is the parietal membrane?
membrane that lines the body cavity
What is the visceral membrane?
membrane that covers the organ
What is the pictured body plane?
frontal plane
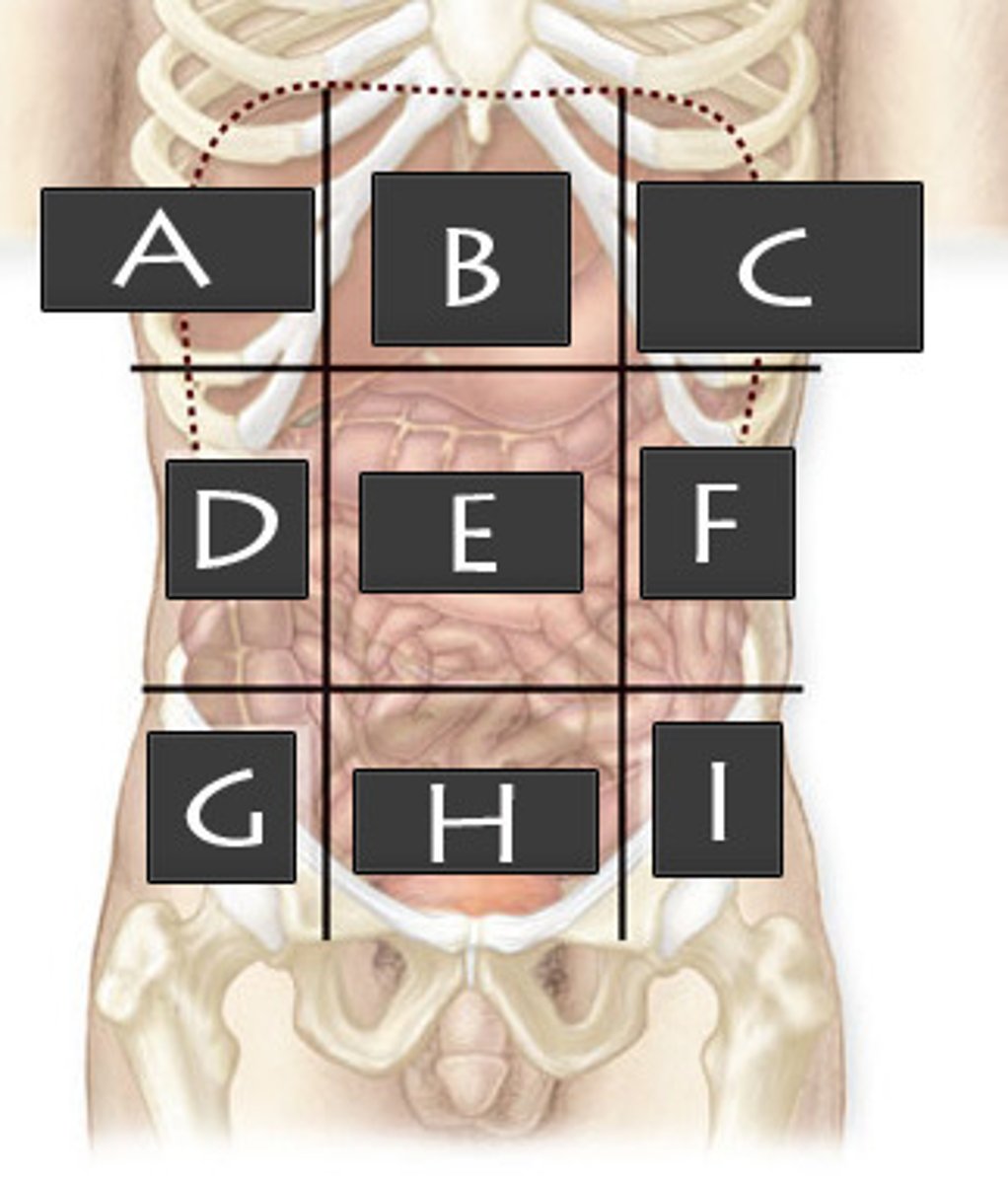
What are the 9 abdominopelvic regions?
A)right hypochondriac B)epigastric
C)left hypochondriac
D)right lumbar
E)umbilical
F)left lumbar
G)right iliac
H)hypogastric
I)left iliac
What are the 4 types of tissues?
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
What is muscle tissue?
tissues responsible for movement
What is nervous tissue?
tissue that generates and transmits electrical signals
Is epithelial tissue vascularized?
no
What are 2 types of epithelial tissue classifications?
simple
stratified
What is a simple epithelium?
a single layer of cells
What is a stratified epithelium?
multiple layers of cells
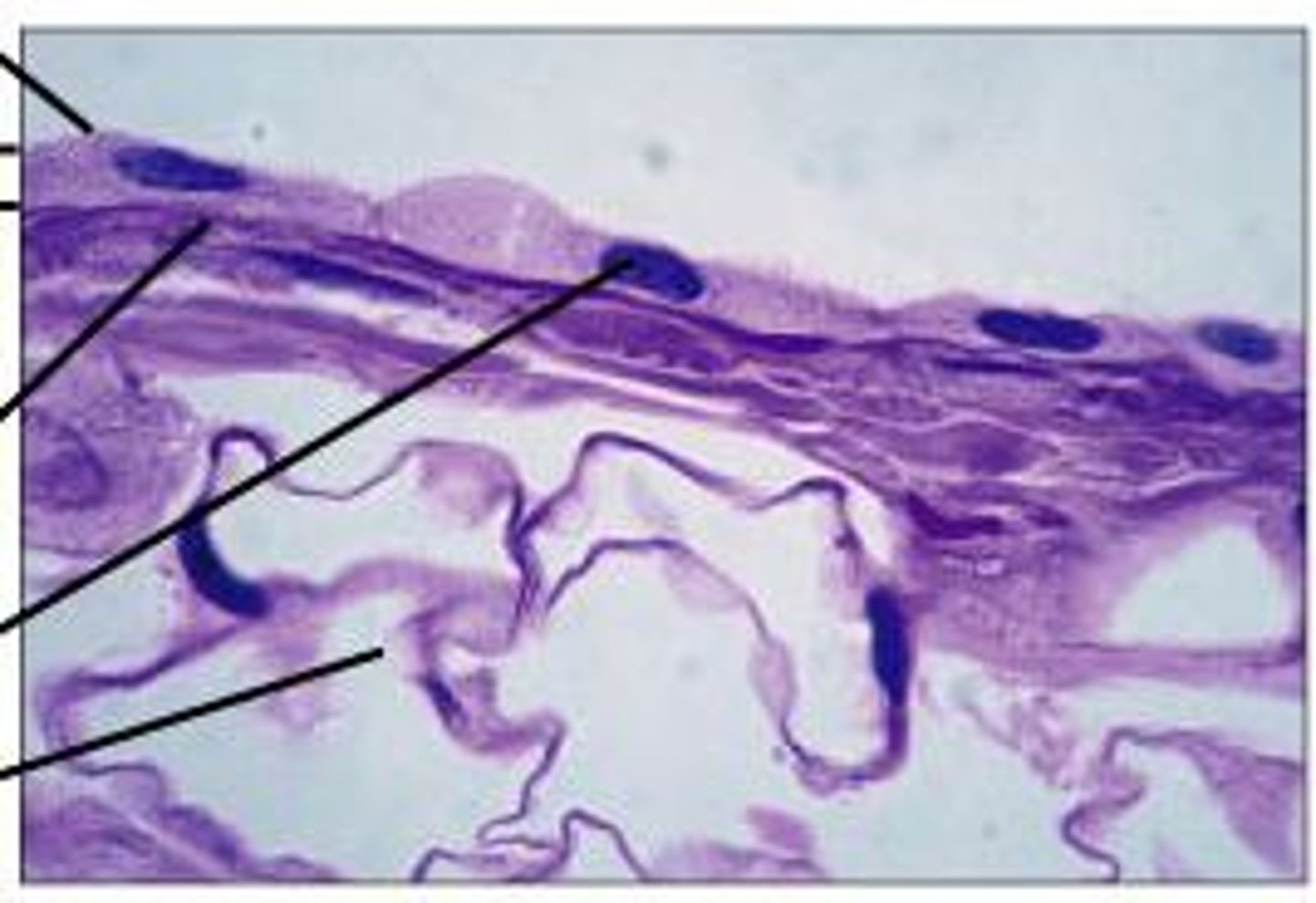
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-epithelial tissue
-simple squamous epithelium
-single layer of flattened cells
-diffusion or filtration
-air sacs of lung, capillaries, kidney tubules
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
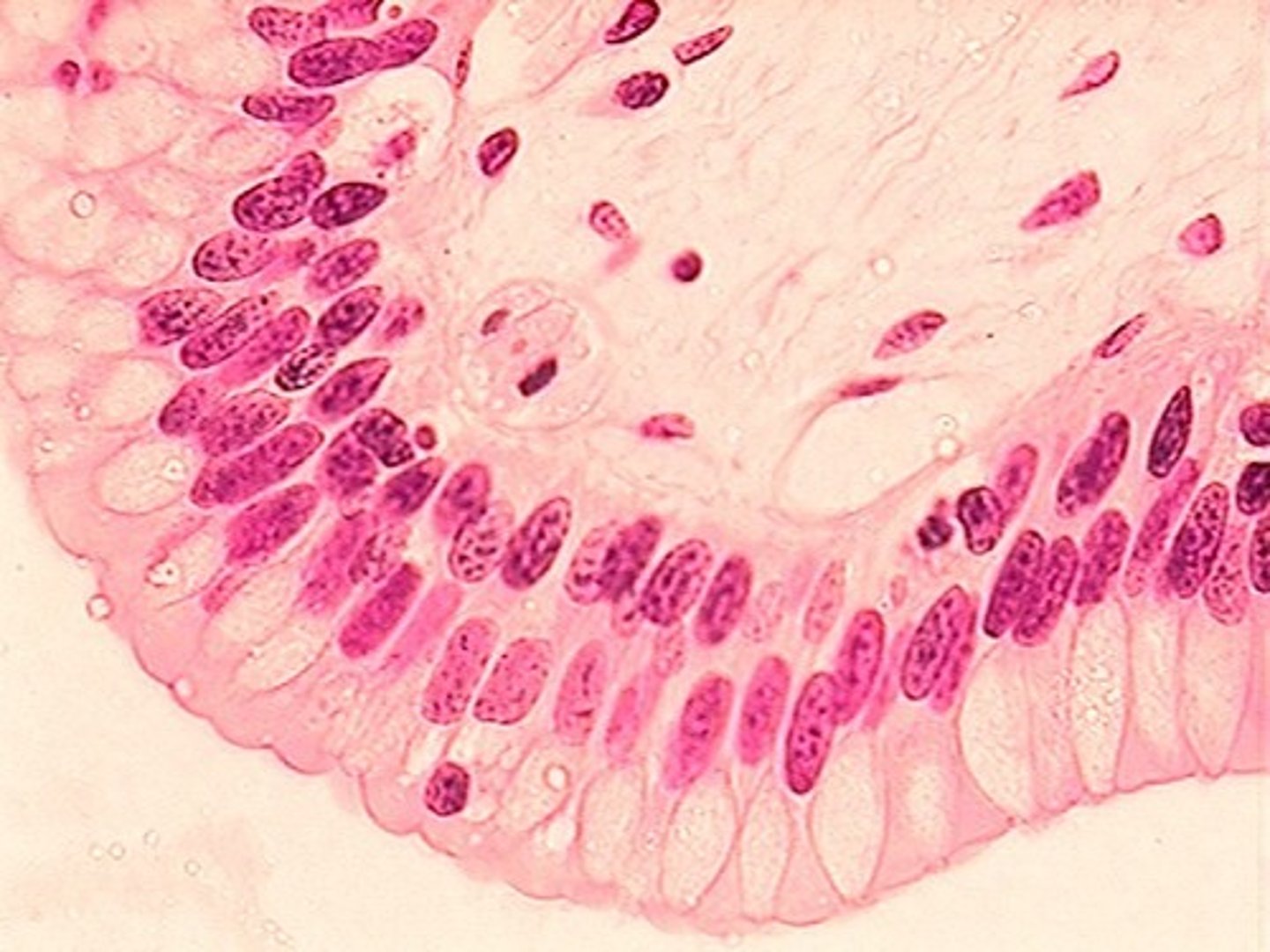
-epithelial tissue
-Stratified columnar epithelium
-many layers of columnar cells
-Protection and secretion
-Vas deferens, Part of urethra, Pharynx
