A&P Chapter 12.
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
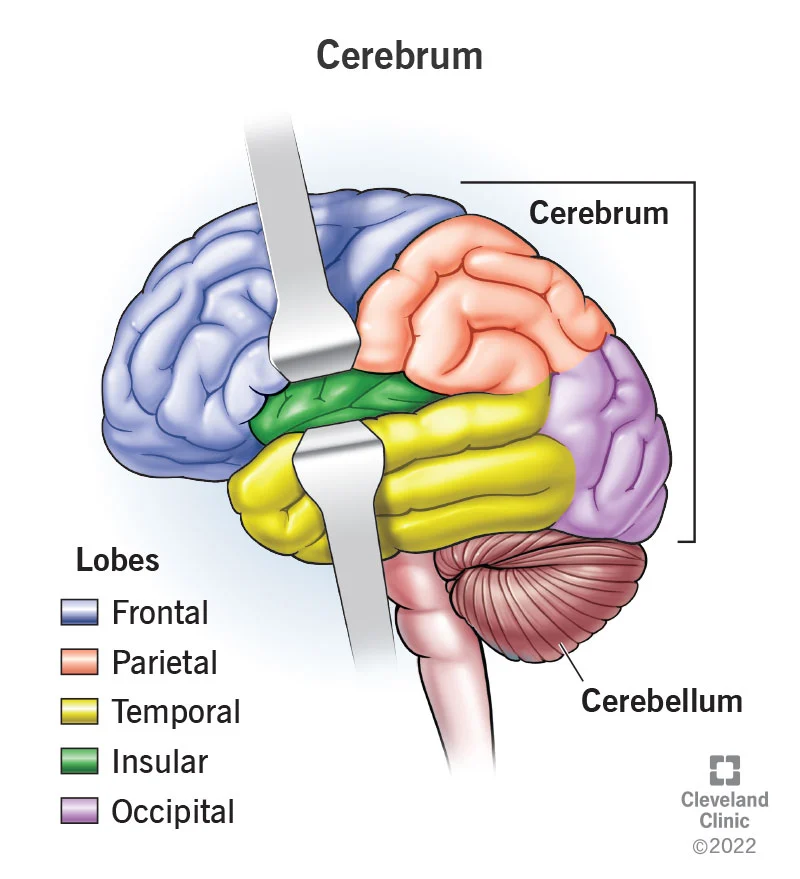
Cerebrum
Makes up 40% of brains mass.
Sulci and Gyri increases its surface area
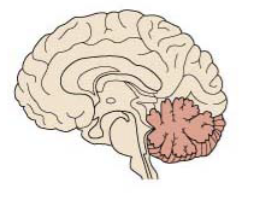
Cerebellum
Processes information from the cerebrum cortex
Provides instruction for the cerebral motor cortex. Therefore, resulting in smooth coordinated skeletal muscle movements
Responsible for balance & posture
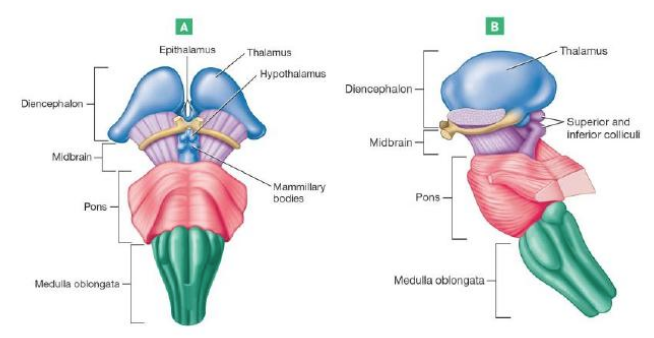
Brainstem
Composed of the: Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla Oblongata
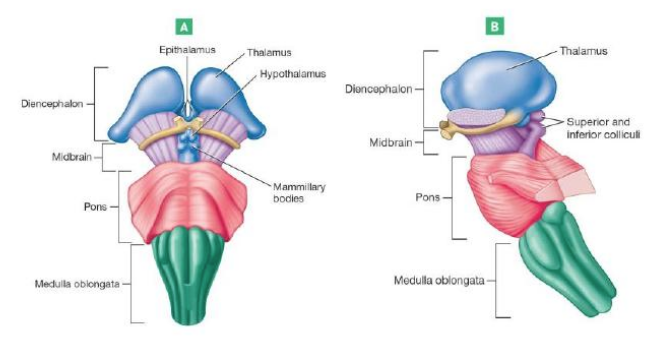
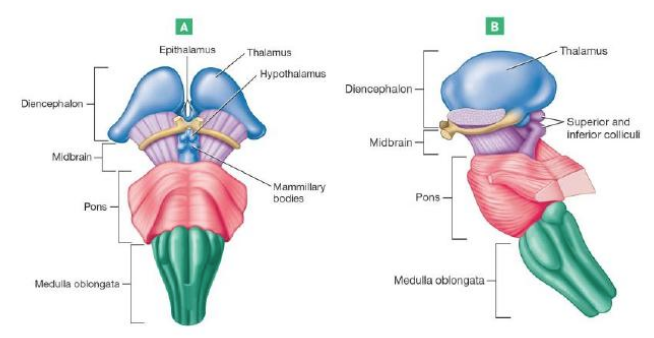
Midbrain
Contains visual and auditory reflex centers
Contains subcortical reflex centers
Contains nuclei for cranial nerves 3&4
Contains projection centers
Pons
Relays information from cerebrum to the cerebellum
Controls respiratory rate and depth
contains nuclei for cranial 5-7
Contains projection fibers
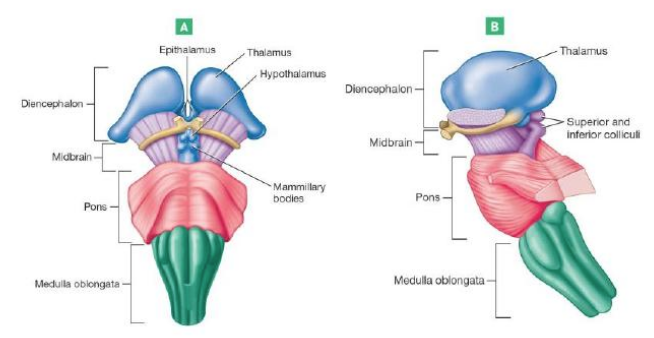
Medulla Oblongata
Controls heart rate, blood vessel diameter, respiratory rate, vomiting, coughing, etc. (autonomic activities)
Relays sensory information to the cerebellum through inferior olivary nuclei
Contains cranial nerves 8,9,10 & 12
Contains projection fibers
Site where pyramids cross
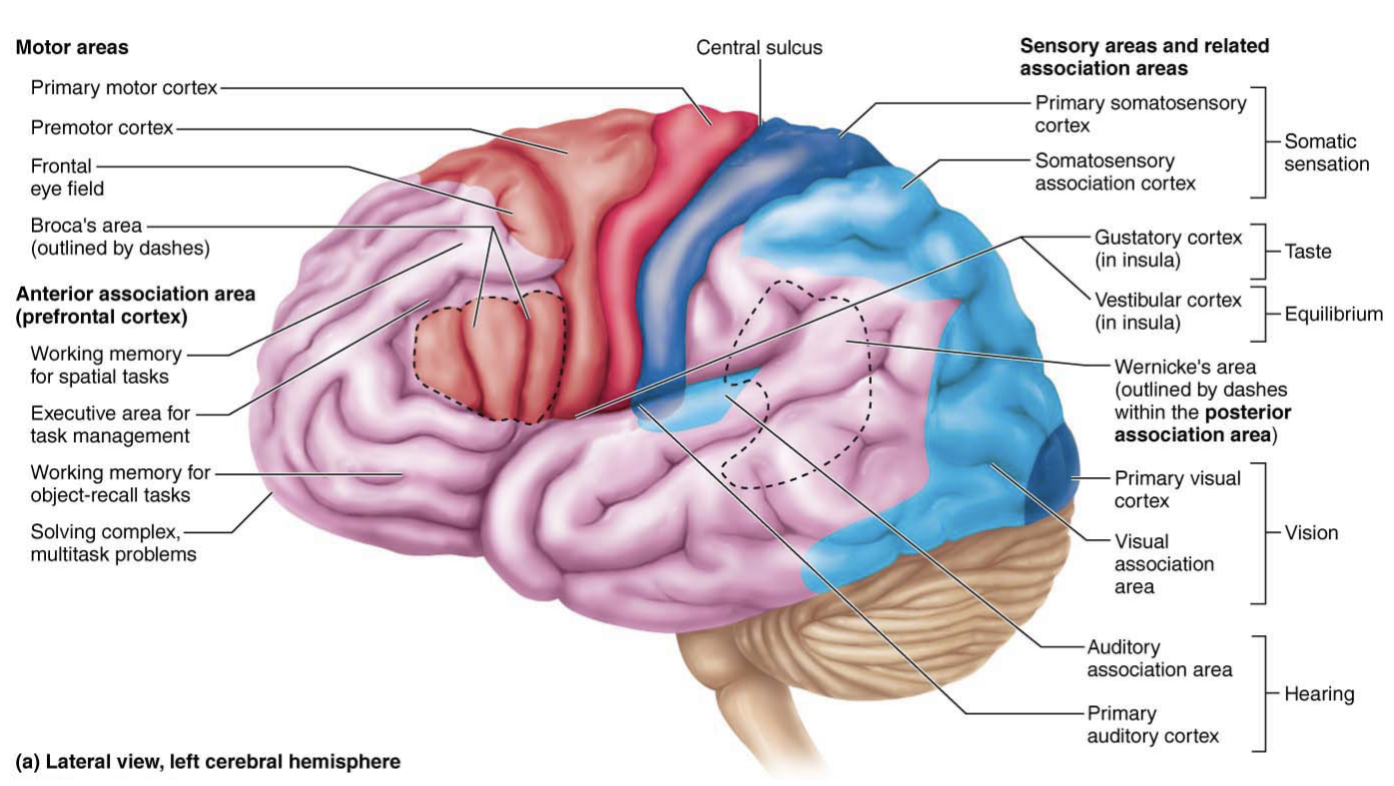
Frontal Lobe
Primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, Broca’s area, and the frontal eye field
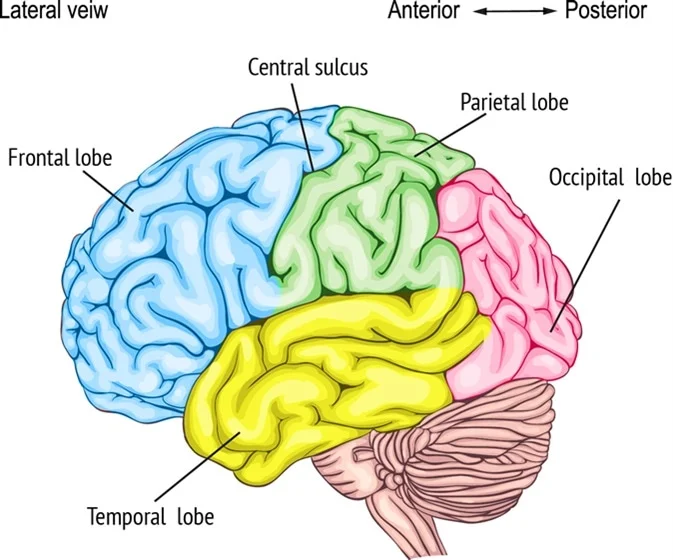
Parietal Lobe
Contains the Primary somatosensory cortex
Is an area that is concerned with conscious awareness of sensation, the sensory areas of the cortex
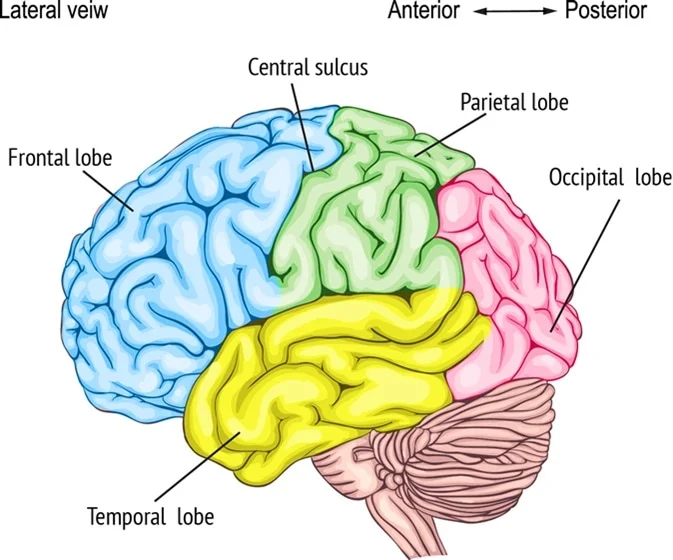
Temporal Lobe
Primary auditory cortex, primary olfactory (smell) cortex, and gustatory (taste) cortex
Is an area that is concerned with conscious awareness of sensation, the sensory areas of the cortex
