Cell Division Mechanisms in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Binary Fission
Asexual reproduction in prokaryotes via division.
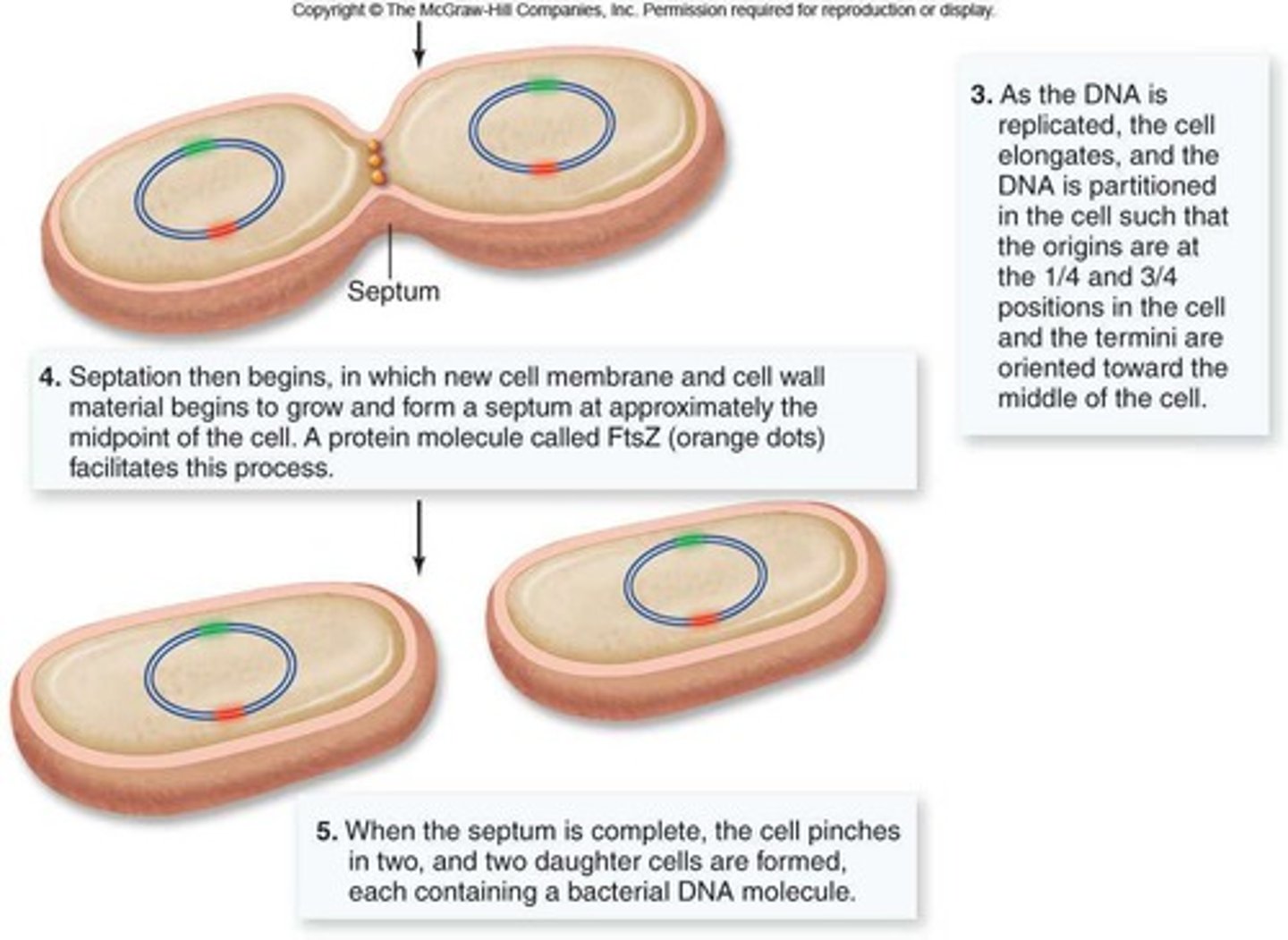
FtsZ Protein
Protein forming a ring for cell division in prokaryotes.
Septum
Structure that divides a cell during binary fission.
Kinetochore Microtubule
Attaches chromosomes to spindle poles during mitosis.
Centrioles
Organelles that help organize spindle fibers in cell division.
Eukaryotic Chromosomes
Linear DNA structures organized with proteins.
