AICE Environmental Management AS Level Exam Review (UNITS 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8)
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
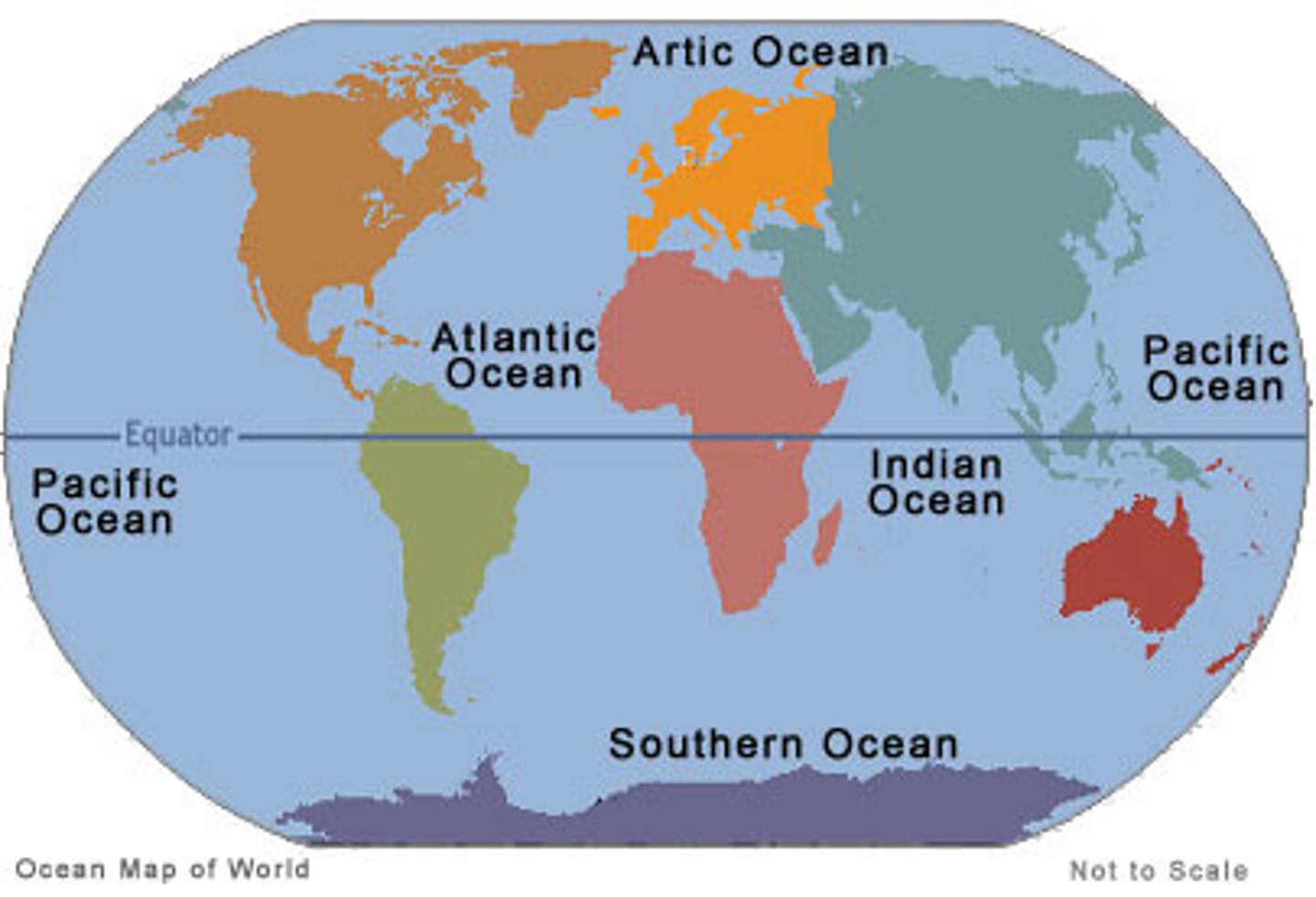
identify & name world's continents and major oceans
WTR: PAAIPS acronym. look at how the oceans are lined up (pacific, atlantic, arctic, indian, pacific again, and then southern at the bottom)
low income country
gross national income under 1k (afghan)
middle income country
gross national income btwn 1000-13000 (egypt)
high income country
gross national income above 13000 (US)
sustainability
ability to meet needs of present w/o compromising ability of future generations to meet their own needs
condensation
gas -> liquid
precipitation
any form of water from clouds
interception
water can't reach surface bc trees/grass
infiltration
water on ground surface enters soil
surface run-off
water stays on soil SURFACE, RUNS OFF to source
through flow
water FLOWS THROUGH the soil
groundwater flow
water flows beneath ground
transpiration
water evaporates from plant leaves
earth's major atmosphere gases
WTR: "NOCAWT"
nitrogen,
oxygen,
carbon,
argon
water vapor
trace gases
atmosphere layers
(farthest -> closest)
WTR: TMST mnemonic - the mess started there
thermosphere
mesosphere
stratosphere
troposphere
ozone layer
in the stratosphere, absorbs portion of sun's UV rays preventing skin cancer and cataracts.
