Muscle pathology I
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What are myofibers
Long multi-nucleated cells w/ little to no regenerative capacities
What does a satellite cell do?
Stem cells to regenerate a bit of damage muscles
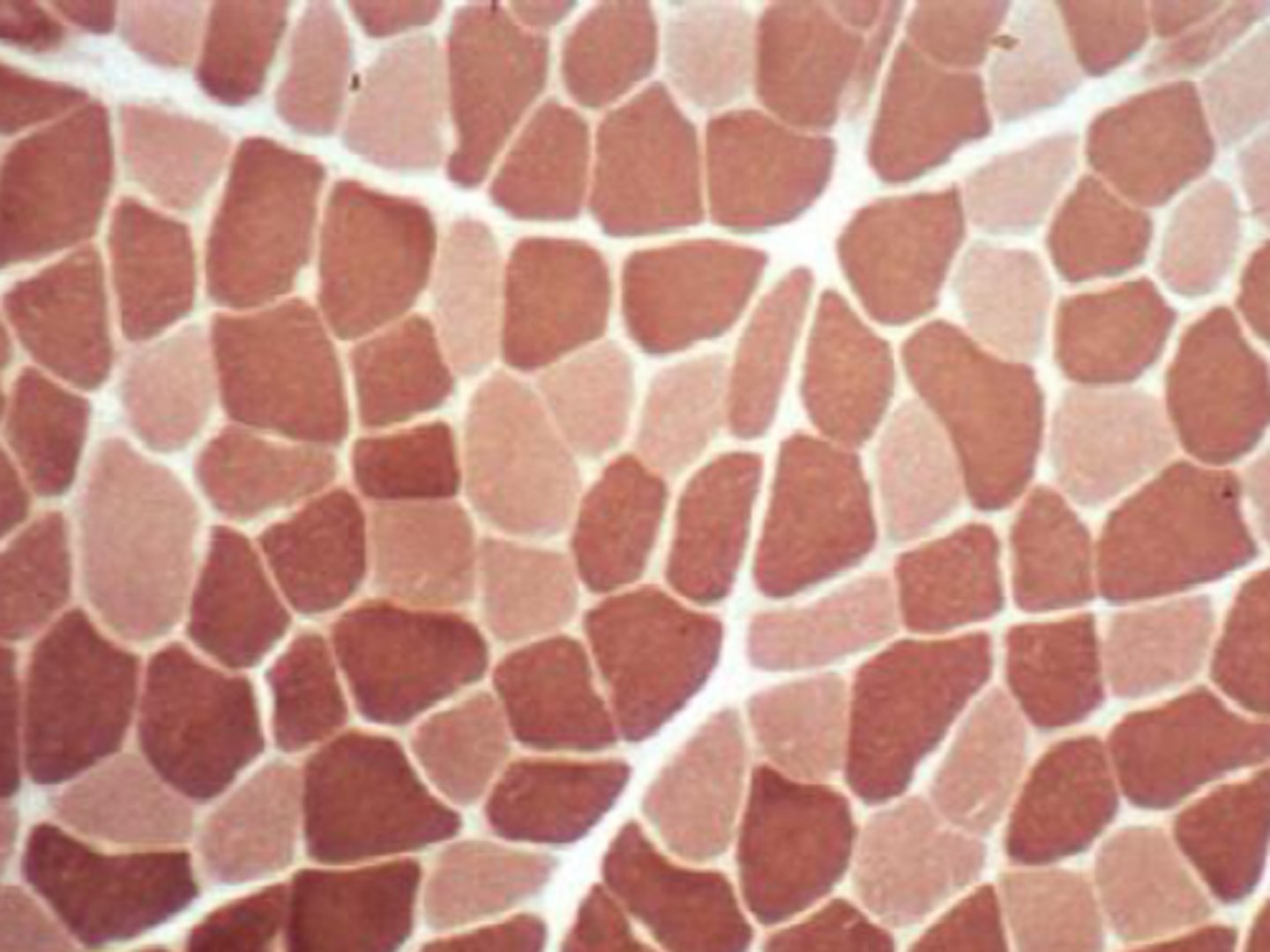
What are type 1 skeletal muscle Fibers?
Slow twitching oxidatie red muscles - aerobic
Type 1 skeletal muscle will have ____ mitochondria
Many
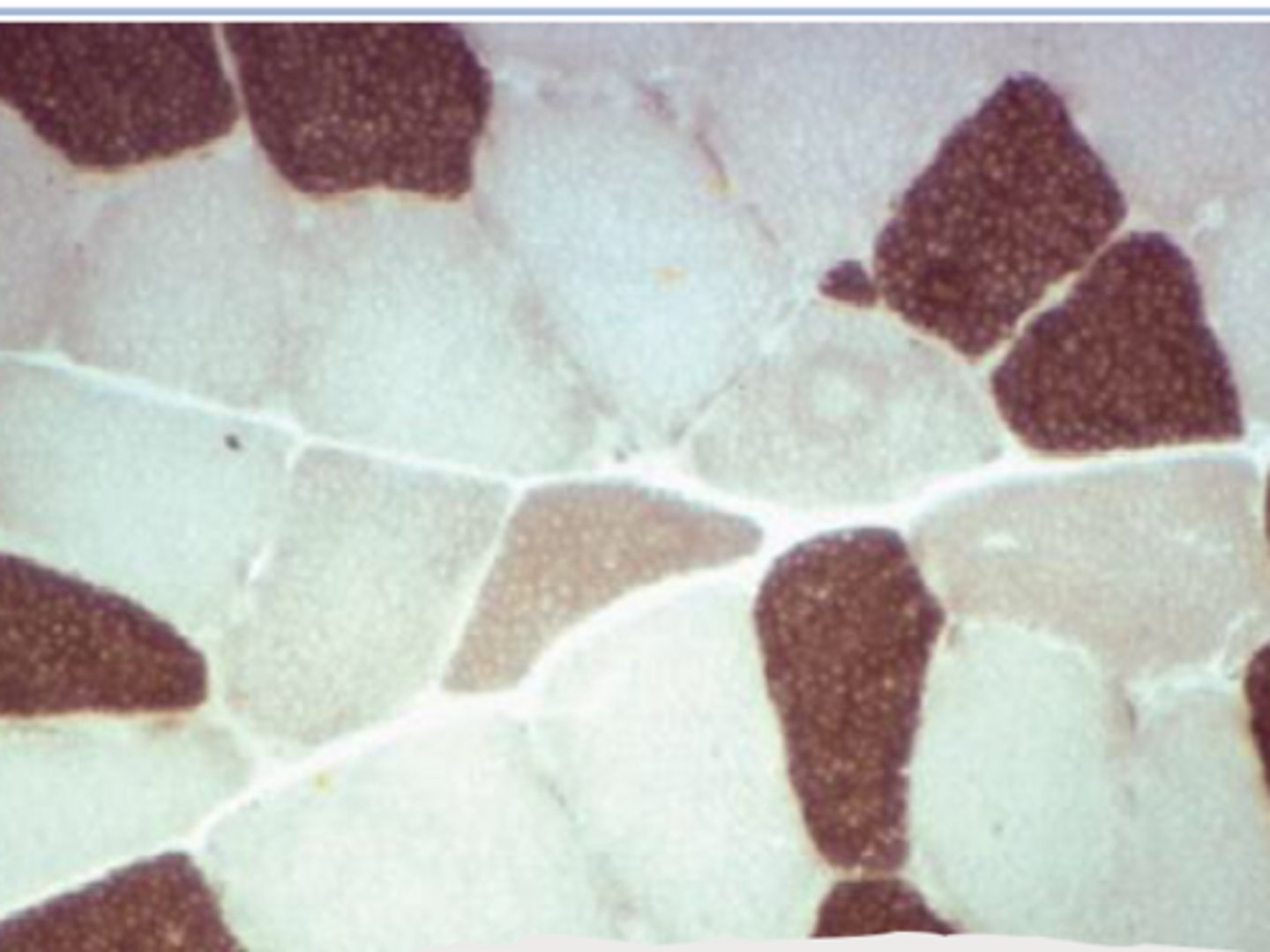
What are type 2A SK muscle fibers?