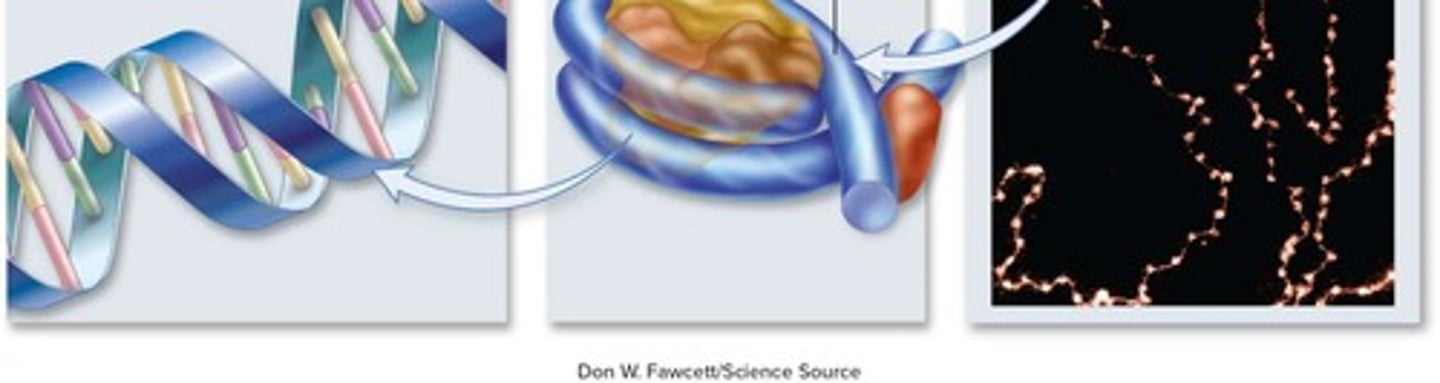
Nucleosome
DNA wrapped around histone proteins.
Karyotype
Arrangement of chromosomes in an organism.
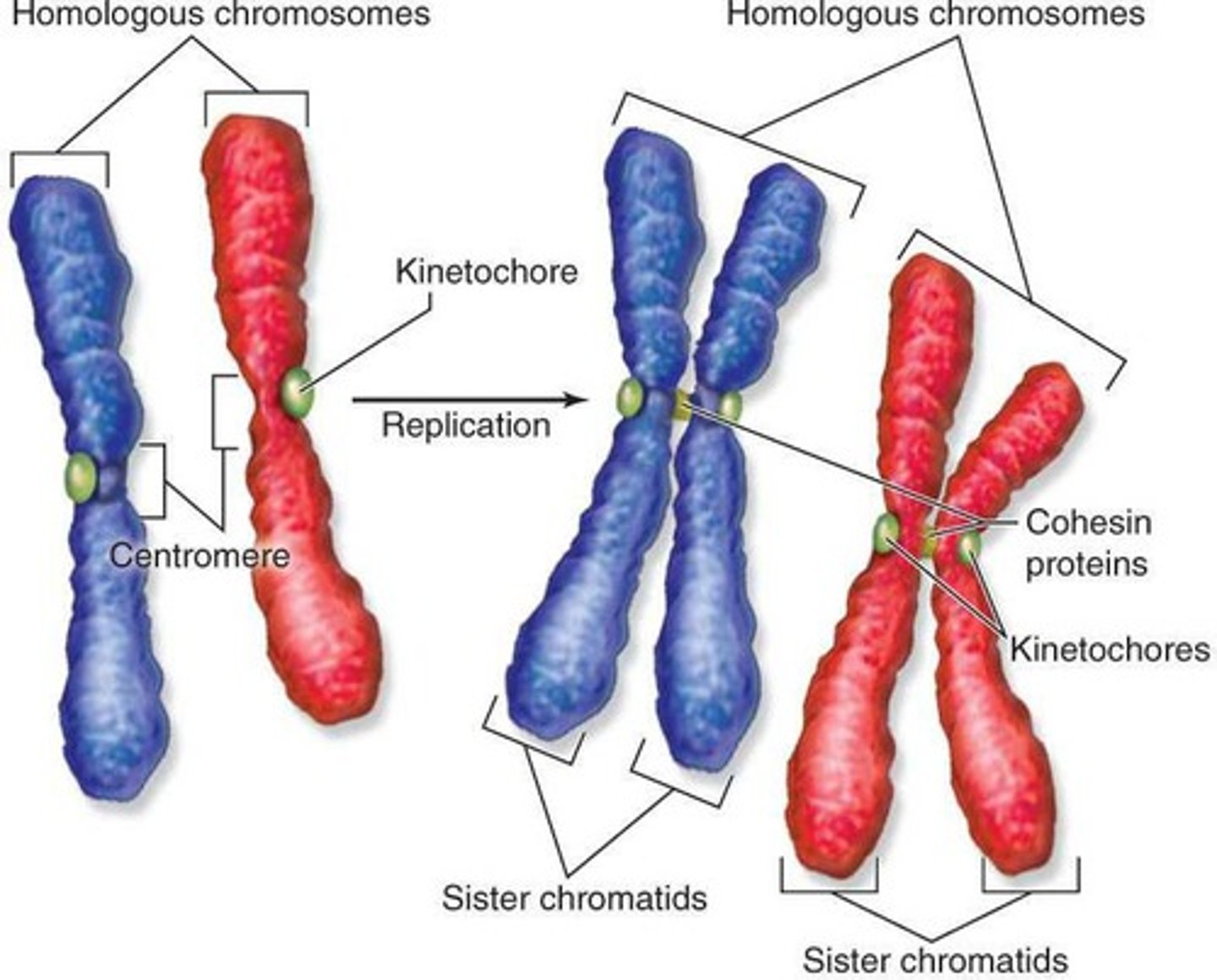
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome connected at centromere.
