Chapter 10: An Introduction to Management Accounting
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Managerial Accounting
The field of accounting designed to meet the needs of internal users.
Financial Accounting
Accounting primarily designed to satisfy the information needs of external users such as investors and creditors.
Product Costs
Costs associated with manufacturing a product, including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Direct Materials
Raw materials that can be easily traced to specific products.
Direct Labor
Labor costs that can be easily traced to specific products in order to be classified as a direct cost.
Manufacturing Overhead
Costs that cannot be easily traced to specific products, considered indirect costs, such as utility costs and rent for manufacturing facilities.
Cost-Plus Pricing
A common business practice where the cost of a product is calculated and a markup is added to determine the selling price.
Level of Aggregation
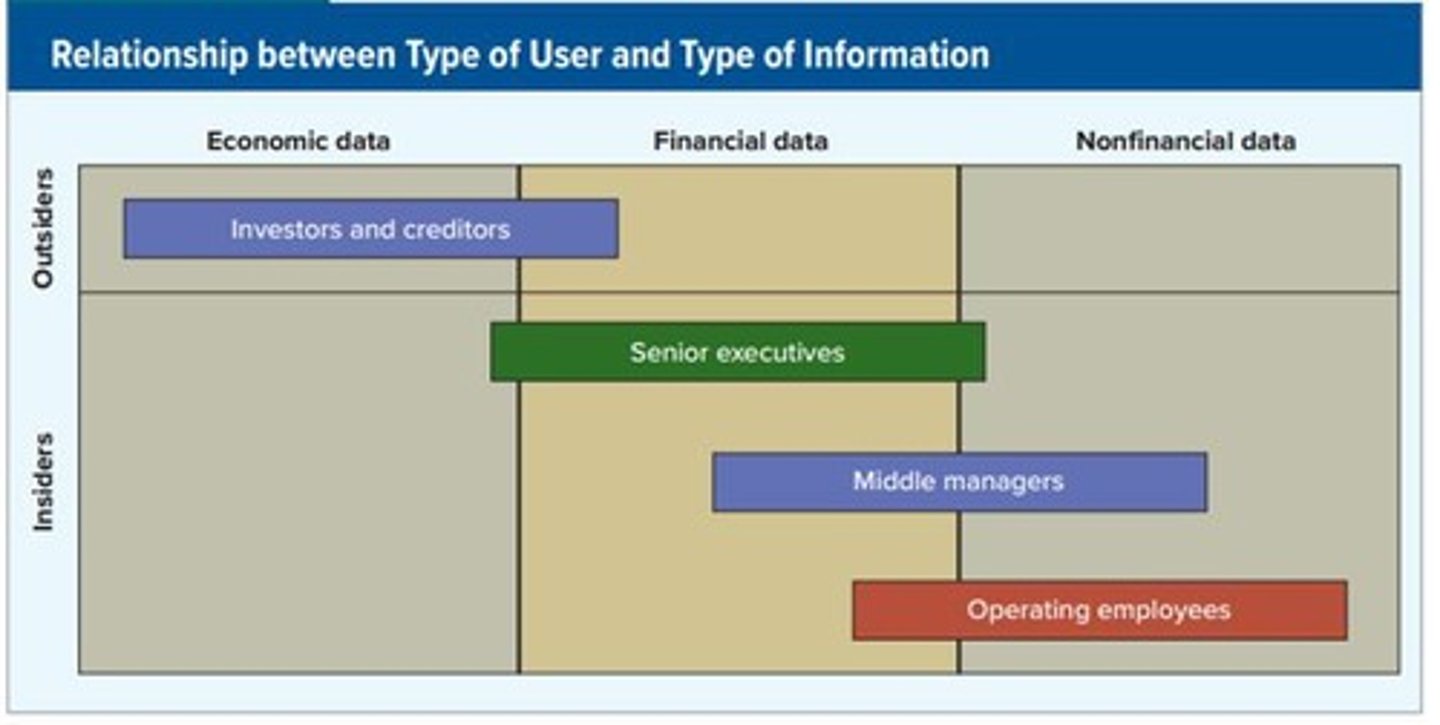
The degree to which financial data is summarized; external users desire global information while internal users focus on detailed information.
