Types of Inorganic Colloids in Soil
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the two types of inorganic colloids?
Soil colloids and crystalline silicate minerals.
What are the two main categories of soil colloids?
Organic colloids (humus) and inorganic colloids (clay).
What are non-crystalline silicate minerals?
Soils formed from volcanic ash, consisting of very fine particles (0.001µ - 1µ) and are highly chemically reactive.
What is allophane?
A non-crystalline hydrous aluminosilicate commonly found in tropical soils.
What is the size range of particles in non-crystalline silicate minerals?
0.001µ to 1µ (micron).
What are some examples of non-crystalline minerals?
Allophane, Imogolite, Fe and Al oxides.
What is the significance of soil colloids?
They are centers of chemical activities in soil.
What defines crystalline silicate minerals?
They are stable and persistent silicates that occur as weathering products in the clay fraction of soil.
What is the size limit for particles in crystalline silicate minerals?
0.001µ to 2.0µ.
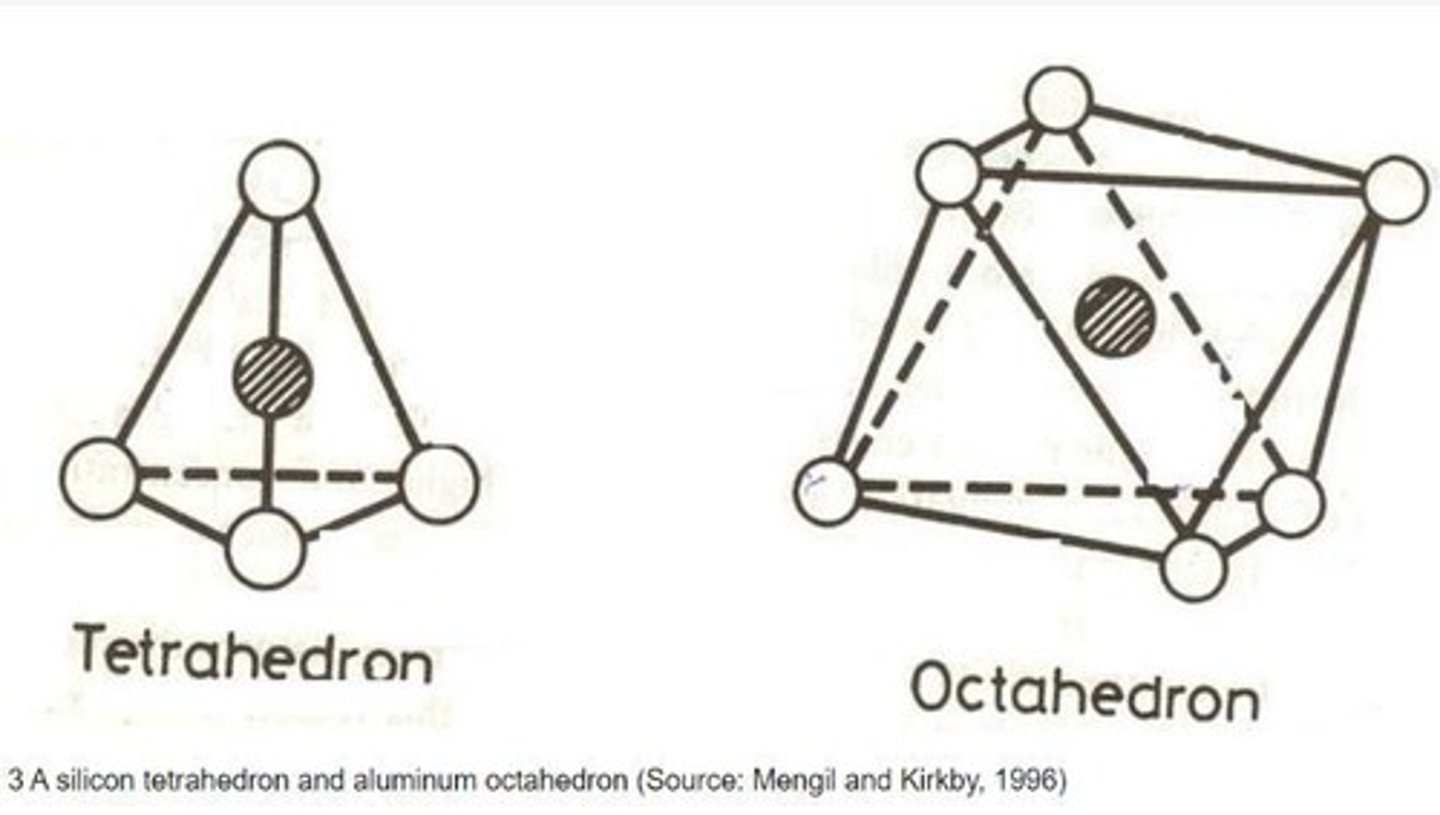
What are the basic building blocks of silicate minerals?