Fast twitch oxidative glycolytic - fatigue resistant
Type 2A SK muscle fibers will have ___ mitochondria?
Intermediate
What are Type 2b SK muscle fibers?
Fast twitch
Fatigue sensitive
White muscle
Anaerobic
Type 2B SK muscle fibers will have ___ mitochondria?
Few
What are functions of muscles?
Posture / movement
homeostasis
The function of SK muscles wil lbe related to the function of the ___?
Peripheral nervous system
What is a neuropathic?
Effect/ absence of nerve supply
What are myopathics?
Changes w/in muscle cell fibers
Neuromuscuar dz will involve what?
Lower motor neurons and peripheral nerves
Expalin the healing process of muscles?
Necrosis cleaned up by macrophages
satellite cells enlarge and develope into myoblasts
Myoblasts start proliferating and regenerate myofibers
What kind of necrosis does SK muscle go through?
Coagulation necrosis
What are clinpath findings of SK muscle inj?
Creatine kinase elevation
AST/ LDH elevation
Carbonic anhydrase III
What does carbonic anhydrase III insufficiency suggest?
Myasthenia gravis - acetylocholine receptor degredation
Pallor suggests ____?
Necrosis - anemia
Pale streaking suggests?
Necrosis and mineralization
What does dark red molting suggest?
Congestion/ hemorrhagic necrosis
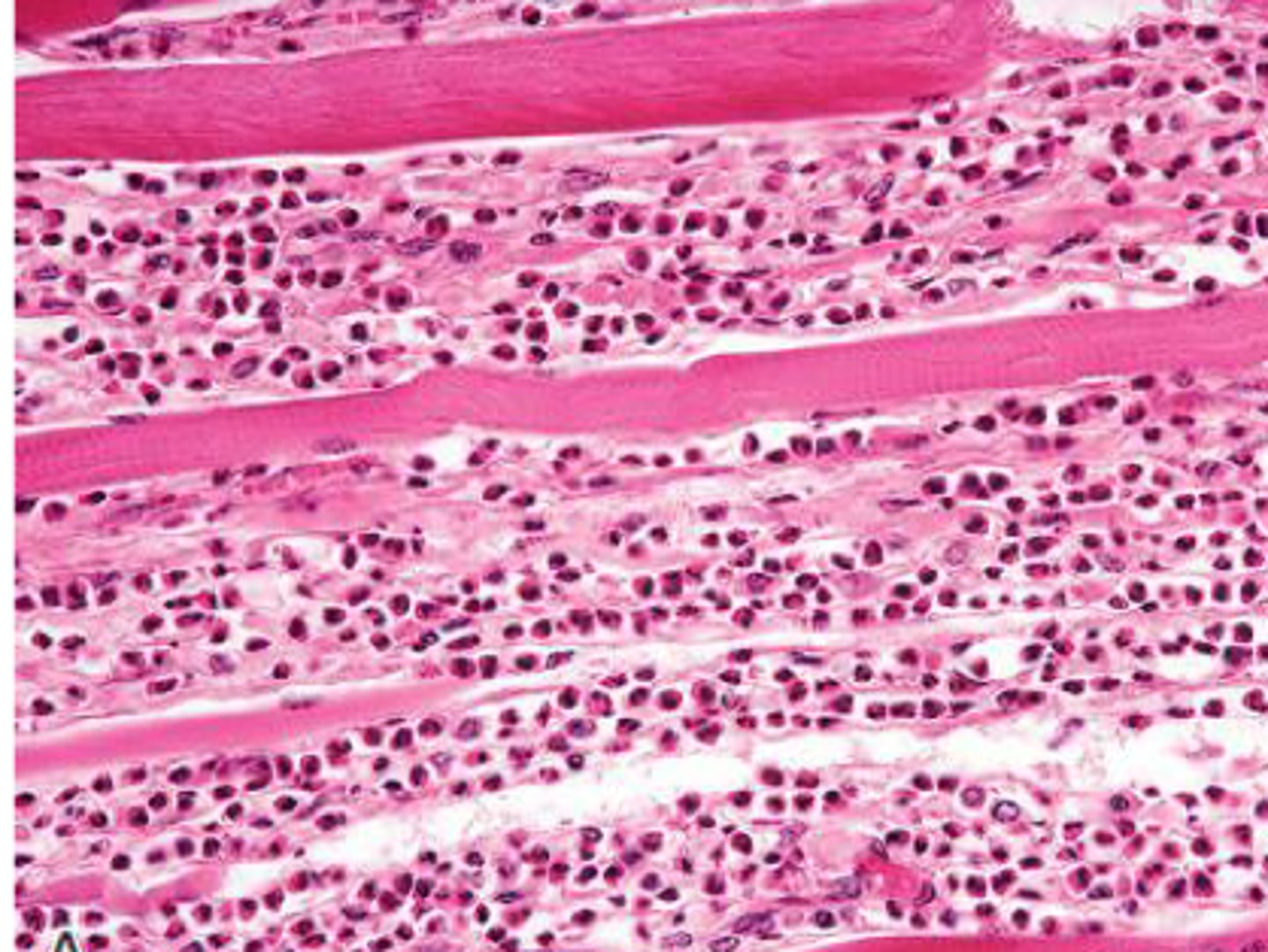
Green muscle suggests?
