Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
what is cellular respiration
when chemical energy in organic molecules is harvested to generate ATP
energy flows
linearly
catabolic pathways break down ____ to release ____
glucose, oxygen
what is fermentation
partial degradation of organic compounds, without oxygen
what is aerobic respiration
complete breakdown of organic compounds with oxygen
what is anaerobic respiration
full breakdown of organic molecules without oxygen
what are examples of organic compounds
carbs, fats, proteins
what are redox reactions
the transfer of electrons to release the energy stored in organic molecules
where do electrons move
from a less electronegative atom to a more electronegative atom
what does the released energy from redox reactions create?
ATP
a reactant that is oxidized
is the reducing agent, and loses electrons
a reactant that is reduced
is the oxidizing agent, and gains electrons
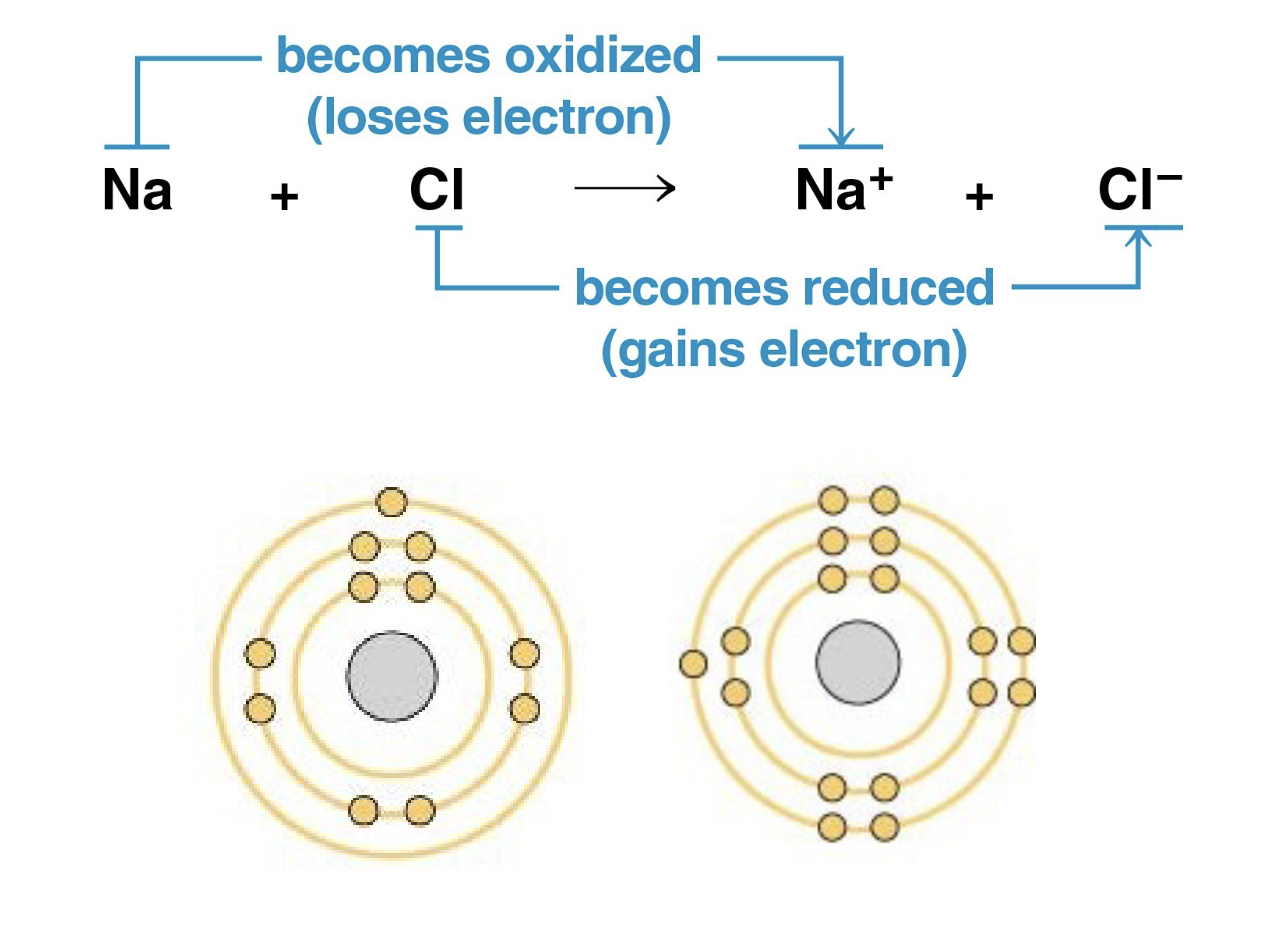
what kind of reaction is happening here
redox
some redox reactions don’t transfer electrons, but instead…