Silica-tetrahedra and alumina-octahedra.
What is the structure of kaolinite?
One layer of aluminum octahedral sheet sandwiched between two silica tetrahedral sheets.
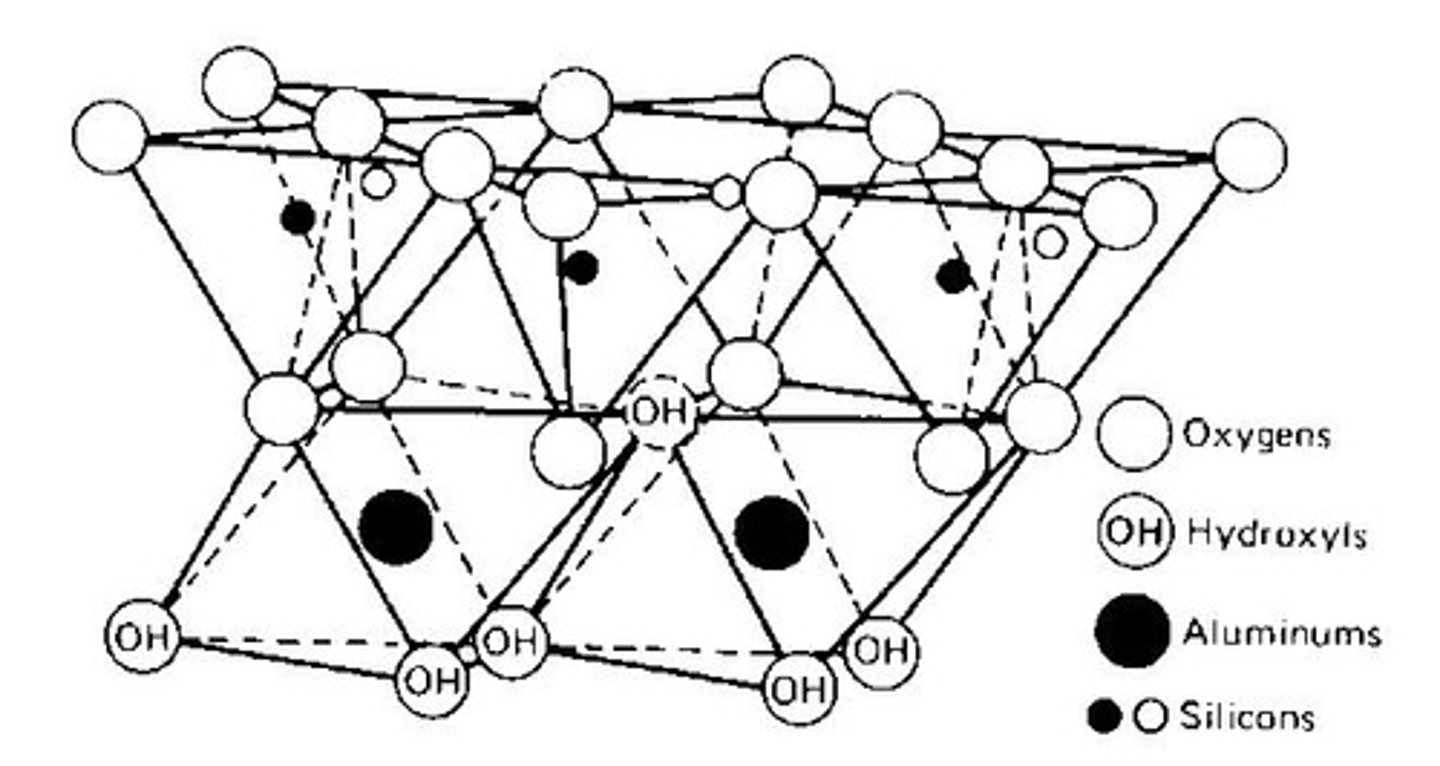
What is the importance of kaolinite?