natural greenhouse effect
- UV rays goes thru atmosphere & get absorbed by earth's surface
- some of that energy goes back into the atmosphere as IR rays
- greenhouse gases absorb the IR rays & prevent it from leaving the atmosphere.
biome
broad area of similar ecosystems, soils, and climates spread out around world based on latitude
ecosystem
place where organisms meet needs (food, shelter, water)
habitat
natural enviroment where organism lives
population
# of individuals of same species/area/time
community
grps of diff organisms living @ same place/time
niche
organism role in ecosystem
biotic factors of an ecosystem
- producers
- consumers (1st, 2nd, 3rd)
- decomposers
abiotic examples
- temperature
- humidity
- water
- oxygen
- salinity
- light
- pH
biotic interactions
- competition (interspecific & intraspecific)
- grazing
- predation
grazing
wild herbivores eat grass
WTR: graz = grass

biotic factors affecting organism size/diversity
- disease
- predation
- parasitism
- competition
photosynthesis word process
plants synthesis glucose using carbon dioxide, water and energy from sunlight
in land/oceans, it's a vital part of the carbon cycle & has important effect on CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere by forming carbon stores.
photosynthesis word/chemical equations
6CO2 + 6H2O →light→ C6H12O6 + 6O2
carbon dioxide + water →light→ glucose + oxygen
photosynthesis rate limiting factors
- water/light availability
- CO2 concentration
trophic levels
feeding levels within food chains
food chain
energy transferred btwn organisms, starting w/ producer
how much energy is lost in food chains?
90%
aerobic respiration chemical/word equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
aerobic respiration
chemical reactions in cells breaking down glucose molecules & releasing energy, CO2, and water
factors influencing whether to use random/systematic strategy
- size
- ease of access
- environment knowledge
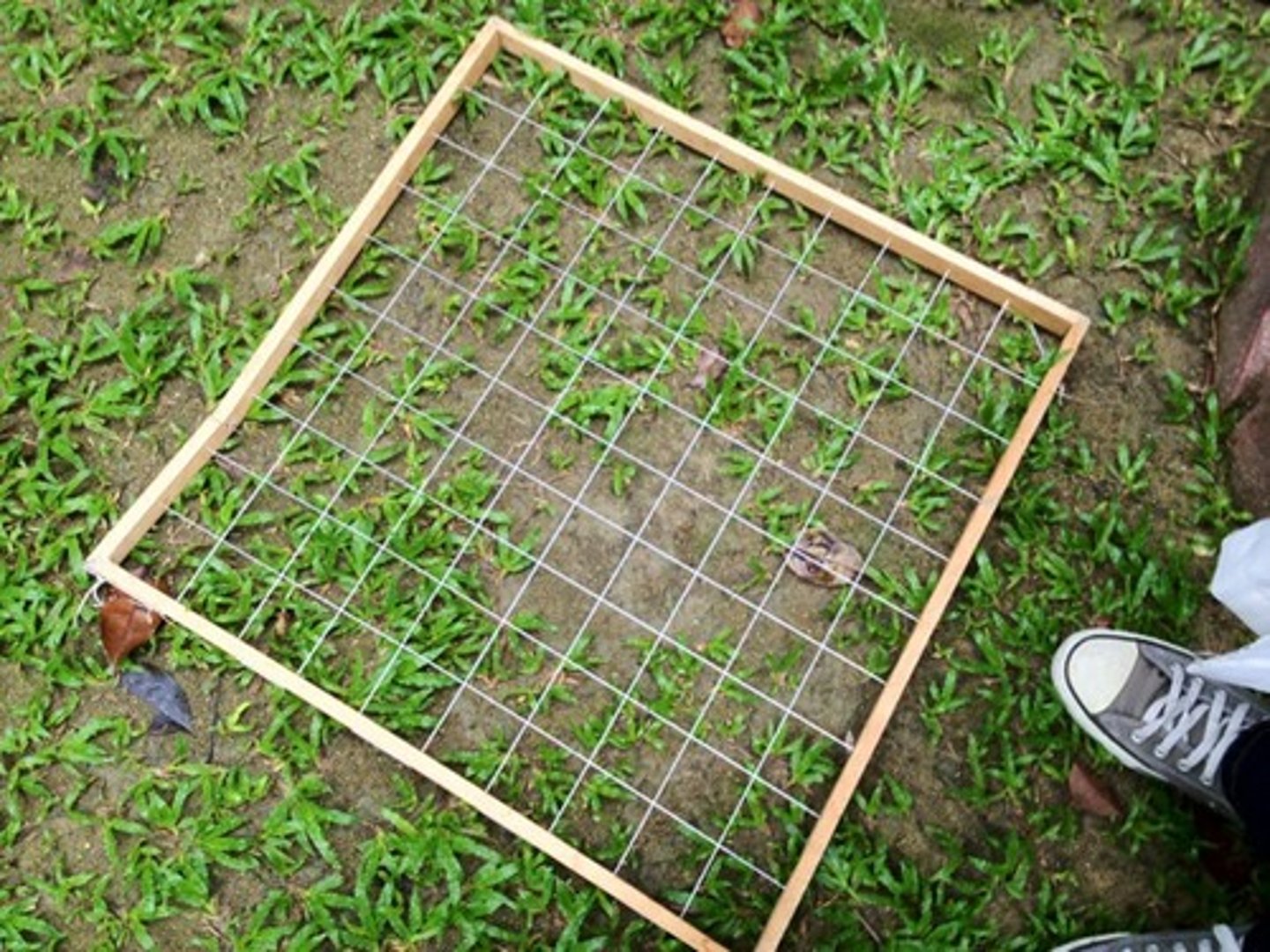
frame quadrat (pros & cons)
square frame divided into small grid. species type & number in each grid is recorded.