Cost of Manufacturing a Product
The total costs incurred to produce a product, including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Asset Exchange
A type of transaction where one asset is exchanged for another, such as inventory for cash.
Expense Recognition
The process of recognizing expenses in the financial statements when the related inventory is sold.
Inventory
Goods available for sale that are recorded as assets until sold.
Financial Statements
Reports that summarize the financial performance and position of a business.
Internal Users
Executives, managers, and employees who need information to plan, direct, and control business operations.
External Users
Investors and creditors who require general economic information.
Cost Classification
The categorization of costs based on their nature and behavior.
Tabor Manufacturing Company
An example company used to illustrate the concept of expense recognition and cost calculation.
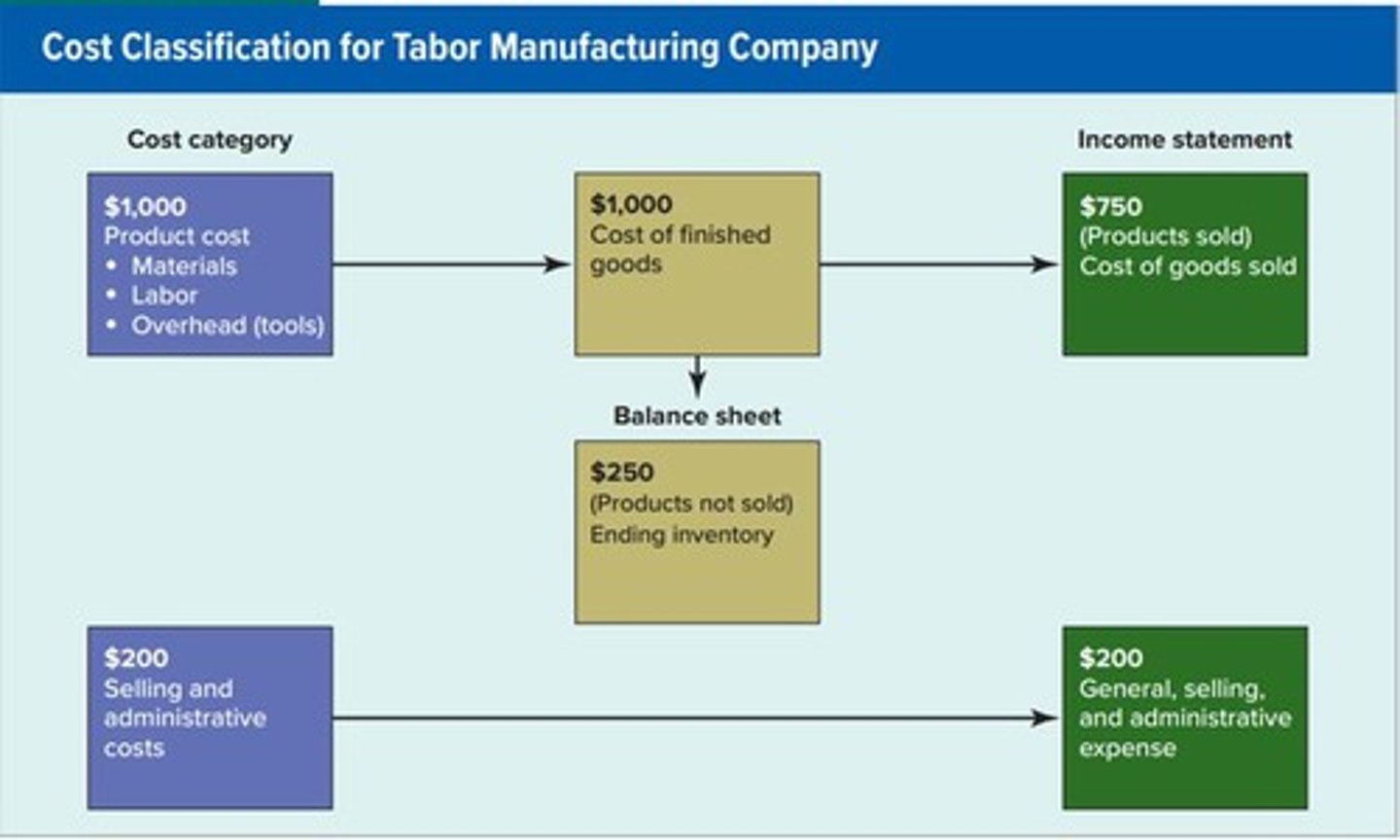
Expense
Costs that are recognized in the financial statements in the period they are incurred, excluding product costs.