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
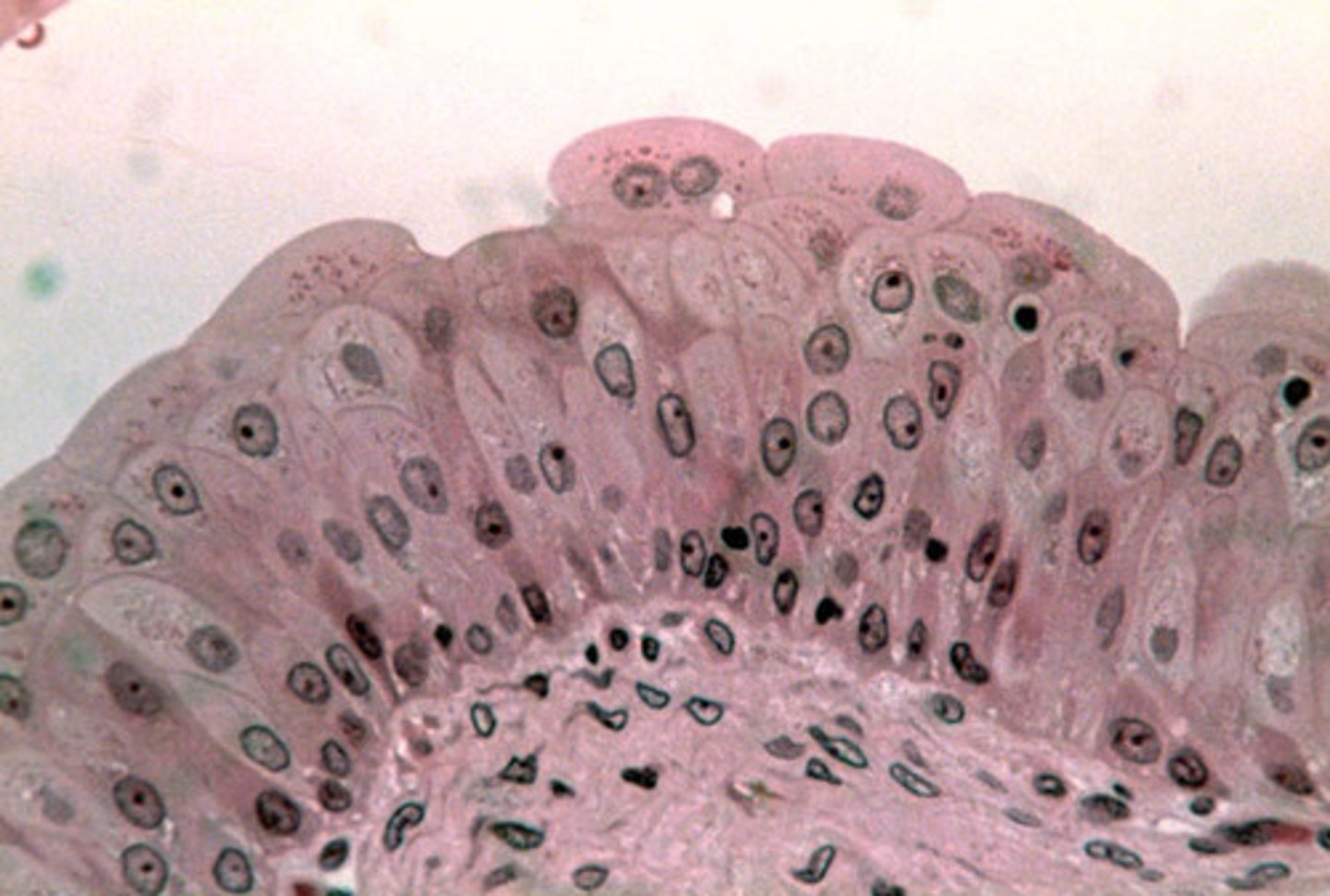
-epithelial tissue
-Transitional epithelium
-Many layers of cuboidal and columnar cells
-Dispensability, protection
-Inner lining of urinary bladder, Lining of ureters and urethra
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
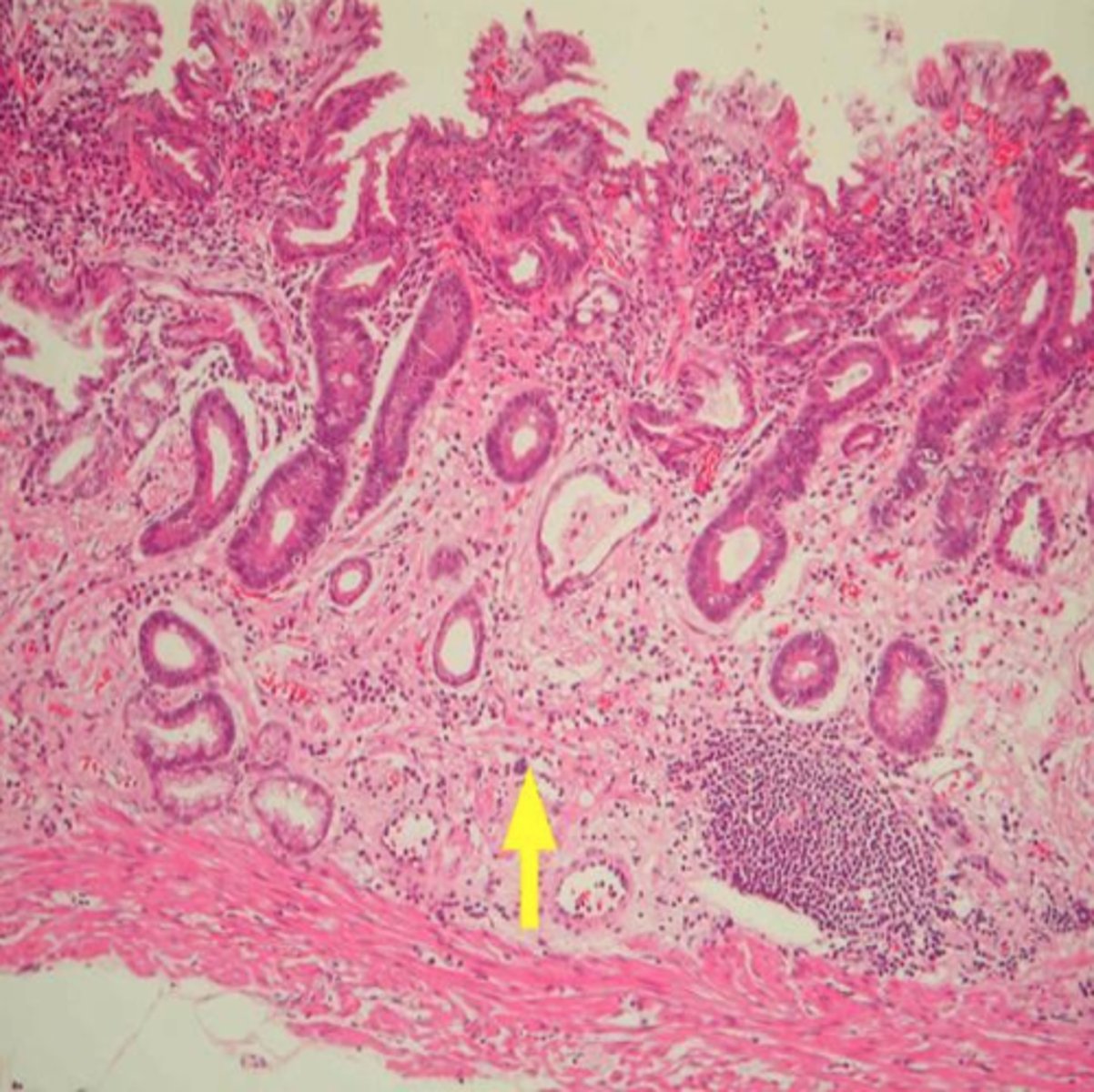
-epithelial tissue
-glandular epithelium
-Made of cuboidal or columnar cells
-Specialized to produce and secrete chemical substances into ducts or body fluids
-Exocrine glands
Endocrine glands
What are the 4 cells that make up connective tissue?
Fibroblast
Chondroblast
Osteoblast
Hemocytoblast
What is the function of osteoblasts?
form bone
What is the function of hemocytoblasts?
form blood
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
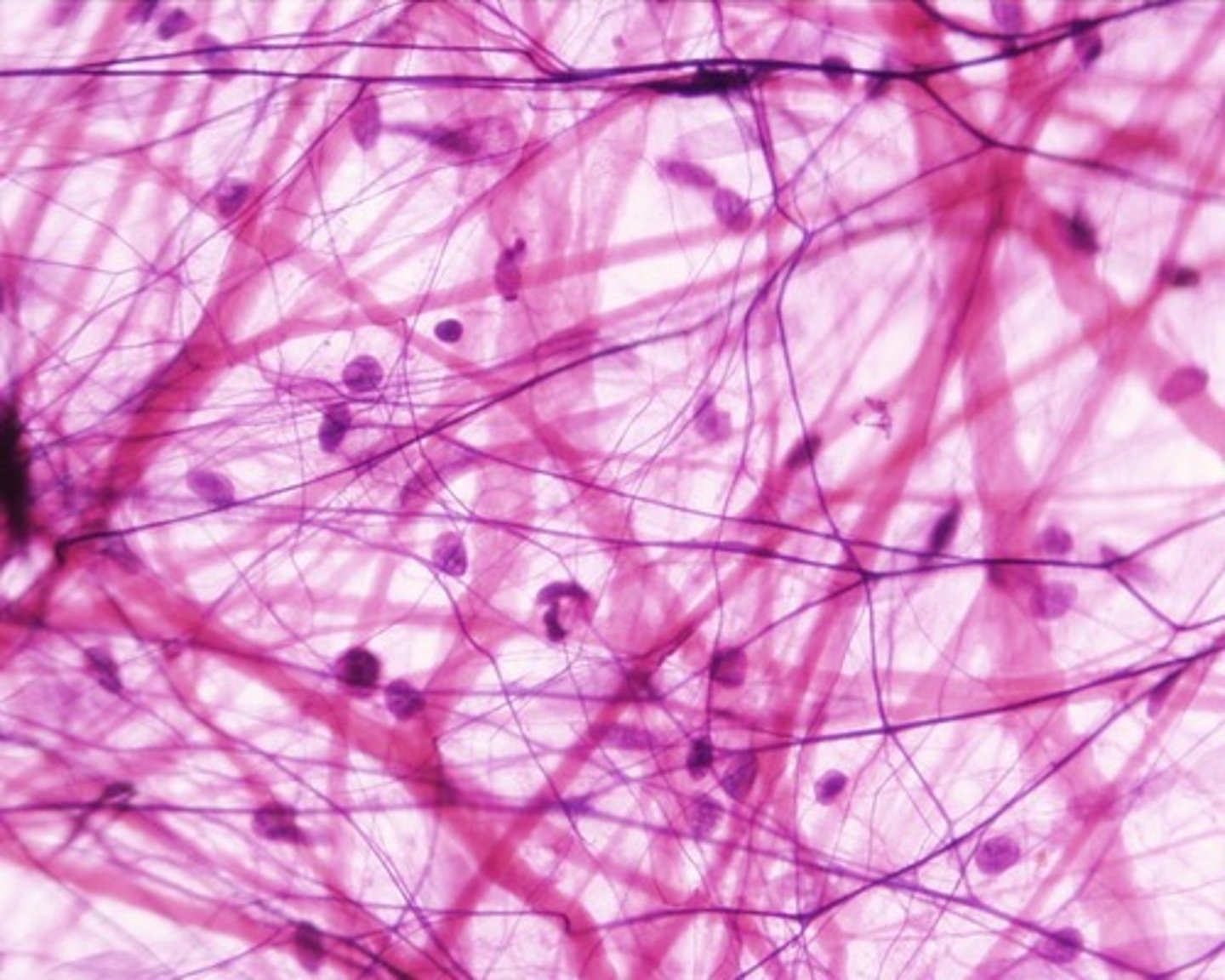
-connective tissue
-Loose (areolar) connective tissue
-Consists of fibroblasts, collagen fibers, and elastic fibers
-Forms delicate, thin membranes throughout body
-Binds skin to underlying organs, fills space between organs and muscles
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-connective tissue
-Reticular Connective Tissue
-Resembles loose areolar tissue but only has reticular fibers
-structural support
-Spleen, Bone marrow, Lymph
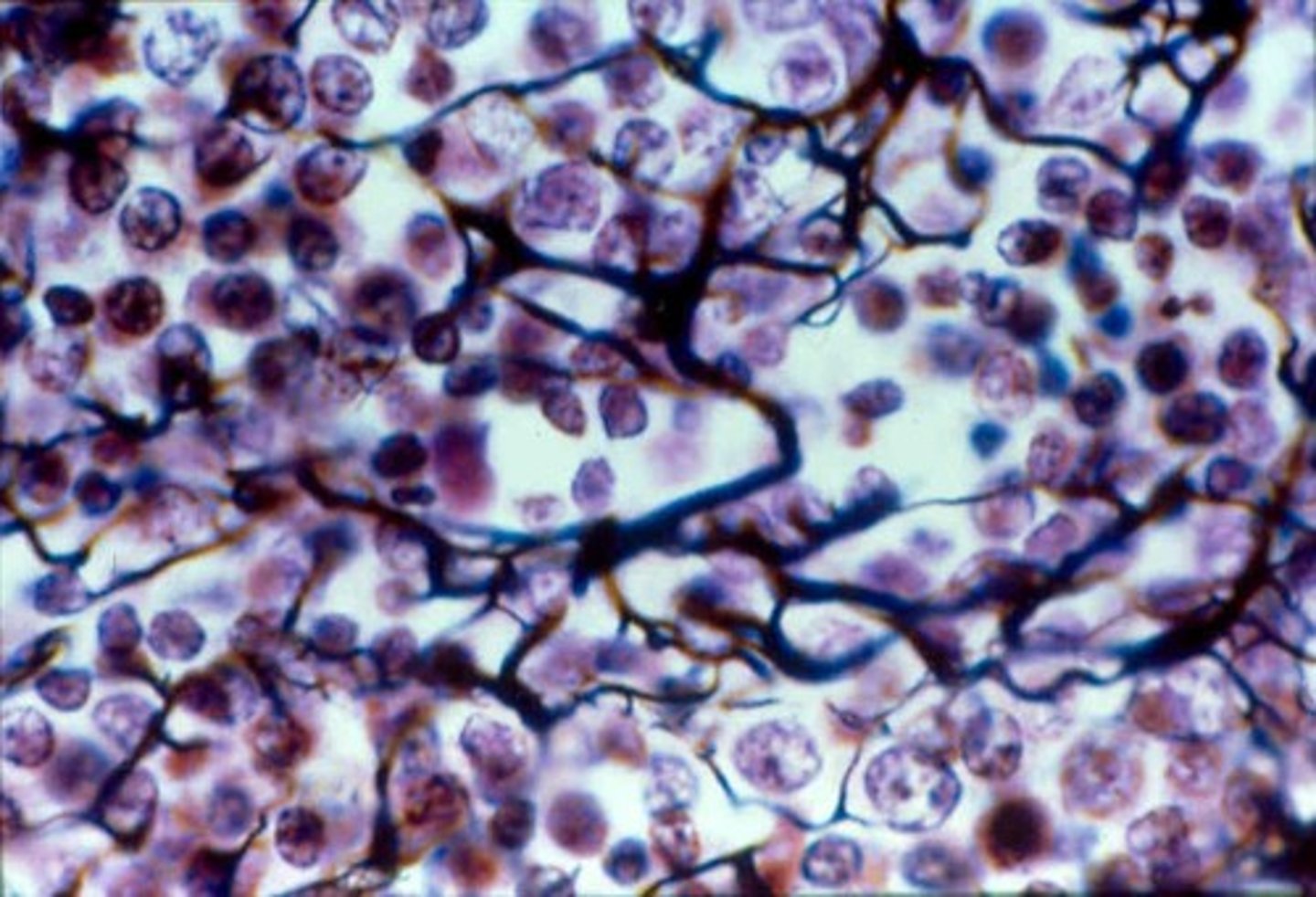