Eosinophilic inflammation / putrefaction - Sarcocystis - parasitic
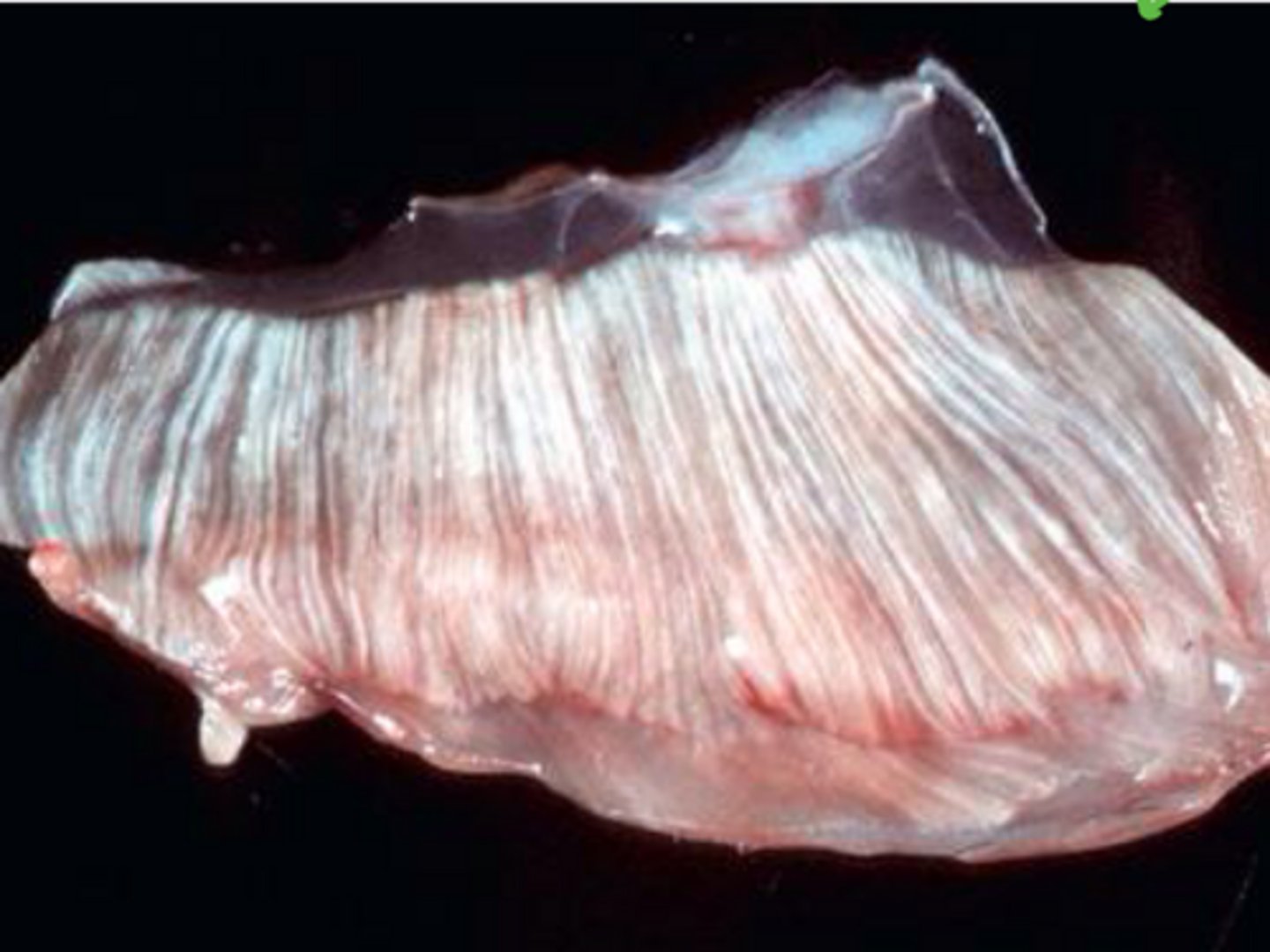
What is an example of pale streaks in SK muscles in dogs?
Canine X - linked muscular dystrophy - duchenne's type
What is dystrophin?
A structural link between muscle cytoskeletin and ECM
What is going to cause canine x linked muscular dystrophy?
Defected dystrophin genes
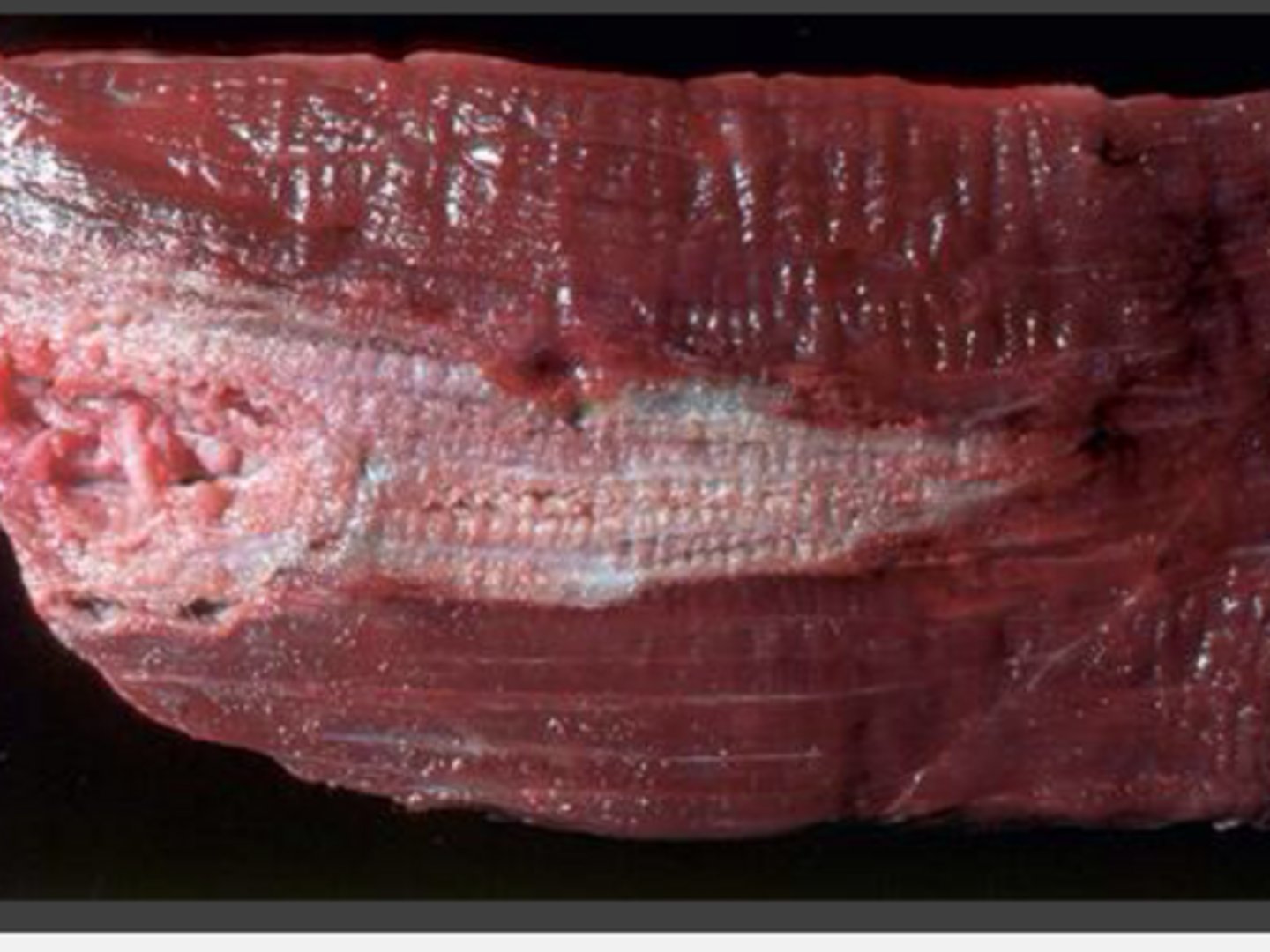

What are causes of localized pallor?
