L8 Cultural evolution
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What is culture
socially transmitted information
What is a culture
a group of people who share culturally transmitted customs etc
What 2 types of info do not count as culture
information acquired genetically or learned individually/asocially
Who challenged Victorian genetic determinism in cultural differences (think frank and a feather ?)?
Franz Boas
What is SSSM
the standard social science model
What is the Standard Social Science Model (SSSM), view on culture?
The view that culture is highly variable and largely unconstrained by biology.
4 examples of cultural universals
burial rituals, sex role differentiation, number system, dance
What is evoked culture - arise from what that is trigged by what?
Cultural practices arising from universal psychological mechanisms triggered by environmental conditions
What are the two components of evoked culture?
A universal underlying mechanism and environmental variation in activation.
What is transmitted culture, 3 processes involved?
Culture passed through imitation, teaching, and modelling — “normal” culture.
How does cultural evolution differ from genetic evolution (in terms of inheritance)?
Cultural evolution is Lamarckian (acquired traits can be transmitted/inherited), whereas genetic evolution is not.
Why are humans considered a cultural species, considering how we adapt in response to environmental changes?
Humans adapt to environments primarily through cultural rather than genetic change.
4 reasons cultural is adaptive
Quicker, cheaper, easier, and cumulative
Why are genes described as “blind” to within-generational change?
Genetic evolution occurs over many generations and cannot respond quickly.
Why is it easier to learn socially vs asocially, what is not required for the former
cheaper and easier, does not require trial and error
What is cumulative cultural evolution
each generation of people contributes to the population’s knowledge and technology, don’t have to start from scratch
What is unique to human cultural evolution
cumulative culture
Can cultural traits be maladaptive?
Yes
What 3 criteria must cultural evolution meet to be Darwinian?
Variability, selection, and heritability.
What 3 things (random) demonstrate variability in culture?
The vast number of languages, religions, and websites.
What is cultural selection and what is an example of this?
Some cultural traits spread more successfully than others, for example the greater spread of regular compared to irregular verbs
What parallels exist between genetic and cultural evolution, what Darwinian features do they feature?
Both involve variation, selection, and inheritance
Name a few ways the parallels between cultural and genetic evolution don’t work (consider sex, extinction and transmission)
sexual selection doesn’t occur in cultural evolution, things can be re-introduced/re-invented in cultural evolution, transmission is different
What does Wilson’s “genes hold culture on a leash” metaphor suggest?
Genetic constraints ultimately limit cultural variation.
How does Dennett’s “launching pad” metaphor contrast with Wilson’s view?
Genes enable wide cultural exploration rather than tightly constraining it.
What is a meme in cultural evolution
a hypothetical unit of cultural transmission
According to Dawkins, what 3 properties define a replicator (either biological or cultural)
fidelity, fecundity, longevity
What is fidelity
accurately copied
What is fecundity
makes many copies
What is longevity
persists over time
Why is defining a meme controversial?
Cultural traits are difficult to isolate and transmission is often imperfect
What is an example of a potentially maladaptive meme
religious beliefs
What is dual-inheritance (gene–culture coevolution) theory?
Human behaviour results from interacting genetic and cultural inheritance systems.
Why has behaviour changed rapidly while human biology has not?
Culture allows rapid adaptation without genetic change.
How do genes influence culture?
By enabling social learning capacities.
How does culture influence genes?
By altering selection pressures and gene frequencies.
What is niche construction?
species to modify their environments, altering selection pressures.
What is cultural niche construction?
Human cultural practices reshape environments and evolutionary pressures.
What is social learning vs asocial learning?
Behavioural change resulting from observing others vs learning from individual action
Name 4 biases in social learning
content biases, model-based biases, frequency-dependent biases, no bias/cultural drift
What are content biases in social learning of traits?
Preferences for learning/remembering certain types of traits
What are model-based biases?
Copying traits from prestigious, successful, or older individuals.
What are frequency-dependent biases?
Copying common (conformity) or rare (anti-conformity) traits.
What is cultural drift?
Random copying without bias.