change the electron sharing, from nonpolar to polar
as polar covalent bonds are created, electrons fall towards
the more electronegative atom
holding electrons away from an electronegative atom
is an energy consuming process
as electrons move towards electronegative atoms
energy is released
what is oxidized during cellular respiration
the fuel
what is reduced during cellular respiration
oxygen
the oxidation of organic molecules results in
a lot of energy
electrons lose
potential energy
what kind of molecule would result in a great amount of energy change following oxidation
a hydrocarbon
in cellular respiration, where are electrons transferred
to coenzyme NAD+
what is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
NAD+
NAD+ accepts
2 electrons and 1 H+
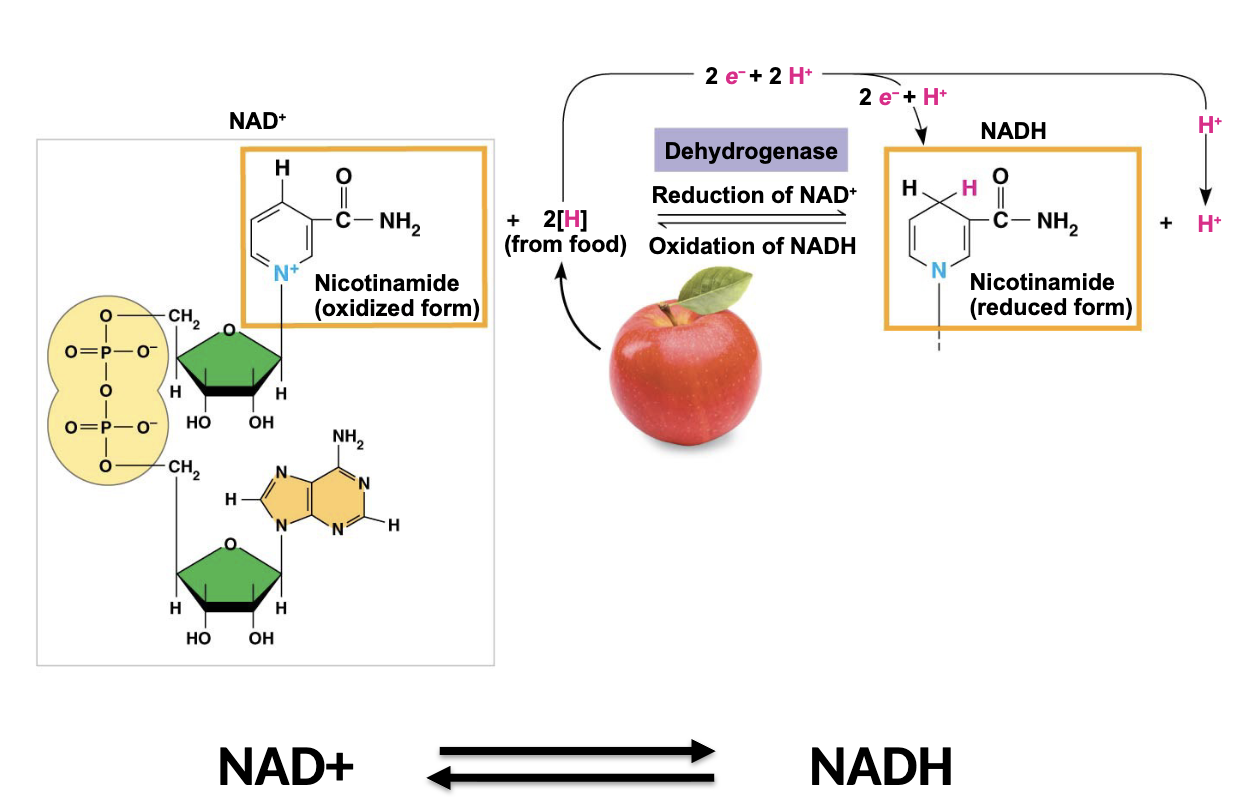
what happened to NAD+ here
it was reduced
NADH molecules represent
stored energy
NAD+ can go between
oxidized and reduced forms
NADH passes electrons to
an electron transport chain
electrons are transferred to atoms of increasing
electronegativity
what is the release of energy from electrons used to regenerate?