Inj site necrosis
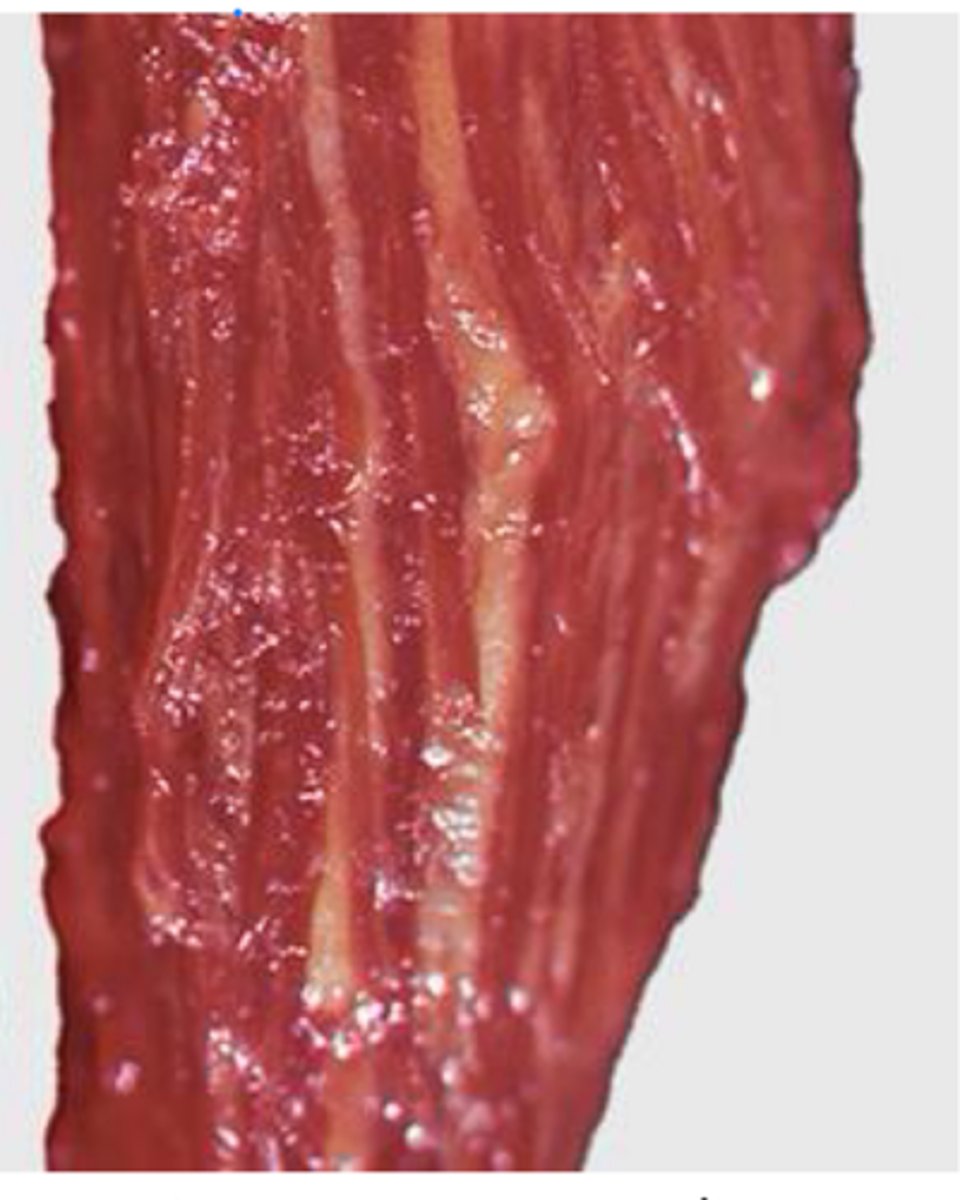

What pathological changes can we see in equine motor neuron dz?
Collagen and fat infiltration due to denervation atrophy
What muscle biopsy would we take for a horse of w/ Equine motor neuron dz?
Type 1 postural
What muscle biopsy would we take for equine polysaccharide storage myopathy?
Type 2 SK muscle - Locomotory
What sample would we take for masticatory myositis of dogs?
Temporal or masseter
What is the ideal muscle biopsy?
1cm myofibers running lengthwise - avoid contracting band artifact
What are direct injury to muscle?
Penetrating wounds/ IM Inj
bone fractures causeing trauma adjacent muscle
External pressure
Name some defense mechanisms of muscle?
Skin - structural barriers
Vasculature - collateral circulation
Immunologic responses
Name a few disturbances of circulation?
Occlusions
Pressure
Swelling impeding blood supply
What is an example of external pressure causing circulation disturbances?
Downers cow syndrome
What is white muscle dz?