- easy to collect sample
- easy to estimate size
- can be time-consuming
- may not be evenly spaced

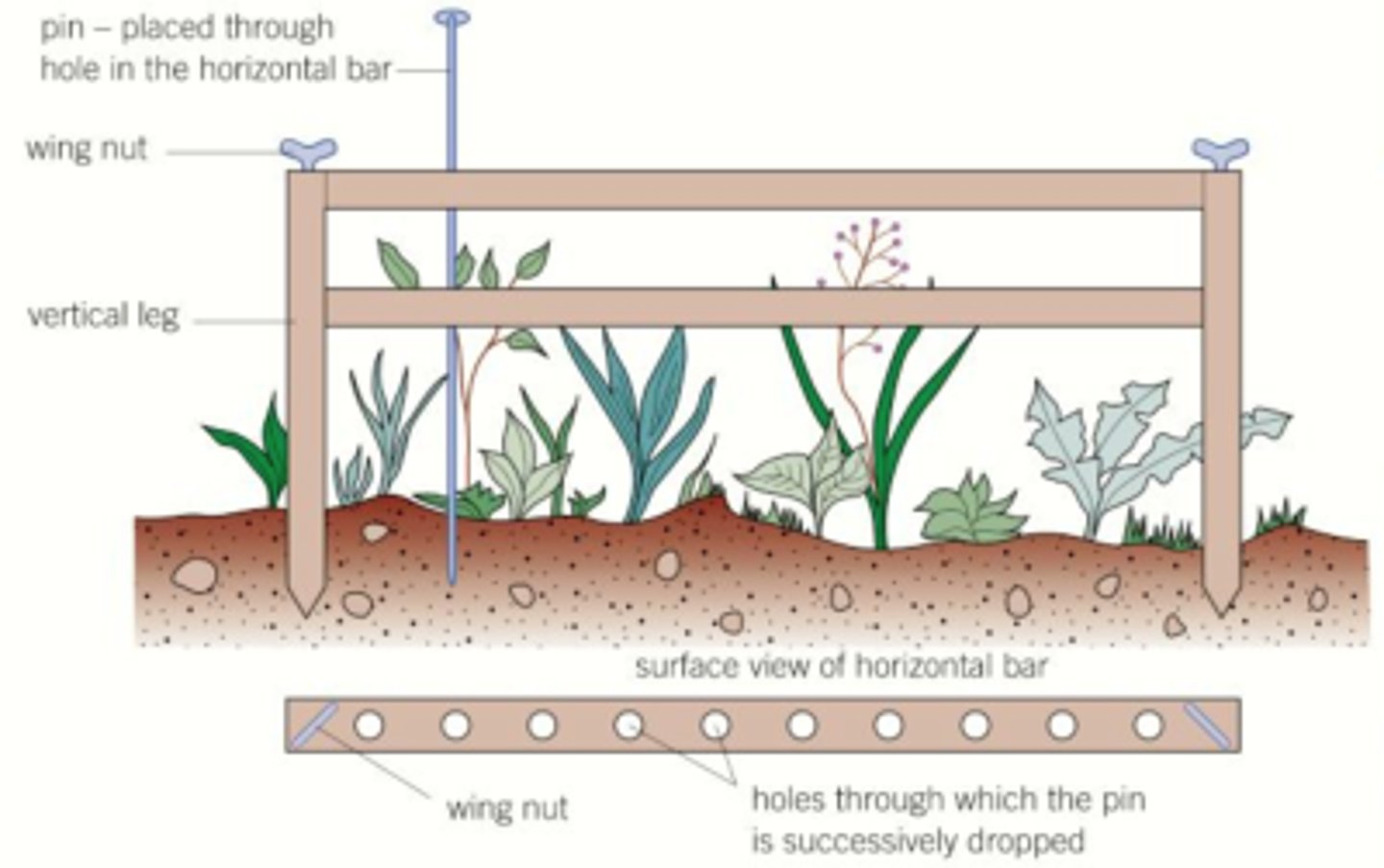
point quadrat (pros & cons)
frame w/ horizontal bar & set intervals for points in ground. each plant touching point is recorded.