ATP
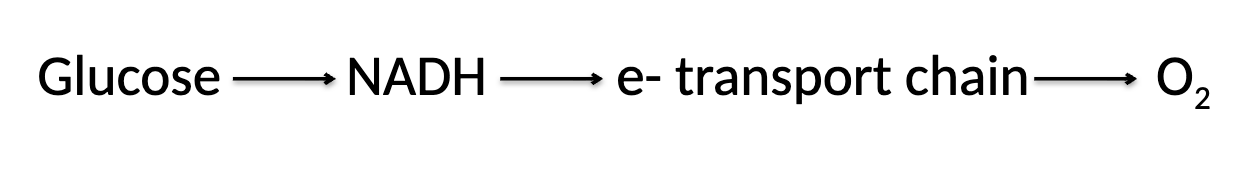
what is this illustrating
the electron path
what are the three stages of cellular respiration
glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
what is glycolysis
the beginning of the breakdown of glucose
what is the citric acid cycle doing
completing the breakdown of glucose
what is oxidative phosphorylation
using the energy harvested in the first two steps to synthesize ATP
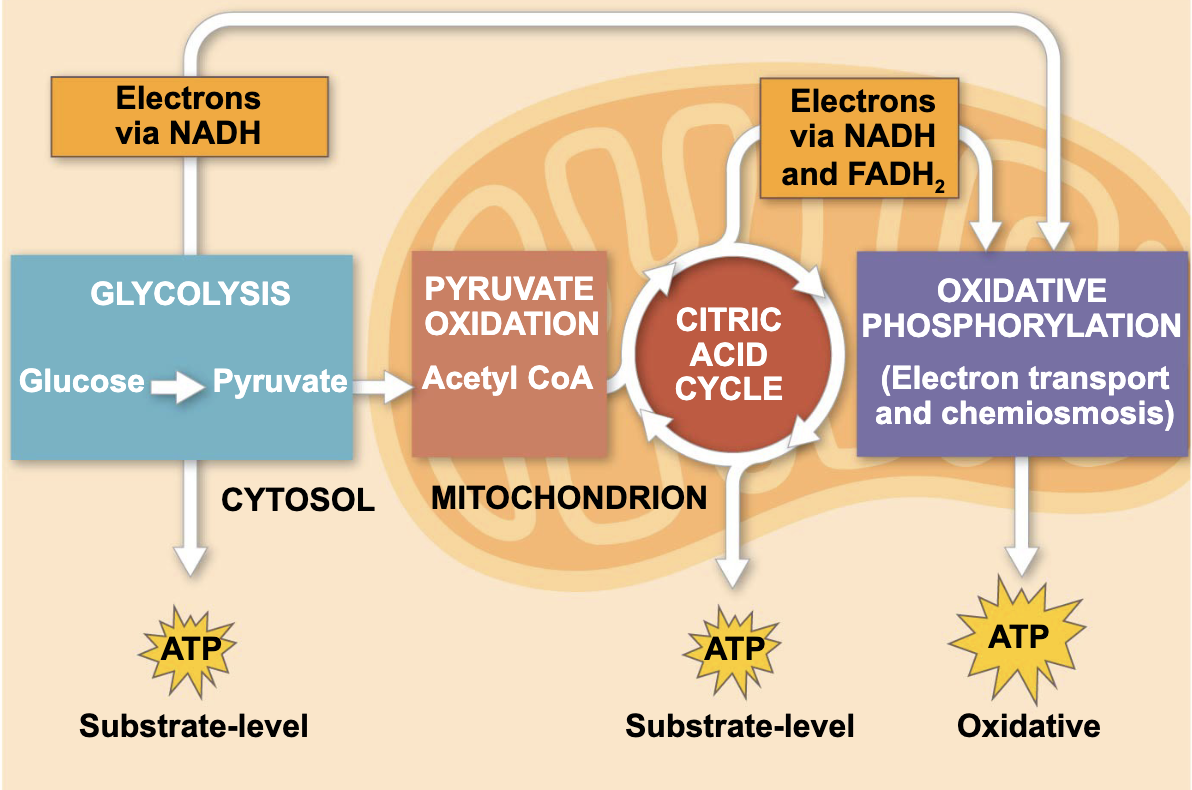
what is this
the steps for cellular respiration
where does glycolysis occur
in cytosol
where do pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation occur?