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm following mitosis.
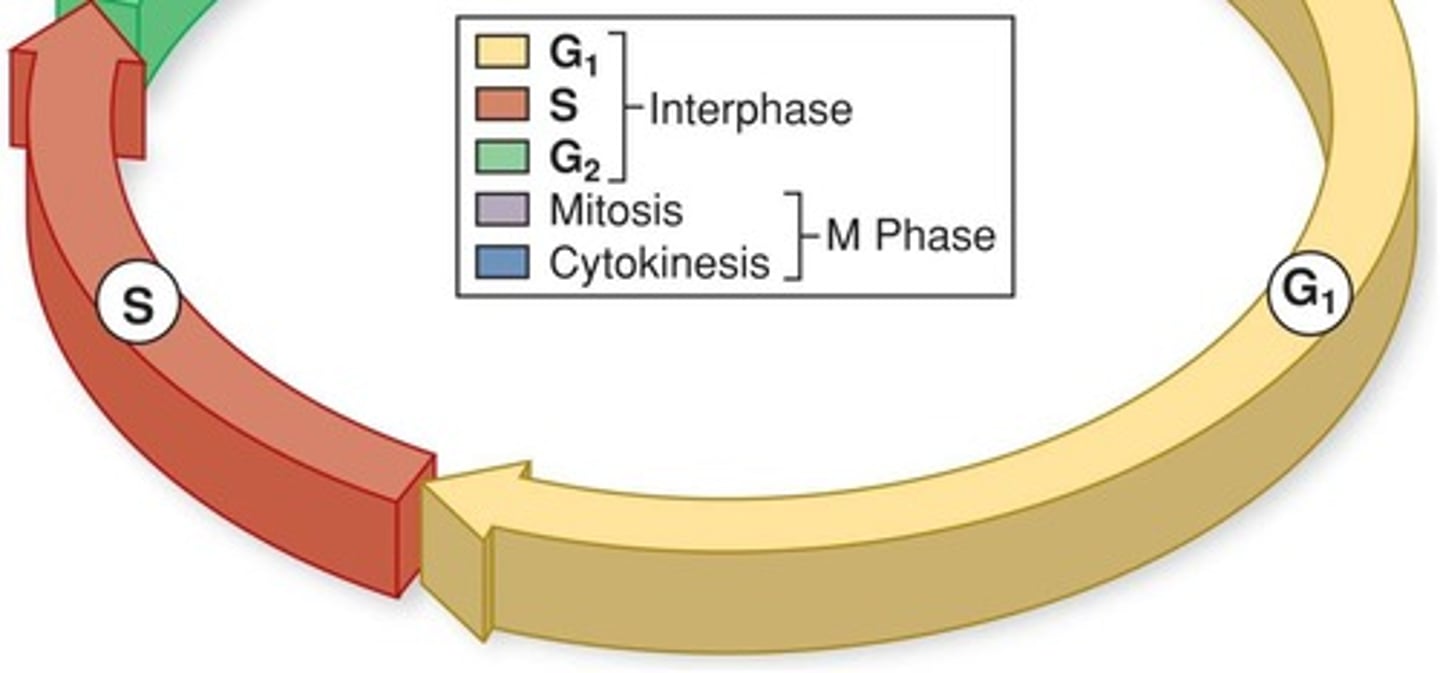
G1 Phase
First growth phase in the eukaryotic cell cycle.
S Phase
Phase where DNA is replicated.
G2 Phase
Second growth phase; organelles replicate.