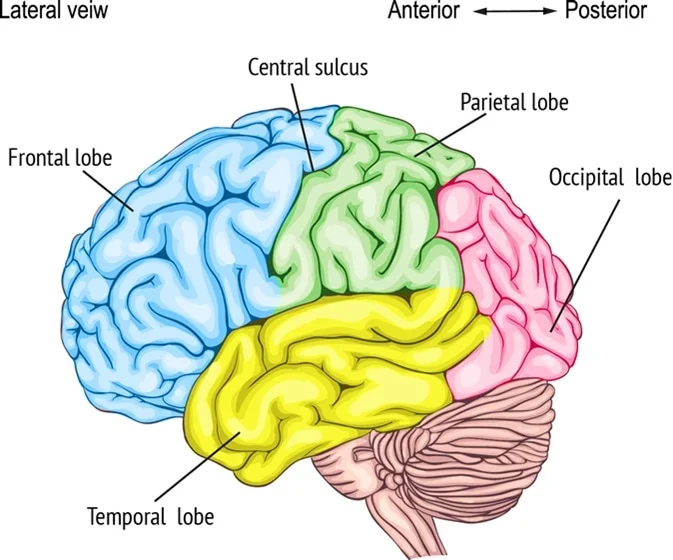
Occipital Lobe
Is an area that is concerned with conscious awareness of sensation, the sensory areas of the cortex
Primary visual cortex, visual association area, and posterior association area
Blood Brain Barrier
Astrocytes facilitate this formation
Prevents many substances in the blood from entering the brain tissue.
Contains tight junctions that ensure substances pass through and not around the endothelium wall
Pituitary Gland
An endocrine organ that is connected to the hypothalamus
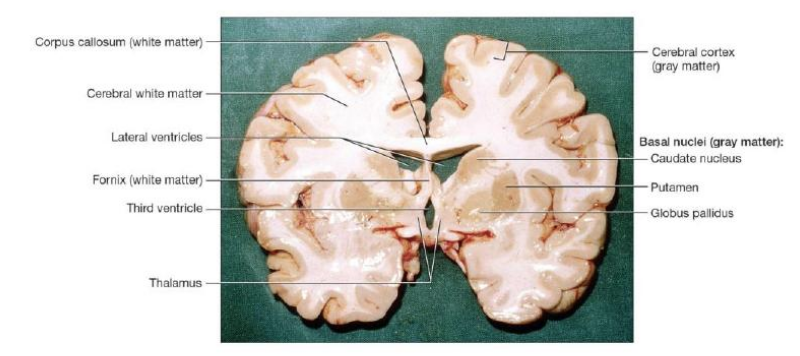
White Matter
Myelinated fibers bundled into large tracts; provides for communication between cerebral areas and lower CNS centers
Limbic System
Contains cerebral and diencephalon
Mediates emotional response
Involved in memory processing
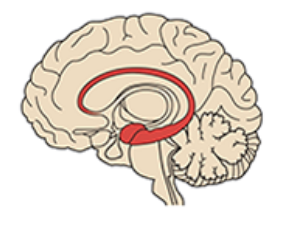
Corpus Callosum
Connects left to right cerebral hemispheres
Arbor Vitae
The cerebellar white matter inside the cerebellum
Has a resemblance to the branches of a tree.
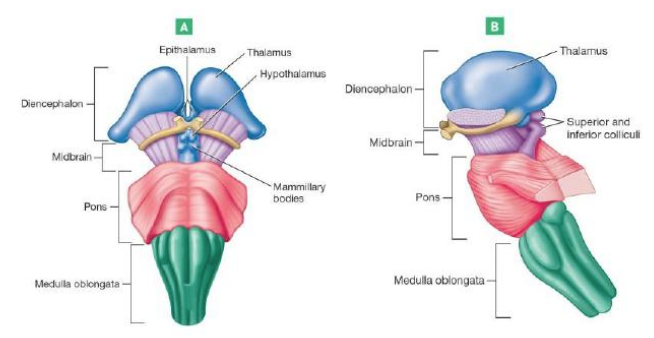
Hypothalamus
Chief integration center of autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
Regulates body temperature, food intake, water balance, thirst, and biological rhythms and drives
Regulates hormonal balance through the pituitary gland (Acts as endocrine organ)
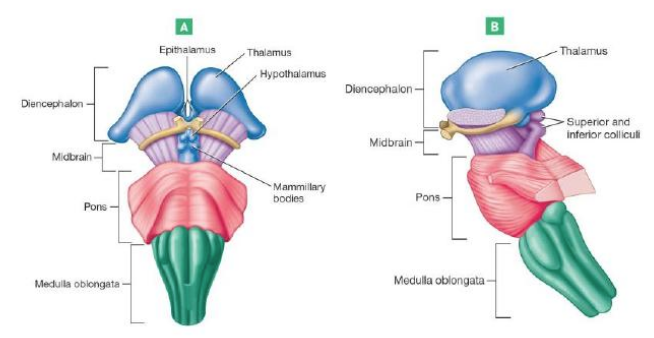
Thalamus
Relays impulses to the cerebral cortex
also Relays impulses to the motor centers & cerebellum
Memory Processing
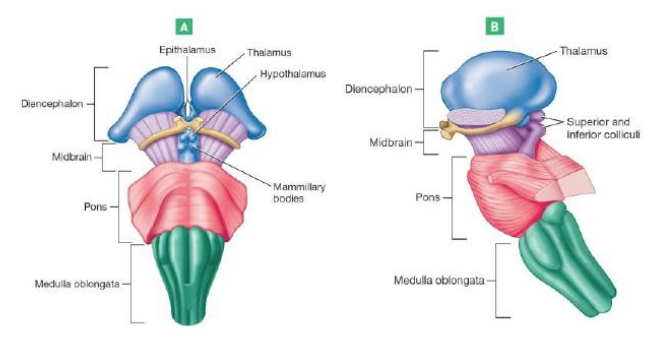
Epithalamus
most dorsal/posterior portion of diencephalon
forms roof of third ventricle
Contains pineal gland: important for secreting melatonin regulates sleep
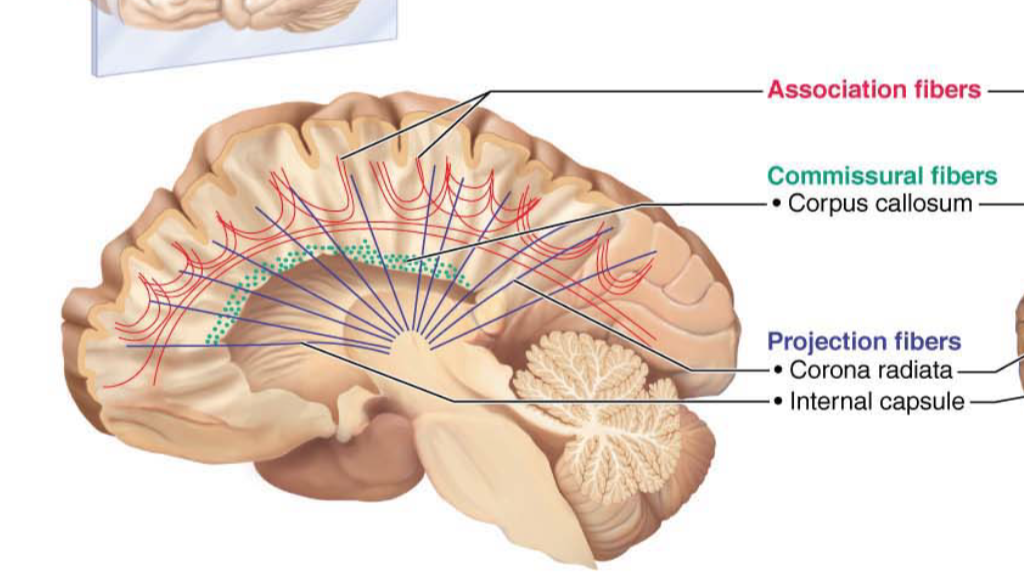
Association Fibers
Connect different parts of the same hemisphere
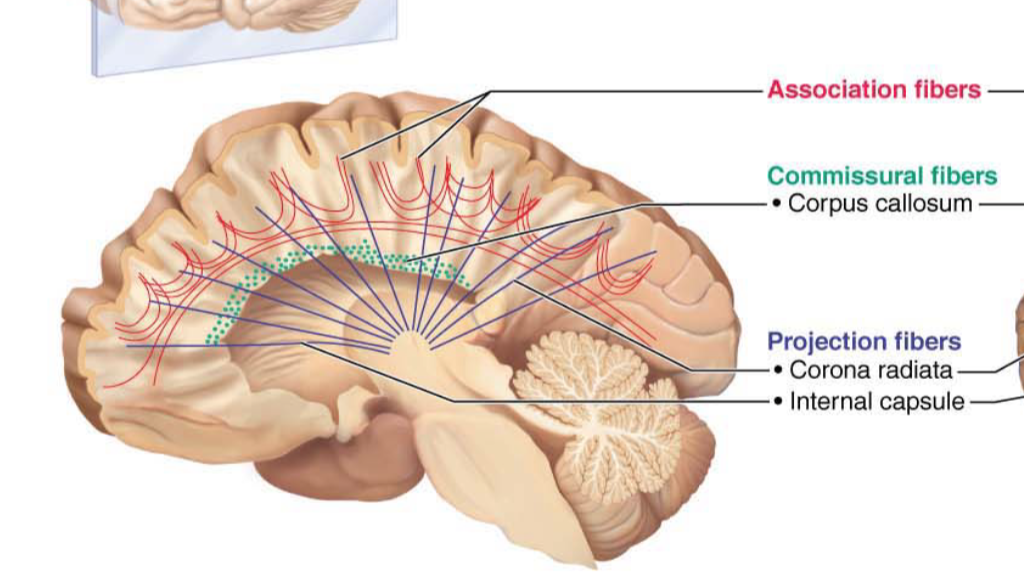
Commissural Fibers
Connect corresponding gray areas of the two hemispheres.
