Color Vision Anomalies
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the rate of people in the population affected by color vision anomalies?
nearly 1/20 people (5% of the general population)
Why does CV hereditary anomalies mainly affect males?
they only have 1 X chromosome and it is sex linked
about 8% of males are affected (1 in 12)
There are two classifications of color anomalies, what are they?
inherited (missing or anomalous photopigment)
acquired (loss of cones due to disease, neurological, ocular changes (i.e. cataracts)
What are some characteristics associated with inherited (genetic) CV deficiencies?
common
non-progressive
bi-ocular and symmetric
males mainly
99% red green deficiencies (L or M cone anomalies)
What are some characteristics associated with acquired CV deficiencies?
rare
occurs later in life
associated with ocular disease
acute onset, progressive, variable
not gender specific (no male or female prediction)
monocular or bi-ocular but asymetric
blue-yellow deficiencies (s-cone anomalies) more dominant than red-green
What are the two classes of color anomalies?
Missing a photopigment
Anomalous cone photopigment
What is the most severe kind of color vision anomaly in which the L, M or S-cone photopigment is completely missing?
a -nopia (i.e. protanopia - erythrolabe completely absent)
What is it when all 3 cones are present but there is a genetic defect that affects the opsin/photopigment and causes an anomalous absorption spectrum?
-anomalous (i.e. protanomalous- erythrolabe is abnormal)
If the photopigment is gone, does the pt still have the same number of cones?
yes, there is still the same number of cones with missing photopigment
What is a dichoromat?
patient with only two cone photopigments, they are missing a photopigment
In a dichromat with photopigment missing, how does the retinal cone density change?
the retinal cone density remains the same as the cone photopigment is replaced by OPSIN
What is a protonopia?
erythrolabe replaces with cholorlabe (L—>M cone)
What is a deuteranopia?
chlorolabe replaced (missing chlorolabe) with erythrolabe (M—> L cone)
shift towards longer wavelengths
What is a trianopia?
cyanolabe replaced with either erythrolabe or chorolabe
What is a -nopia?
"nope” I don’t have it.
What is an anomalous trichromat?
someone with 3 cones but one is defective (NOT missing an entire photopigment)
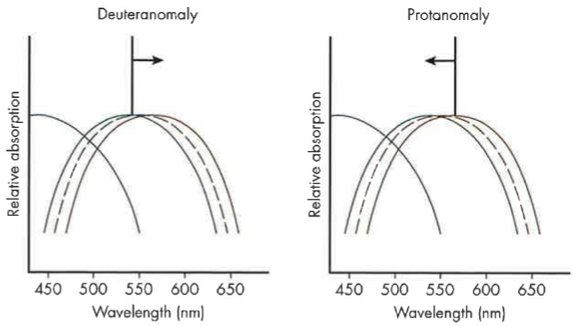
Protanomalous Trichromat
erythrolabe is abnormal and its absorption is shifted towards shorter (M-cone spectrum) wavelengths
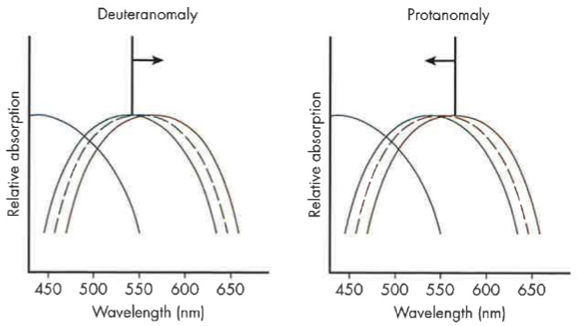
Deuteranomalous Trichromats
barely shift (v lamdba function is essentially the same)
chlorolabe is defective and shifted toward longer (L-cone spectrum) wavelengths
red-green defects (confusion)
What is a trianomaly?
cyanolabe is defective- this is very rare and the absorption spectrum change is unknown
What is an ‘nomalous?
photopigment present but defective
Vλ function in dichromats?
Vlambda curve normally peaks at 555 nm so you shift in a person with anomalous shorter wavelengths (based on missing photopigment -nopia)
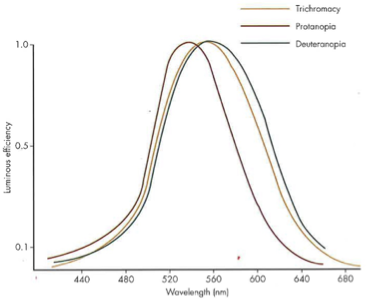
Vλ function in anomalous trichromats?
protanomalous trichromats show similar reduction in sensitivity to longer wavelengths but not as much as protanopes
deuteranomalous trichromates have a nearly normal Vlambda function (even more normal than a nope)
Who is more likely to get into driving accidents?
Protanopes/protanomalous have reduced sensitivity to long wavelengths (red) and red lights appear more dim/less saturated.
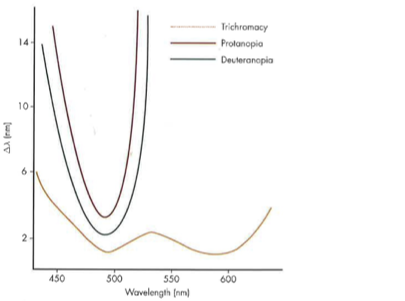
Color deficient wavelength discrimination in nopes
Only one minima (wavelength of best discrimination)
Significantly worse discrimination of all other wavelengths (compared to normal trichromats)
No ability to discriminate between wavelengths above ~545nm…why? because they are basically monochromats incapable of discriminating based on color alone
Who shoes a mildly abnormal wavelength discrimination function?
tritanopes because they are basically dichromats