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-connective tissue
-Adipose Tissue
-Modified from loose connective tissue
Specialized to store fat via adipocytes
-Serves as a protective cushion for joints and organs, Insulates body, Stores energy
-Under skin, Around kidneys, Around eyes, Within abdomen, Breasts
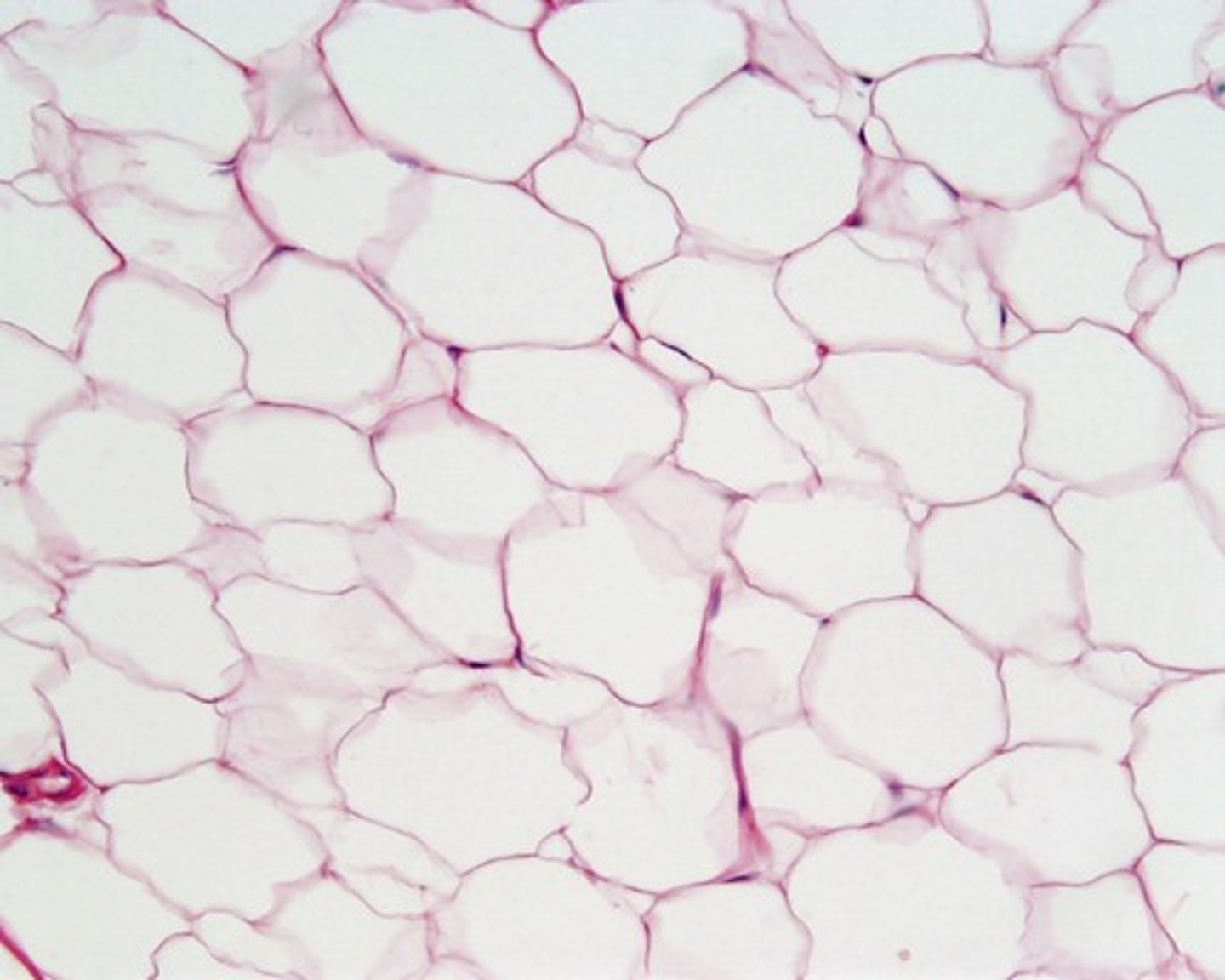
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-connective tissue
-Dense Regular Connective Tissue
-Contains closely packed bundles of collagen fibers
-connects organs and muscles
-Tendons, Ligaments
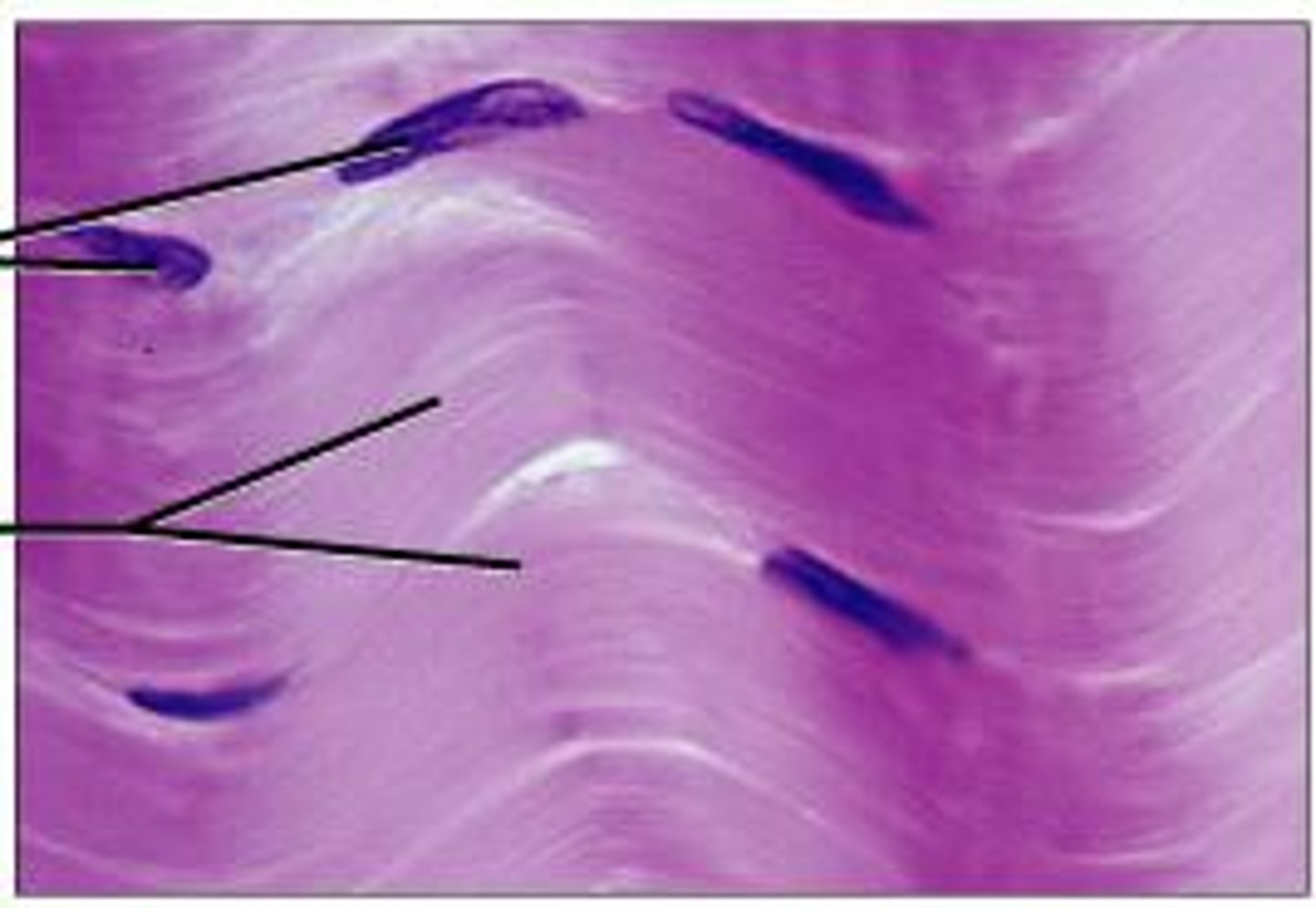
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-connective tissue
-Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
-Arranged irregularly, Thicker collagen fiber bundles
-strength
-Forms dermis (inner skin layer)
What are the 2 distinguishing characteristics of cartilaginous tissue?
-Consist of cells called chondrocytes which are found in cavities called lacunae
-cartilage is AVASCULAR
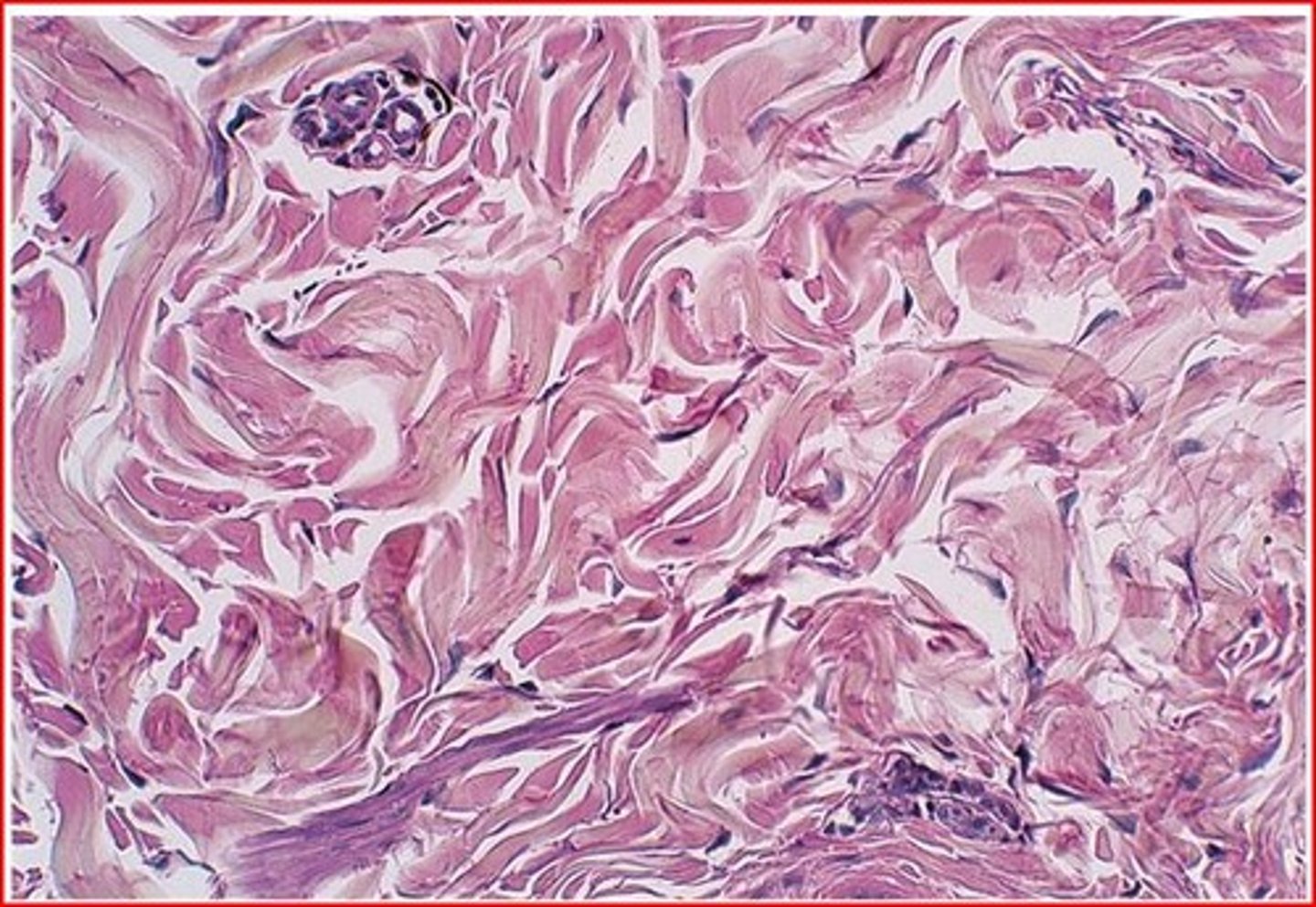
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-connective tissue
-Hyaline Cartilage
-Contains fine collagenous fibers in the matrix
-Ends of joints
-Surrounding trachea
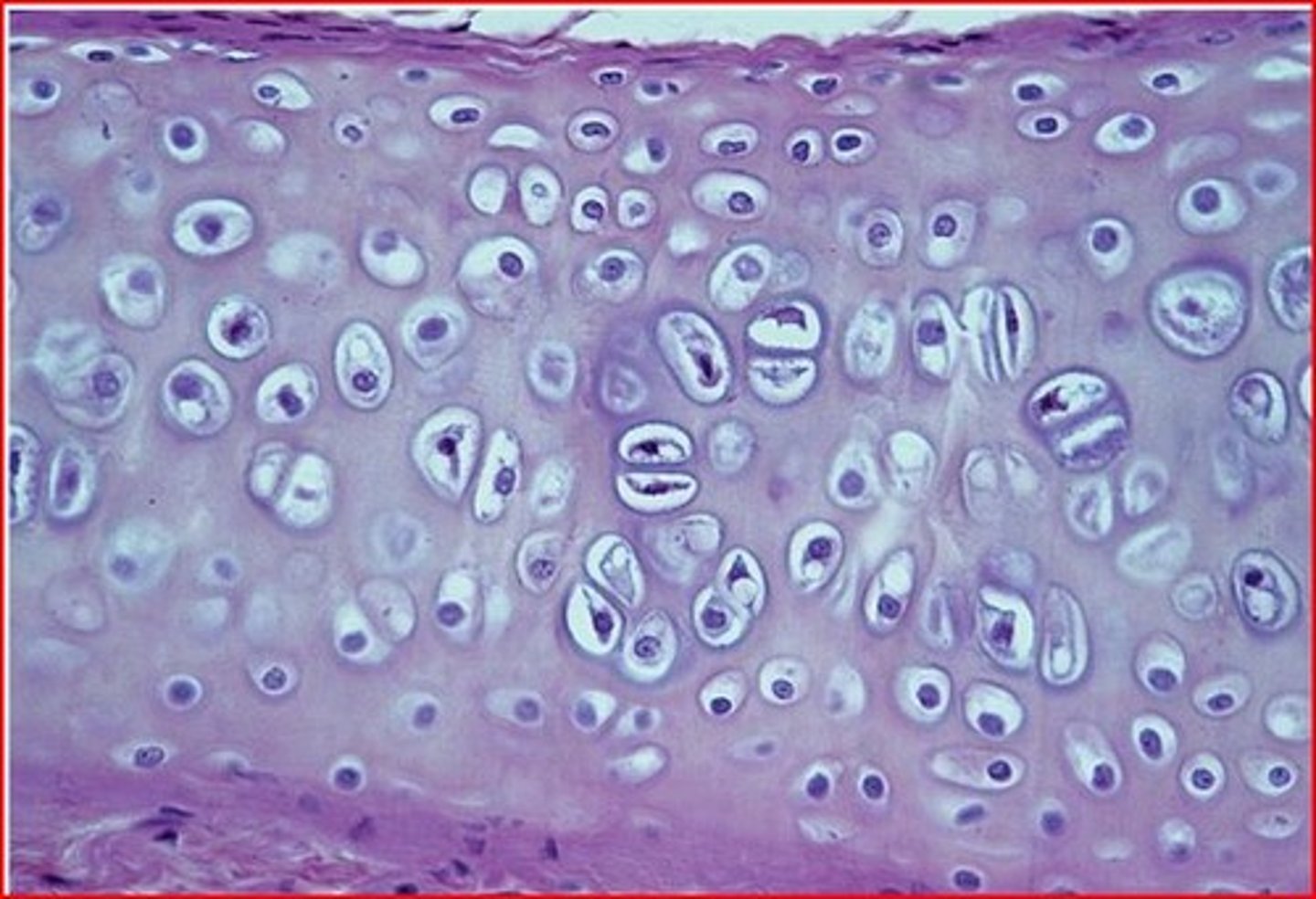
What is the most common type of cartilage?