Allow the two hemispheres to function as a coordinated whole.
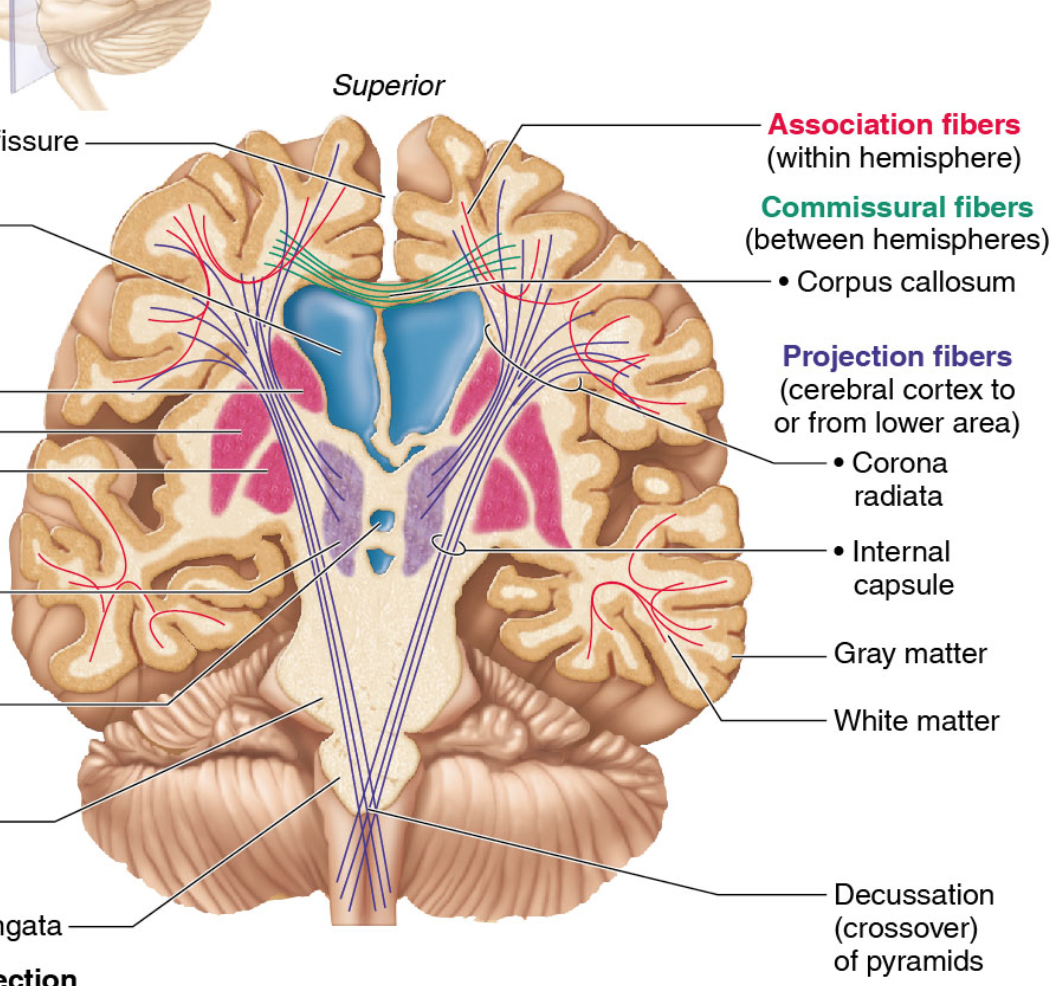
Projection Fibers
A type of white matter tract that connects the cortex with other areas in the CNS
Run horizontally
They tie the cortex to the rest of the nervous system
Grey Matter
Localizes and interprets sensory inputs
Controls voluntary and skilled skeletal muscle activity
Functions in intellectual and emotional processing
Unmylienated
Inner layer in spinal cord
Outer layer in cerebrum & cerebellum
Dura Mater
Outermost and toughest of the three meninges & covers the brain and spinal cord
Double fussed layer and meningeal layer
Arachnoid Mater
Middle meningeal layer. Separated from dura mater by subdural space
Pia Mater
Clings tightly to the brain
Is the last meninge and composed of delicate connective tissue
Subarachnoid Space
Spiderweb like extensions that secure the arachnoid mater to the Pia mater
Filled with CSF
Meninges
Three membranes that surround and protect the brain
Brocas Area
Anterior to the inferior region of the premotor area
Speech production
Activates when we prepare and think about speech
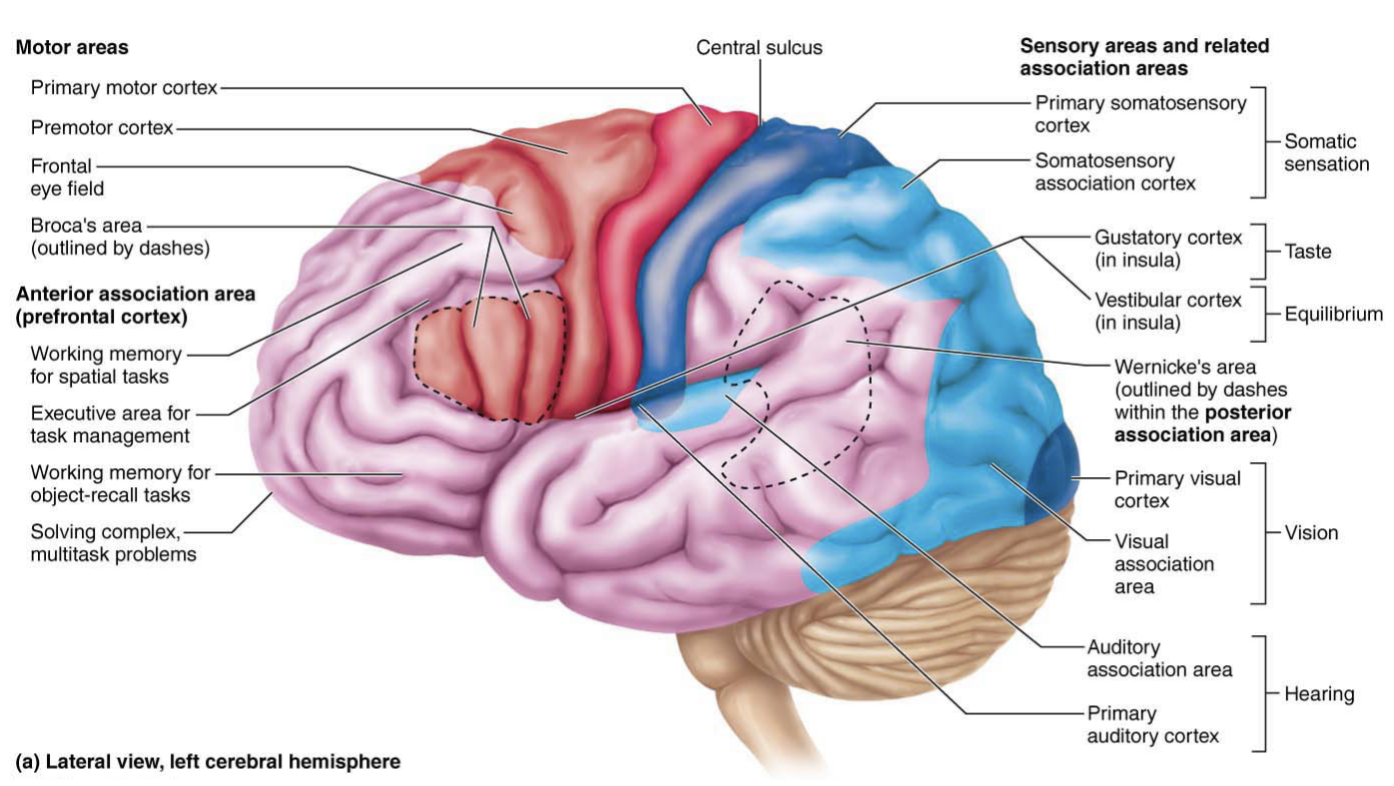
Wernickes Area
Understanding spoken and written language
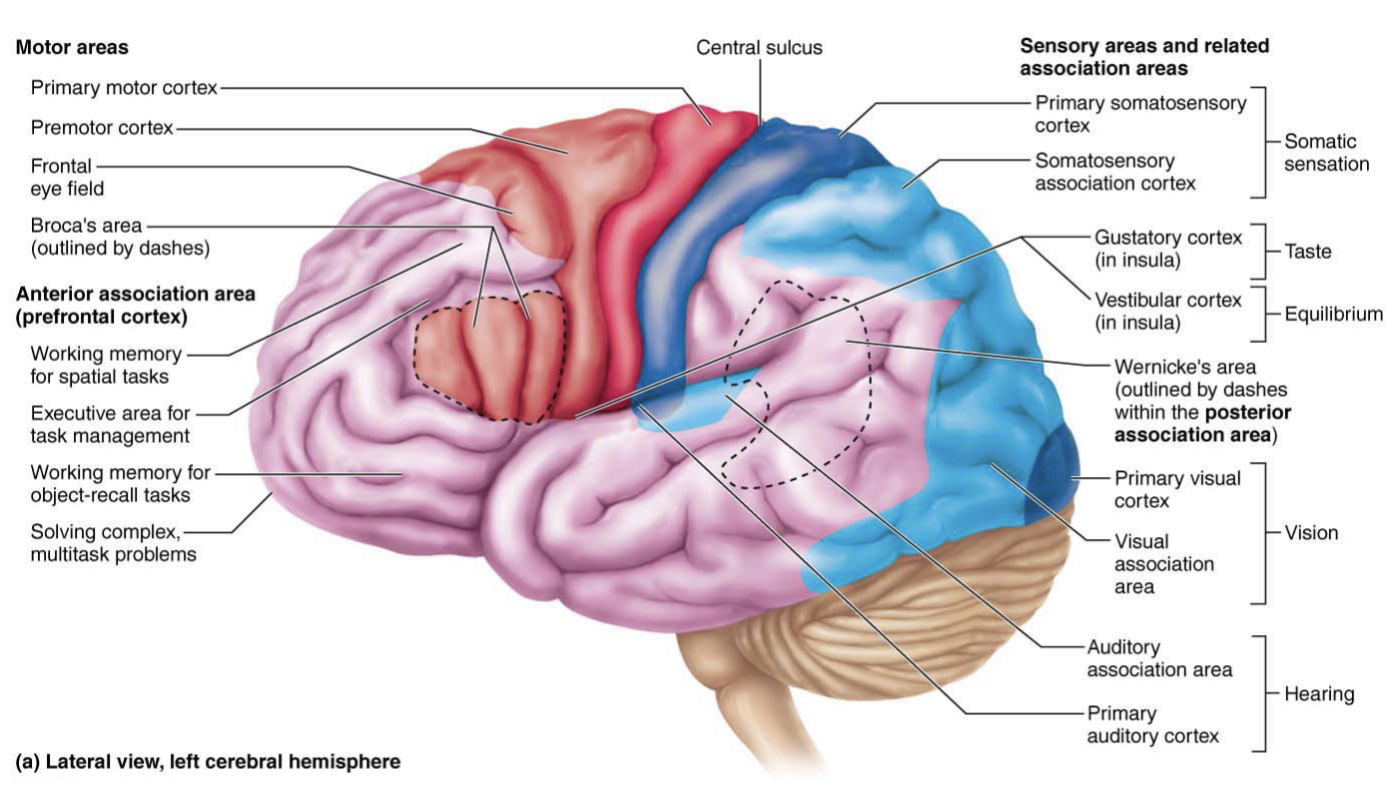
Primary Somatosensory cortex