- accurate bc u can see the plant touching point
- easy to collect data
- can damage plant
- time consuming
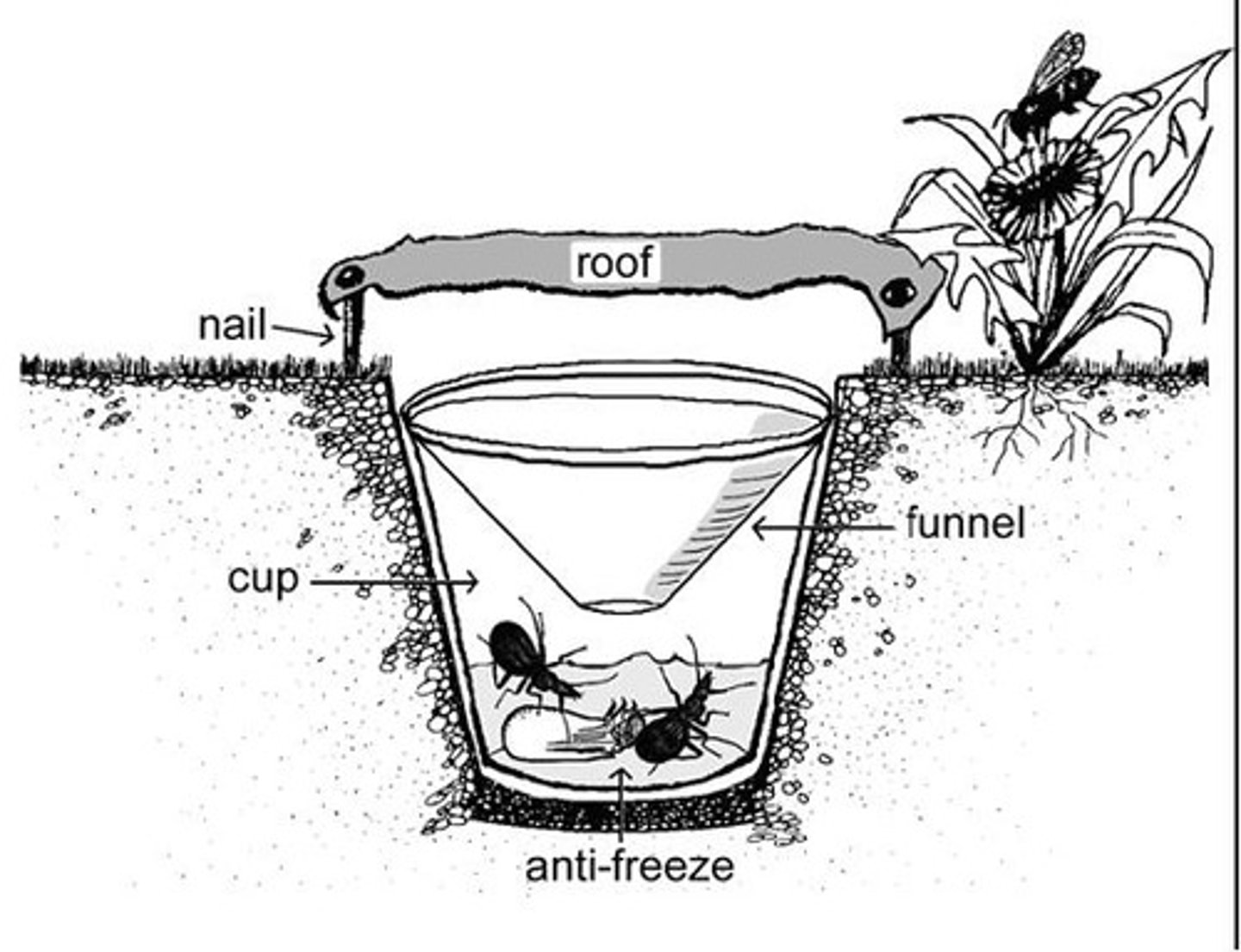
pitfall traps (pros & cons)
dig hole ground lvl, put antifreeze cup & funnel before covering w/ tarp
- estimate of insect population
- insects wont escape antifreeze
- predators can eat insects
- hard to identify insects
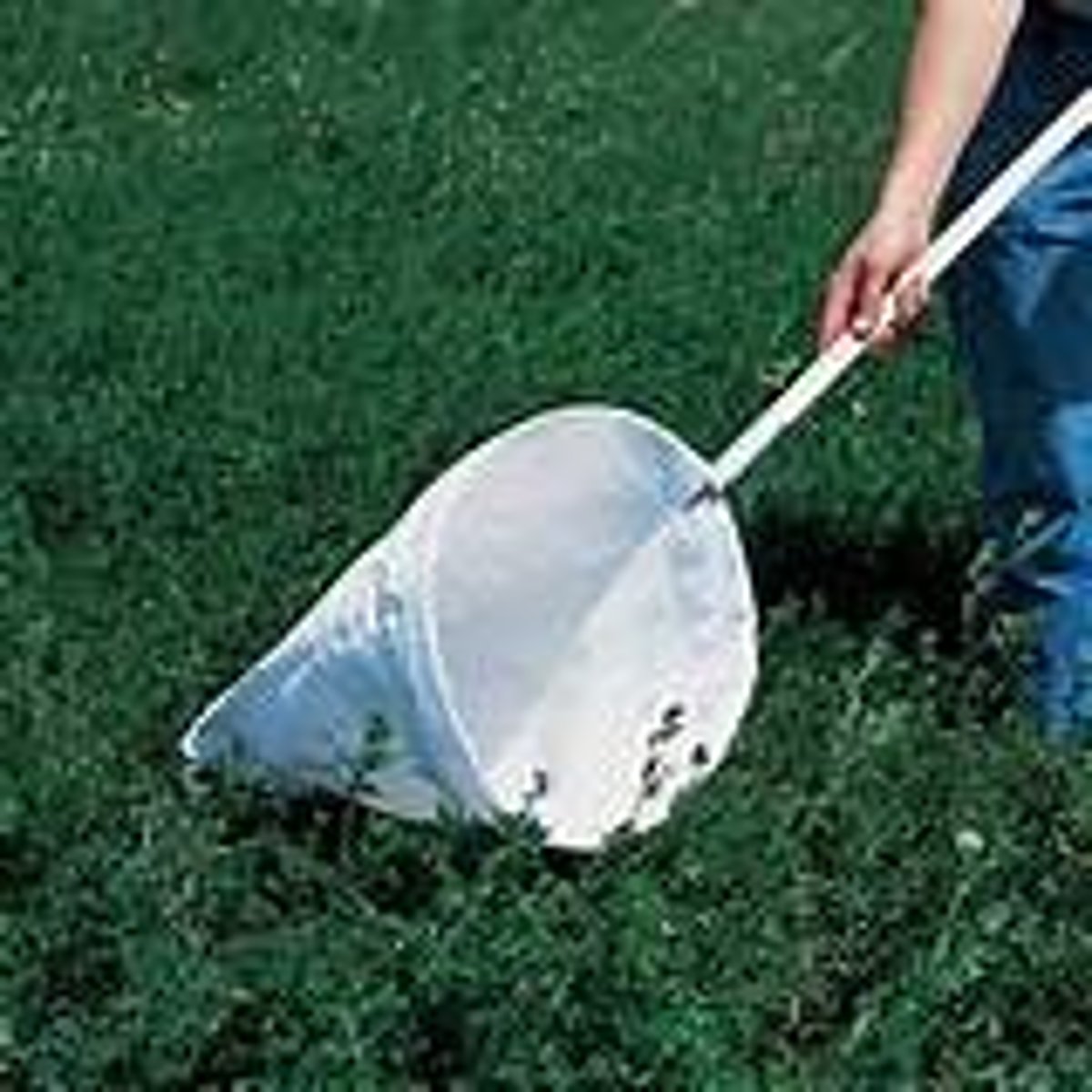
sweep nets (pros & cons)
catch insects in areas of long grass
- time consuming
