Zoology final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:02 AM on 4/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
1
New cards
What are the basic characteristics of Life?
1. biogenesis
2. organization
3. sensitivity
4. metabolism
5. homeostasis
6. movement
7. reproduction
8. life stages
2
New cards
Biogenesis
originates from an organism (asexual) or organisms (sexual) of the same species, not spontaneously.
3
New cards
Organization
composed of one or more cells of the same basic types of atoms and molecules
4
New cards
Sensitivity
responds to stimuli
5
New cards
\
Metabolism
Metabolism
require energy and produce waste products
6
New cards
Homeostasis
maintaining stable internal conditions different from surroundings
7
New cards
Movement
capable of self-generated movement of some type
8
New cards
Reproduction
capable of reproducing
9
New cards
Life Stages
growth and development processes; beginning, growth, maturity, decline, and death
10
New cards
What is life?
Life is the capacity for self-motion (nutrition, growth, decay→ self-initiated & self-directed change)
11
New cards
Hierarchy of Life:
1. elements
2. molecules
3. macromolecules
4. cells
5. tissues
6. organs
7. organisms
8. populations
9. communities
10. ecosystems
11. biomes
12. biospheres
12
New cards
DNA
genetic code for proteins, only found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells but free floating in prokaryotic cells
13
New cards
RNA
serves as the messenger and organizer for building proteins
14
New cards
Cell Theory
1. All living things are composed of cells and their products
2. cells are the basic unit of life
15
New cards
Embryogenesis
Germ layers of cells form that become the external covering and internal structures as an animal develops from a fertilized egg
– When development ends with the invagination, the mouth and anus are at the same place (one opening)
– When development ends with the invagination, the mouth and anus are at the same place (one opening)
16
New cards
Germ Layers
1. Ectoderm
2. Endoderm
3. Mesoderm
17
New cards
Ectoderm
Outer germ layer
18
New cards
Endoderm
Invaginates to for the gastrocoel (the cavity formed w/ opening called blastopore)
19
New cards
Mesoderm
during gastrulation some cells migrate inward to form a 3rd layer b/t the endoderm and ectoderm
20
New cards
Diploblasitc
All Cnidaria have two layers of cells
21
New cards
Triploblastic
Other animals have three layers of cells.
22
New cards
Body Symmetry
geometric design of the parts in an animals body
1. Asymmetry
2. Spherical Symmetry
3. Radial Symmetry
4. Bilateral Symmetry
1. Asymmetry
2. Spherical Symmetry
3. Radial Symmetry
4. Bilateral Symmetry
23
New cards
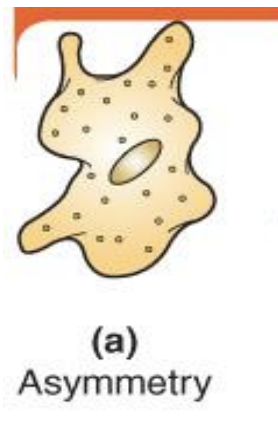
Asymmetry
body lacks any definite form or geometry
24
New cards
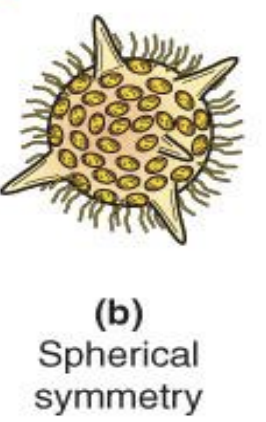
Spherical Symmetry
basically round w/ its parts concentrically arranged around a central point.
25
New cards
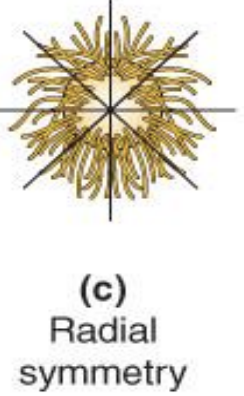
Radial Symmetry
parts arranged around and radiate outward from central axis that is shaped like pie, wheel, or column
26
New cards
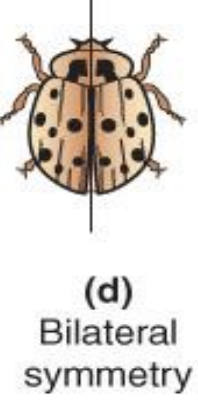
Bilateral Symmetry
two-sided; one side of body mirrors other
27
New cards
Cephalization
development of a head w/ a concentration of sensory organs and a brain. Allows for better motility.