Conscious awareness of sensation
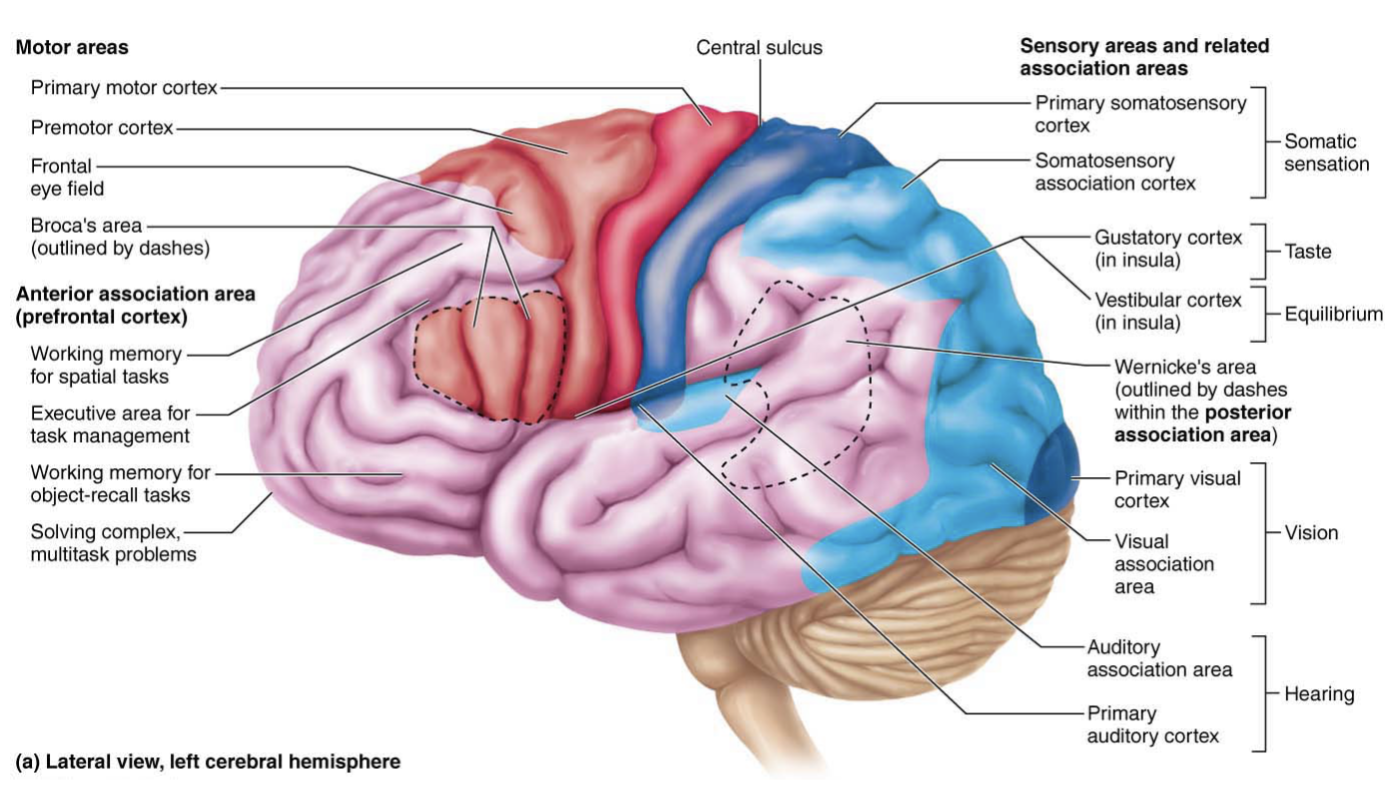
Somatosensory association cortex
helps understand objects ex: size, tempature, texture, shape
Processes information with touch
Ex: feeling into your pocket and being able to identify keys or coins
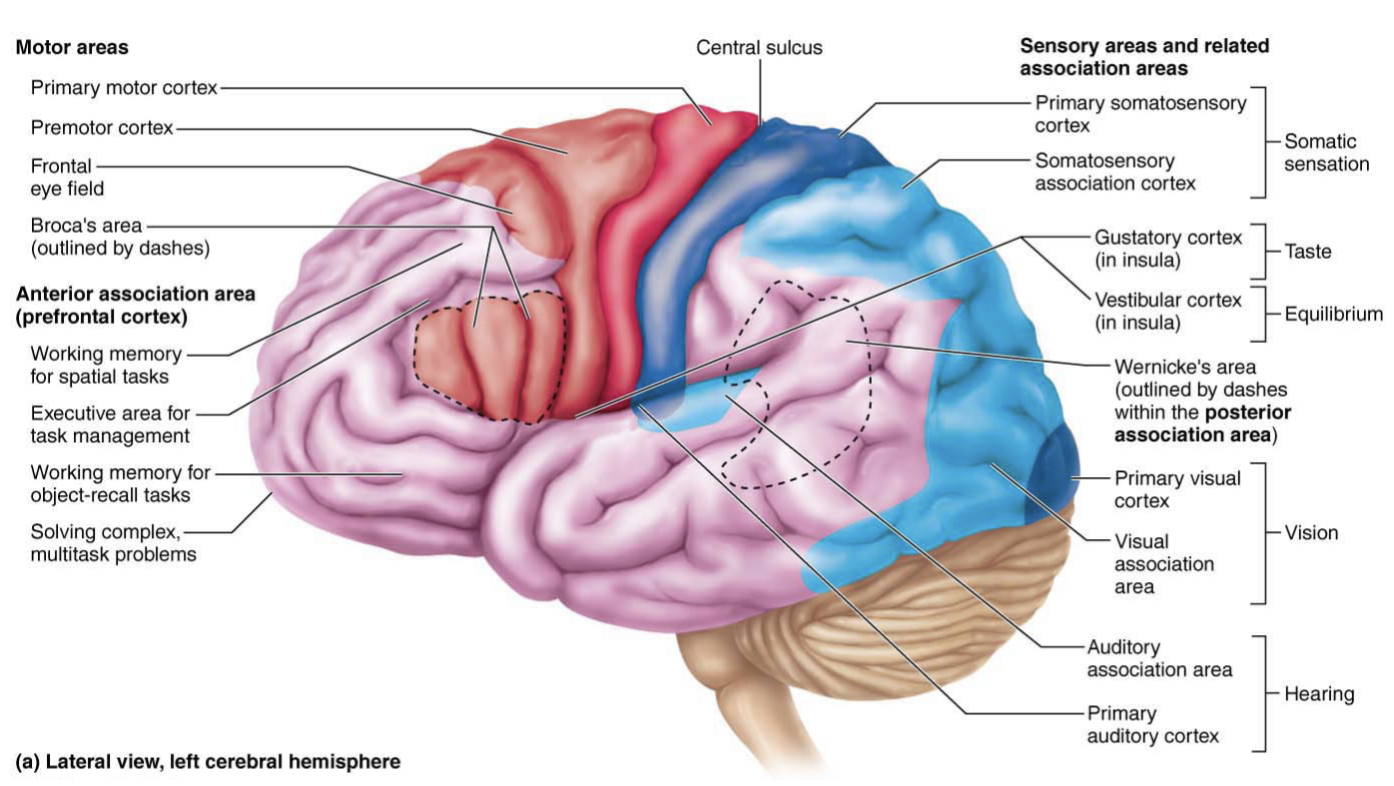
Primary visual (striate) cortex
Posterior tip of occipital lobe
receives visual information from retinas
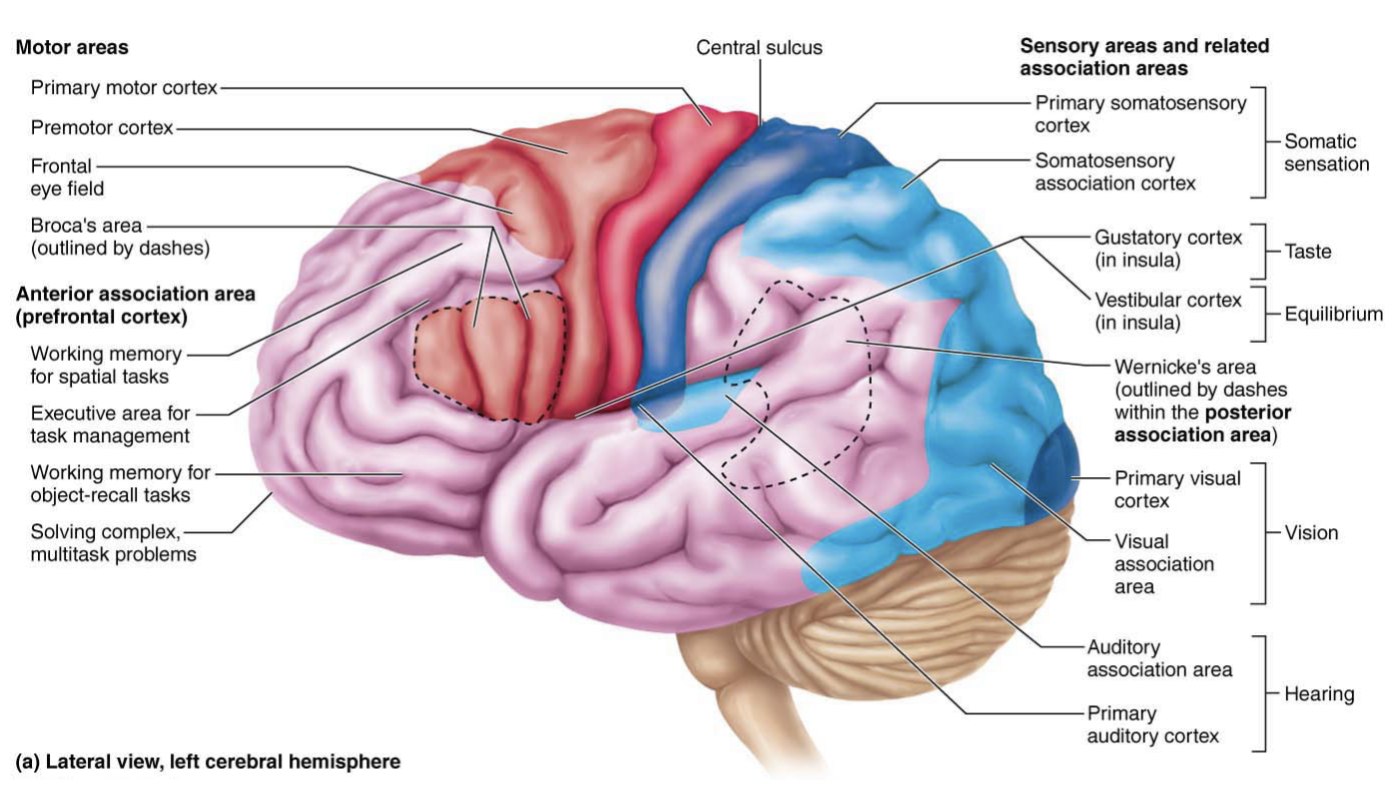
Visual association area
Communicates with the Primary visual cortex to Interpret visual stimuli
Looking at words and being able to understand their meaning
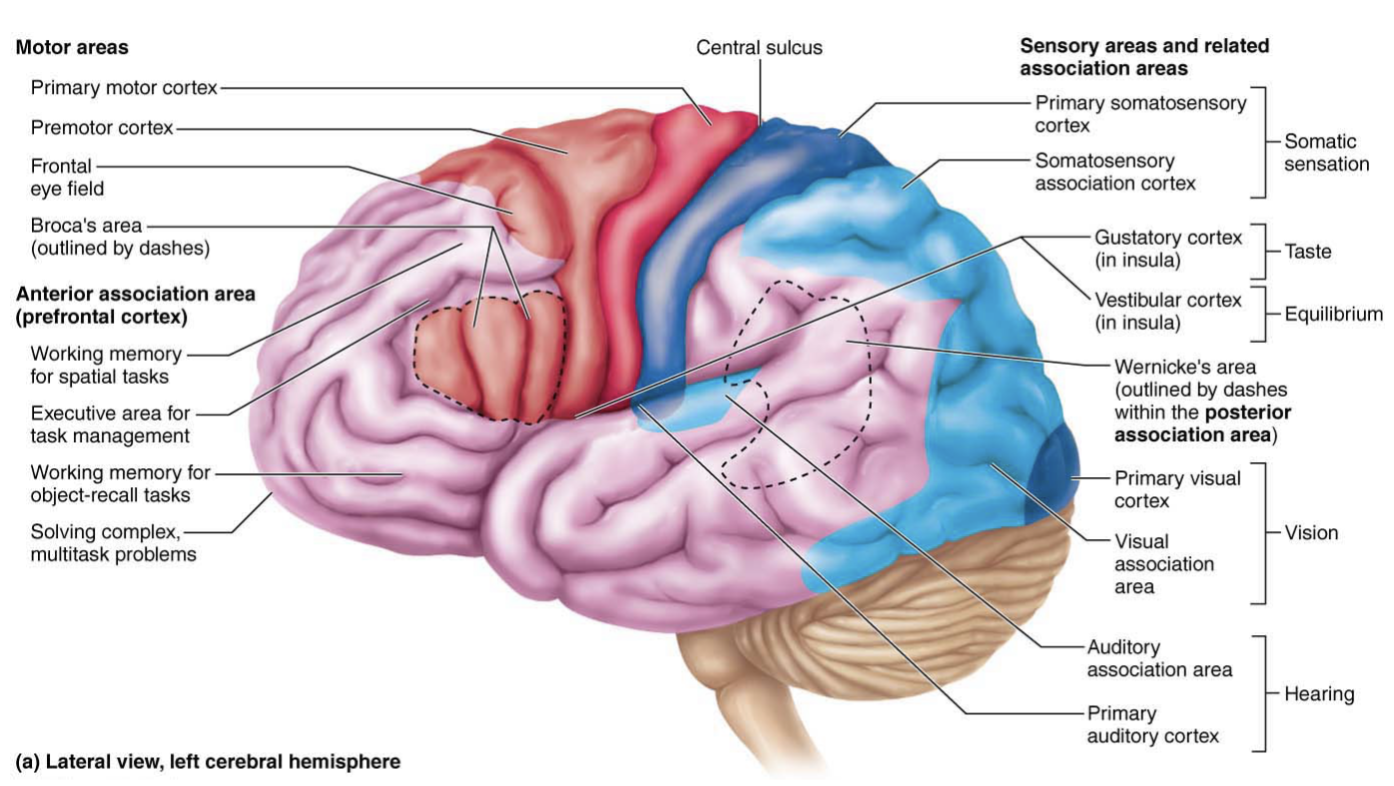
Primary auditory cortex
Located in the superior margin of temporal lobe
Interprets information from the inner ear
ex: pitch, loudness, location
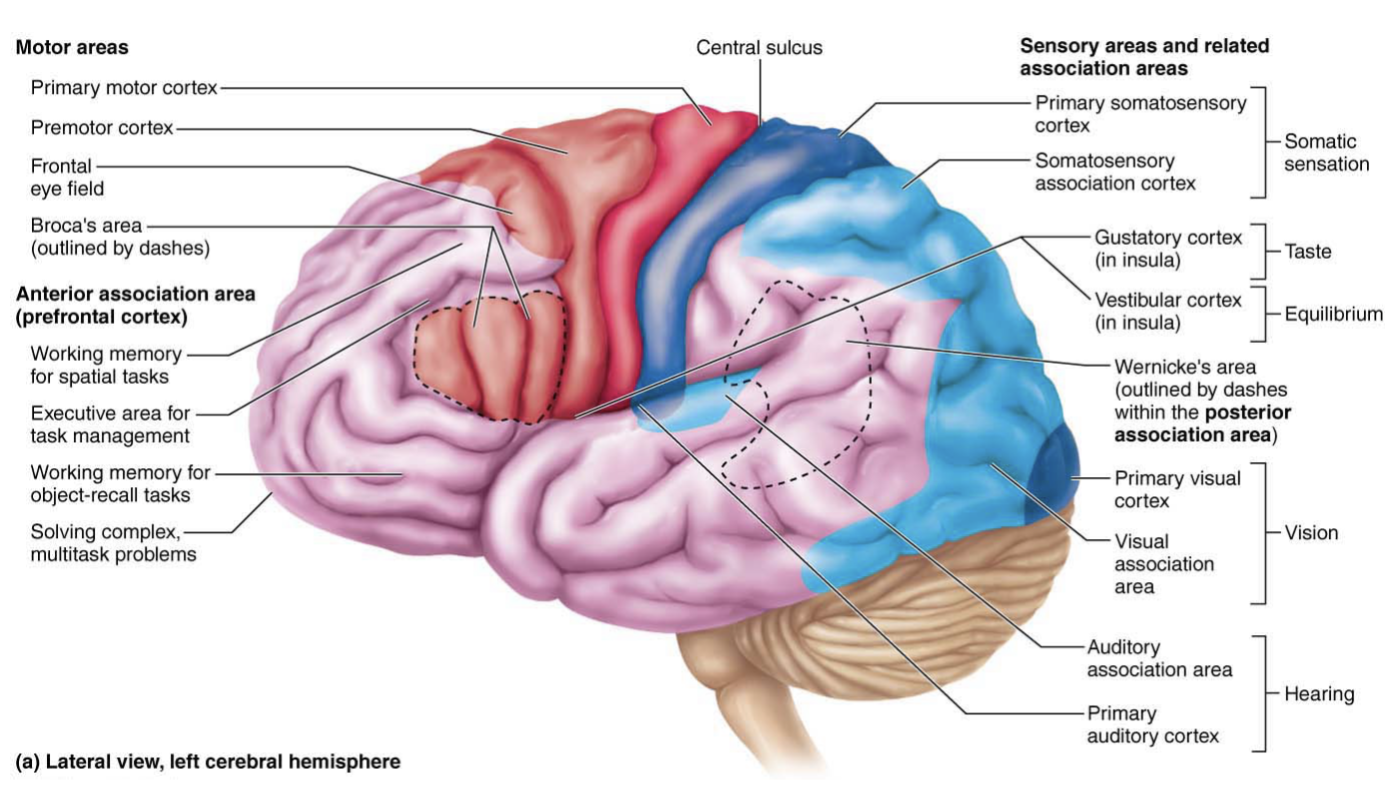
auditory association area
Perception of sound stimulus
Stores memories of sounds from the past
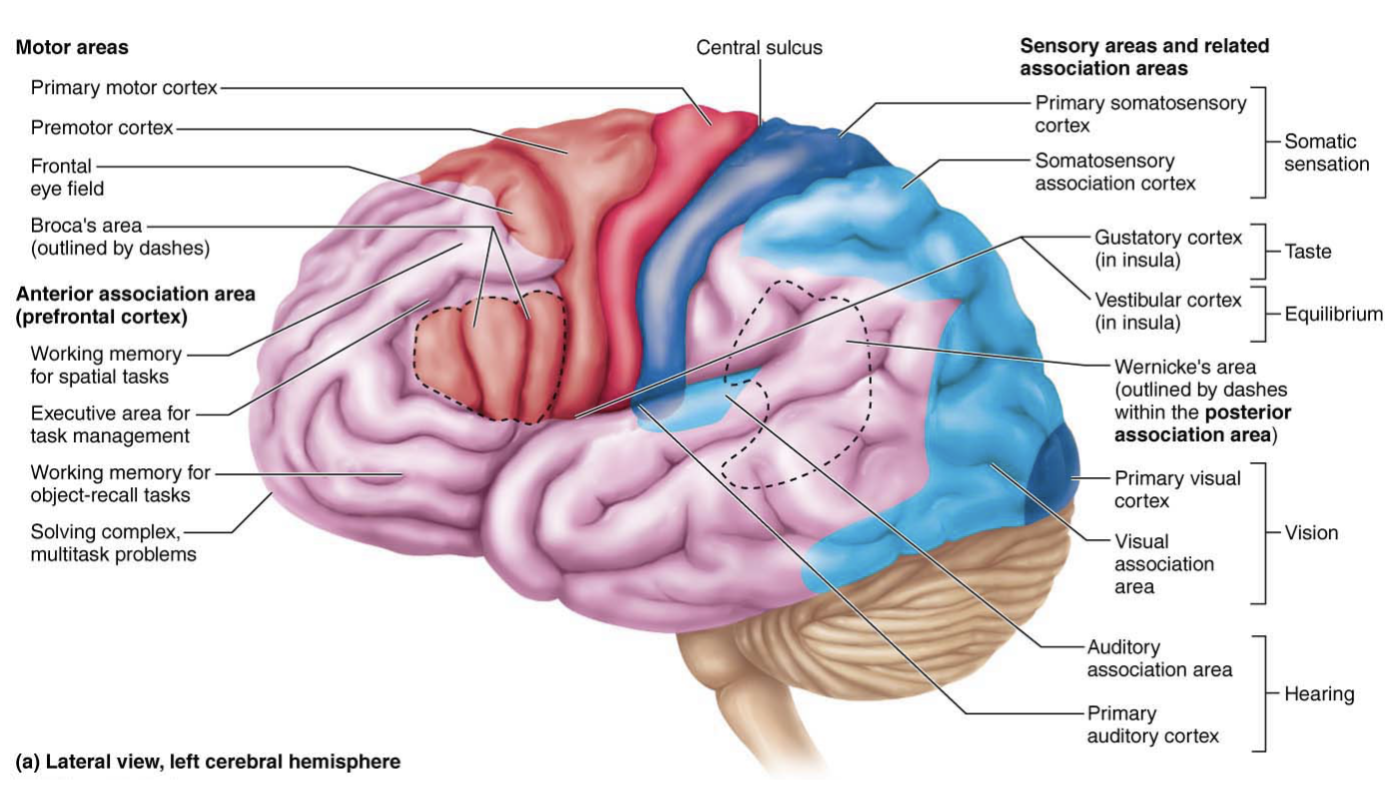
vestibular cortex
Important for balance and the position of our head in space
Being conscious of surrounding and obstacles
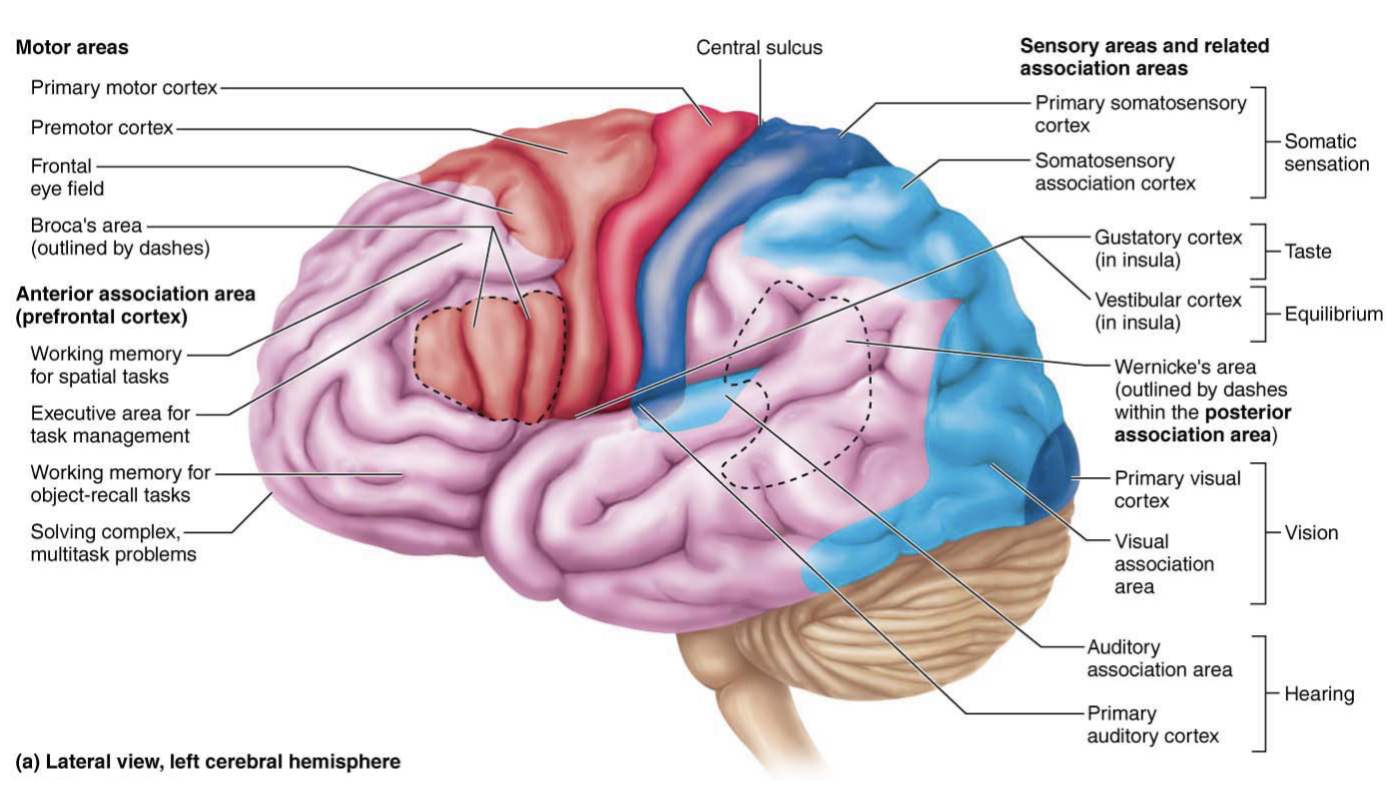
olfactory cortex
Medial aspect of temporal lobe
Conscious awareness of different odors
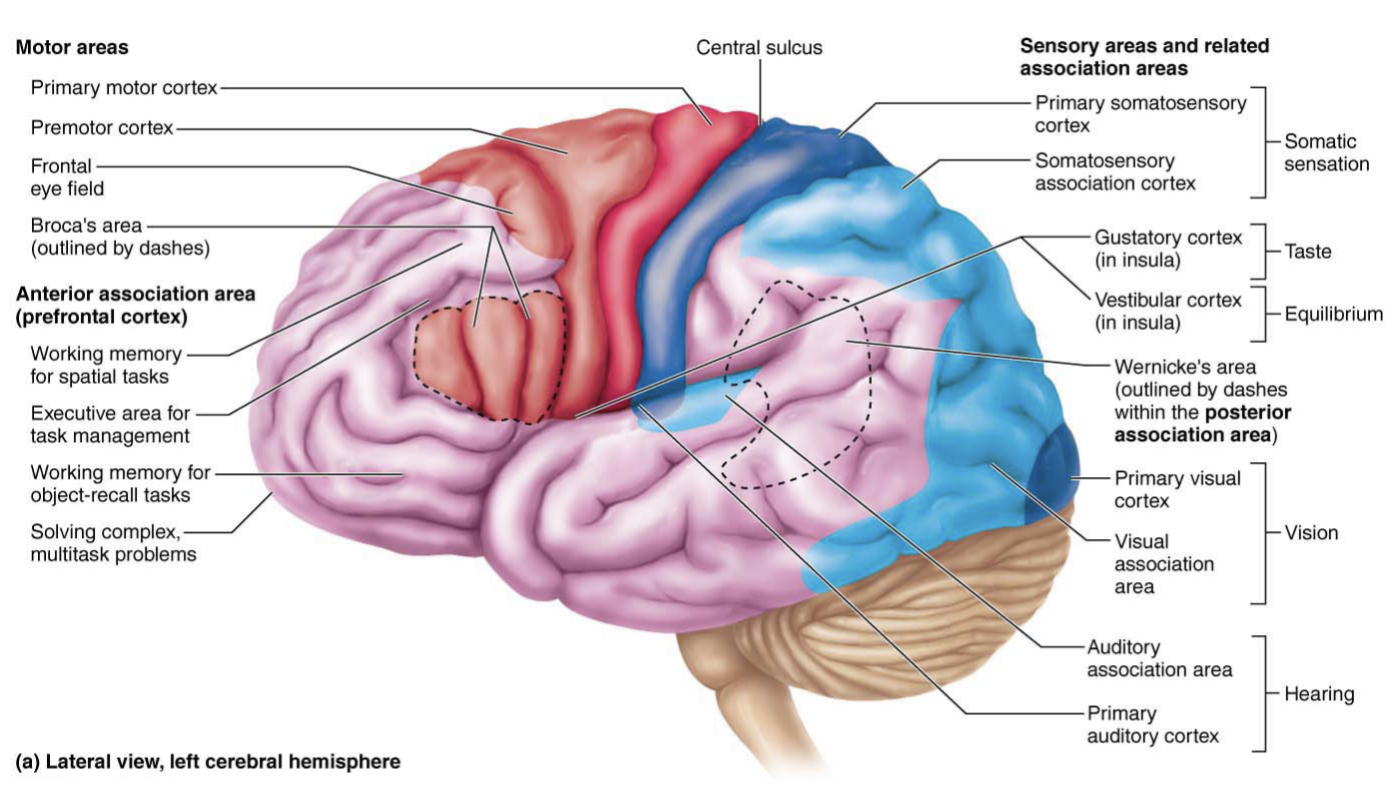
gustatory cortex
Locates in insula, deep to temporal lobe