- can damage plants
- easy to do
- cheap

beating trays (pros & cons)
lightly hit branch and collect falling insect w/ tray
- cheap
- easy to do
- can damage plant
- time consuming
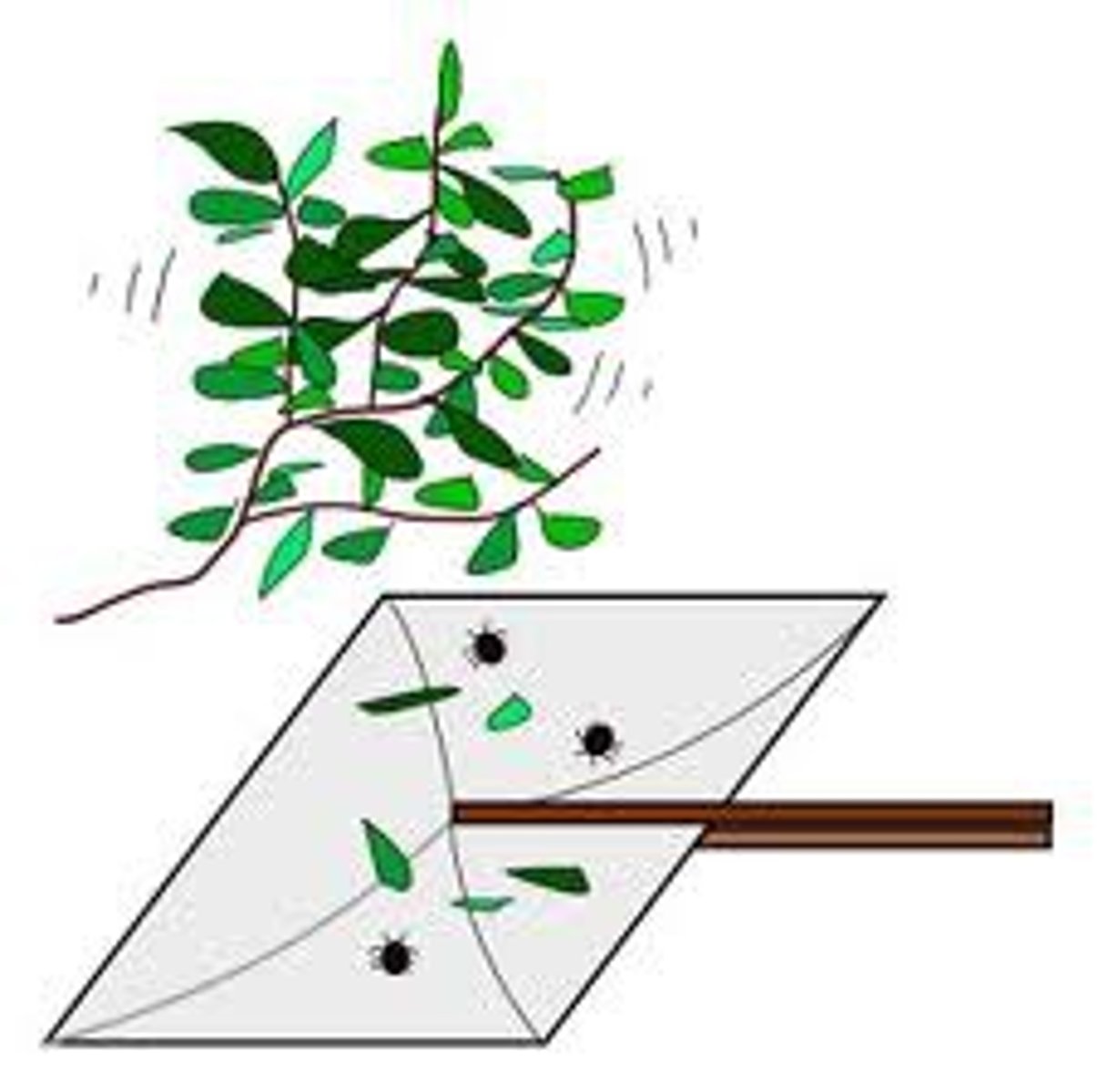
kick sampling (pros & cons)
kick water, hold net opposite flow & catch any organisms flying out.
- easy to get large sample
- good for deep waters
- species can be stuck to rocks
- small species can be missed

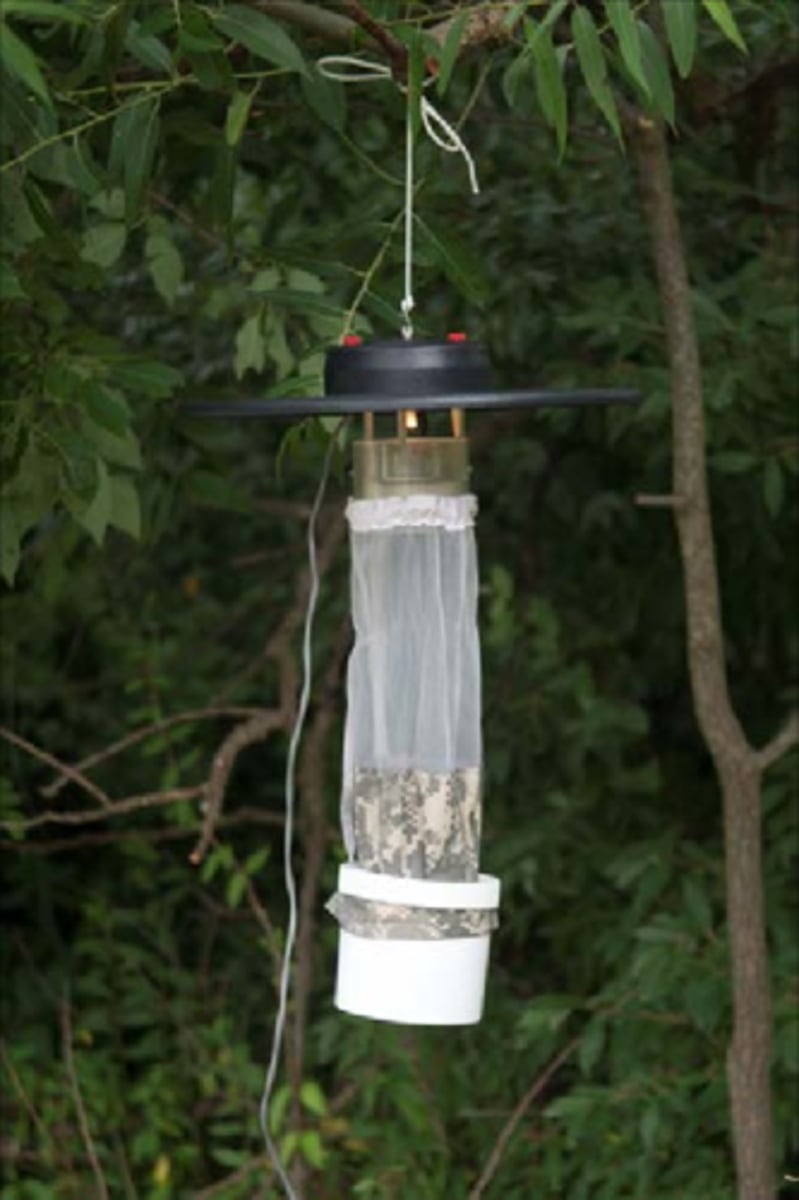
light traps (pros & cons)
