EDLit 189 - Role of Schema, Linguistic Competence and Metacognition in Content Literacy
1/3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Schema
Also called prior knowledge, is the building block of knowledge.
Readers connect their prior knowledge with what they are reading to make meaningful interpretations of the text
Linguistic Competence
Knowledge of the form and features of language
contributes to excellent comprehension.
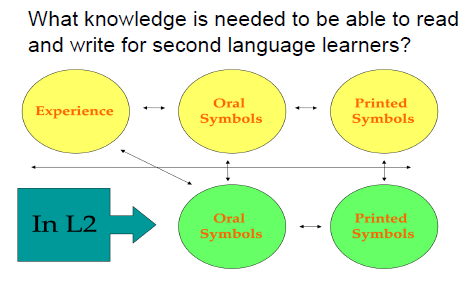
Experience <—> Oral Symbols <—> Printed Symbols
In L2 = Oral Symbols <—> Printed Symbols
Metacognition
knowing how you get to know what you know
know what to do when
they experience
can also read and learn on their own
can monitor their progress in reading.
How to develop Metacognitive Skills in content learning?
Through teacher questioning instruction to reflect on the process of thinking
How did you figure out the meaning of ___?
Using think-aloud strategies
learn to monitor their thinking as they read and improves their comprehension.
re-read, read ahead, and/or look for clues to make sense of what they read.
helps students internalize effective reading strategies and develop metacognitive skills.
“I’m thinking…” “I wonder…” “This makes me think of…”
Ano ang alam ko sa paksang ito? Naunawaan ko ba ang binasa ko? Manilanaw ba ang detalye ng binasa ko? Ano-ano ang mga mahalagang malaman tungkol sa binasa ko?