Perception of taste
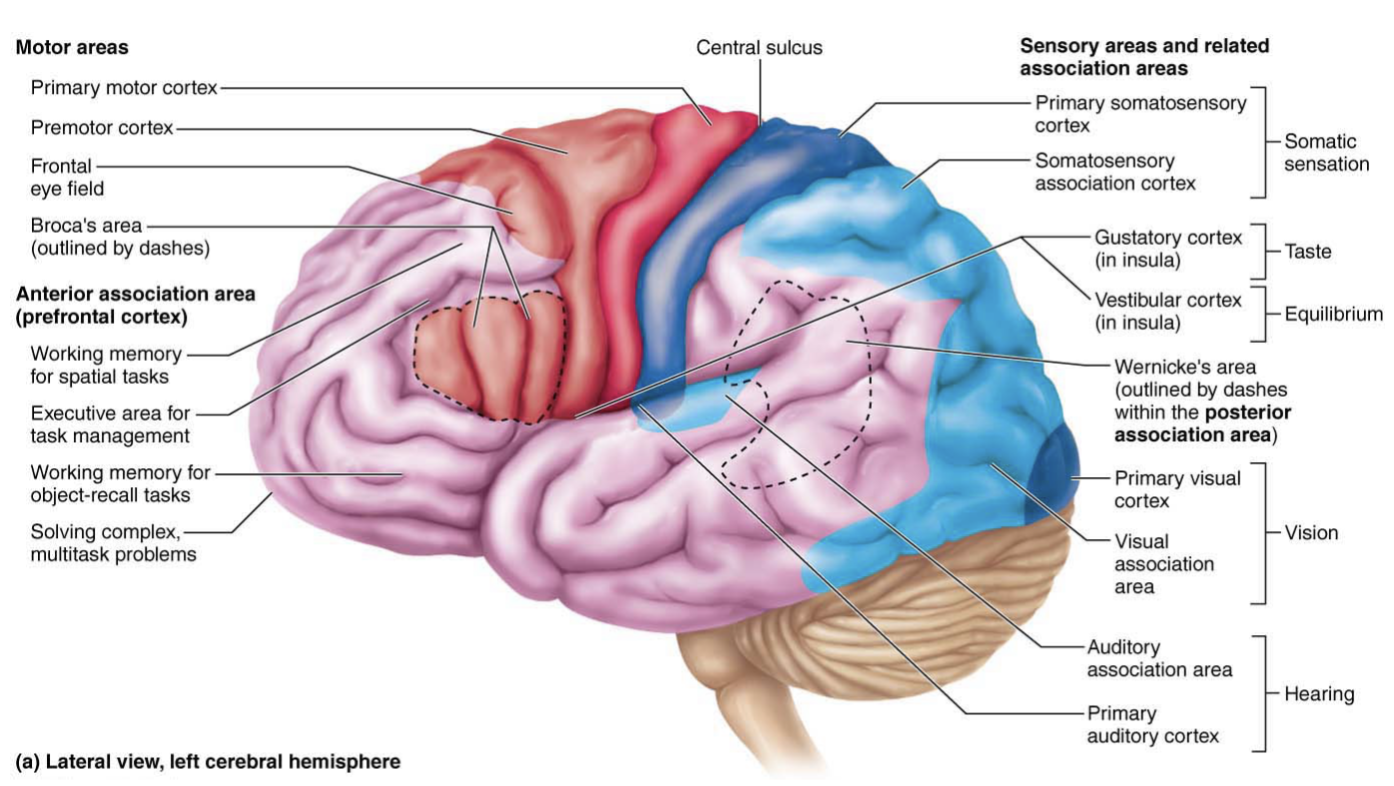
visceral sensory area
Located posterior to gustatory cortex
Conscious perception of visceral sensation
ex: upset stomach, bladder being full, being thirsty
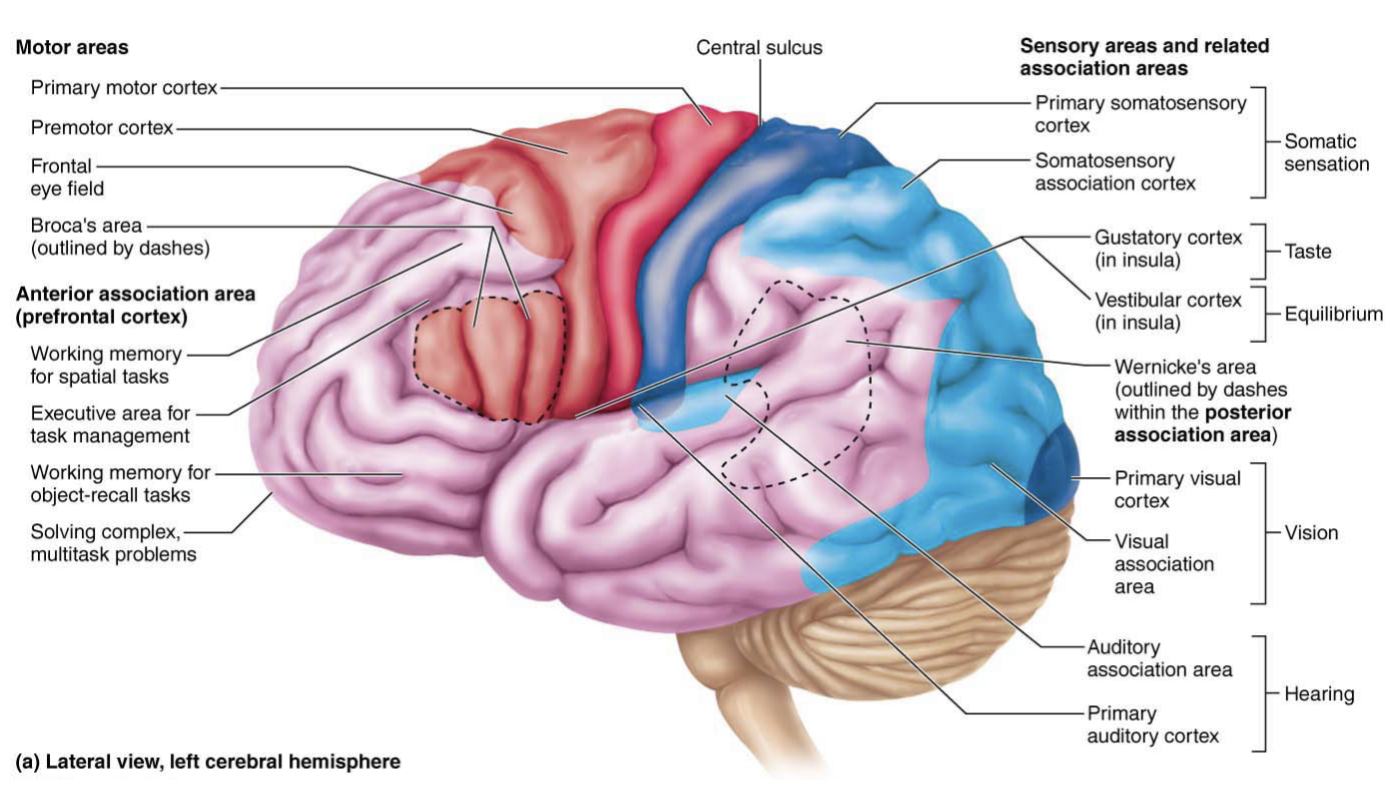
Primary motor cortex
Located in the pre central gyrus of the frontal lobe of each hemispheres
Conscious and precise control of voluntary movement
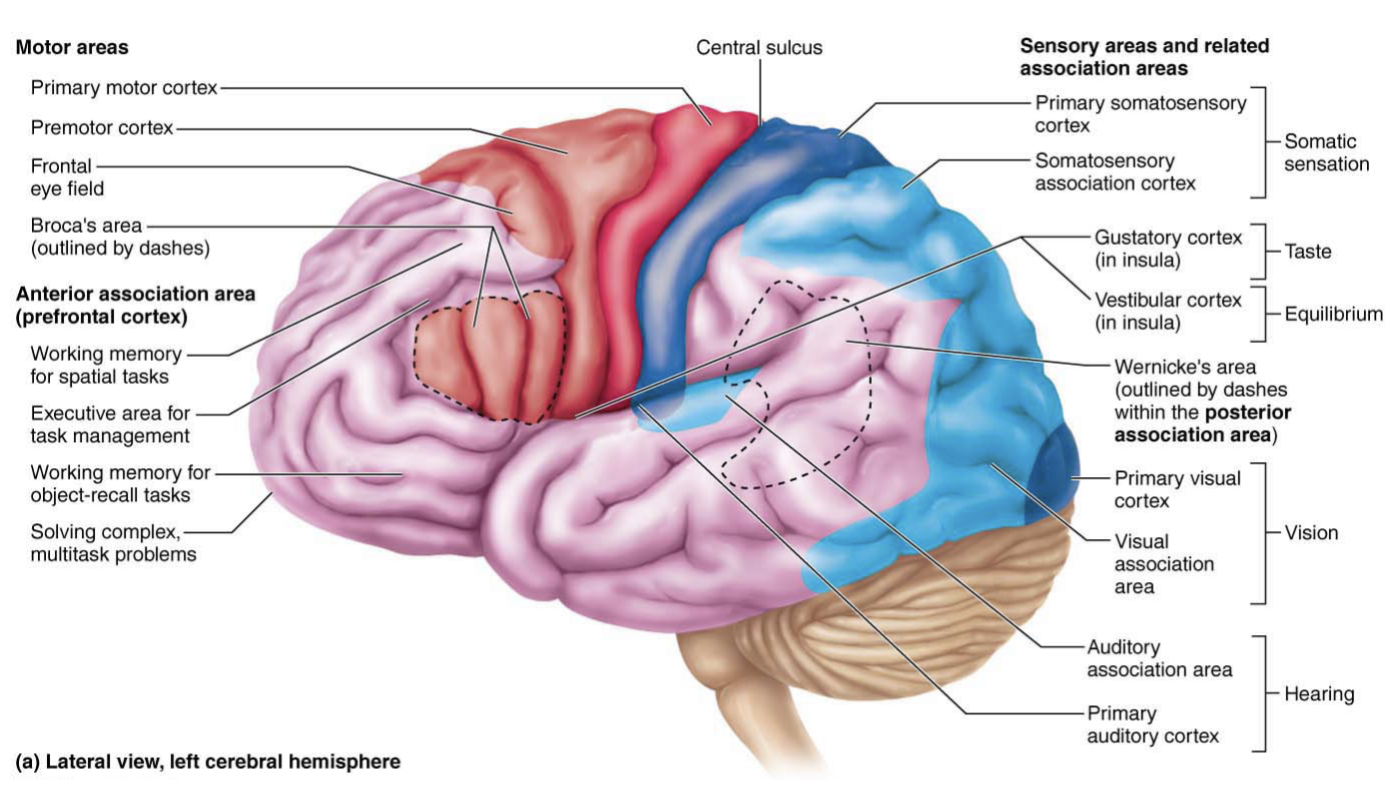
Premotor cortex
Anterior to pre-central gyrus
Controls movement
Damage to this area causes muscle paralysis
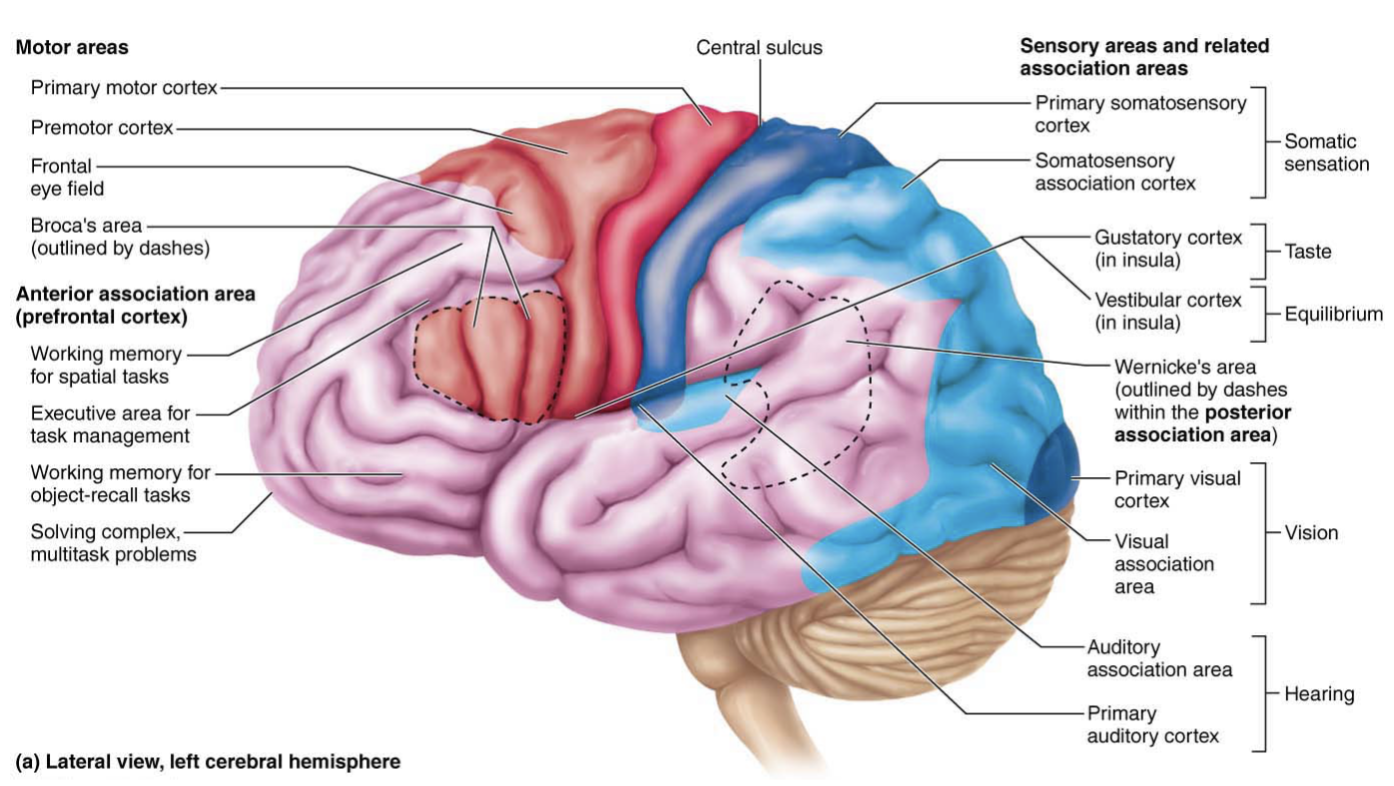
Frontal eye field
Anterior to pre-motor cortex & superior to Broca’s area
Controls voluntary eye movements
Hearing a door open and looking in its direction
Thinking about the sounds around you and responding to them
Pyramidal (corticospinal) tracts
Send information down motor tracts to the spinal cord
Spinocerebellar Tracts
Motor tracts that relay conscious information of the lower limbs and trunk to the cerebellum

Alpha Waves
Awake but relaxed
Frequency 8-13
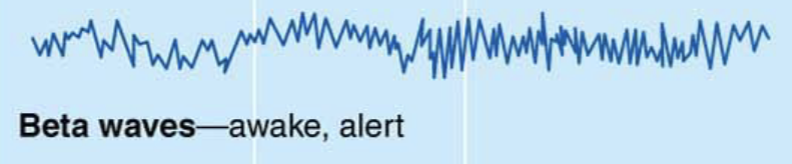
Beta Waves
Awake, alert
Frequency 14-30, Rapid
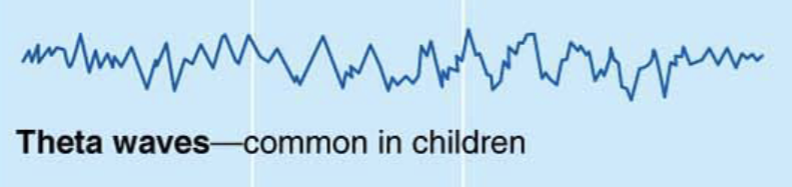
Theta Waves
Common in Children
Frequency 4-7
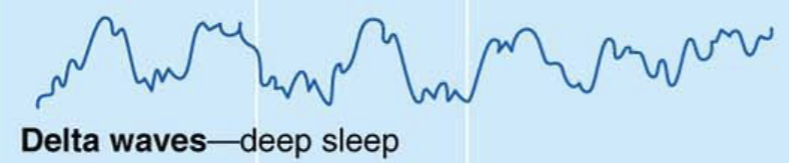
Delta Waves
Deep Sleep
Frequency less than 4