A nutritional deficiency - vit E/ Selenium deficiency
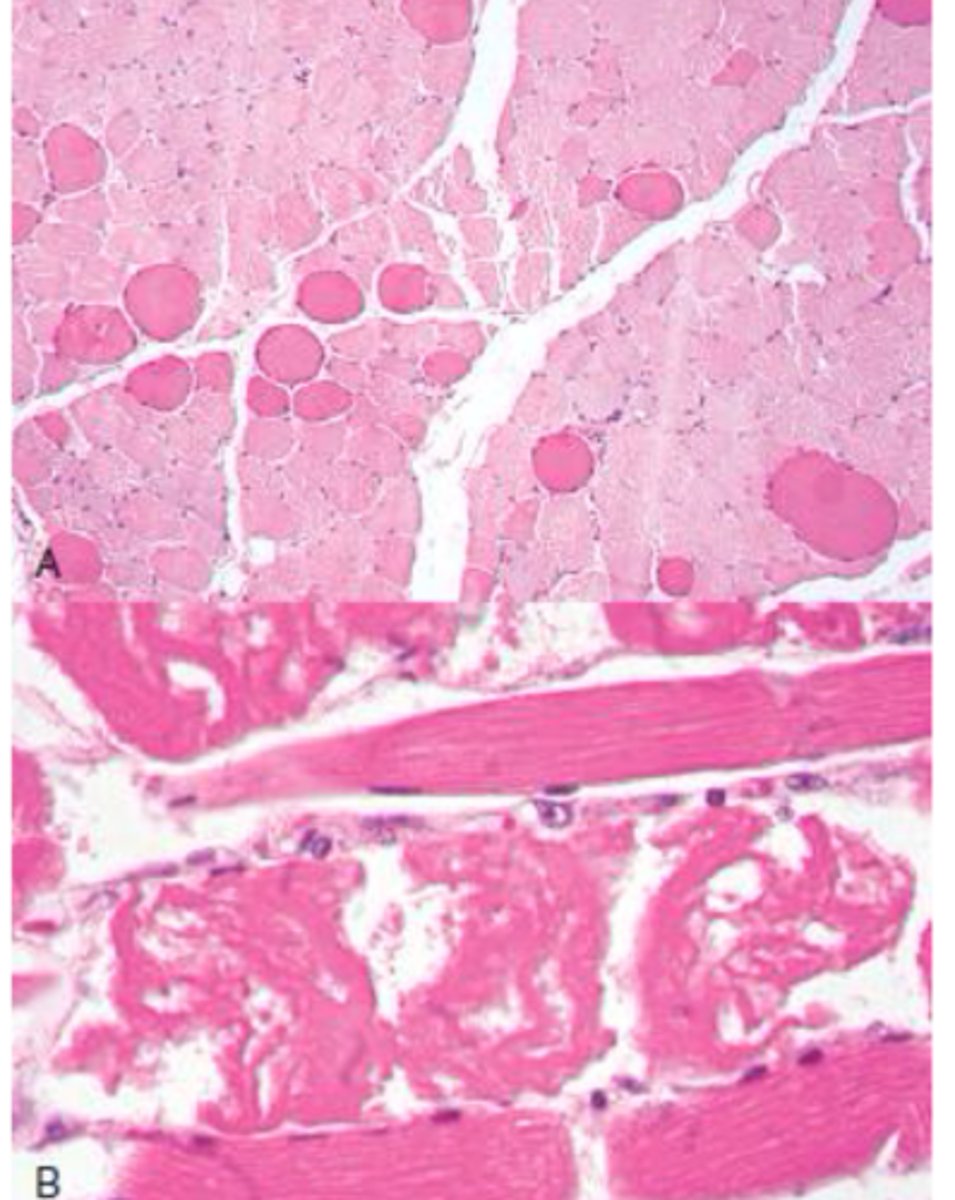
What does Ionophore toxicity do?
Calcium overload causing too much contraction leading to muscle necrosis
Ionophore is most common toxicity in what animals?
Horses
What is the most common myotoxic plant in cattle?
Senna occidentalis
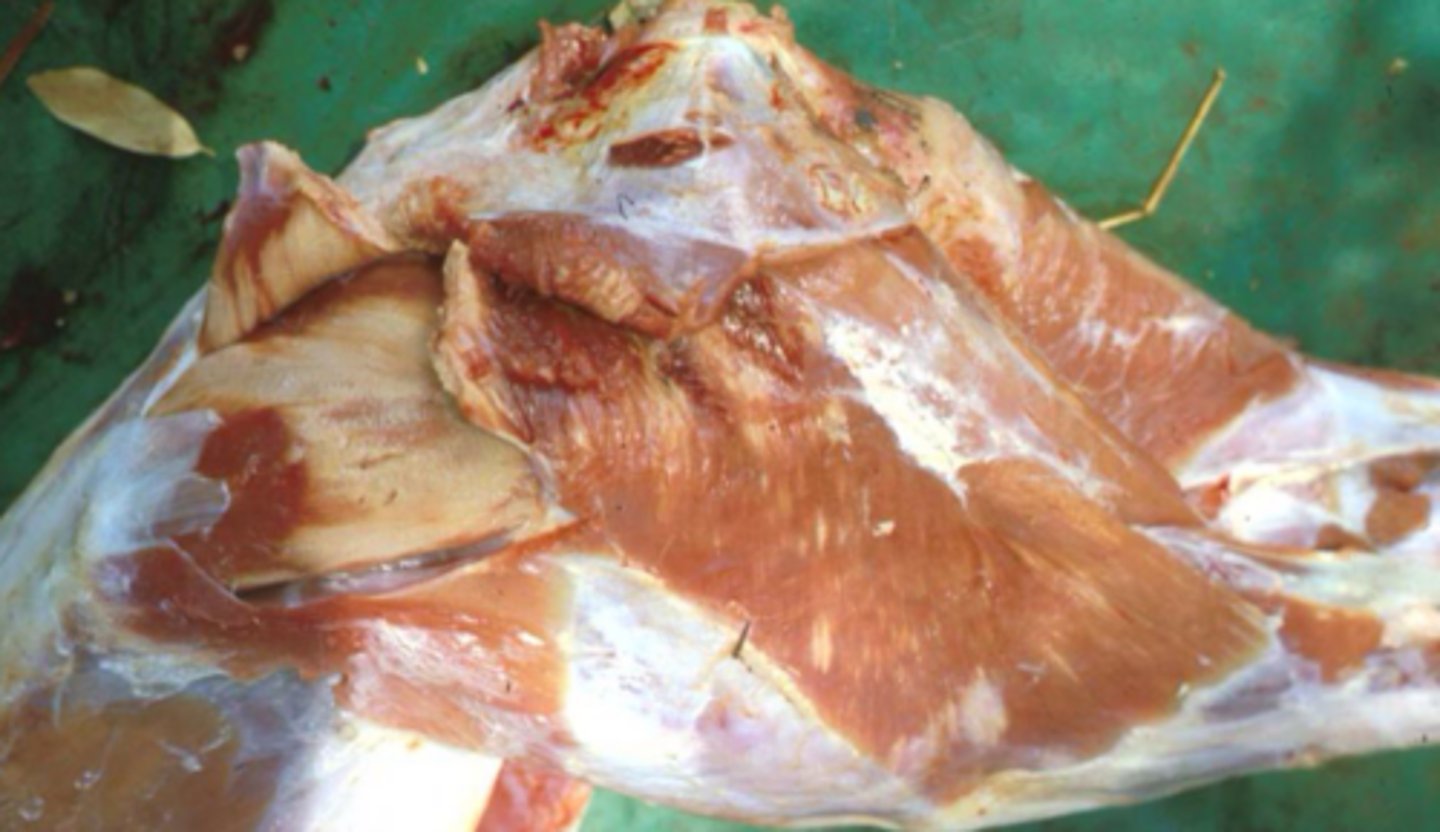
What is capture myopathy?