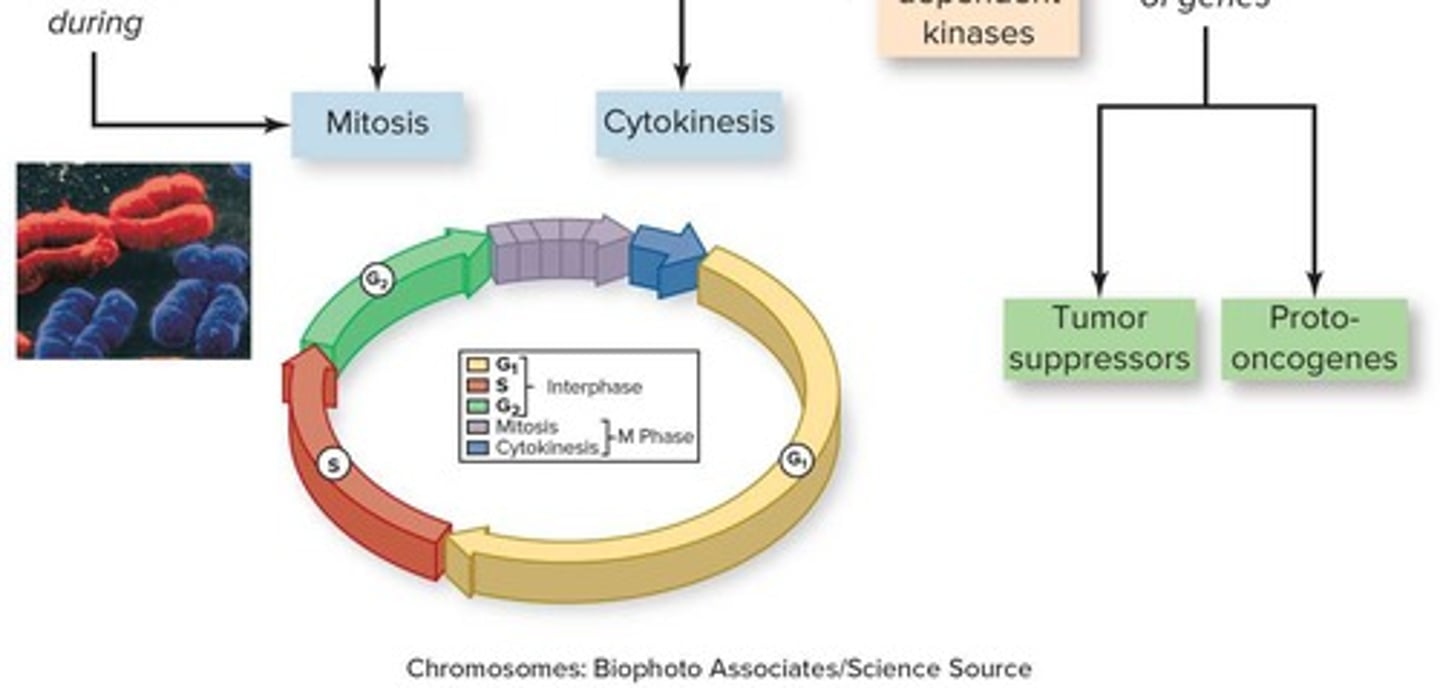
Mitosis
Nuclear division process with five phases.
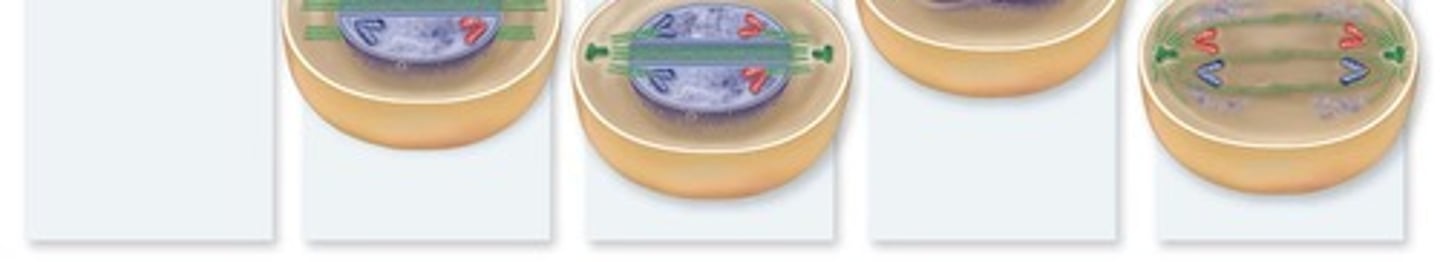
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and spindle apparatus assembles.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align on the metaphase plate.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles.
Telophase
Nuclear envelopes reform around separated chromosomes.