Sleep Stages
Cortical activities are depressed
Brainstem activity is still active (heart rate & breathing)
After abt 90 minutes it will repeat itself

REM sleep
Rapid Eye Movement
Most dreaming occurs
Skeletal muscles are inhibited
Eye muscles & diagram are still moving

NREM Stage 1
Non Rapid Eye Movement
EEG alpha waves, easily awoken

NREM Stage 2
Non Rapid Eye Movement
Irregular EEG patterns, waking up is harder

NREM Stage 3
Non Rapid Eye Movement
Theta & Delta waves, deep sleep occurs…change in breathing

NREM Stage 4
Non Rapid Eye Movement
Delta waves, not waking up to alarms, sleepwalking, night terrors, and bed-wetting may occur
Declarative Memory
Fact memory
Ex: names, faces, words, dates
Short term memory & Long term Memory
Procedural Memory
Memory of skills
Ex: Mariano Rivera
Motor Memory
Muscle memory
ex: riding a bike
Emotional Memory
How we link experiences to emotions
Ex: racing heart after after hearing a rattlesnake
Short Term Memory
Working memory
Can hold 7-8 pieces of information
Long Term Memory
Has limitless amount of memory storage
Hippocampus
Area of brain associated with Memory
Retrograde Amnesia
Can’t remember the past
Anterograde Amnesia
Can’t retain new memories
ex: 50 First Dates
Absence Seizure
Expressions going blank for a moment
Mild seizure
Tonic-Clonic Seizure