Manufacturing Product Cost Summary
A summary of the major components of product costs, including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Zero Expense
The expense recognized by Tabor Manufacturing Company for a specific transaction.
Cost of Each Table
$250, calculated as $1,000 divided by 4 tables.
Revenue Recognition
The principle that revenue is recognized when inventory is sold.
Indirect Costs
Costs that cannot be traced directly to specific products.
Material Costs
Materials used to make products are usually called raw materials. The costs of materials that can be easily and conveniently traced to products are called direct raw materials costs.
Direct raw materials costs
The costs of materials that can be easily and conveniently traced to products.
Labor Costs
The salaries paid to selling and administrative employees and the wages paid to production workers are accounted for differently.
Direct labor costs
Labor costs that can be easily and conveniently traced to products.
Overhead Costs
Costs that cannot be traced to products and services in a cost-effective manner are called indirect costs.
Cost allocation
A process of dividing a total cost into parts and assigning the parts to relevant cost objects.
Depreciation cost
Totaled $1,600 ($600 on office furniture and $1,000 on manufacturing equipment).
Indirect materials
Materials used in a manufacturing company that cannot be directly traced to the product.
Salaries of accounting employees
Salaries of employees working in the accounting department.
Sales commissions
Commissions paid to sales staff.
Interest on mortgage
Interest on the mortgage for the company's corporate headquarters.
Indirect labor
Labor used to manufacture inventory that cannot be directly traced to the product.
Attorney's fees
Fees paid to protect the company from frivolous lawsuits.
Production employee salaries
Salaries paid to employees directly involved in production.
Office supplies cost
The front office cost of supplies used by the clerk at a doctor's office.
Depreciation on office furniture
Depreciation on the office furniture of the company president.
Repair & maintenance salary costs
Salary costs associated with repair and maintenance of a manufacturing facility.
Repair & maintenance supplies costs
Supplies costs associated with repair and maintenance of a manufacturing facility.
Quality department costs
Costs associated with the quality department of a manufacturing facility.
Plant manager salary
Salary paid to the plant manager.
Depreciation on production equipment
Depreciation on the production equipment in a manufacturing facility.
Period costs
Include all selling costs and administrative costs.
Product Cost
Initially classifying a cost as a product cost delays, but does not eliminate, its recognition as an expense.
Service Companies
Organizations provide services to customers, rather than physical products.
Merchandising Companies
Businesses are sometimes called retail or wholesale companies; they sell goods to other companies.
Manufacturing Companies
Companies make the goods they sell to their customers.
Difference between Manufacturing and Service Companies
The primary difference is that the finished products provided by service companies are consumed immediately.
Inventory Holding Costs
Many inventory holding costs are obvious: financing, warehouse space, supervision, theft, damage, and obsolescence.
Hidden Inventory Costs
Other costs are hidden: diminished motivation, sloppy work, inattentive attitudes, and increased production time.
Just-in-Time Inventory (JIT)
A strategy where businesses reduce their inventory holding costs and increase customer satisfaction by making products available just in time for customer consumption.
JIT Example
Paula Elliott supports herself by selling flowers and reengineered her distribution system by purchasing her flowers from a florist within walking distance.
Raw Materials Inventory
Includes lumber, metals, paints, and chemicals that will be used to make the company's products.
Work in Process Inventory
Includes partially completed products.
Finished Goods Inventory
Includes completed products that are ready for sale.