hyaline cartilage
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-connective tissue
-Elastic Cartilage
-Contains elastic fibers in the matrix
-provides elastic support
-External ear, larynx
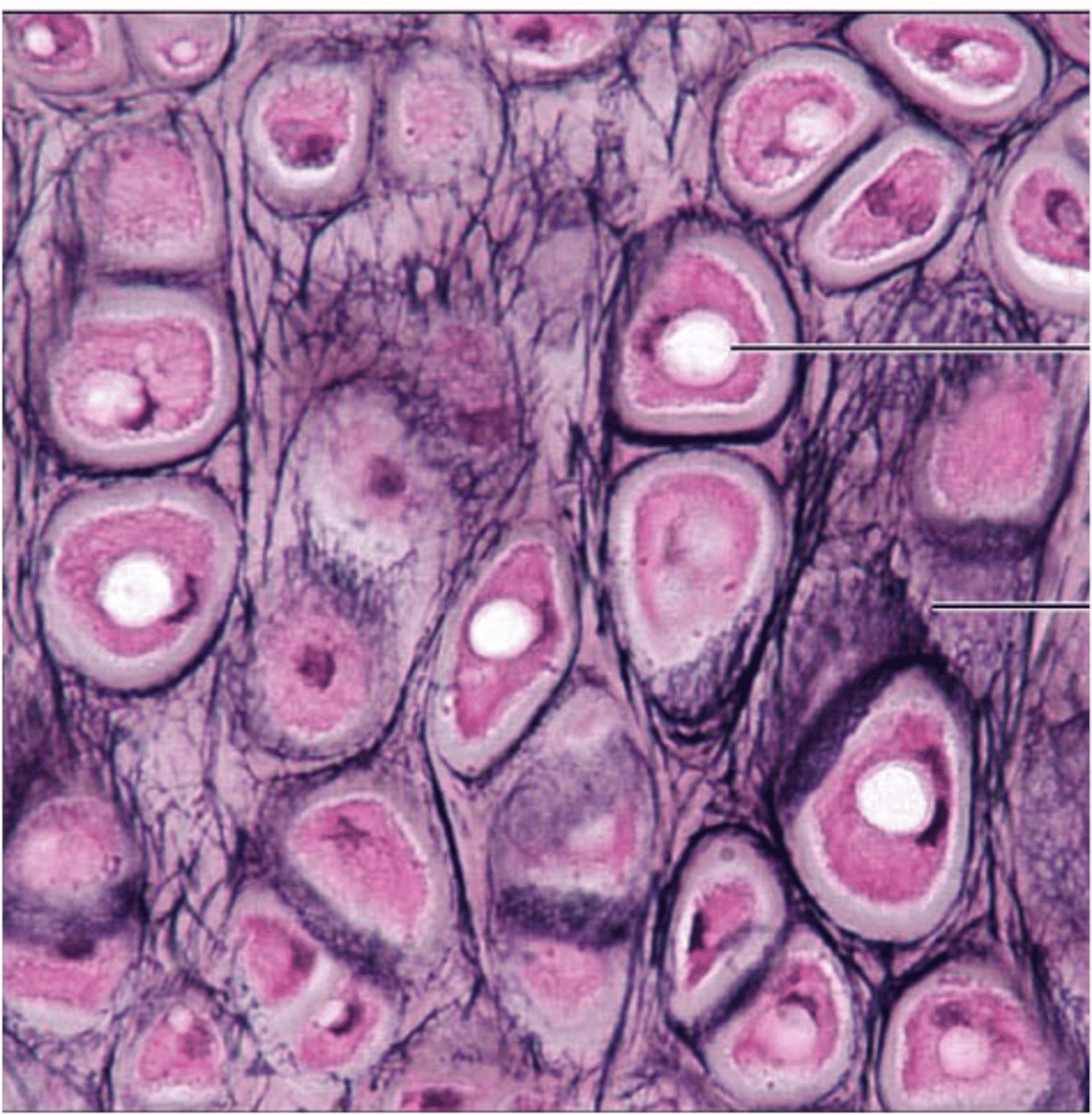
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-connective tissue
-Fibrocartilage
-Contains thick collagen fibers in the matrix
-Acts as shock absorbers
-Intervertebral discs, Knee bones, Pelvic bones
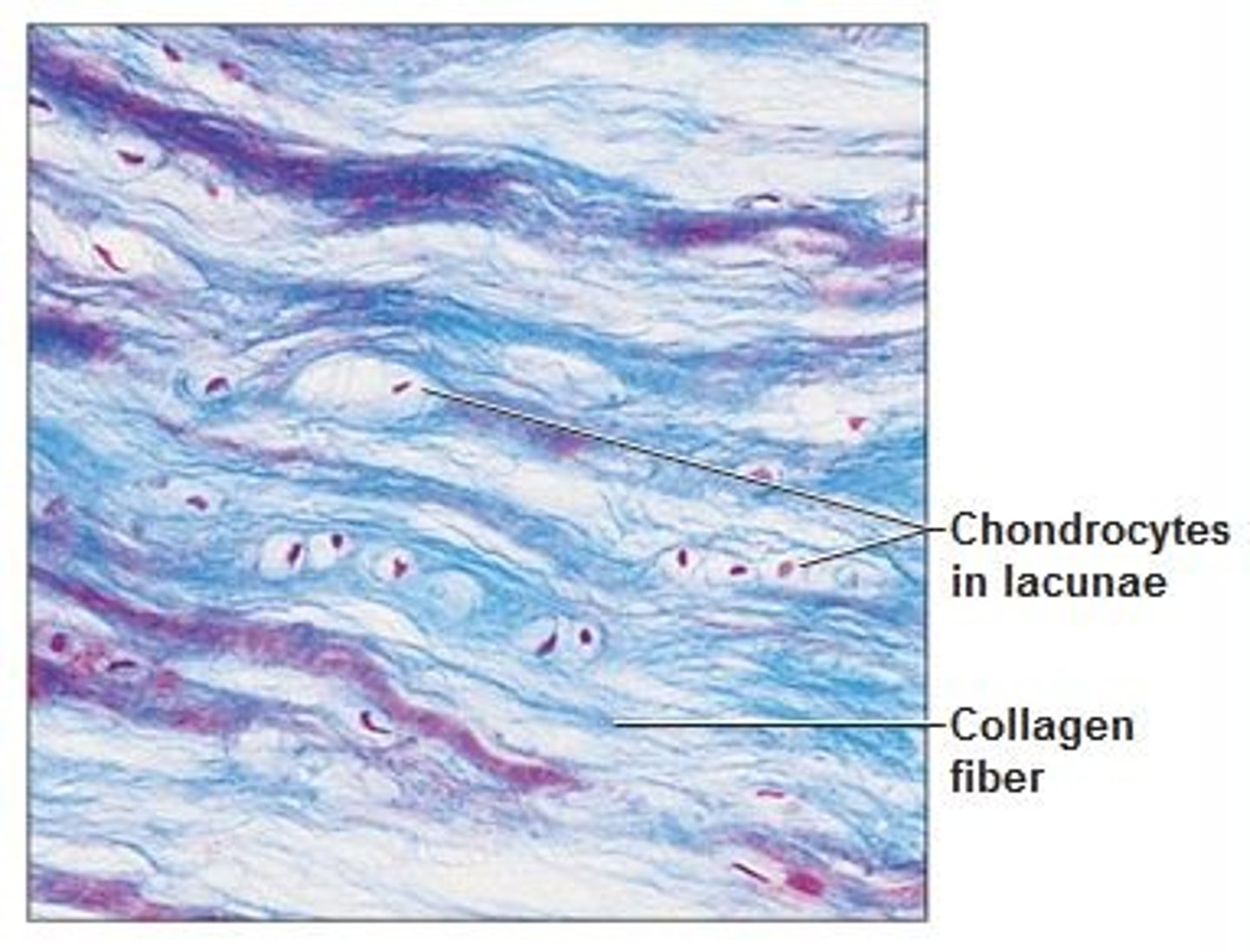
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-muscle tissue
-Skeletal muscle
-Multinucleated,
Striated
-Can contract with powerful force
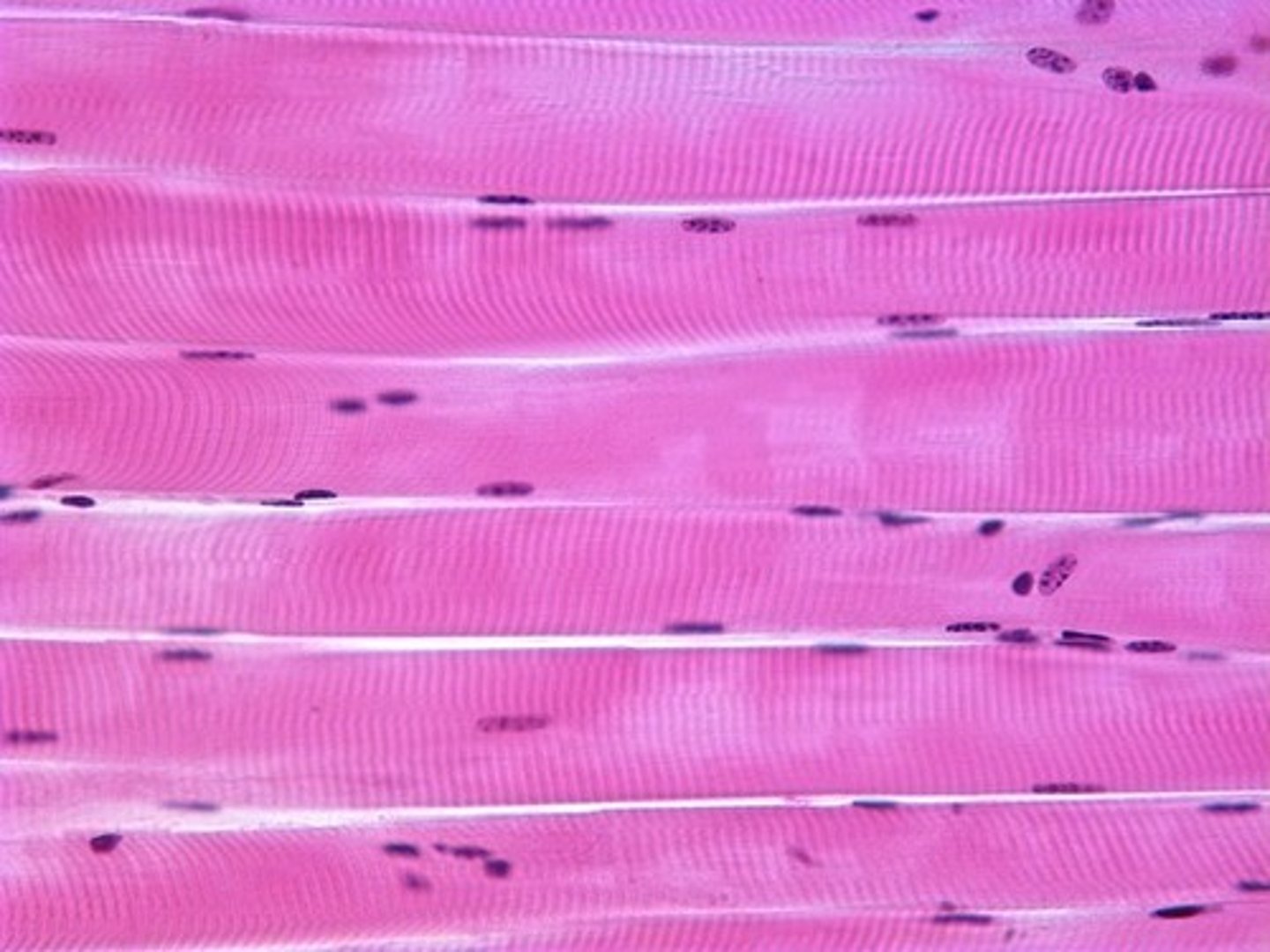
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-muscle tissue
-cardiac muscle
-Uninucleated, Cross-striated, From interconnected branches, intercalated discs
-Can contract continuously and rapidly
-Walls of the heart
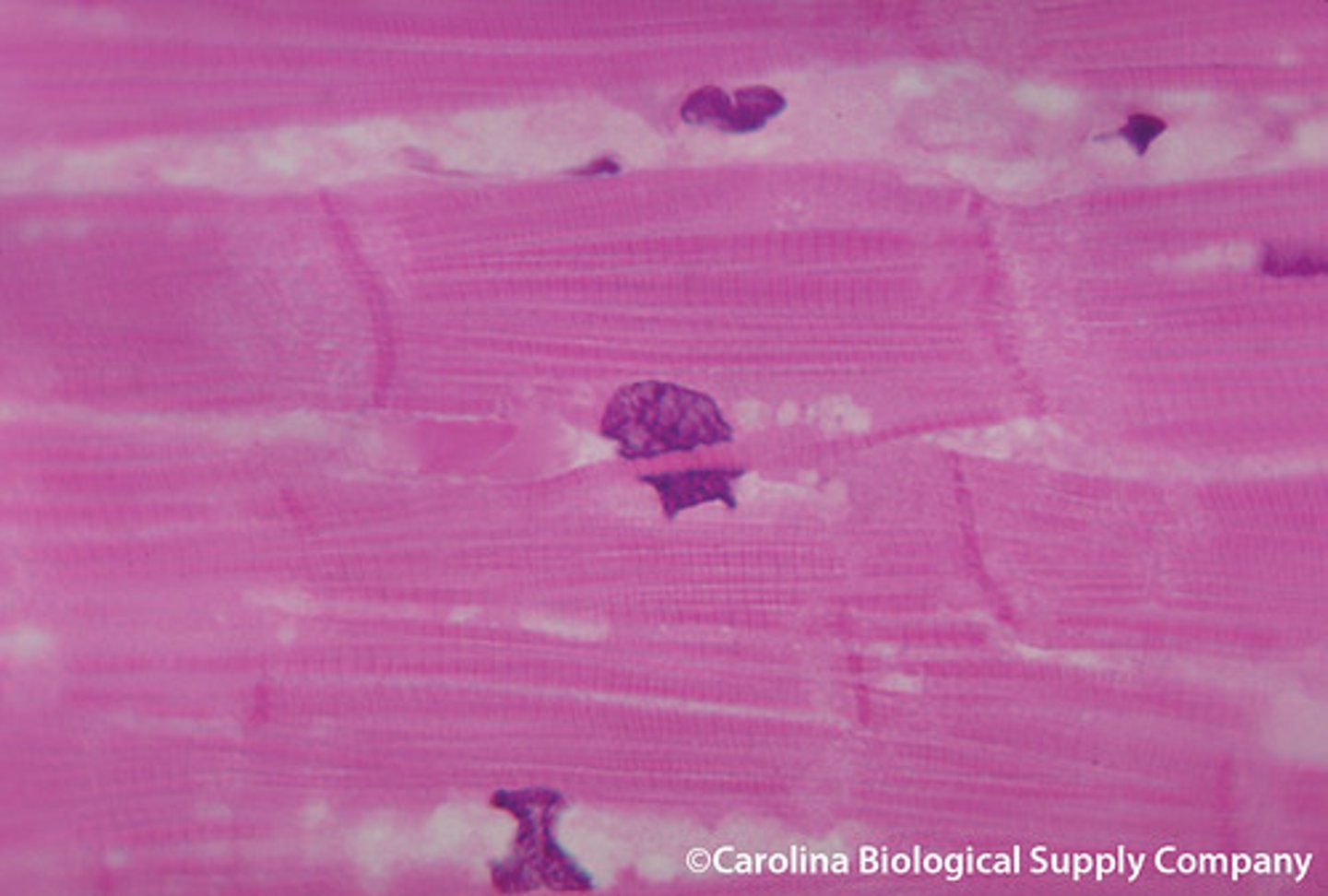
What is the tissue pictured? What type of tissue is it? (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous) What is its structure, function(s), and where can it be found?
