Microeconomics Concepts (for S1 final)
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Law of Demand
As price increases, quantity demanded decreases; ceteris paribus
Ceteris Parabus
All other things being equal
Demand Schedule
A table showing the relationsip between price and quantity demanded
Direction of a demand curve’s slope
downward sloping due to the law of demand
Causes of a shift in the demand curve
A change in the good’s own price
Normal Goods
Goods where demand increases as income increases
Inferior Goods
Goods where demand increases as income falls
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
How sensitive the demand of a good or service is to a change in price
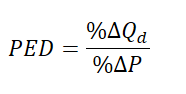
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
How sensitive a good’s demand is to a change in a consumer’s income
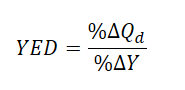
Market Failure
When the free market fails to allocate resources efficiently, resulting in a loss of social welfare
Ex. Pollution, under-provision of education
Allocative Efficiency
Occurs when resources are distributed in a way that maximizes total social welfare (where MSC = MSB)
Ex. Optimal output of healthcare
Social Cost (SC)
The total cost to society from producing or consuming a good
SC = PC + EC
Social Benefit
The total benefit to society from a good
SB = PB + EB
Externalities
A cost or benefit felt by third parties not involved in an economic transaction
Negative Externality of Production
External costs created during production
Ex. Factory emissions, water pollution
Negative Externality of Consumption
External costs created during consumption
Ex. Cigarette smoke, drunk driving
Positive Externality of Production
External benefits generated during production
Ex. Renewable energy R&D that benefits society
Positive Externality of Consumption
External benefits from consumption
Ex. Vaccinations, education
Marginal Private Cost (MPC)
Prices paid by the consumer in addition to purchase price
Marginal Private Benefit (MPB)
The benefit of an individual consuming one more unit of a good or service
Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
The extra cost to society of producing one more unit of a good or service
MSC = MPC + EC
Marginal Social Benefit (MSB)
The extra benefit of society of consuming one more unit of a good or service
MSB = MPB + EB
Indirect Tax
A tax imposed on expenditure that increases production costs and reduced supplies, usually a flat rate
Used to correct negative externalities
Ad Valorem Tax
A percentage-based varying tax placed on the sale price of a good or service as opposed to a flat rate
Ex. Varying rate depending on product characteristics and price
Subsidy
A payment from the government to firms to reduce production costs and increase supply
Used to correct positive externalities
Regulation
Rules or laws that restrict or mandate certain behaviors
Ex. Bans on smoking in public places
Tradable Permits (Cap-and-Trade)
A market-based system where the government issues permits for pollution that firms can trade
Goal: reduce external costs efficiently
Price Floor
Minimum legal price; set above equilibrium
Ex. minimum wage
Price Ceiling
Maximum legal price; set below equilibrium
Example: rent controls
Command-and-Control Policies
Regulations requiring specific actions
Ex. mandatory filters on factories
Merit Good
A good that is under consumed in the free market because individuals underestimate its private benefits
Ex. Education, healthcare, museums, vaccinations
Demerit Good
A good that is overconsumed because individuals underestimate its private costs
Ex. Alcohol, cigarettes, junk food
Information Asymmetry
A situation in which one party has more or better information than another
Ex. Drug side effects, used car quality
Bounded Rationality
Consumers may make decisions that are not in their best interest due to lack of information, bias, or cognitive limits
Public Good
Non-rivalrous and non-excludable
Ex. street/road lighting, national defense
Issue: Free rider problem
Private Good
Rivalrous and excludable; provided efficiently by markets
Common Access Resources (CARs)
Non-excludeable but rivalrous resources
Ex. Fisheries, forests, oceans
Issues: Overuse, tragedy of the commons
Tragedy of the Commons
Where individuals, acting in their own short-term self-interest, deplete a shared resource that is not privately owned, which ultimately harms everyone in the long run
Sustainability
Meeting current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs
Monopoly Power
The ability of a firm to influence price due to a lack of competition
Ex. Only broadband provider in a region
Cartel
A group of firms colluding to set prices or output
Ex. OPEC's oil production agreements
Equity
Fairness in the distribution of income and wealth
Ex. Progressive taxation rates
Efficiency
Maximizing output/welfare without wasting resources
Ex. The circular economy model