get flying-organisms attracted to light like moths
- gets certain species
- easy to do
- some insects attract light @ long range, not short
- temp/humidity can limit species caught

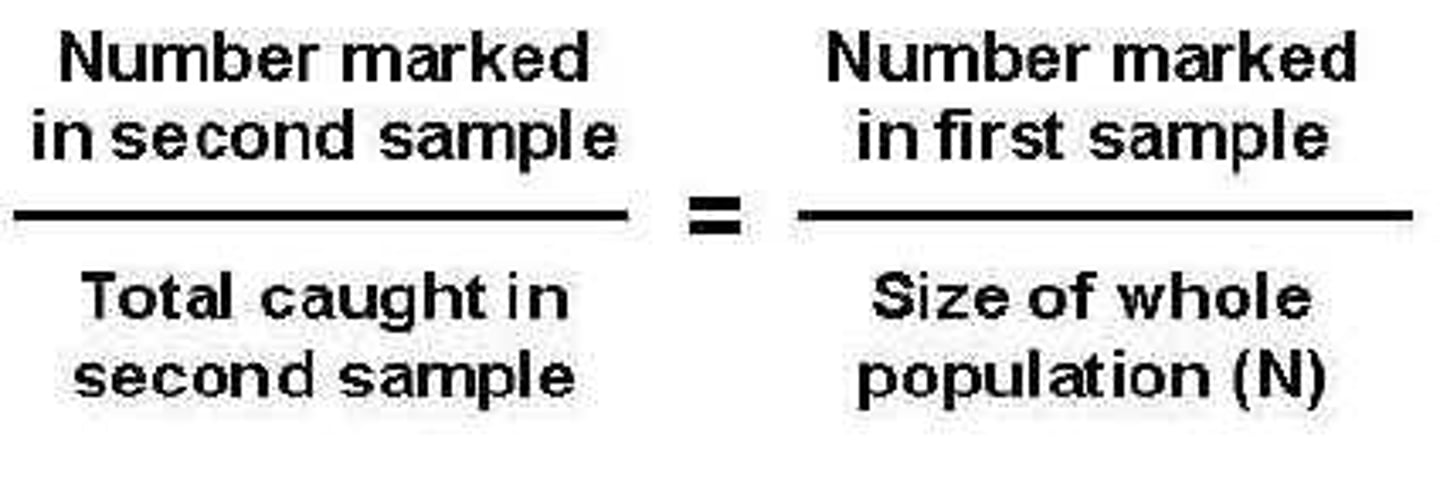
capture-mark-recapture (benefits + lims)
collect sample, mark w paint, release. after some time, collect more & see how many marked.
- shows population growth
- estimate large populations
- increases predation
- paint can kill
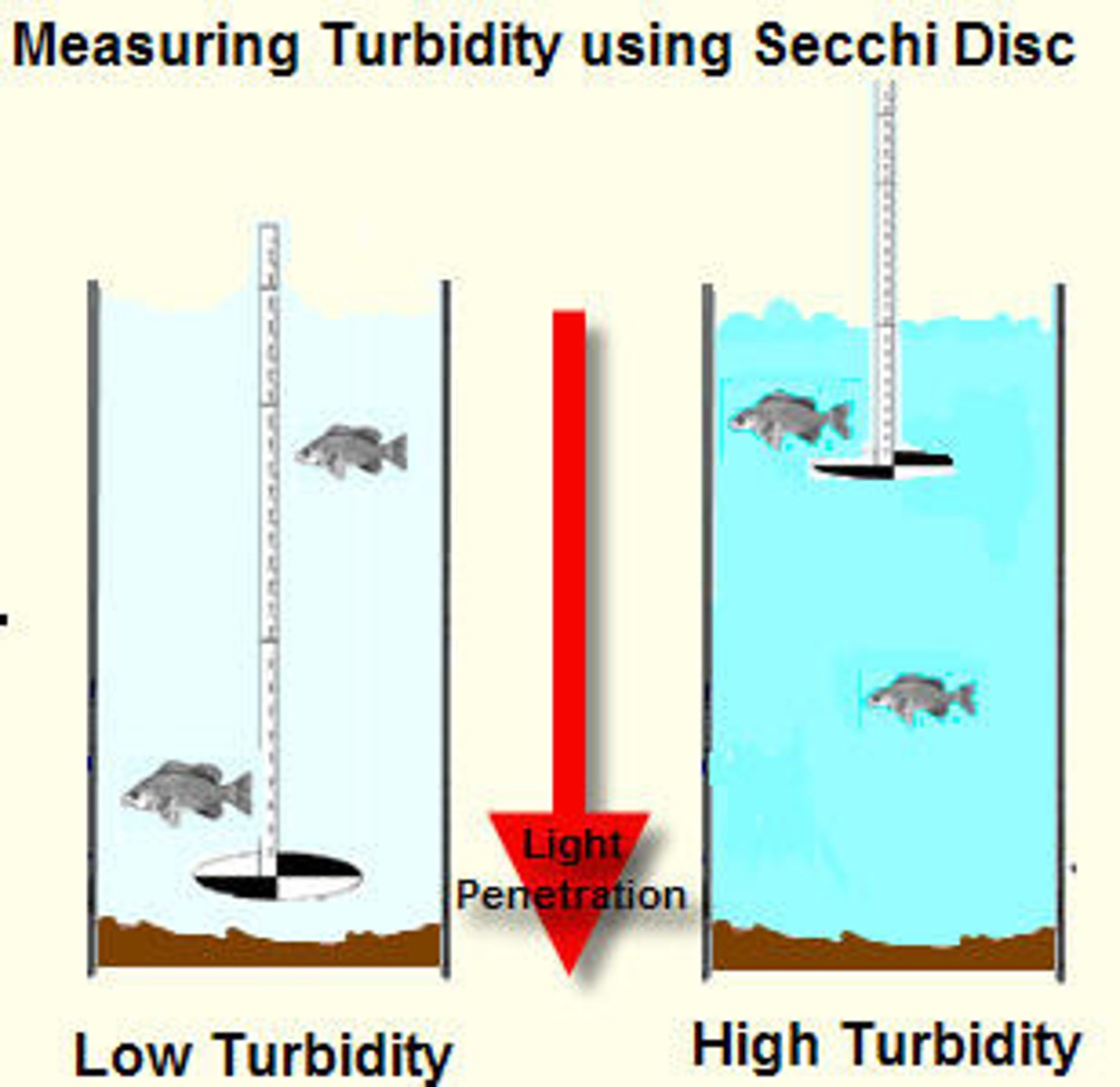
secchi disc (pros & cons)