-muscle tissue
-smooth muscle
-Uninucleated
-slow and consistent contraction
-Walls of hollow organs
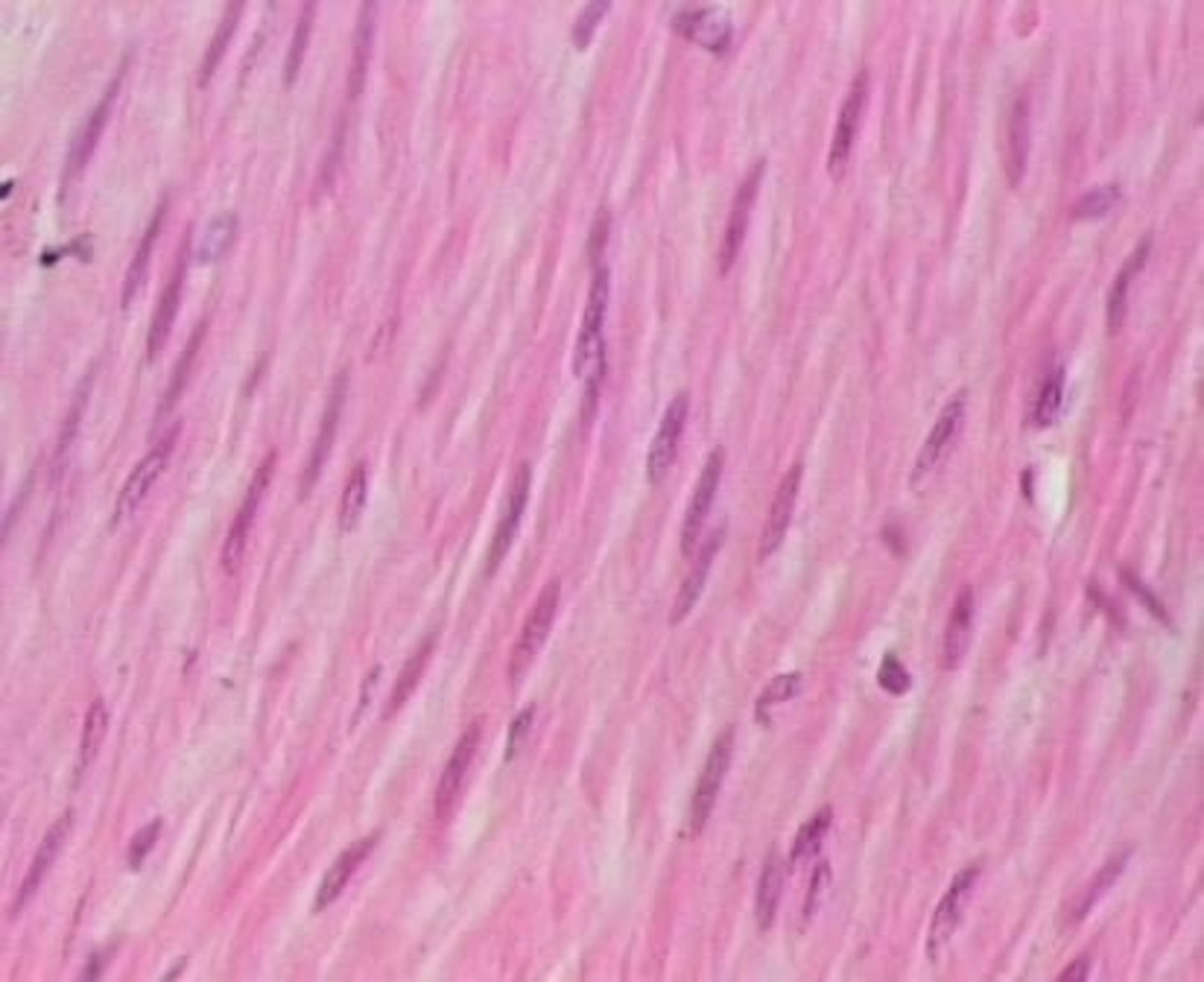
Describe the cutaneous membrane
Skin - dry outermost membrane with dermis and epidermis
Describe the serous membrane
Moist membranes found in ventral body cavity and covering organs, secretes serous fluid that acts as a lubricant
What are the 3 embryonic germ layers?
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
What are the 3 skin layers?
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
What are the 4 primary layers of the epidermis?
stratum corneum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
Which of the layers of the epidermis contain melanocytes?
stratum basale
What type of tissue makes up the epidermis?
stratified squamous epithelium
What type of tissue makes up the dermis?
fibrous connective tissue