Severe seizure
Patients lose consciousness leading to falls, broken bones, and biting of tongue
Can last a few minutes
Aura
Warning signs before a seizure
Reticular Formation
Sleep Cycle
Wakefulness & Consciousness
Insomnia
Chronic inability to obtain the amount or quality of sleep
Orexins
Wake up chemicals
Pre central gyrus
Section of the brain associated with motor activity
Post central gyrus
Part of the brain that is associated with sensory activity
Posterior association area
Allows for the ability to recognize faces
Anterior association area
Higher cognitive functioning such as reasoining, problem solving, and decision making
Prosencephalon (forebrain)
Telencephalon (cerebrum) & Diencephalon
Mesencephalon
Mesencephalon (midbrain)
Rhombencephalon
Metacephalon (pons + cerebellum) & Myelencephalon (medulla oblongata)
Parkinson’s Disease
Dopamine deprived
Basal nuclei become overactive because of the lack of dopamine
Tremors at rest
Huntington’s Disease
High levels of dopamine cause involuntary jerking movements
Contusion
permanent damage to brain
Concussion
Temporary alteration in function
Most common head trauma
Mild/temporary damage
Subdural Hemorrhage
Pressure from blood forces the brainstem through the foramen magnum
Can be fatal
Cerebral Edema
swelling of the brain
How many hours of sleep does a School Age Child Need?
9-12 hours
How many hours of sleep does a Teen Need?
8-10 hours
How many hours of sleep does a Adult Need?
7 or more hours
infundibulum
Stalk of pituitary gland connects the hypothalamus to the posterior portion of pituitary gland
What effects the transferring of memory from short term to long term memory?
Association, Rehearsal, Emotional state, Automatic memory
Damage to the premotor cortex may cause?
Loss of coordination
Lateral Horn
Automatic motor neurons are located
Located in thoracic and lumbar regions
Posterior horns
Contains sensory neurons
Anterior horns
Contains motor neurons
Falx Cerebri
Separates the right and left cerebral hemisphere and houses the dural senses
In longitudinal fissure
Falx Cerebelli
Continues inferiorly from the falx cerebri
Separates cerebellar hemisphere
Tentorium cerebelli
Membranous roof over cerebellum
In transverse fissure
Decussation
Crossing of motor fibers in the medulla oblongata
Emotional State
We learn best when we are alert, motivates, surprised, or aroused
Rehearsal
Repeating the material enhances memory
Association
Tying new information to old information stored in the LTM (Long-Term Memory) helps remember facts
Automatic Memory
Information that we do not store purposely and is unintentionally memorized