28
New cards
Innate Behavior
Instinctive
any behavior that is stereotypical of the species. All individuals repeat the behavior in a predictable series of steps
any behavior that is stereotypical of the species. All individuals repeat the behavior in a predictable series of steps
29
New cards
Imprinting
learning to recognize and bond to members of your own species
1. Filial Imprinting
2. Sexual Imprinting
1. Filial Imprinting
2. Sexual Imprinting
30
New cards
Filial Imprinting
young animals learn what their parent “looks like” and bonds with them.
31
New cards
Sexual Imprinting
young animal learns the characteristics of a desirable mate
32
New cards
Territorial Behavior
When an organism expend energy to exclude others of its species from an area.
For:
1. food
2. mates
3. protection
For:
1. food
2. mates
3. protection
33
New cards
Home Range
area patrolled by mammal regularly, but doesn’t exclude other individuals
34
New cards
Mating Behaviors
Determined by patterns of interactions b/t males and females
4 Main Types:
1. Monogamy
2. Polygamy
3. Polygyny
4. Polyandry
4 Main Types:
1. Monogamy
2. Polygamy
3. Polygyny
4. Polyandry
35
New cards
Monogamy
one male and one female at a time
36
New cards
Polygamy
males and females have more than one mate
37
New cards
Polygyny
males mate with more than one female
38
New cards
Polyandry
females mate with more than one male
39
New cards
De Buffon
Had no mechanism for change but believed in natural change
40
New cards
Lamarck
inheritance of characteristics caused by environment, need, & behavior
41
New cards
Lyell
principle of geology: slow acting forces have altered earth over time
42
New cards
What year is Darwin’s book?
1860-1882 writes book
43
New cards
common descent
all forms of life descended from a common ancestor through branching lineage
44
New cards
gradualism
many small increments changes over long periods of time generate the large anatomical differences of various species
45
New cards
natural selection
individuals of a species have variations within traits from each other, those with traits allow them to best use the changing environment will survive better and those traits will be dominate in future generations- ‘survival of the fittest’
1. produce more then will survive
2. competition (limited resources)
3. Variations that provide advantages and produce a new species
1. produce more then will survive
2. competition (limited resources)
3. Variations that provide advantages and produce a new species
46
New cards
What mechanism in nature corresponds to selecting hand of man?
Perpetual Change
47
New cards
Natural selection is analogous to what?
look alike because of the survival of the fittest
48
New cards
Homology
study of similarities of features based on descent from a common ancestor
49
New cards
Analogy
the development of similar looking structures by the adapting to similar environments through convergent evolution
50
New cards
Microevolution
change of gene frequency with a population over time, even short periods of time, even short periods of time
51
New cards
Macroevolution
the pattern seen in the tree of life populations are transformed into new species by accumulation micro-evolutionary differences
52
New cards
Mutation
a change in the DNA of an organism, usually occurring because of errors in perlication or repair
53
New cards
Speciation
54
New cards
Genetic Drift
random change
55
New cards
Bottleneck
decrease in population, when it increase there is less genetic diversity
56
New cards
Founder Effect
small number of individuals splinters from a larger population
57
New cards
Gene Flow
genes flow from one population to another
58
New cards
What is taxonomy? who is the founder of modern taxonomy?
scientific classification grouping
nomen name of living things
nomen name of living things
59
New cards
Binomial Nomenclature
developed by Carlos Linnaeus to replace the multiple name system
each species has a name made up of Genus and Species
each species has a name made up of Genus and Species
60
New cards
3 classes of porifera
1. Demospongiae
2. Calcarea
3. Hexactinellida
61
New cards
Demospongiae
most diverse, containing 90% of all living sponges
62
New cards
Calcarea
Calcareous sponges
63
New cards
Spicules
s (skeletal elements) composed of calcareous or siliceous crystalline combined w/ spongin (modified collagen fibers)
– Maintains structure, hold pores open and keep sponge shape.
– Maintains structure, hold pores open and keep sponge shape.