What 2 tissues make up the hypodermis?
adipose tissue
loose connective tissue
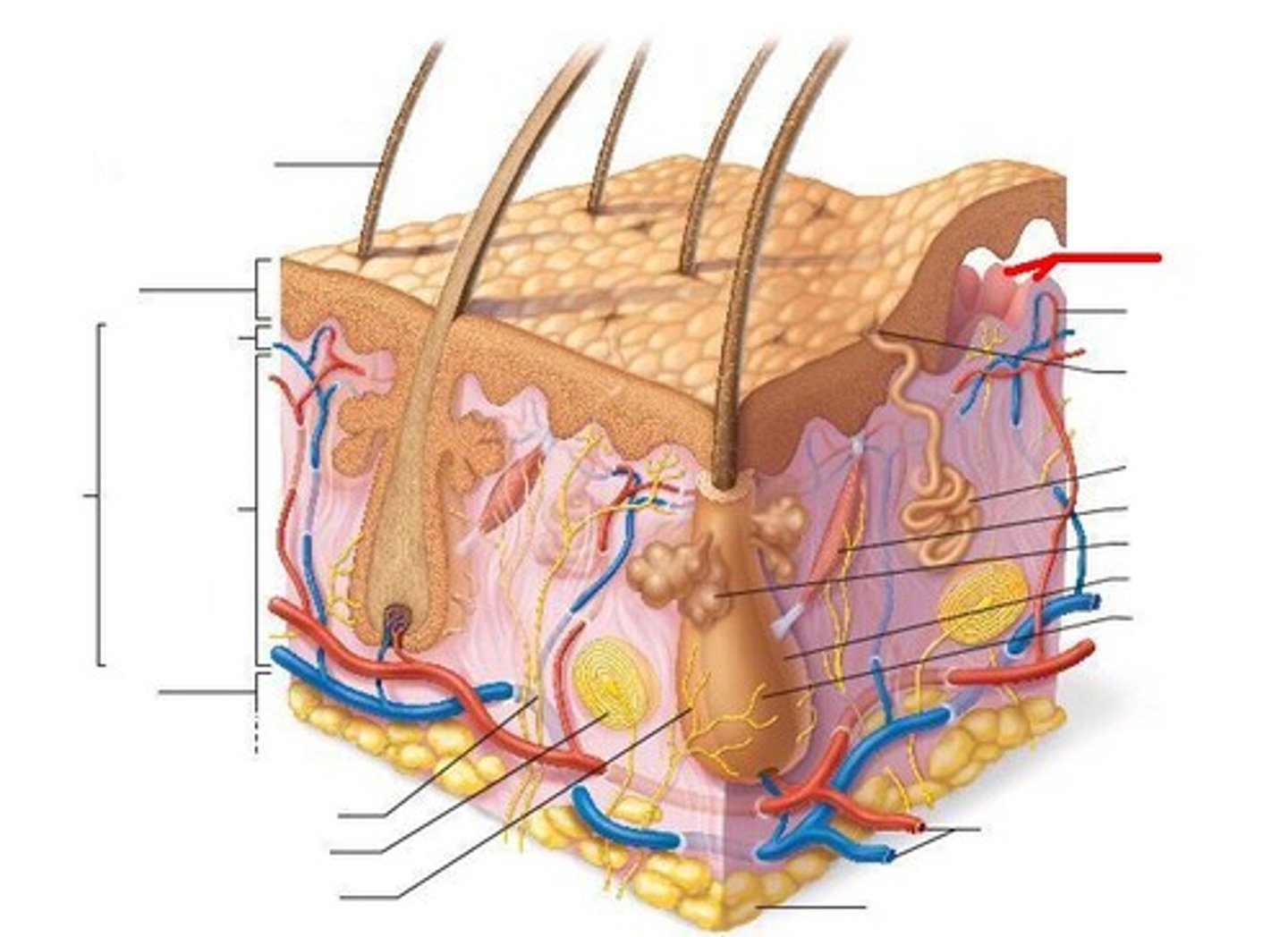
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
hair follicle
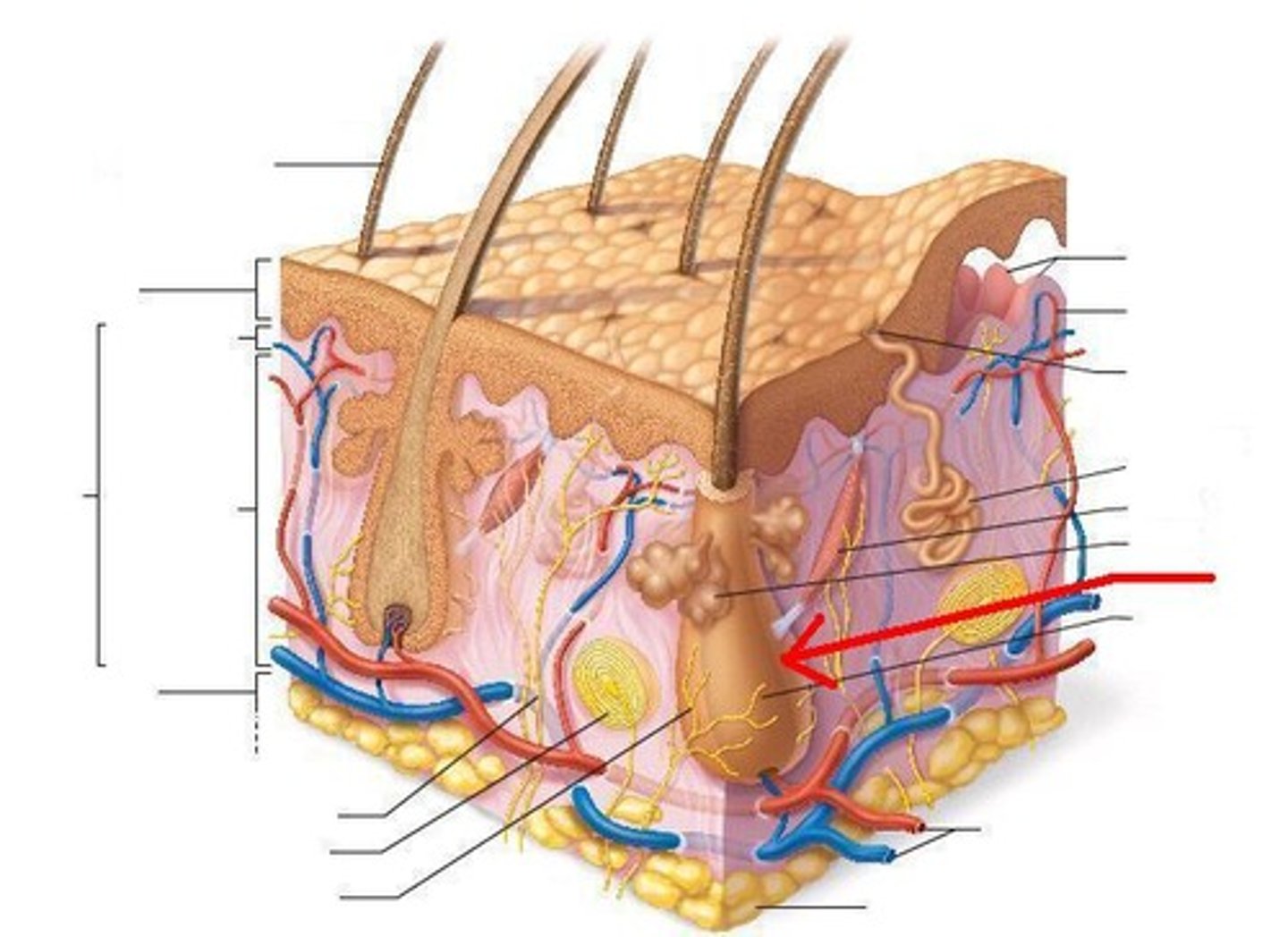
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
sebaceous gland
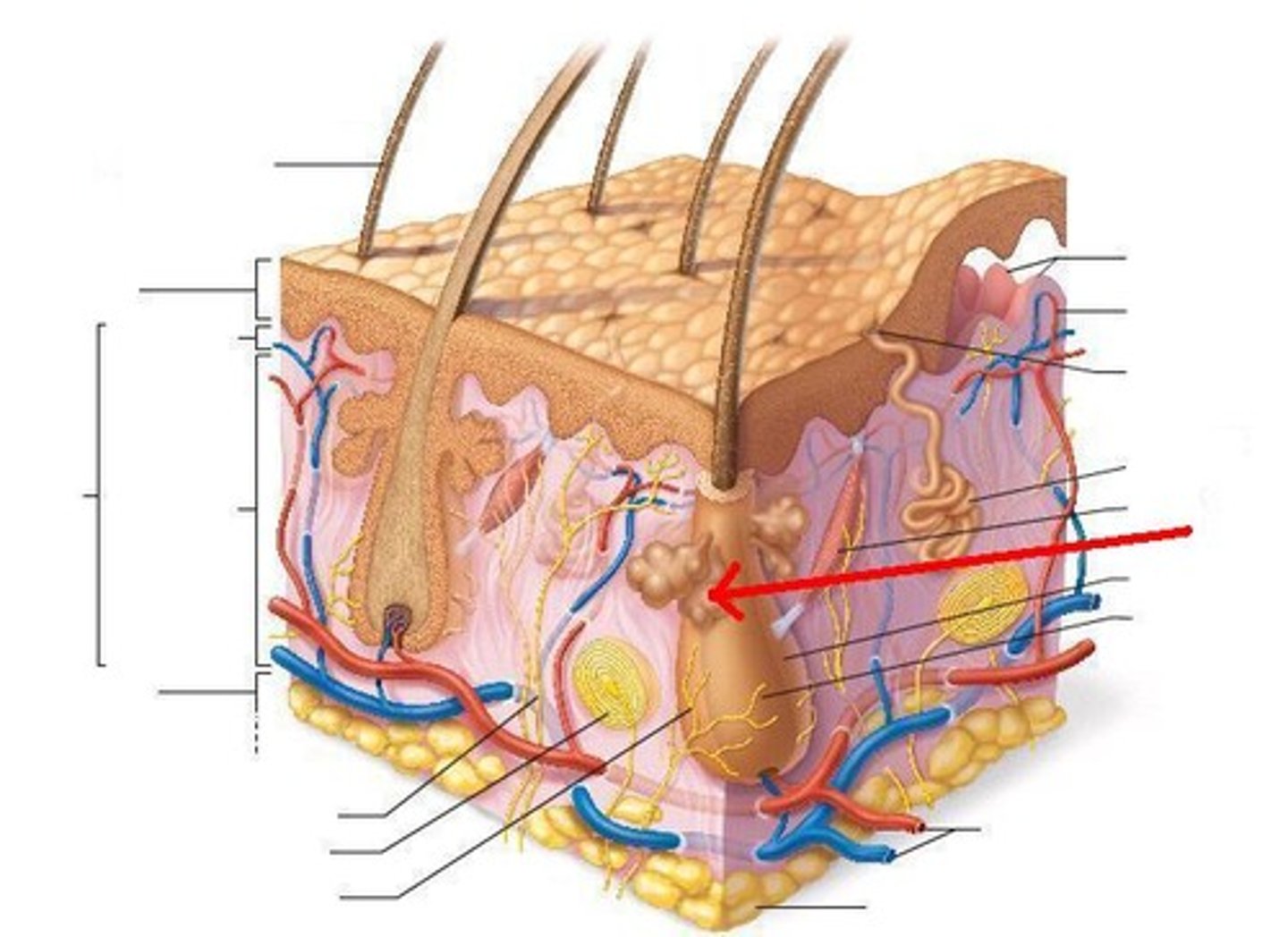
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
sweat gland
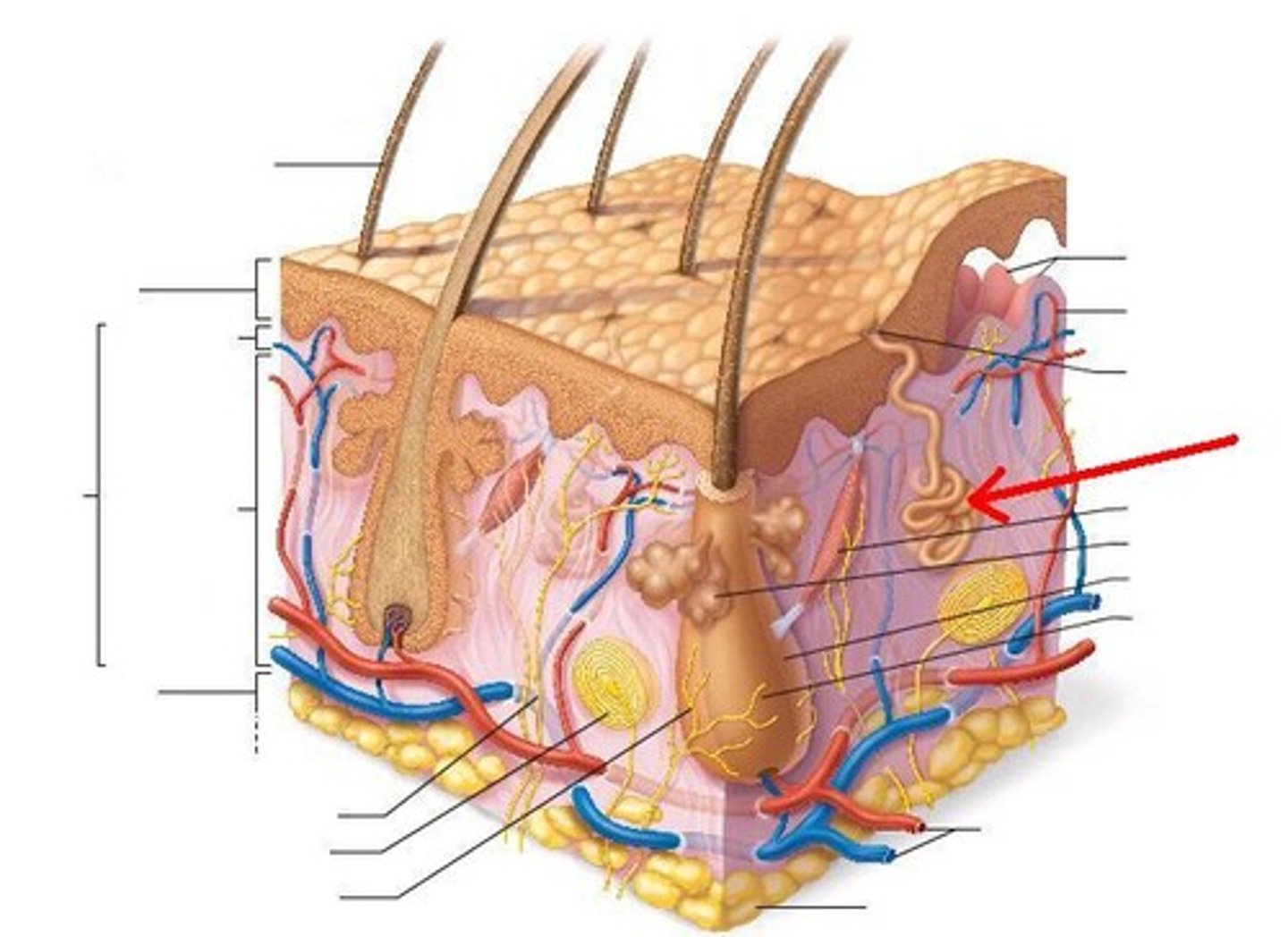
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
arrector pilli muscle
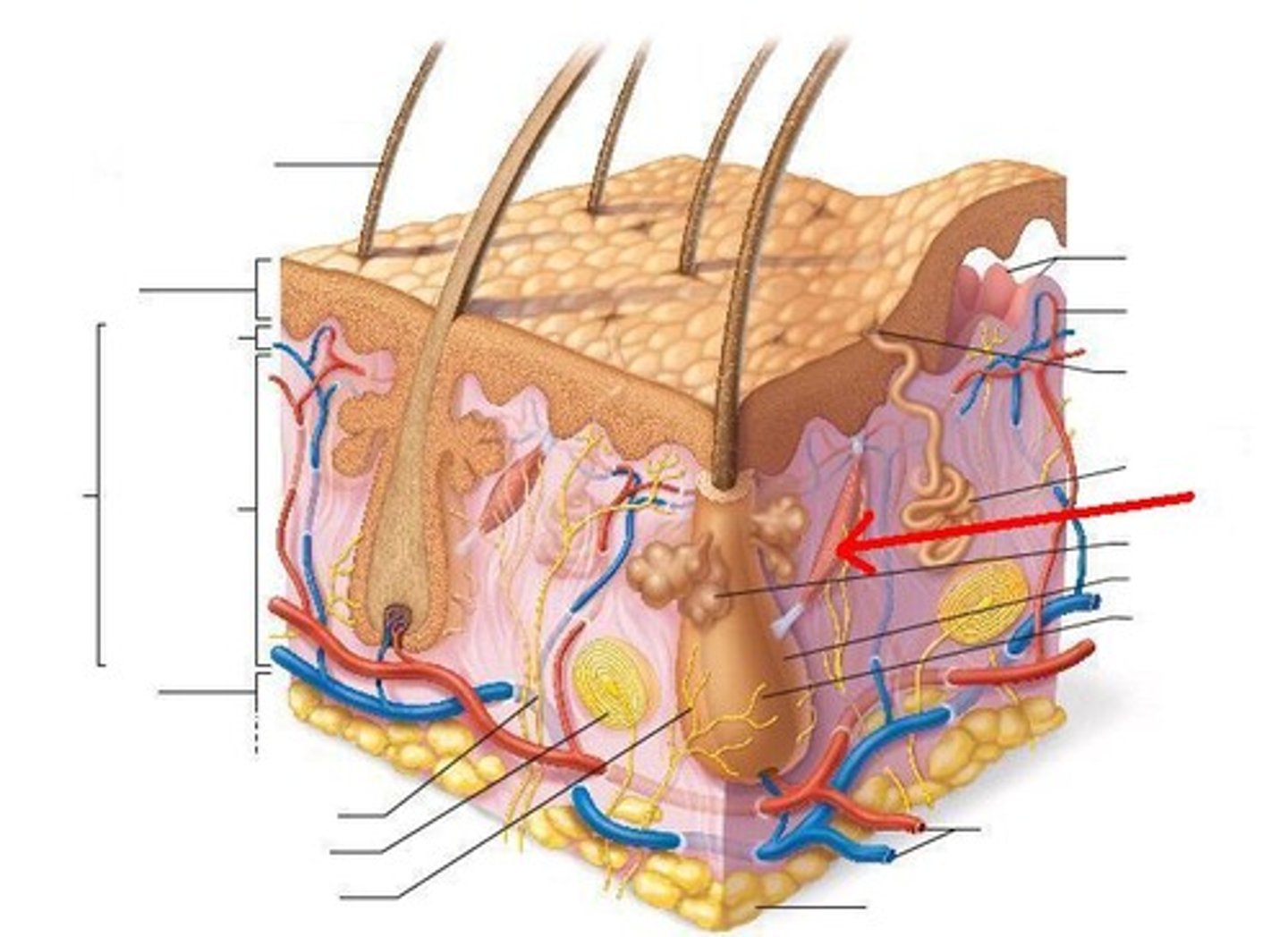
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
sweat pore
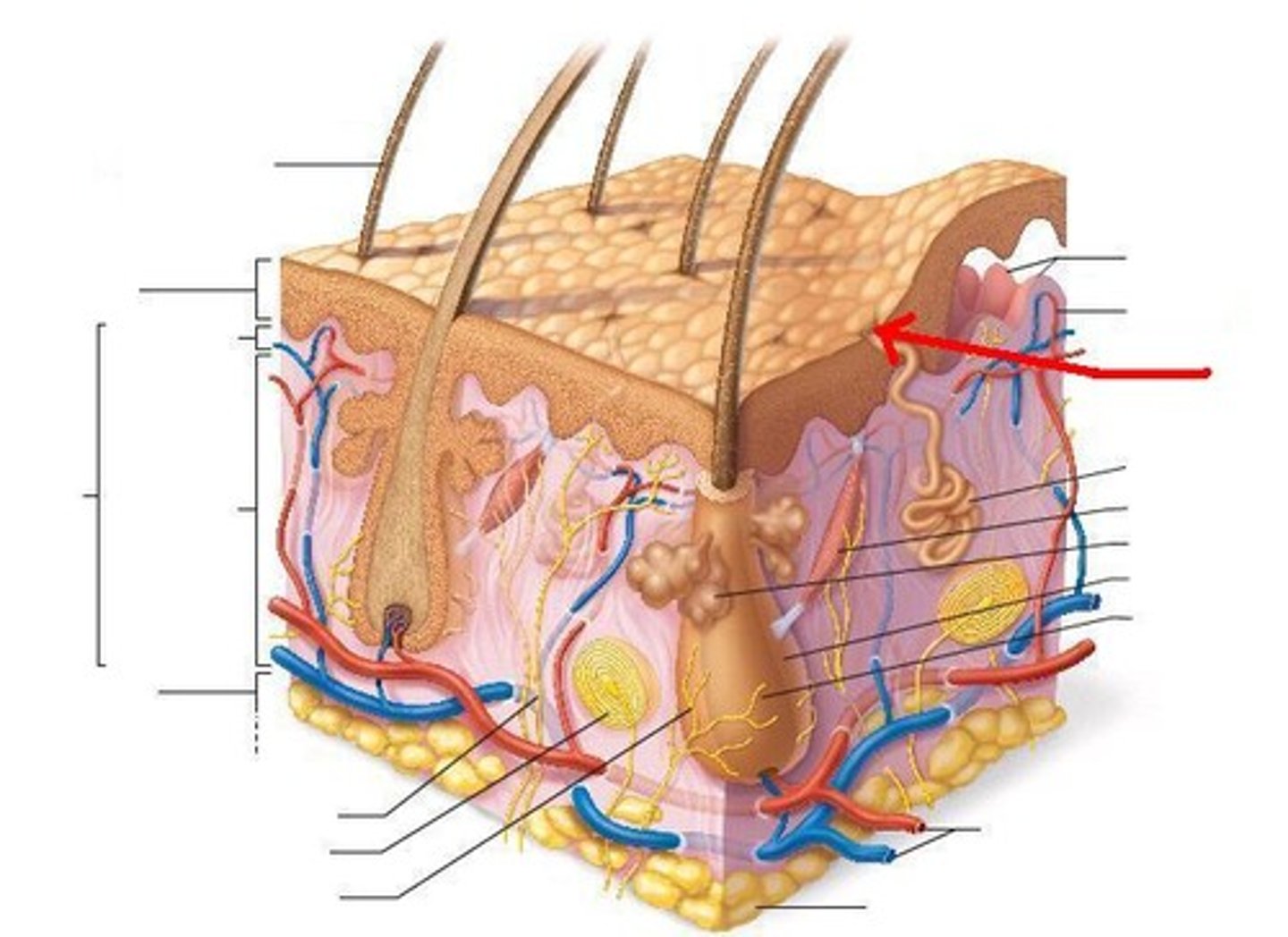
What accessory structure is the red arrow pointing to?
nerve
What are the functions of the hypodermis ?
anchors skin, acts as a cushion and insulator
What makes bones so durable and strong?