mitochondria
glycolysis breaks glucose down into
2 molecules of pyruvate (C3H4O3)
what are the two phases of glycolysis
energy investment phase, energy payoff phase
glycolysis will occur with or without..
oxygen
to break down glucose, how many ATP are used
2
what is the equation for glycolysis
glucose → 2 C3H4O3 + 2H2O
how many ATP are generated in pyruvate oxidation
4
how many net ATP in pyruvate oxidation
2
what is the NAD+ equation for pyruvate oxidation
2NAD+ + 4 electrons + 4H+ —> 2 NADH + 2 H+
how is ATP made during glycolysis
substrate level phosphorylation
what happens during substrate level phosphorylation
a substrate attaches the phosphate from ADP to form another ATP
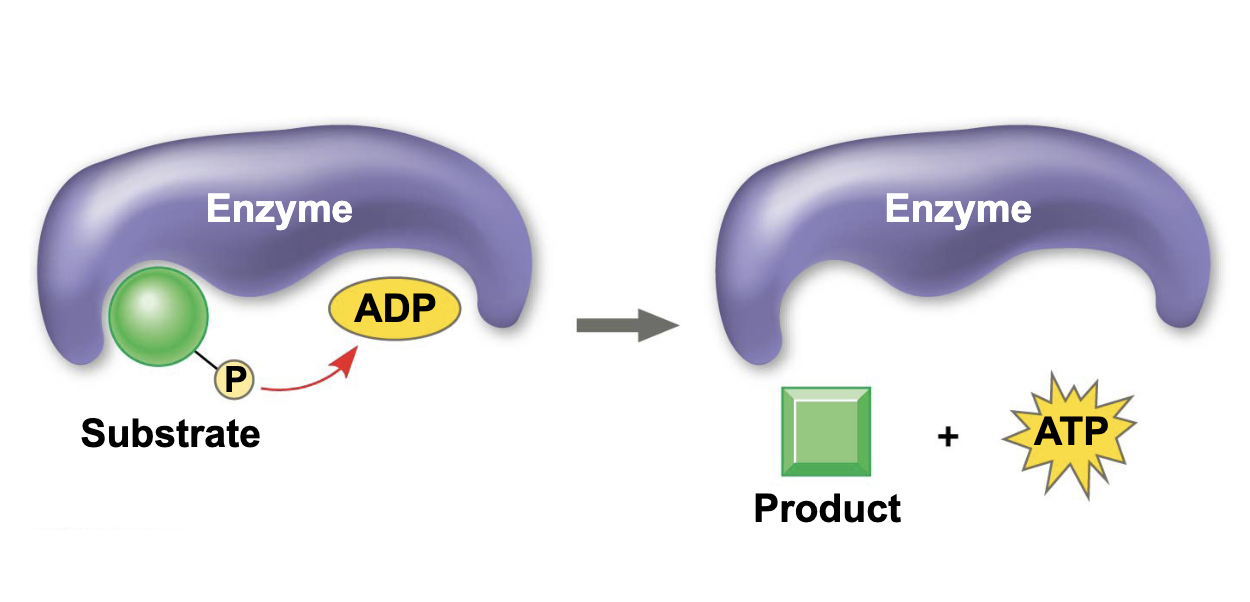
what is this
substrate level phosphorylation
what happens to pyruvate after glycolysis
it is converted to acetyl conezyme A by being oxidized
what is the citric acid cycle
it completes the break down of pyruvate to CO2
the citric acid cycle generates
1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2
how many steps in the citric acid cycle
8
what happens in step 1 of the citric acid cycle
the acetyl group of acetyl CoA joins the cycle by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate
what happens in steps 2-8 of the citric acid cycle
decomposing citrate back to oxaloacetate
NADH and FADH2 do what in the citric acid cycle
carry electrons to the next step
energy is in the NADH and FADH2 because of
electrons
how do the electrons get added back to NADH and FADH2
oxidative phosphorylation
what is the final step of cellular respiration
oxidative phosphorylation
substrate level phosphorylation produces how many ATP
2 from glycolysis and 2 from citric acid cycle
where is the remainder of ATP generated
oxidative phosphorylation (24)
majority of the energy from the oxidation of glucose is stored in
the reduced coenzymes
how many NADH in glycolysis
2
how many NADH in pyruvate oxidation
2
how many NADH in the citric acid cycle
6
how many FADH2 in the citric acid cycle
2
oxidative phosphorylation accounts for what percent of ATP
90%
oxidative phosphorylation is powered by
redox reactions
what are the two major processes of oxidative phosphorylation
electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
what is the electron transport chain
Collection of molecules embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion
the increased surface area of the chain means
there are 1000s of copies of it
most components of the ETC are
proteins in numbered complexes
what are the non-proteinous groups of the ETC
prosthetic groups necessary for catalysis
electrons are passed down the ETC to…
O2
electron carriers oscillate between
reduced and oxidized states
why does NADH enter the chain earlier than FADH2
it is associated with greater free energy
water is formed when reduced oxygen atoms…
pick up hydrogen ions from the aqueous environment
the ETC generates
no ATP directly, and rather, releases free energy
what is chemiosmosis
proton diffusion from high to low concentration (exergonic) coupled with the formation of ATP (endergonic)
electron transfer in the ETC causes proteins to pump
H+ across the inner membrane
H+ is pumped from
the matrix to the intermembrane space (low to high concentration)
H+s diffuse across the membrane, passing through
ATP synthase
what is ATP synthase
an enzyme that drives ATP production
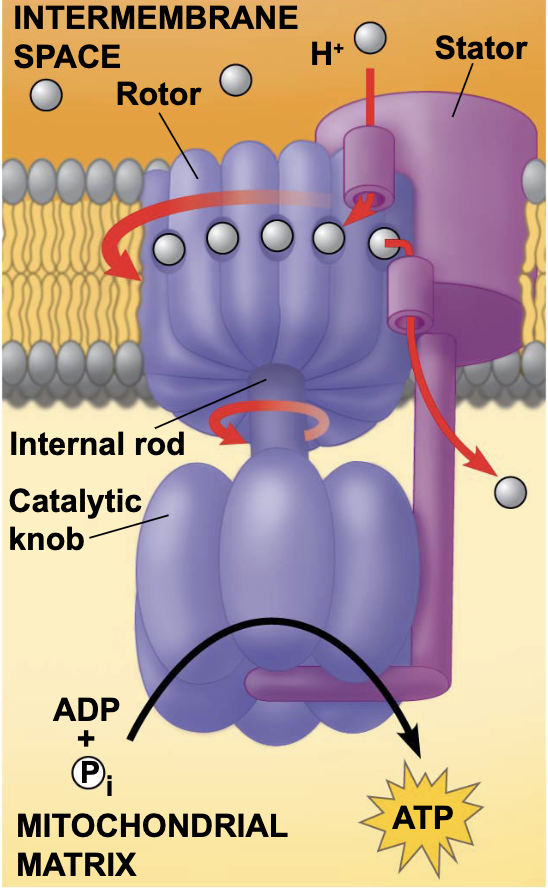
what is this?
ATP synthase
how does energy flow in cellular respiration
glucose —> NADH —> ETC —> proton motive force —> ATP
why is the number of ATP not known exactly?
several reasons, including 1 NADH = 2.5 ATP, phosphorylation and redox are not directly coupled
34% of energy is transferred to ATP, where does the other amount go?
lost to heat
anaerobic respiration uses the ETC, but uses which electronegative acceptor?
SO4 2-
fermentation produces ATP via
substrate level phosphorylation
what are the two common types of fermentation
alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation
pyruvate is converted to ethanol in
alcohol fermentation
what is the first step of alcohol fermentation
CO2 released to create acetaldehyde
what is the second step of alcohol fermentation
Redox reaction reduces acetaldehyde to
ethanol, and oxidizes NADH
in lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced directly to
lactate
human muscles use lactic acid when
O2 is scarce
lactic acid fermentation by fungi and bacteria is used to make
cheese and yogurt
fermentation and respiration use
glycolysis
fermentation and respiration have
different mechanisms for oxidizing NADH and produce different amounts of ATP
what is fermentation’s mechanism for oxidizing NADH
an organic molecule acts as a final electron acceptor