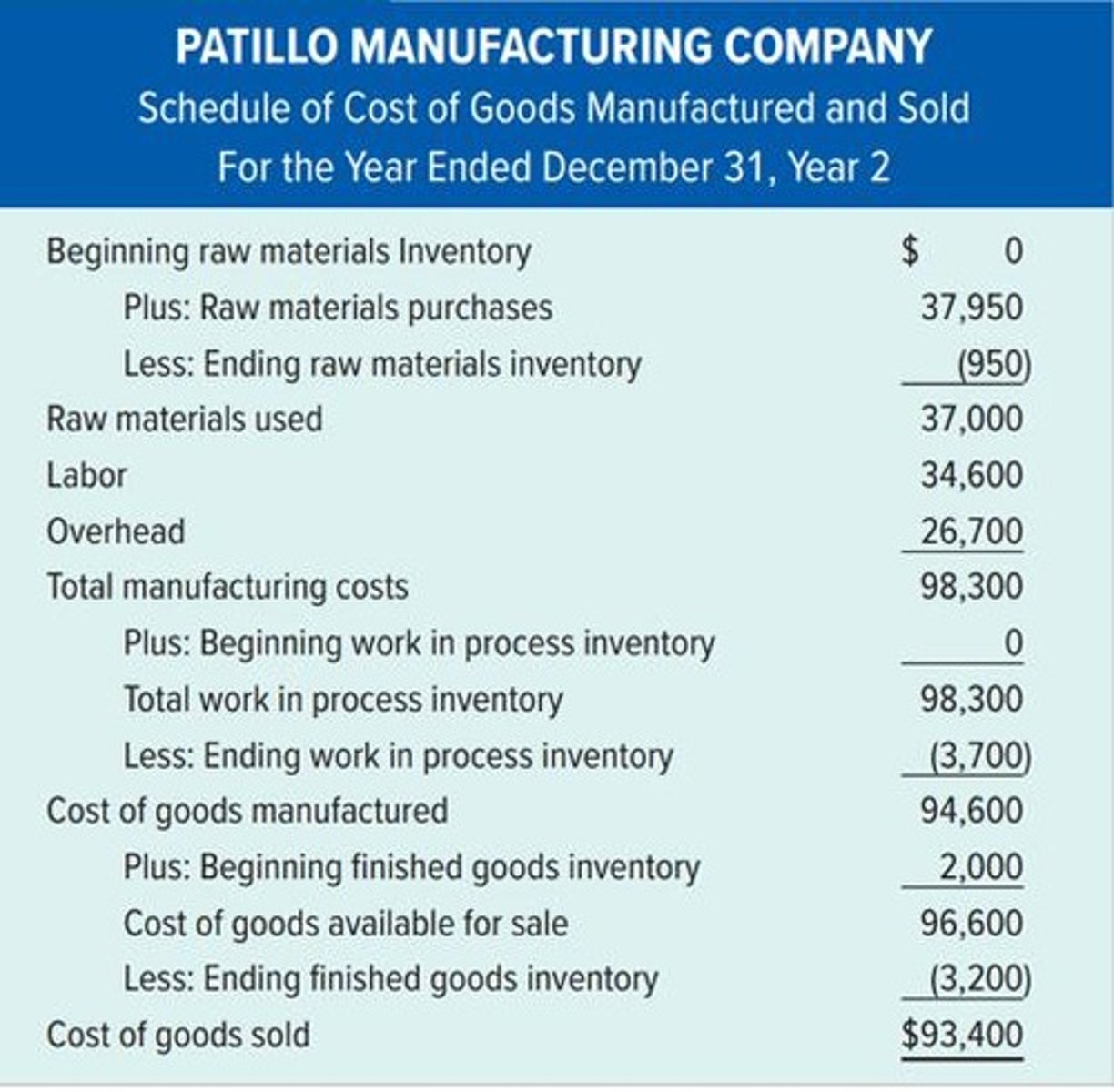
Schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured and Sold
A financial statement that summarizes the total cost of producing goods that were completed during a specific period.
IMA Statement of Ethical Professional Practice
A set of standards that includes Competence, Confidentiality, Integrity, Resolution of Ethical Conflict, and Credibility.

Management Accountants - Potential Conflicts of Interest
Management accountants can face pressure to undertake duties they have not been trained to perform competently.
Ethical Considerations
Management accountants are frequently required to abide by organizational codes of ethics.
Consequences of Ethical Violations
Failure to adhere to professional and organizational ethical standards can lead to personal disgrace, loss of employment, or imprisonment.
Cost of Goods Manufactured
The total cost of producing goods that were completed during a specific period.
Finished Goods Inventory (FGI)
The inventory of completed products that are ready for sale.