Medical sciences exam 2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
When we produce voice what postion are hte vocal folds in?
Adducted.
what are the 3 key components necessary for phonation to occur?
vocal fold adduction
An exhaled airstream (egressive pulmonary airstream)
vocal fold vibration.
what is an exhaled airstream called?
Egressive pulmonary airstream (from lungs as we breathe out)
As pitch decreases what do the vocal folds do?
shorten.
As pitch increases what do the vocal folds do?
lengthen.
Which muscle contracts to lengthen the vocal folds?
The cricothyroid.
what is a mucosal wave?
repetitive vibration, regular movements of the upper layers of the vocal folds that produces voice.
which CN supplies sensory to the larynx?
CN X vagus
what are the 2 branches of CN X vagus and where do they provide motor supply to?
(paired right and left).
superior laryngeal nerve - motor supply to cricothyroid muscle only.
reccurent laryngeal nerve- motor supply to all intrinstic laryngeal muscles EXCEPT cricothyroid.
How many muscles of facial expression are there and how can they be divided?
14- 10 relate to movement of the lips, 4 relate to movement of other parts of the face.
Which cranial nerve supplies motor function to muscles of facial expression?
CN VII Facial
Which cranial nerve supplies sensation to the face?
CN V trigeminal
what are the 4 muscles of other parts of the face, and what do they do?
Frontalis - raises eyebrows
orbicularis- closes eyes
platyma- tenses skin of neck and lower face
Buccinator- presses cheek against molars.
what are the 10 facial muscles of the lips?
Orbiculars oris (purses the lips and forms lip seal)
Zygomatic minor (raises upper lip)
Zygomatic major (raises and retracts angle of mouth)
Levator anguli oris (raises corners of mouth upwards)
Levator labii superioris (raises upper lip)
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi (raises upper lip and dilates nostril)
Depressor labii inferioris (pulls lower lip down)
Depressor anguli oris (pulls corners of mouth down)
Mentalis (pulls lower lip out to protrude and elevates chin)
Risorius (retracts lips at corners).
Which cranial nerve provides the larynx with sensory supply?
CN X vagus
What is actually vibrating when we phonate and why?
the cover of the vocal fold (layers above the thryoartyenoid muscle) that vibrate
it is due to the upper layers of the vocal folds being blown apart as the exhaled airstream passes though them
the upper layers then immediately come back together again
the proccess of blowing apart then coming back together again to meet in the midline occuts over and over again in repeated cycles.
what causes the repeated cycles of vocal fold vibration to occur?
the exhaled pulmonary airstream generates the cycles of mucosal waves as we breathe out
if the airstream changes then the voice will be effected.
what 4 things happen/are needed for vocal fold vibration to happen?
vocal folds adduct so the vocal folds mucosa of the left and right vocal folds is in contact at the midline
a pulmonary egressive airstream causes the approximated vocal folds to vibrate
vibration is the repetive regular movment of the upper layers of the vocal fold this is known as the mucosal wave
when a person stops speaking the vocal folds abduct and return to the rest postion again.
When do the mucosal wave occur?
when the vocal folds are adducted.
What are the main functions of the larynx?
to protect the airway during swallowing
to produce phonation (voice)
What are the movement patterns of the larynx?
It raises (elevation) and lowers (depression) during swallowing
Vocal folds adduct and abduct
vocal folds lengthen and shorten (to change pitch)
What does the itrinstic laryngeal muscle allow us to do and how?
allow us to produce phonation (voice)
by abducting the vocal folds and altering the length and tension of the vocal folds to vary the pitch of the voice.
What muscles abducts the vocal folds?
Posterior cricoarytenoid- pair of muscles right and left abducts (opens) the vocal folds
where are the arytenoid cartilages and where are they?
move to open and close the vocal folds, do this by the action of muscles that attach to the artneoid cartilages
there are 2, left and right
lie on top of the posterior cricoid cartilage.
what are the 3 muscles that adduct the vocal folds and how are they grouped?
Transverse arytenoid muscle
oblique arytenioid muscle
= collectively known as the inter arytenoid msucles
lateral cricoarytenoid muscles.
what muscle lengthens and shortens the vocal folds?
cricothyroid- pair of muscles left and right.
What does the cricothyroid muscle do?
tips the thyroid cartilage forwards and down.
this lengthens space between thyroid cartilage and the arytneoids, stretching and thinning the vocal folds
voice increases in pitch as the vocal folds stretch and become longer.
What is the thyroarytenoid and where is it?
the muscle that lies within the true vocal fold itself
pairs of muscles left and right.
tenses and relaxes the vocal fold and helps with adduction.
Which CN supplies motor function and sensory supply to the mucosa lining and internal larynx?
All CN X vagus
Which CN provides sensory nerve supply to the larynx?
Vagus nerve CN X
superior laryngeal nerve branch: provides senosry supply to the laryngeal mucosa.
Which CN provides motor supply to they larynx?
Vagus CN X
branches paired right and left.
What is the neurocranium?
Houses + protects the brain.
What is the visceriocranium?
supports the face, includes the mandible.
What are the bones of the neurocranium?
1. Frontal
2. Pariental
3. Occipital
4. Temporal
5. Sphenoid
6. Ethmoid
What can the skull be broken into?
neurocranium and visceriocranium
What bone of the neurocranium cannot be seen from a lateral view and what is it?
The Ethmoid bone
located between lateral wall of the nose + medial wall of the orbit (eye socket)
forms parts of roof and lateral wall of the nose.
Where is the sphenoid bone?
Not just the part you see on external neurocranium, also forms part of the base of skull.
What are the 8 bones in the visceriocranium?
1. Maxilla
2. Zygomatic
3. Lacrimal
4. Nasal
5. Vomer
6. Nasal Turbinates (conchae)
7. Palatine
Mandible
What bones form the hard palate?
The maxilla and the palatine bone
What can the conchae be divided into?
superior nasal concha
middle nasal concha
inferior nasal concha
Tell me about the Nasal Cavities
Divided into the right and left by the nasal septum
3 bony plates: the turbinates (cochae) project into the cavities to increase surface
Covered in respitory mucosa
Purpose- to warm, filter and humidfy air.
External nose is formed by the nasal bone and cartilage.
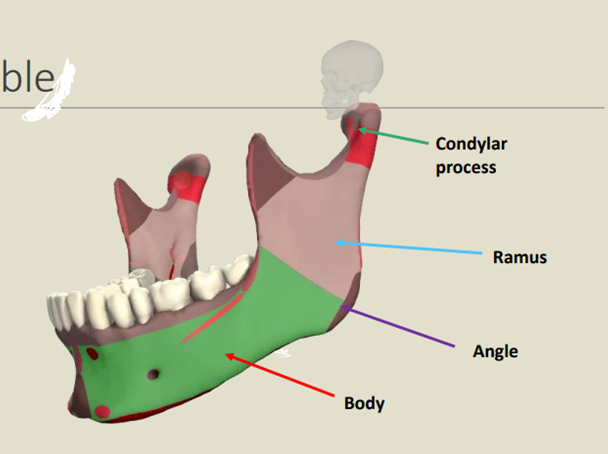
Name the parts of the mandible bone
Condylar proccess
Ramus
Angle
Body
What are the sinuses we need to know?
Frontal
Ethmoid
Maximallary
Sphenoid
All are paired (left and right cavity for each)