Vascular and Ventricular System
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the origin for the arteries found in the anterior circulation
Internal carotid artery
What is the origin for the arteries in the posterior circulation
Vertebral artery
Where does the internal carotid originate
Common carotid; left CCA from the aortic arch; right CCA from brachiocephalic trunk
Where does the vertebral artery originate
Subclavian artery
Segments of the ICA
Cervical segment → Petrous segment → Cavernous segment → Supraclinoid segment
Branches of the ICA (in the order it branches)
Ophthalmic, PComm, Anterior choroidal, anterior cerebral, middle cerebral
What does the anterior cerebral artery supply
Cortex on anterior medial side surface of brain (frontal to anterior parietal)
MCA superior division supplies what areas
Lateral frontal and superior parietal (brain above the sylvian fissure)
MCA inferior division supplies what areas
Structures below sylvian fissure → lateral temporal
MCA deep division supplies what
Branches into the lenticulostriate artery that supplies basal ganglia and internal capsule
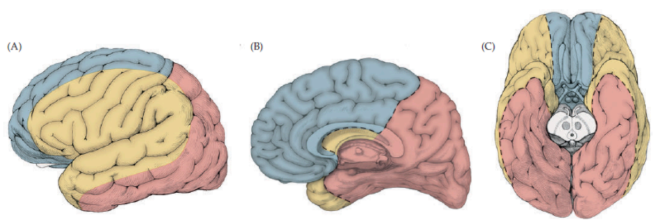
Describe which arteries are being supplies to each highlighted section
Blue = ACA, Yellow = MCA, Red = PCA
What does the anterior choroidal artery supply
Globus pallidus structures and posterior internal capsule
What does the recurrent artery of Heubner supply
Branch of ACA; supplies caudate, anterior putamen, globus pallidus
Left MCA superior division infarction causes what deficit
Face and arm weakness + Broca aphasia on the RIGHT side
Left MCA inferior division infarction causes what deficit
Wernicke aphasia + visual field deficit on the RIGHT side
Left MCA deep division infarction causes what deficit
Pure motor hemiparesis on the RIGHT side (proportionate)
Left MCA stem infarction causes what deficit
Motor hemiparesis, numbness, visual field deficit, Global aphasia
What is the difference between left and right MCA infarction
Left side presents with aphasia, right side is neglect
Right MCA superior division infarction causes what deficit
Face and arm weakness on the LEFT side + hemineglect
Right MCA inferior division infarction causes what deficit
Left hemineglect + visual field and sensory deficit are also common
Right MCA deep division infarction causes what deficit
Pure motor hemiparesis on LEFT side
Right MCA stem infarction causes what deficit
Sensory loss, motor loss, visual field defect, hemineglect
ACA infarction causes what deficit
leg weakness + sensory loss on the OPPOSITE side of lesion
What forms the circle of willis
PComm and AComm that connect ACA and PCA
What does PICA supply
Lateral medulla and inferior cerebellum
What does AICA supply
Lateral caudal pons and small region of cerebellum
What does SCA supply
Superior cerebellum and small part of rostral laterodorsal pons
Branches of the posterior circulation
PCA, Basilar, SCA, AICA, PICA
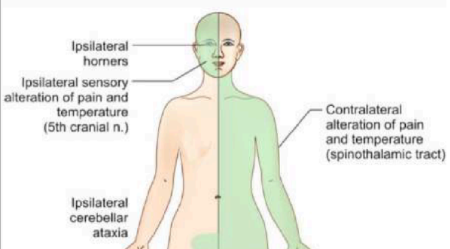
A patient presents with numbness in this distribution, where is the lesion and cause
Lesion in the lateral medulla, cause is PICA infarction causing Wallenberg syndrome
What are the symptoms and etiologies of Wallenberg syndrome
Ipsilateral ataxia → Inferior cerebellar peduncle
vertigo, nystagmus and nausea → Vestibular nuclei
Facial numbness → Trigeminal nucleus and tract
Decreased pain and temperature sense → Spinothalamic tract
Ptosis/Horner syndrome → Descending sympathetic tract
Hoarse voice → Nucleus ambiguus
Decreased taste → Nucleus solitarius
AICA syndrome is caused by a lesion in what area
Lateral caudal pons
What can be used to separate PICA from AICA syndrome
PICA syndrome DOES NOT have motor dysfunction; AICA main symptom is ATAXIA
What symptoms can be found in PICA syndrome but NOT AICA syndrome
Hoarse voice (nucleus ambiguus), decreased taste (nucleus solitarius)
What are the symptoms of SCA syndrome and where is the lesion
Ipsilateral ataxia; lesion of dorsolateral pons
Symptoms of PCA syndrome
Contralateral vision loss and alexia with agraphia (can read but not write)
Ventricular pathway
Lateral ventricle → Foramen of Monro → Third ventricle → Cerebral aqueduct → Forth ventricle → Foramen magendie → Spinal cord → Brain
Venous drainage pathway from confluence of sinus to jugular vein
Confluence of sinus → Transverse sinus → Sigmoid sinus → Jugular foramen → Jugular vein