It is important in the production of ceramics and porcelain.
What characterizes 2:1 non-expanding minerals like illite?
Layers held loosely by weak bonds, with potassium ions acting as binding agents.
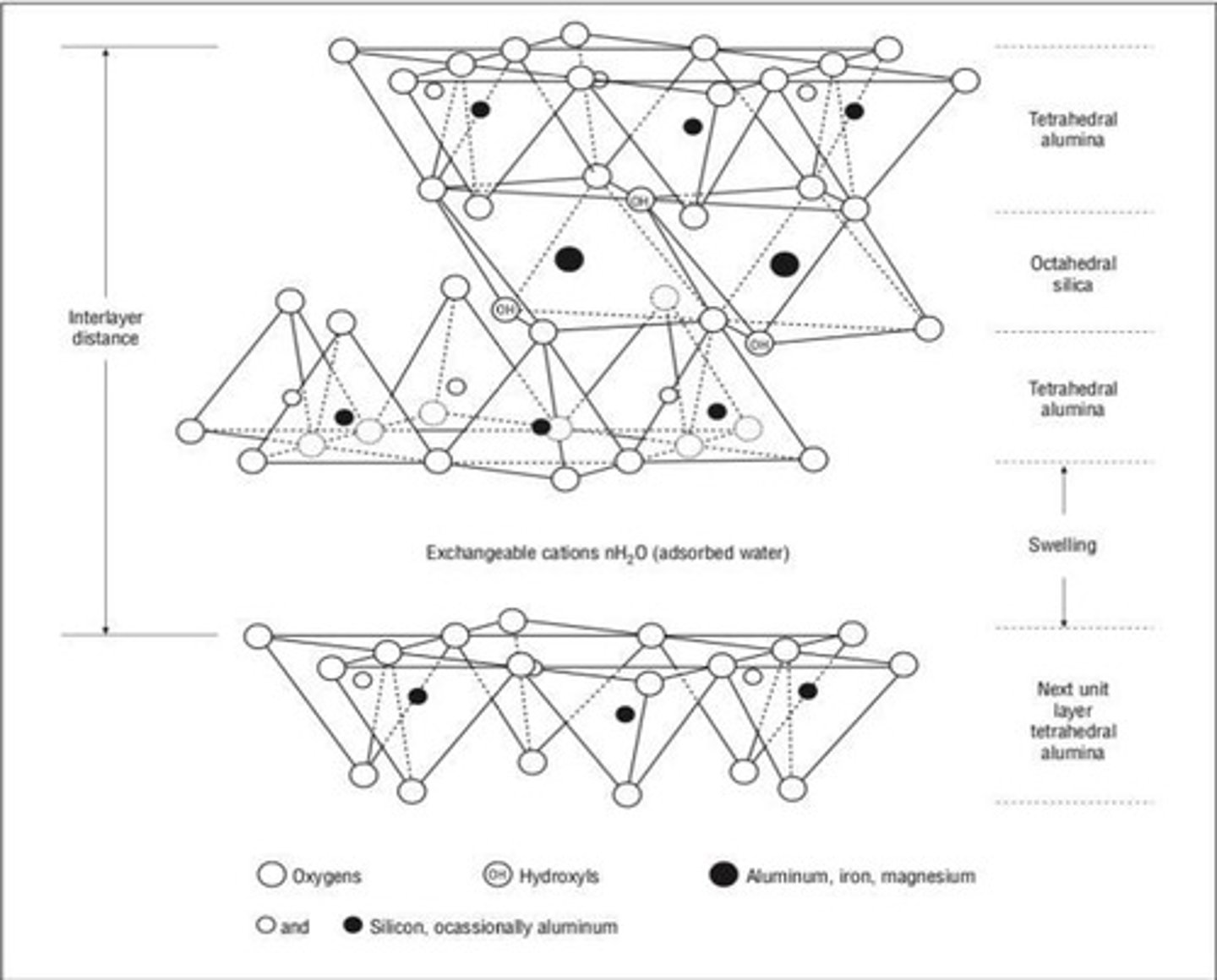
What happens to illite if potassium ions are removed?