Exercise induced myonecrosis
What is tying up?
Equine exertional rhabdomyolysis
-stiff gait - high grain feeding - lack of regular exercise
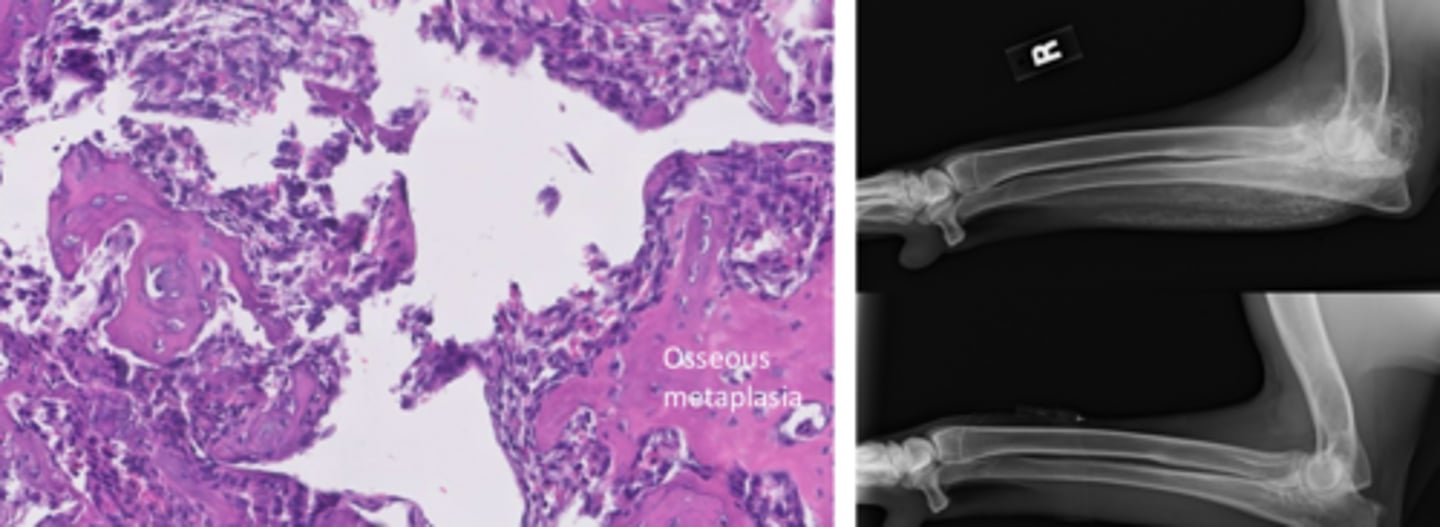
What is myositis ossificans?
Focal lesions of fibrosis w/ osseous metaplasia caused my muscle trauma
How do you treat myositis ossificans?
Painful - sx excision
Ducheene's muscular dystrophy in cats and dogs is an example of what?
Inherited progressive degenerative primary dz of myofibers
What is myotonia?
A channelopathy due to abnormal ion channel function
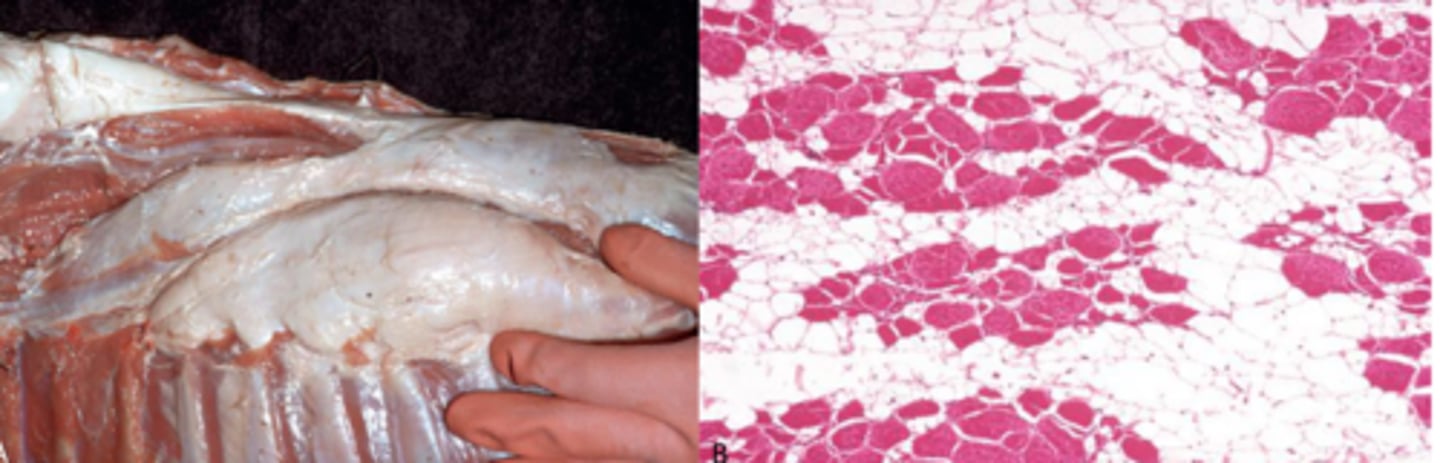
What is neonatal calf denervation atrophy?
Muscles replaced by fat,
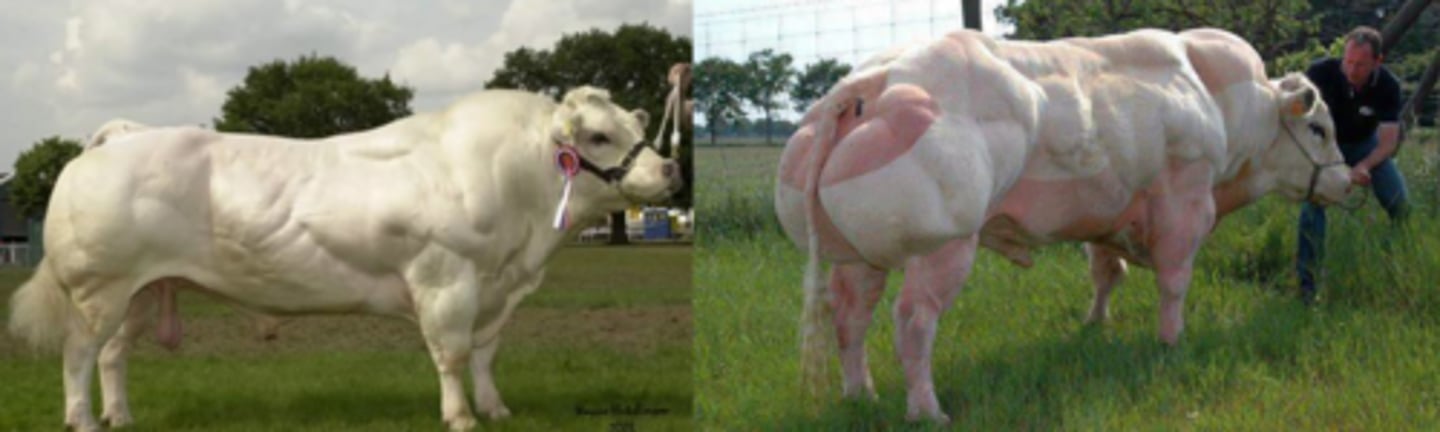

What is congenital muscle hyperplasia?
