1.2.5 - price elasticity of supply
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
define price elasticity of supply
measures the responsiveness of supply of a good to a change in price of the good
price elasticity of supply abbreviation
PES
PES formula
percentage change in supply/percentage change in price
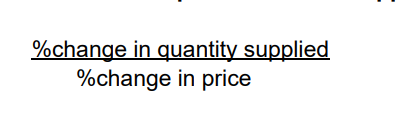
PES relationship
positive (upwards sloping)
so the number will always be positive
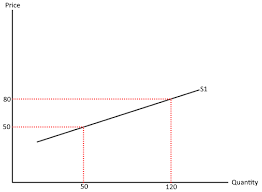
elastic supply
cuts the price axis (PES > 1)
means that firms can increase supply quickly at little cost
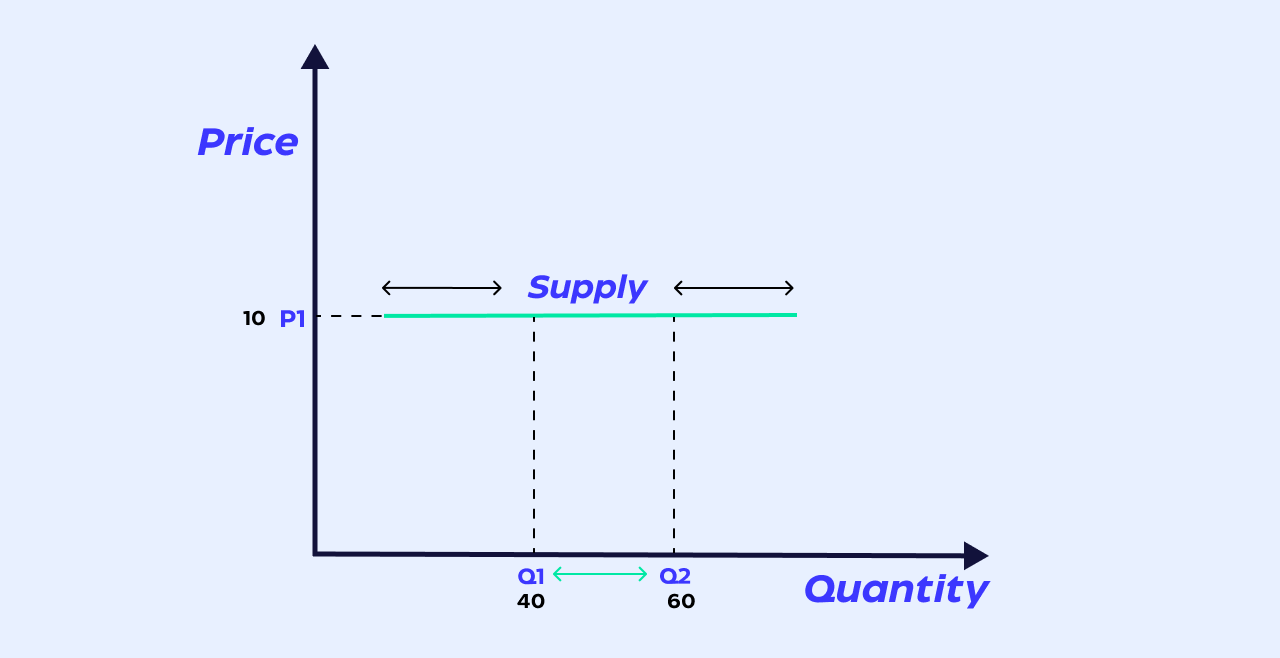
perfectly elastic
horizontal graph (PES = +∞)
supply any quantity at one price, change price and supply nothing (infinitely responsive to price)
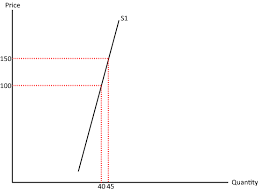
inelastic supply
cuts the quantity axis (PES < 1)
increase in supply will be expensive and take time
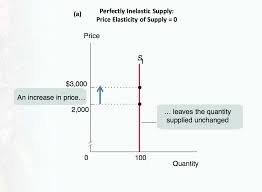
perfectly inelastic
vertical supply curve (PES = 0)
supply same quantity for every price (completely unresponsive to price)
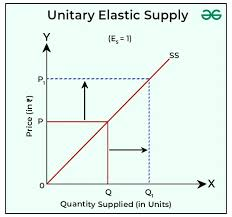
unitary elasticity
supply curve intersects the origin (where the axes meet)
PES = 1
factors affecting PES
less elastic
less time
operating at full capacity
low/perishable stocks
unsubstitutable FOPs
more elastic
more time
spare capacity
stockpiles available
very substitutable FOPs
define the ‘short-run’
the period of time in which at least one FOP is fixed (cannot be changed)
limits a firm’s ability to fully adjust its production capacity
in the short run, supply is more inelastic
define the ‘long-run’
the period of time in which all factors of production are variable
in the long run, supply is more elastic