It can turn into vermiculite.
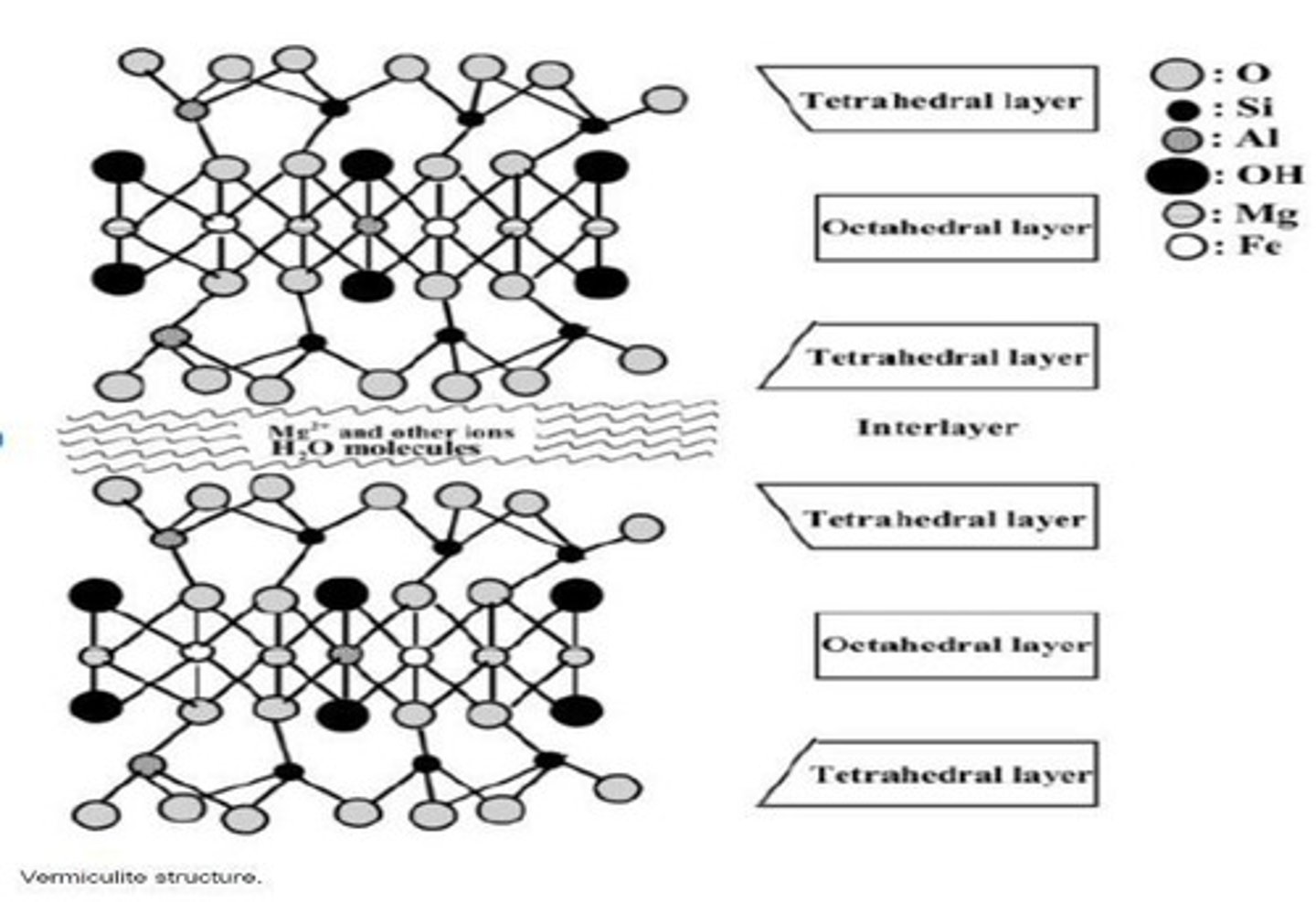
What is a characteristic of montmorillonite?
It can hold more water than its volume and has negative charges due to isomorphous substitution.