64
New cards
Choanocytes
Collar Cells
65
New cards
Amoebocytes
totipotent cells
66
New cards
Sexual Reproduction
can be external or internal fertilization eggs and sperm; larvae are ciliated and free-swimming
67
New cards
Asexual Reproduction
budding, fragmentation, or gemmules
68
New cards
Aquiferous System
compensates for lack of tissues and organs in gaining nutrients
69
New cards
Osculum
large excurrent opening at top (“door”)
70
New cards
Spongeocoel
interior cavity that opens to the outside through the osculum (“sponge cavity”/atria)
71
New cards
Choanocytes
traps small food particles
72
New cards
Totipotent Cells
repair damage and growth quickly
73
New cards
Plasticity of body form
allows individuals to fill available spaces “quickly” to maximize resources
74
New cards
Three general layers
1. Pinacoderm
2. porocyte
3. choanoderm
75
New cards
Pinacoderm
Outer surface of sponge
Consists of flattened pinacocytes (“skin cells”)
Consists of flattened pinacocytes (“skin cells”)
76
New cards
Porocyte
form ring-shaped openings in pinacoderm that bring water in (incurrent pores)
77
New cards
Choanoderm
inner surface of sponges
Consists of flagellated choanocytes
Consists of flagellated choanocytes
78
New cards
Skeletal Elements
Spicules (produced by the sclerocytes) made of either calcium carbonate (CaCO3 ) or silica dioxide (SiO2 )
Spongin: fibrous protein that adds support similar to collagen
Spongin: fibrous protein that adds support similar to collagen
79
New cards
3 forms of skeletal structure
1. Asconoid
2. syconoid
3. Leuconoid
80
New cards
Asconoid
simple vase-like shape, always small
81
New cards
Syconoid
fold in and out to form finger-like projections to increase surface area
82
New cards
Leuconoid
increased surface area due to chambers with choanocytes
Very efficient at moving water to allow for large body sizes
Very efficient at moving water to allow for large body sizes
83
New cards
Gas Exchange
(O2 in and CO2 out) mainly by simple diffusion
84
New cards
4 class of Cnidaria
1. Hydrozoa
2. Scyphozoa
3. Cubozoa
4. Anthozoa
85
New cards
Hydrozoa
Hydroids
86
New cards
Scyphozoa
true jellyfish
87
New cards
Cubosdzoa
Box jellyfish
88
New cards
Anthozoa
Sea Anemones and Corals
89
New cards
Polyp
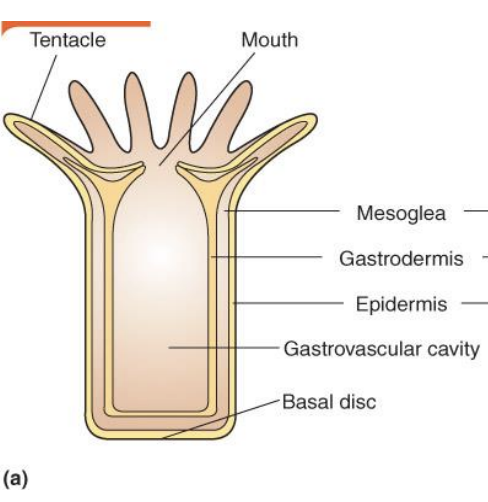
90
New cards
Medusa
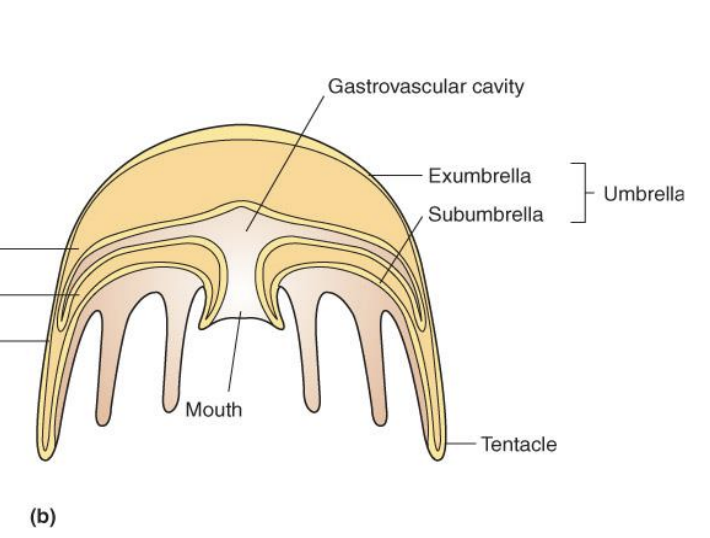
91
New cards
Epidermis
outer layer of cells
92
New cards
Gastrodermis
inner layer of cells
93
New cards
Mesoglea
acellular material derived from the ectoderm w/ few cells living in it
94
New cards
Cnidae
stinging or adhesive cells
95
New cards
alternation of generation
both sexual and asexual reproduction
96
New cards
Hydrozoa
**includes hydra and hydroids**
1. fixed
2. floated
3. independent
1. fixed
2. floated
3. independent
97
New cards
scyphozoa
Skyphos, cup animal
98
New cards
cubozoan
Kybos, cube animal
99
New cards
Life cycle of Aurelia
budding, polyp, strobilation, ephyra, medusa, planula
100
New cards
Anthozoa, what is different?
flower animal