Double muscling - autosomal recessive
- inactivation of the myostatin gene
- IM fat are reduced - large bulky muscles
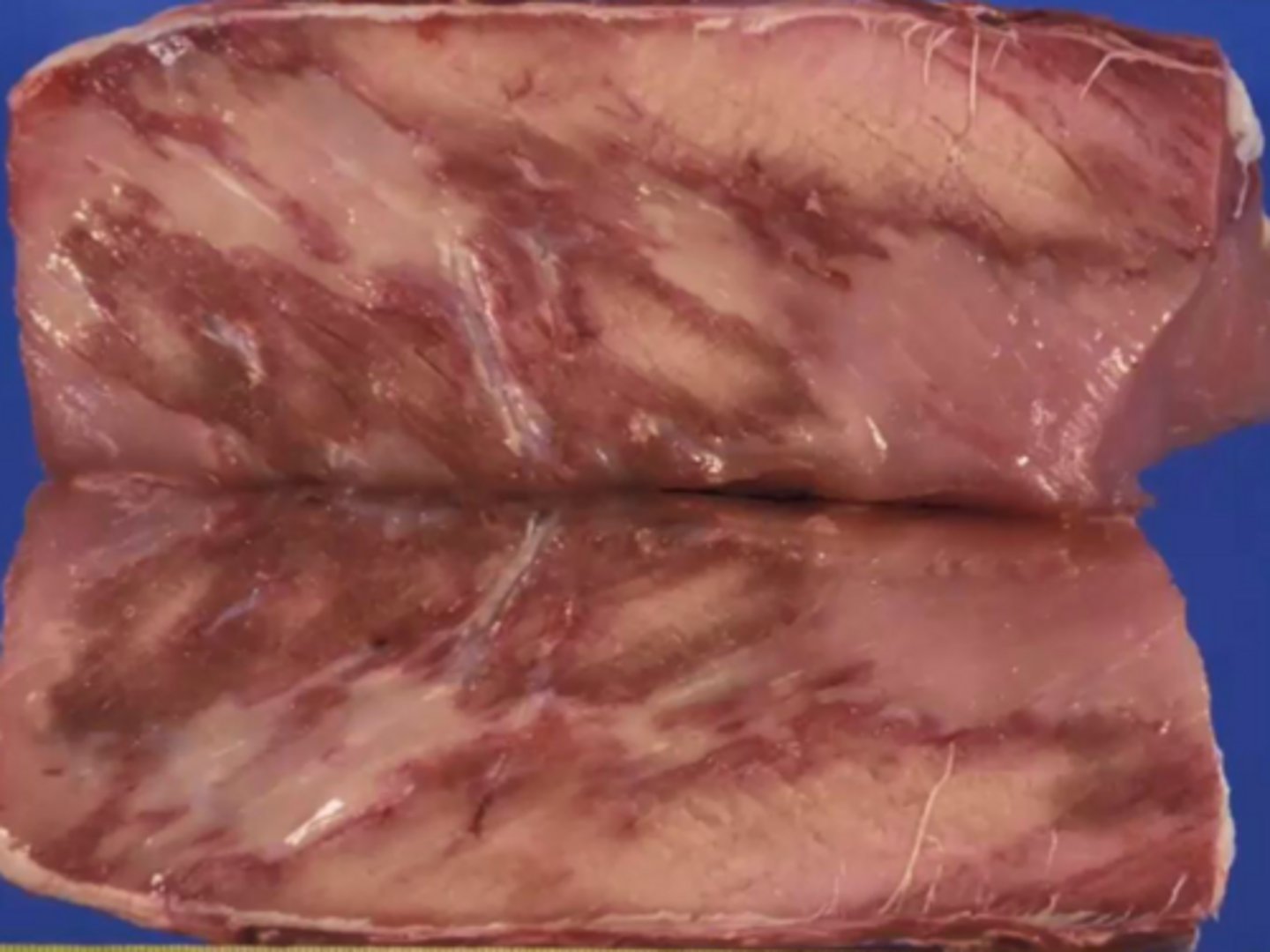

What is malignant hyperthermia?
Unregulated release of calcium leading to increased temp due to defect in ryanodine receptors
What is malignant hyperthermia called in pigs?
Porcine stress syndrome - pale soft exudative
What is the most common type of metabolic myopathies?