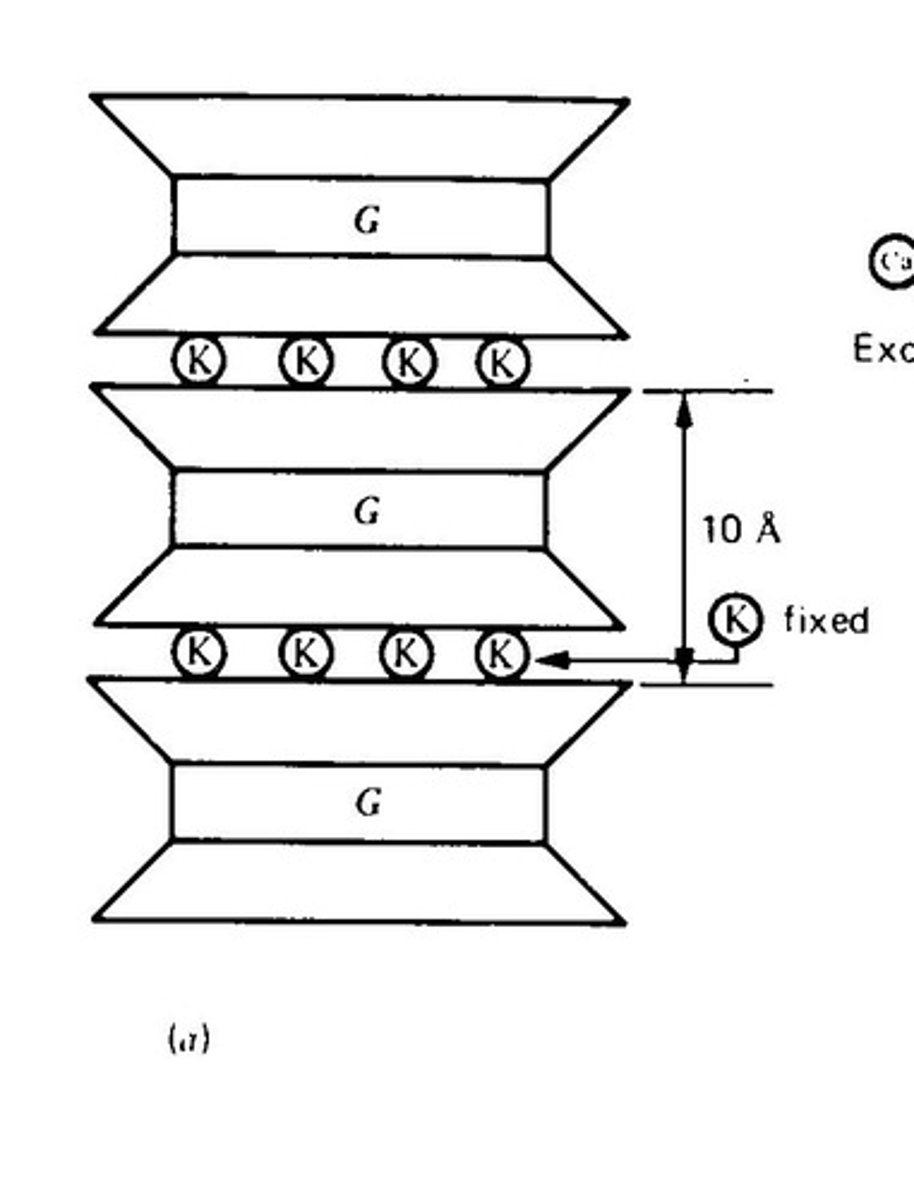
What defines the 2:1 expanding minerals?
They expand when wet due to exchangeable cations and water molecules between layers.
What is the CEC range for kaolinite?
6-15 meq/100 g of soil.
What is the structure of the tetrahedral sheet in silicate minerals?
It forms a four-sided polygon.
What is the structure of the octahedral sheet in silicate minerals?
It forms an eight-sided polygon with six oxygen atoms.
What is the characteristic of hydrated aluminum silicate clays like halloysite?
They have low colloidal properties and are highly impermeable.
What is the significance of the specific surface area in crystalline silicate minerals?
It affects the physical and chemical properties of the minerals.
What is the role of isomorphous substitution in montmorillonite?
It derives negative charges that affect its water retention properties.