Ca2+ deposits in the bone matrix
What are the 4 bone classifications?
long bones
short bones
flat bones
irregular bones
Give an example of a long bone
femur
humerus
give an example of a short bone
carpals
tarsals
Give an example of a flat bone
scapula
cranial bones
Give an example of an irregular bone
vertebrae
What is part 1 and 3 of the long bone pictured called? (same name)
epiphysis
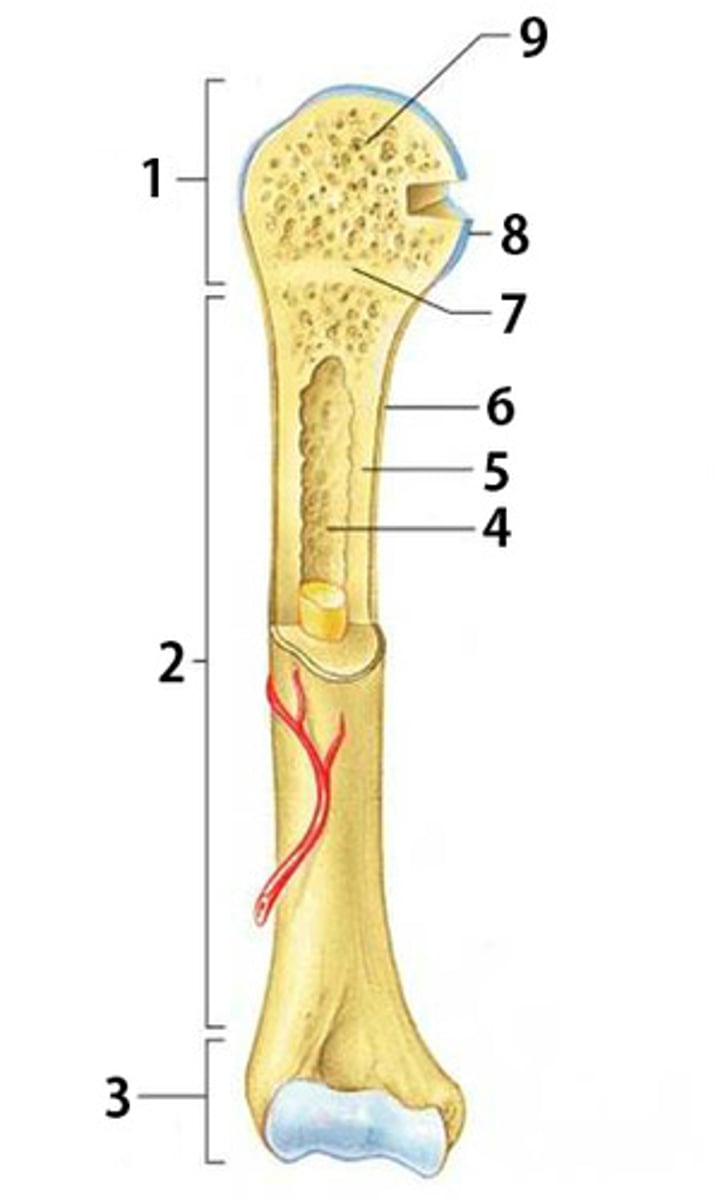
What is part 4 of the long bone pictured called?
medullary cavity
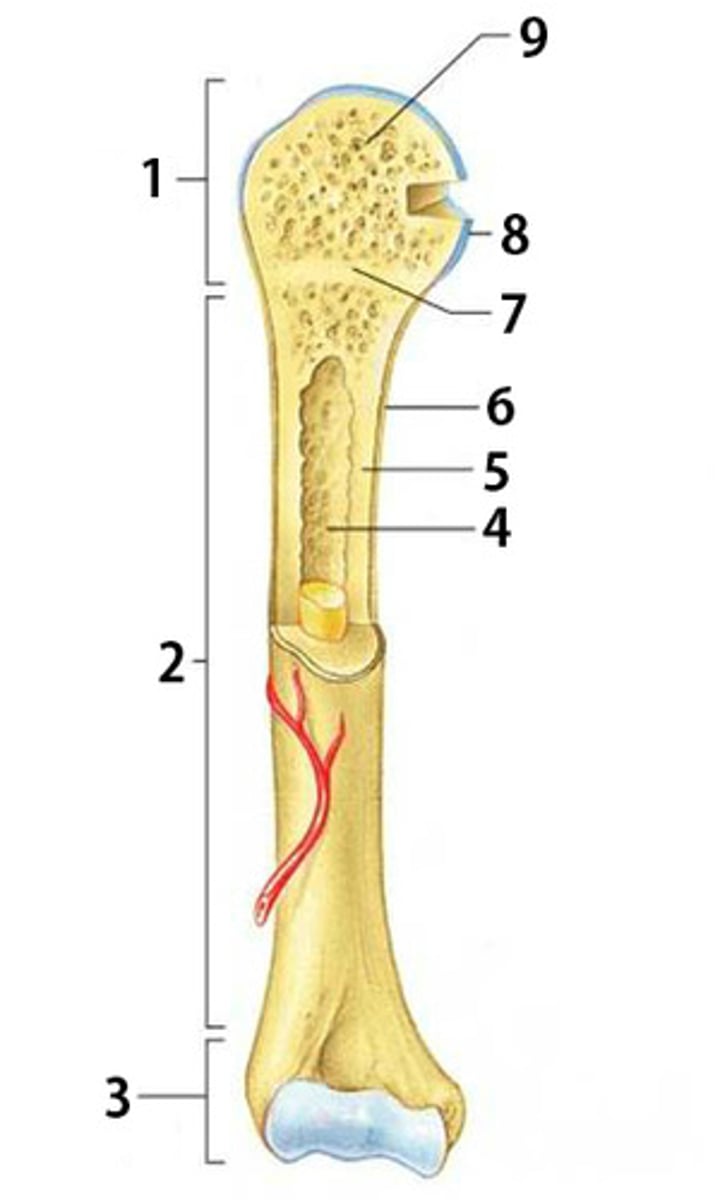
What type of bone is part 5 pointing to? (compact or spongy)
compact bone
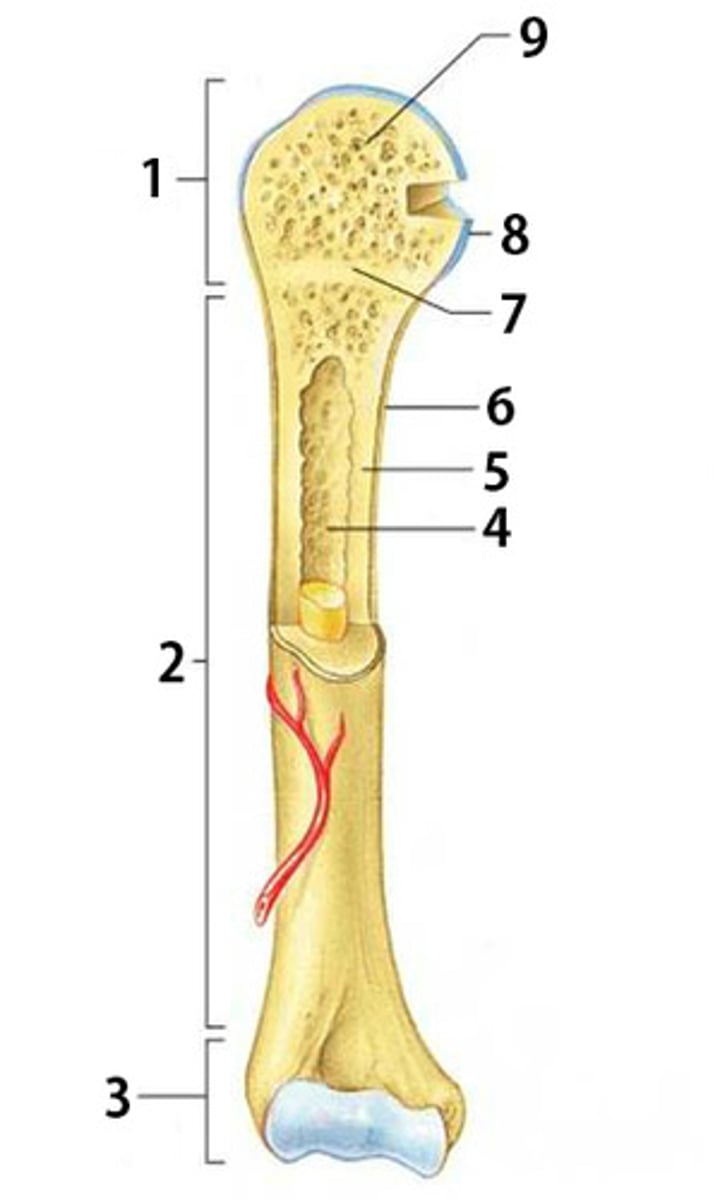
What is part 7 of the long bone pictured called?
epiphyseal disk
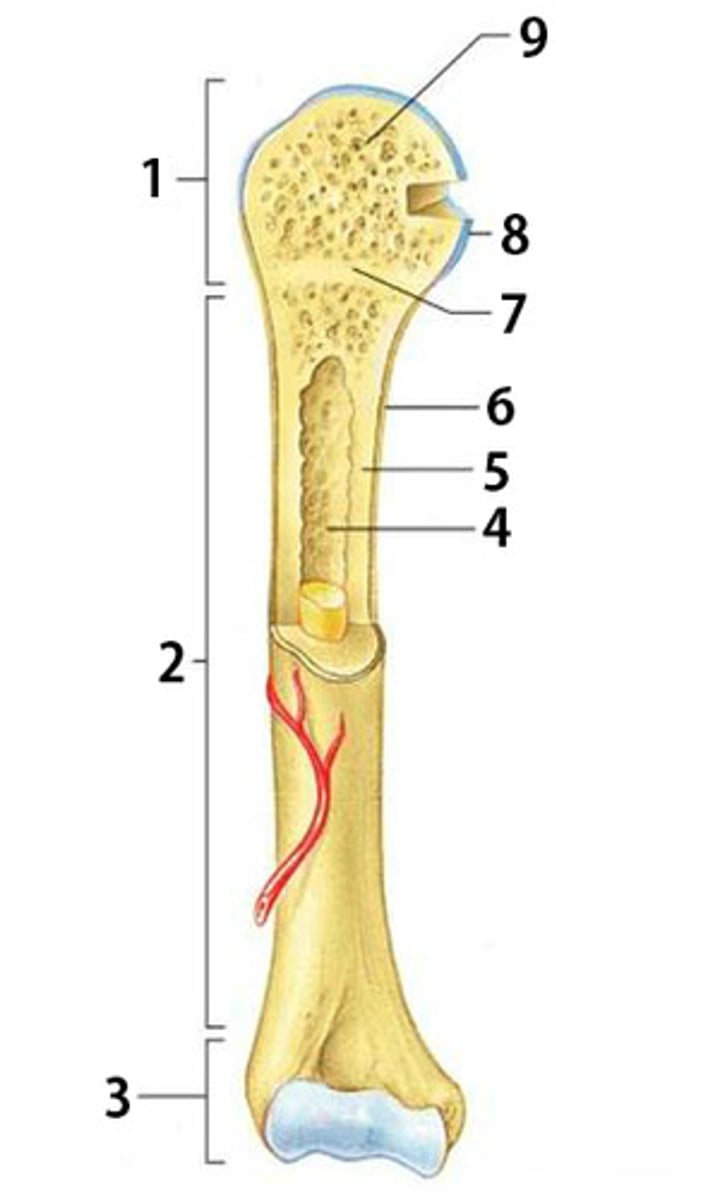
What type of bone is part 9 pointing to? (compact or spongy)
spongy bone
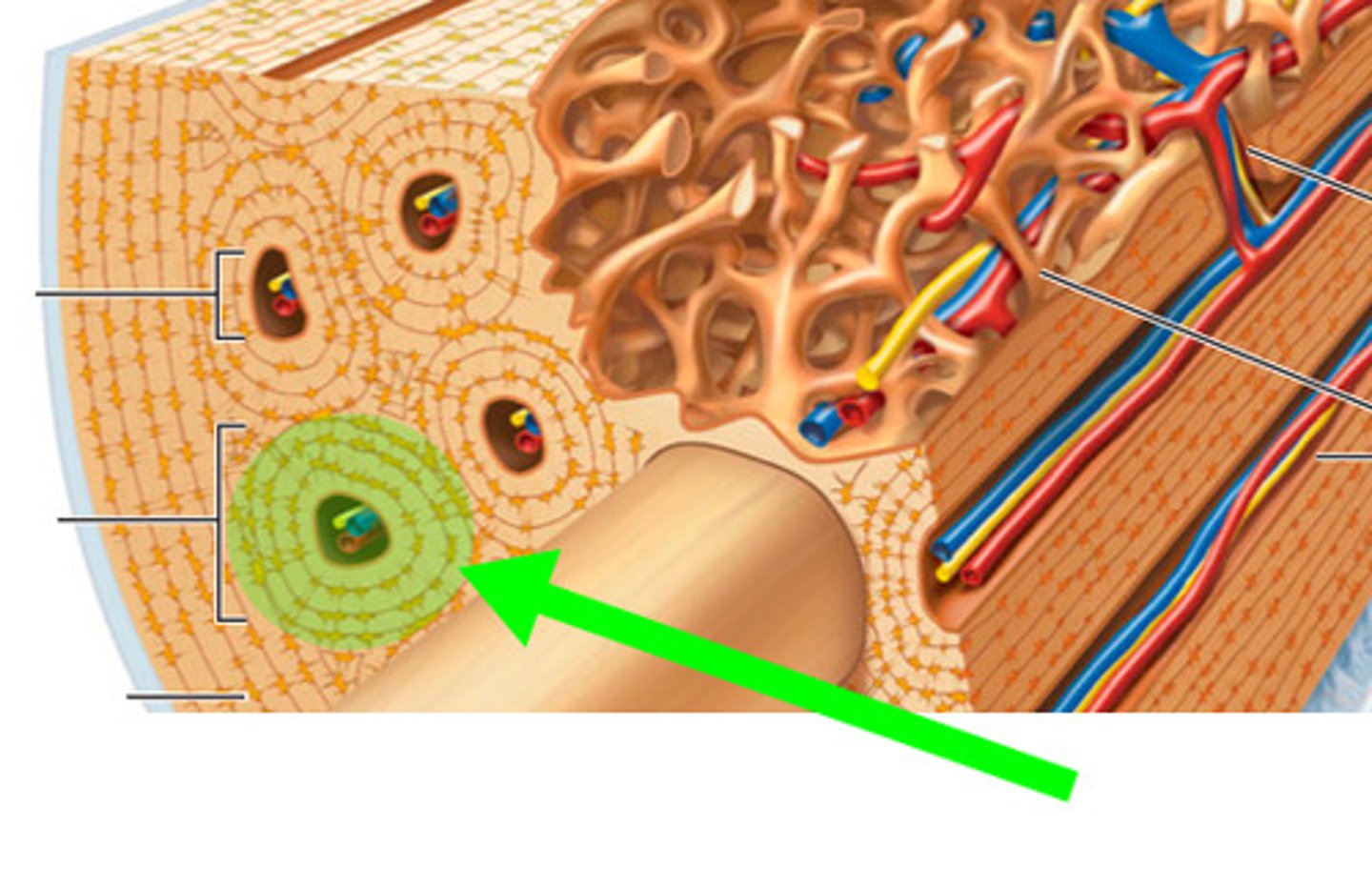
what is this called in compact bone?