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Regulatory points that control cell cycle progression.
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (Cdks)
Enzymes that regulate the cell cycle with cyclins.
Growth Factors
External signals that stimulate cell division.
Proto-Oncogenes
Normal genes that promote cell growth; can mutate.
Tumor-Suppressor Genes
Genes that prevent uncontrolled cell division.
p53
Key tumor-suppressor gene monitoring DNA integrity.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death to eliminate damaged cells.
Cancer
Uncontrolled cell division due to genetic mutations.
Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
Series of phases leading to cell division.
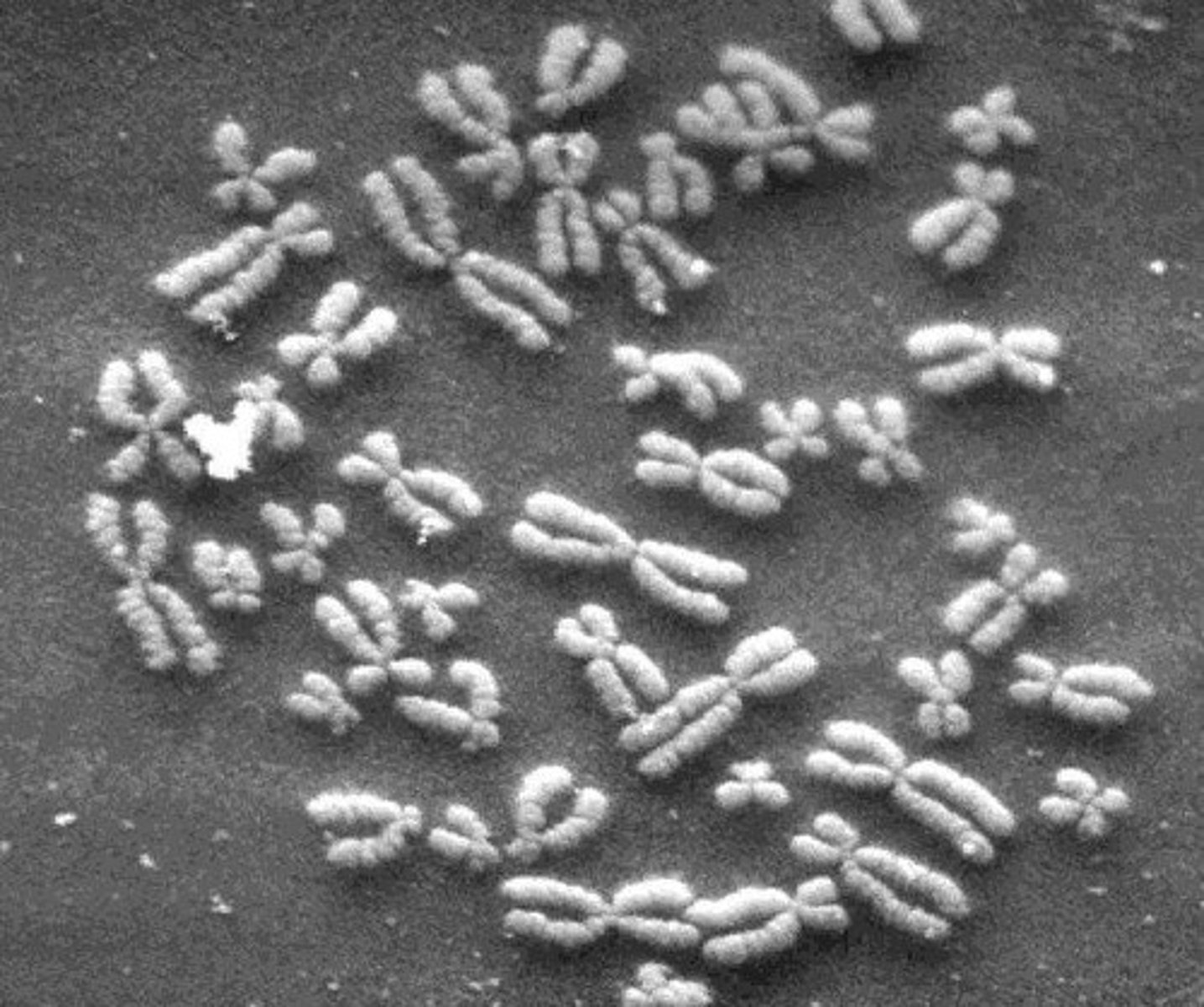
Human Chromosome Count
Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs).
Cleavage Furrow
Indentation in animal cells during cytokinesis.
Cell Plate
Structure that forms during plant cell cytokinesis.