Glycogenosis - glycogen storage dz - Type 4 Glycogen branching enzyme deficiency
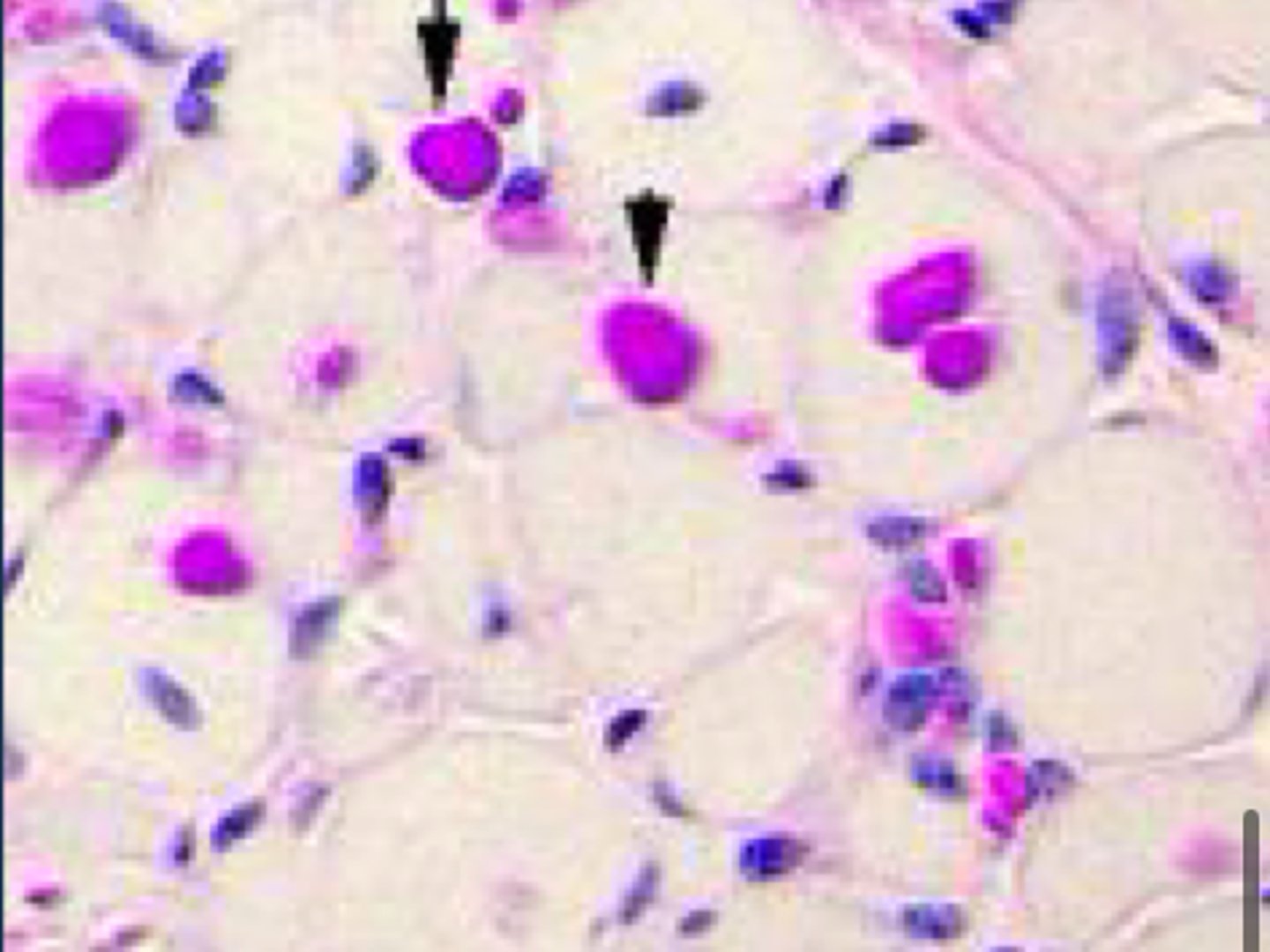
What does a Glyogen branching enzyme deficiency going to do?
Less branching - cant utilize glycogen and leads to muscle necrosis
What stain will highlight Glycogen branching enzyme deficiency?
PAS stain
What is Myasthenia gravis?
Immune-mediated disorder attacking acetylcholine rexeptors
Myasthenia gravis has an associated w/ what?
Thymic abnormalities - thymoma
Botulism will cause a ___ paralysis most common in ___?
Flaccid paralysis - Blocks acetylcholine
Horses
What ticks cause tick paralysis?
Dermacentor and Ixodoes
What does tick paralysis cause?
Toxin Blocks acetylcholine - Flacid paralysis
What is neoplasia of the muscles?
Rhabdomyomoa/Rhabdomyosarcoma
Hemangiosarcoma
What is an infiltrative lipoma?
A lipoma that makes the muscle pale and weak
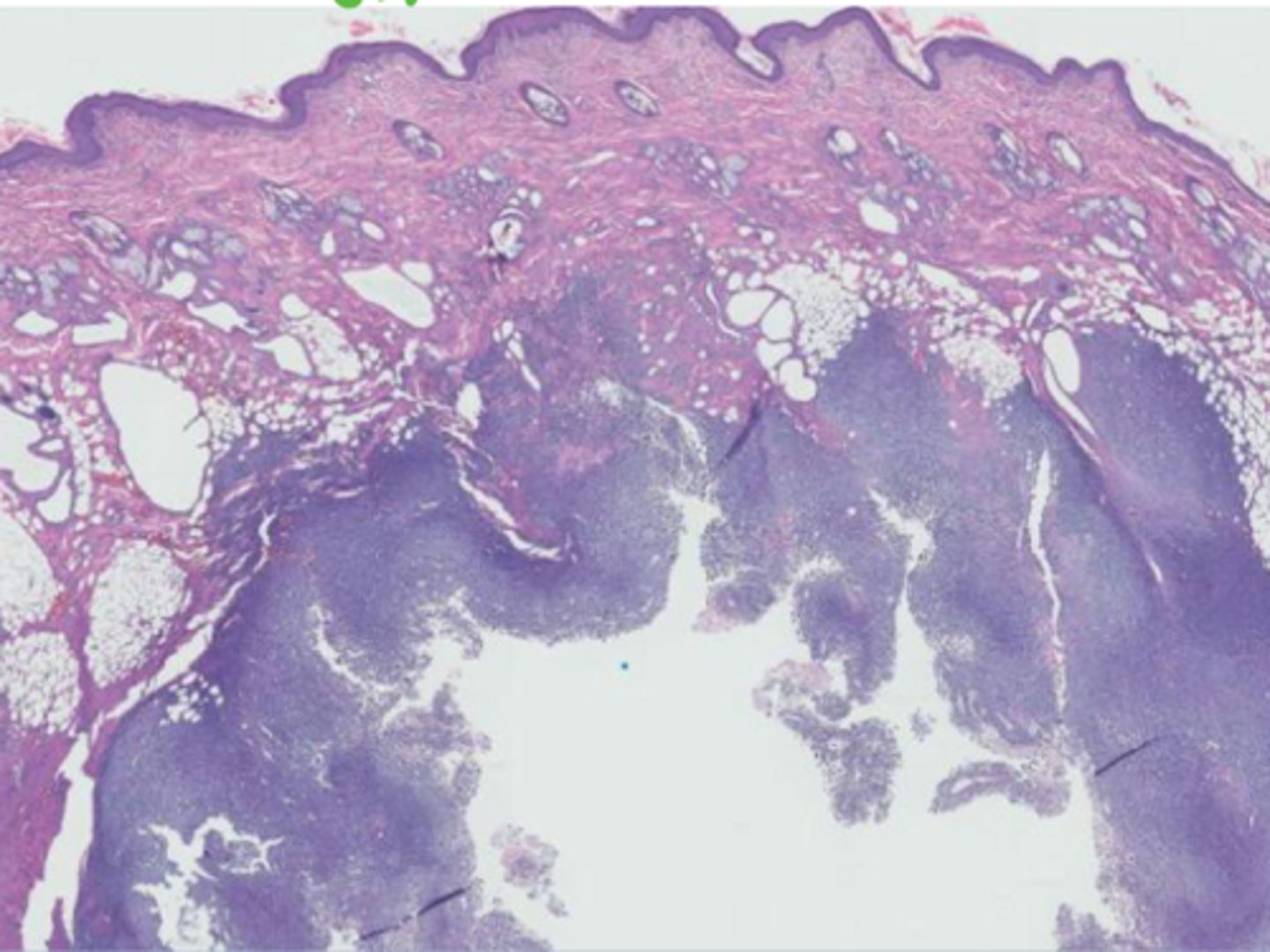
What is animals do vax associated sarcomas related in?
Cats - IM vax sites