osteon
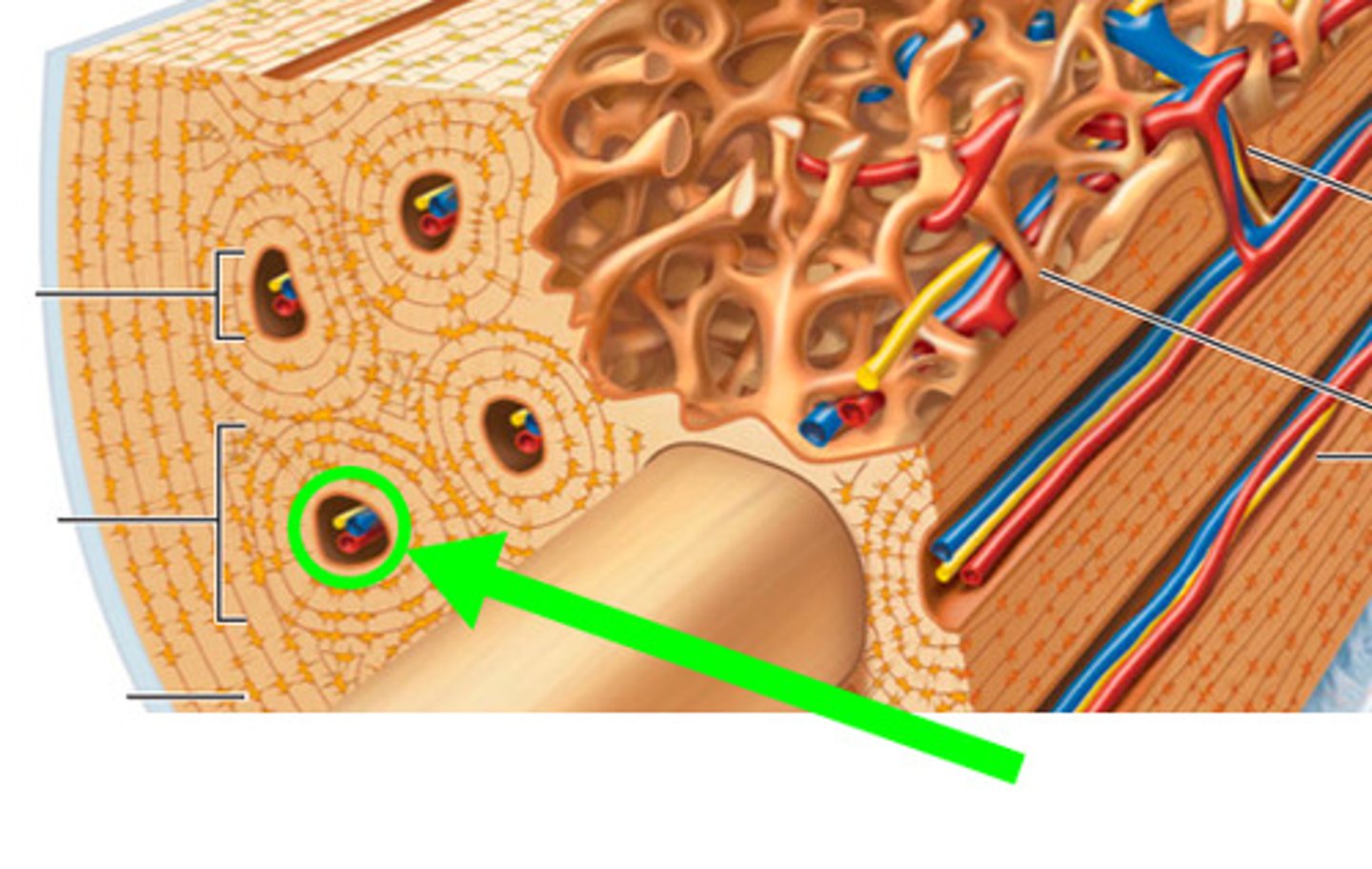
what is this called in compact bone?
osteonic canal
what is this called in compact bone?
osteocyte
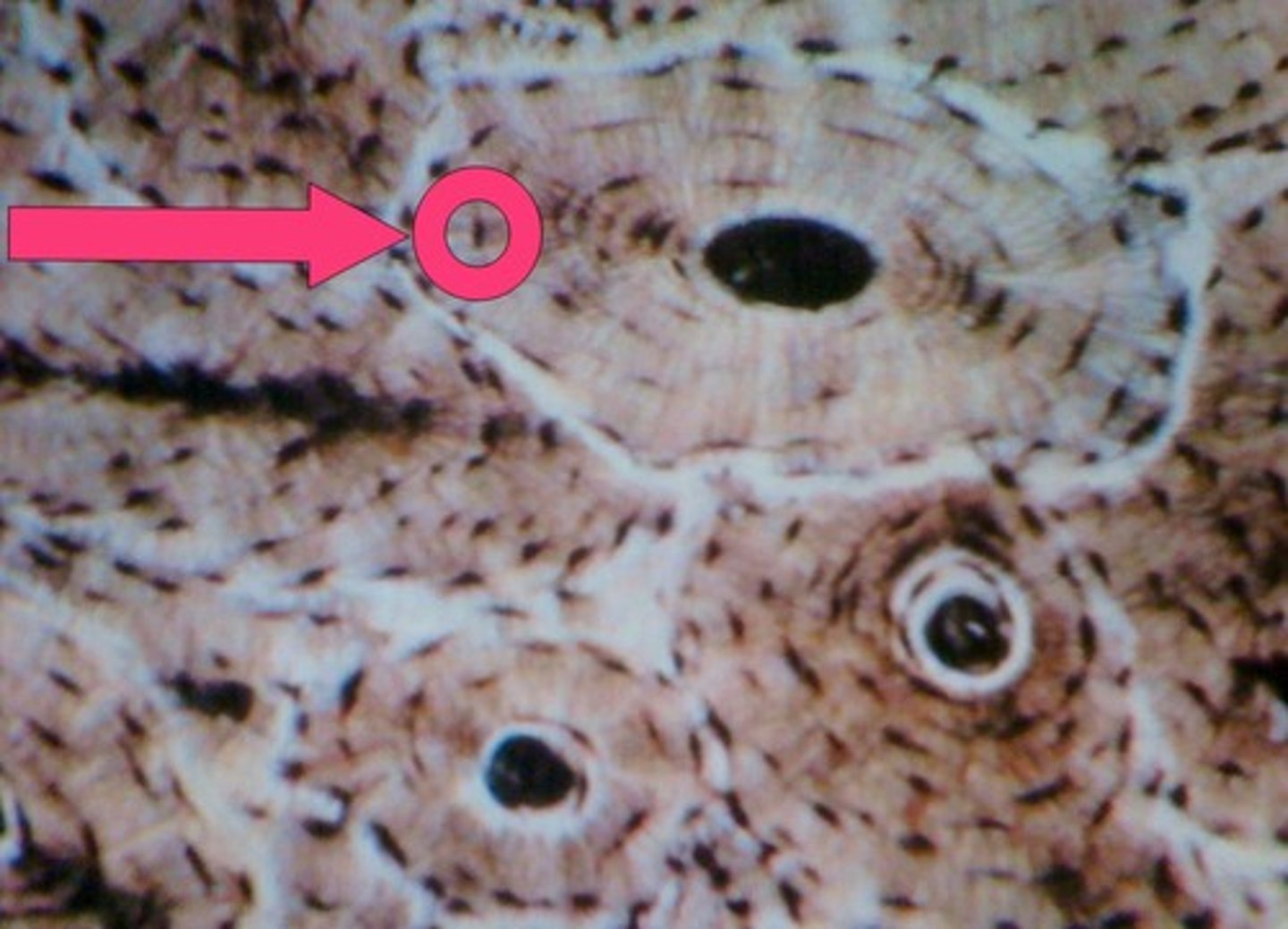
what is this called in compact bone?
lacunae
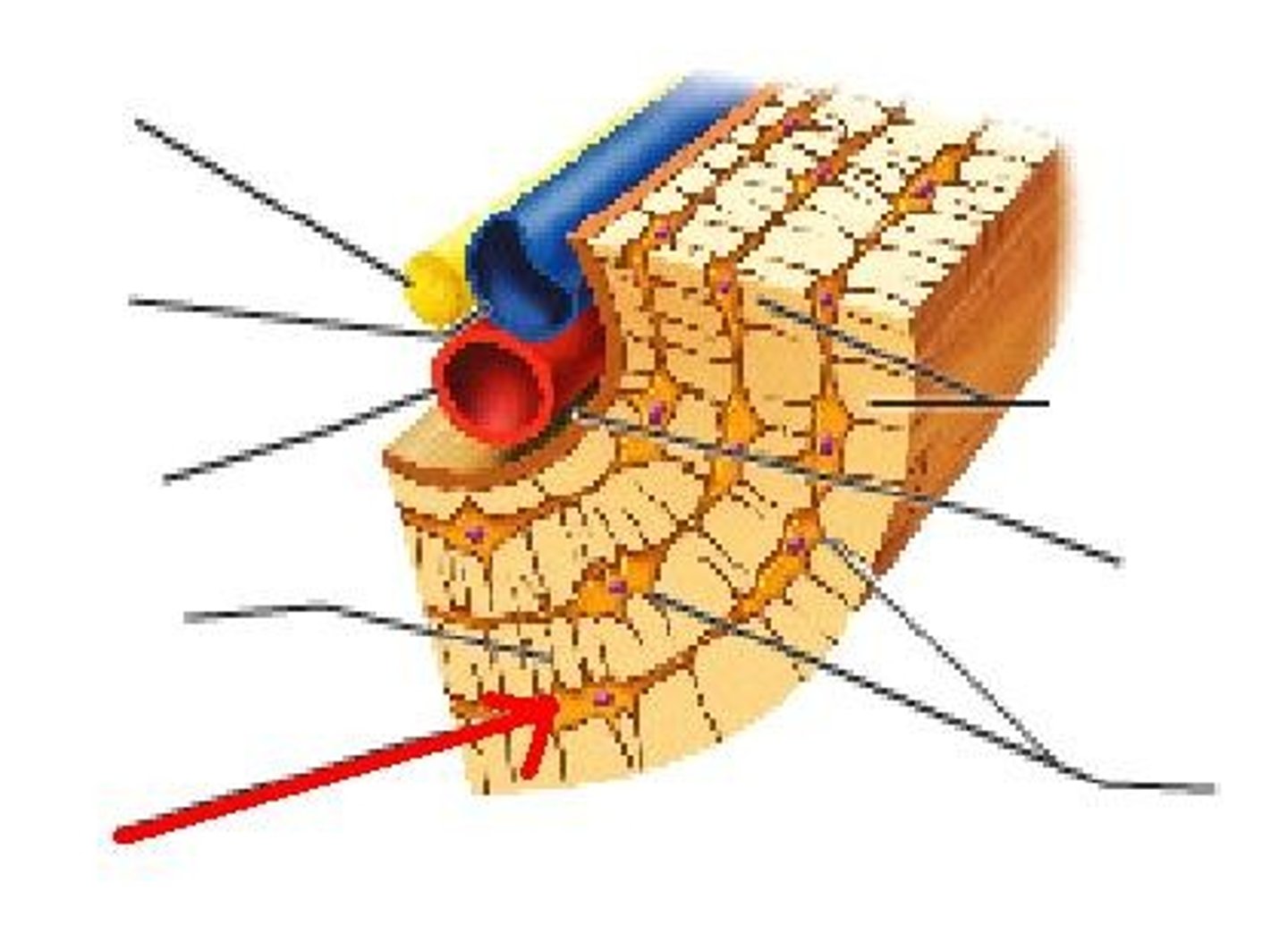
what is this called in compact bone?
lamella
How many bones are in the body?
206