Alkanes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are Alkanes?
Alkanes are Saturated Hydrocarbons meaning they contain olny carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds. They are among the least reactive organic compounds and are used for fuel and lubricants due to their stability.
General Formula - CnH2n+2
Functional Group - None
The C-C angle is approximately 109.5 degrees in alkanes.
Methane, Ethane and Propane have no isomers and after that the amount of isomers increases with the chain length.
What are the Physical Properties of Alkanes?
Polarity - Alkanes are almost non-polar because the electronegativities between carbon and hydrogen are so similar. As as result, there is only van der Waals forces between molecules.
Boiling Points - The increasing intermolecular forces with increasing molecule size cause an increase in boiling point as chain length increases.
Solubility - Alkanes are insoluble in water as the water molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds which are much stronger than the van der Waals forces that act between alkane molecules. However, alkanes do mix with other relatively non-polar liquids.
Reactions - They are relatively unreactive. They don’t react with acids, bases, oxidising agents and reducing agents. They do burn and react with halogens under suitable conditions.
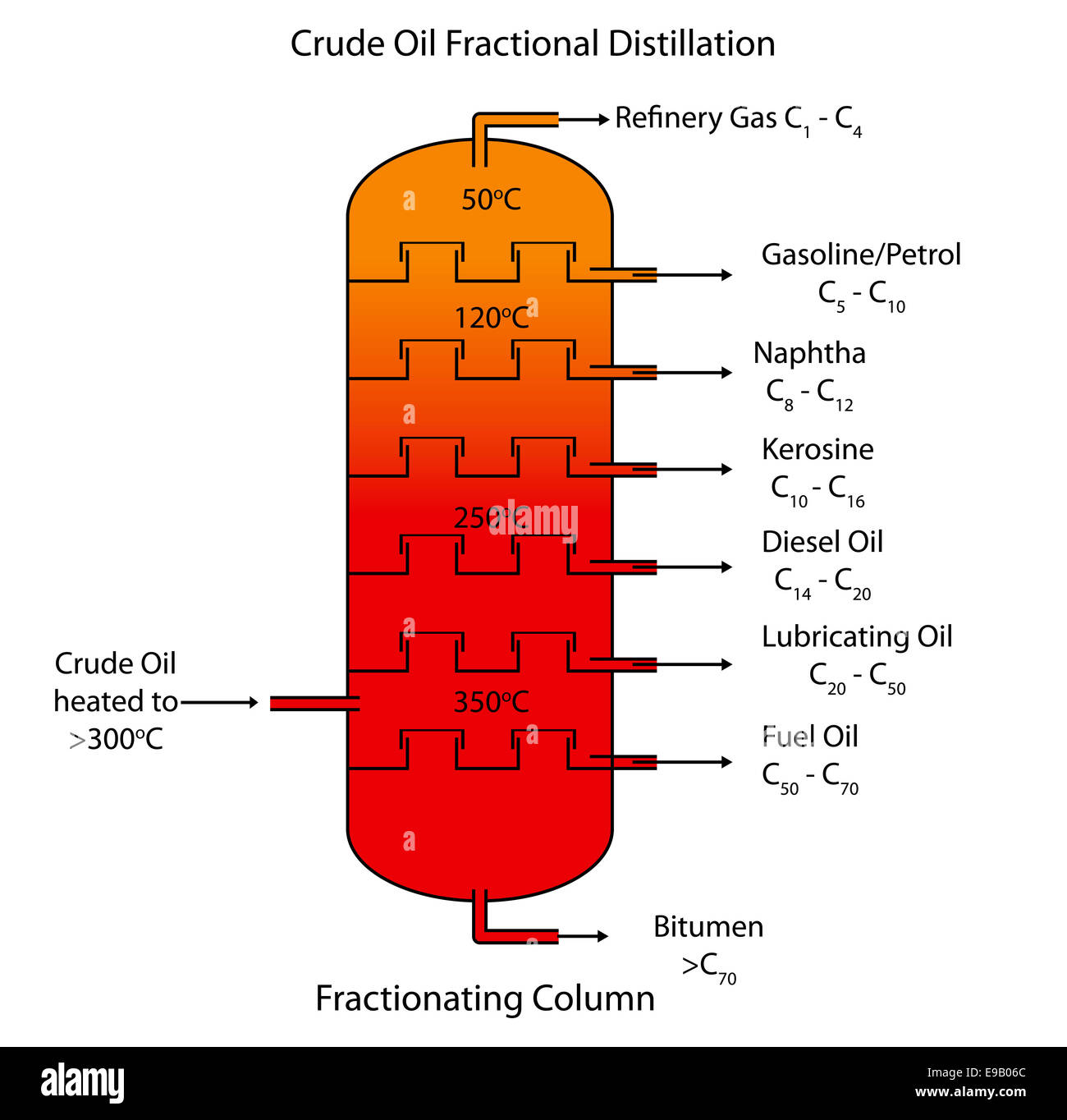
What is Fractional Distillation and Crude Oil?
Crude Oil is a mixture of different hydrocarbons that can be separated out into different molecules by Fractional Distillation
Fractional Distillation:
The Crude Oil is vaporised into the fractionating column
Inside there is a negative temperature gradient meaning it is cooler at the top and hotter at the bottom
The fractions are separated as longer chain hydrocarbons have higher boiling points so they condense into liquids first nearer to the bottom and shorter chain hydrocarbons condense near the top.