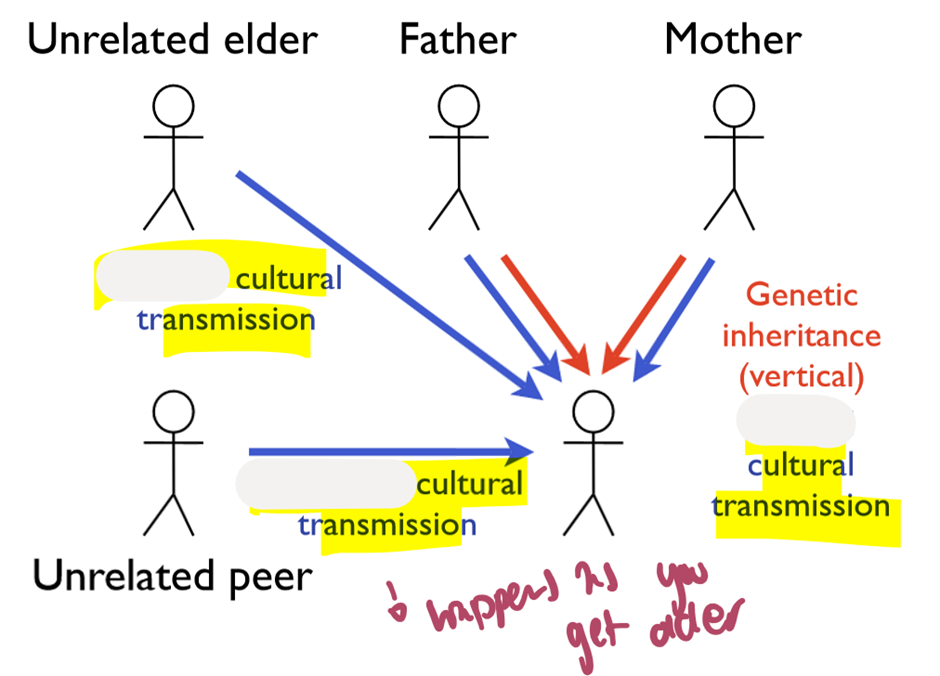
What are 3 methods of social learning transmission (in order of photo)
oblique, horizontal and vertical
When is vertical transmission favoured vs oblique transmission (consider environment and natural selection)?
In stable environments with strong natural selection vs rapidly changing environments with weak/absent natural selection
Who proposed the 5 social learning mechanisms (what do you do with teeth?)
Whiten
What are Whiten’s (2000) social learning mechanisms?
Contagion, stimulus enhancement, observational conditioning, goal emulation, and imitation.
What is contagion in social learning?
Behaviour spreading through simple exposure
What is stimulus enhancement?
Attention drawn to objects or locations used by others.
What is observational conditioning?
Learning when a behaviour is appropriate.
What is goal emulation?
Learning the goal but not the exact actions
What is imitation?
learning the form of the behaviour
What species have we seen teaching occur and not occur in
meerkats and chimpanzees
What is the “idea theft” problem in social learning?
Social learners can outperform individual learners without innovating.
What is the cultural intelligence hypothesis?
Humans evolved specialized social-cognitive skills for cultural learning
At what age in humans do cognitive differences appear between chimpanzees and orangutans
2.5 years old
3 examples of socio-cultural cognitive skills (that humans have but not chimps)
social learning, communication and theory of mind
Why is religion considered a cultural universal?
Religious beliefs appear in nearly all societies.
How can religion function as an adaptation, through what 3 ways?
Through costly signalling, indirect reciprocity, and group cohesion.
Why might religious beliefs be an example of downstream indirect reciprocity
provide benefits to others for personal benefit such as reputation
What is the superorganism hypothesis?
a type of group selection whereby groups with cooperative norms outcompete others
What is the social control hypothesis of religion?
Religious beliefs legitimize hierarchy and social order
How does religion legitimise hierarchy and the rise of organised political states, think a common religious ritual
through human sacrifice to please or appease supernatural beings, establish those who should or shouldn’t be sacrificed
What is cultural group selection?
Groups with advantageous cultural traits outcompete others
What are 3 types of intergroup processes that allow cultural group selection
intergroup competition, imitation of successful neighbours, selective migration
What is intergroup competition relative to cultural group selection
the extinction of less competitive groups
What is selective migration relative to cultural group selection
moving to more desirable societies
Instead of direct adaptation, what 3 possible factors could religion be a by-product of
causal attribution, agency and mental state attribution
Considering the intentional stance, how could religion have emerged as a result of mental state attribution
the use of evolved psychology for understanding complex social worlds by attribution intentions, to create frameworks
What is memetics (explains religion as a product of cultural psychology)
the significance of the survival of the meme, similarly to the persistence of a gene