The products of Fractional Distillation are:
Refinery Gas - BP ~20, Fuels for Vehicles
Petrol - BP ~40-110, Fuel for Cars
Naphtha - BP ~110-180, making Chemicals and Plastics
Kerosene (Paraffin) - BP ~180-250, Jet Fuel
Diesel - BP ~250-350, Fuel for Diesel Engines
Fuel Oil - BP ~350-450, Fuel for Ships
Bitumen - BP ~450+ / Doesn’t Vaporise, Road Surfacing
What is Cracking?
Many of the shorter chain hydrocarbons like naphtha are in more demand than the longer chain hydrocarbons which you get more of in fractional distillation.
Cracking is used to break down these longer chain hydrocarbons into shorter more useful chains, as well also producing alkenes as another product which are much more reactive than alkanes.
The main two ways to carry out Cracking are Thermal Cracking and Catalytic Cracking.
What is Thermal Cracking?
A cracking process which involves heating alkanes to high temperatures of ~1200 K and under high pressure of ~7000 kPa.
The carbon-carbon bond then breaks in such a way that initially one electron from the pair goes to each carbon atom, resulting in two carbon atoms with an unpaired electron (A Free Radical).
As there are then not enough hydrogen atoms to produce two alkanes, one or more alkenes are produced.
Thermal Cracking produces a high proportion of alkenes and shorter chain hydrocarbons, making it effective for increasing the yield of useful products.
What is Catalytic Cracking?
A cracking process that takes place at a lower temperature of ~720k, a lower pressure compared to Thermal Cracking (But above atmospheric pressure) and uses a zeolite catalyst.
Zeolites have a honeycomb structure with an enormous surface area and are also acidic.
This form of cracking is used mainly to produce motor fuels and the products are mostly alkanes, cycloalkanes and aromantic compounds. The products are separated by fractional distillation.
Describe the two types of Combustion of Alkanes?
Combustion - The shorter chain alkanes burn completely in a plentiful supply of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water. Combustion reactions give out heat and have negative enthalpies. The more carbons present, the greater the heat output.
Incomplete Combustion - In a limited supply of oxygen, carbon monoxide is formed and with even less oxygen, carbon (soot) is produced.
What are some Pollutants and their problems?
Carbon Monoxide - A poisonous gas produced by incomplete combustion.
Nitrogen Oxides (NO, NO2, N2O4) - Oxides produced at high temperatures in engines, contributing to smog formation, acid rain and respiratory problems.
Sulfur Dioxide - Produced from sulfur impurities in crude oil and contribute to acid rain.
Carbon Particles/Particulates - Small solid particles that exacerbate asthma and cause cancer.
Unburnt Hydrocarbons - Compounds that escape combustion and enter the atmosphere, contributing to photochemical smog and many health problems.
Carbon Dioxide - A greenhouse gas formed from burning hydrocarbons and is linked to global warming and climate change.
What is Flue gas Desulfurisation?
Sulfuric acid is produced in the air when fuels containing sulfur are burned and the sulfur dioxide reacts with oxygen and water vapour. SO2 + ½ O2 + H2O → H2SO4
These gases given out by power stations are called Flue Gases, so the process of removing sulfur is flue gas desulfurisation.
One method is to spray a slurry of calcium oxide and water into the flue gas to form calcium solfite which can then be oxidised to form calcium sulfate (Gypsum). Gypsum is a saleable product used to make builder’s plaster.
CaO +2H2O +SO2 +1/2 O2 → CaSO4 . 2H2O
This can also be be done with Calcium Carbonate:
CaCo3 + ½ O2 + SO2 → CaSO4 + CO2
What are Catalytic Converters?
They are a honeycomb made of a ceramic material coated with platinum and rhodium metals (They have a large surface area) that act as catalysts to convert harmful emissions into less harmful gases:
2CO +2NO → N2 + 2CO2
These reactions take place on the surface of the catalyst, on the layer of metals.
How do Halogenoalkanes form and what are Free Radicals?
Alkanes react with halogens in the presence of UV light to produce Halogenoalkanes. The UV breaks down the halogen bonds producing reactive intermediates called free radicals.
Free Radicals - A chemical species with an unpaired electron that is usually highly reactive.
These Free Radicals attack the alkanes resulting in a series of reactions: Initiation, Propagation and Termination.
What is Initiation?
The first step of Free Radicals Substitution where the chlorine-chlorine bond is broke to form two chlorine atoms.
The chlorine molecule absorbs the energy of a single quantum of UV light which is enough to break the bond.
Since both atoms are the same, the bond breaks homolytically, meaning one electron goes to each chlorine. These chlorine atoms are free radicals.
There is not enough energy to break the carbon-hydrogen bonds producing reactive in a quantum of UV light.
What is Propogation?
A two stage reaction where the halogen radicals react with alkanes in a chain reaction, where the radical acts as a catalyst.
Step 1: A halogen radicals react with takes a hydrogen from the alkane to form a stable compound: Cl• + CH4 → HCl + •CH3
Step 2: The alkane radical produced now reacts with a halogen molecule, forming a halogen radical and a new stable molecule: •CH3 + Cl2 → CH3Cl +Cl•
The effect of these two steps is to produce a hydrogen halide, a haloalkane and a new halogen radical. These steps can take place 1000s of times before termination.
What is Termination?
The final step in Free Radical Substitution where the free radicals are removed by reacting together, stopping the reaction. However, radicals are more likely to meet a molecule instead of another radical so this step takes a long time.