circular disk to measure turbidity. lower into water until invisible, & depth = turbidity.
- easy to do
- cheap
- measured w/ eyes, vulnerable to research bias
- can be time consuming
ACFOR abundance scale
abundant: 80-99%
common: 60-79%
frequent: 40-59%
occasional: 20-39%
rare: 0-19%
frequency
# of times plant shows up in # of quadrants as %
data collections w/ technology
- geospatial systems
- satellite sensors
- radio trackin
- computer modelling
- crowd sourcing
big data
data so huge that traditional data processing apps can't work
benefits & lims of big data analysis
- amt/type of data stored
- speed which new data generates
- data's trustworthiness
- ways data can be used
factors influencing population density/distribution
- environmental
- economic
- social
- political
- historical
population pyramid stages
1: expanding (preindustrial)
2: expanding (agricultural)
3: stationary (industrial)
4: contracting (post-industrial)
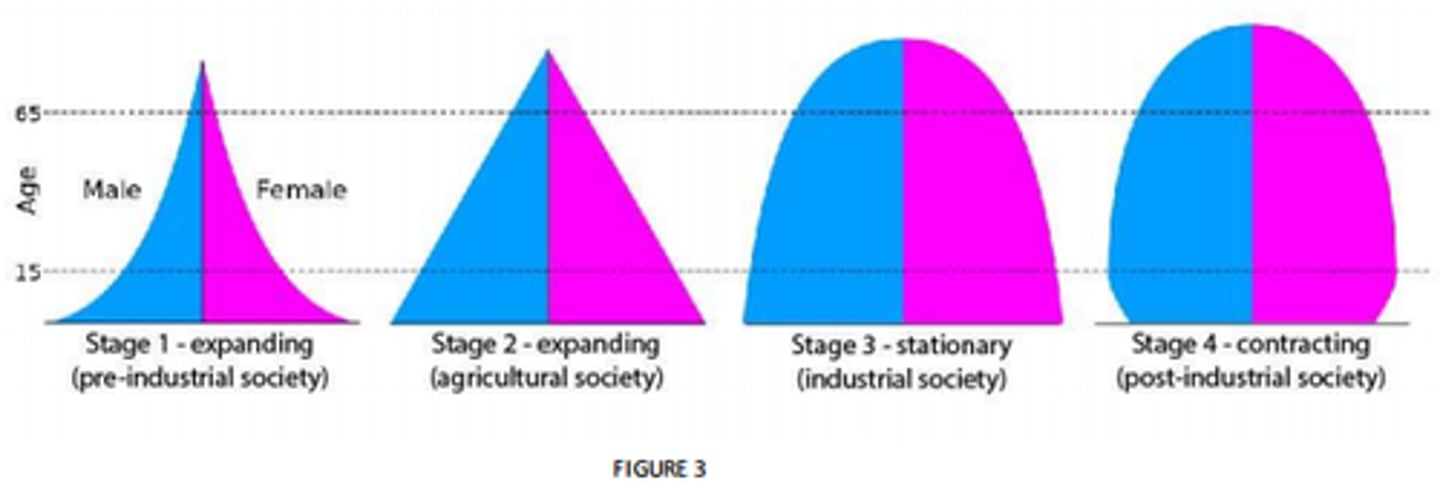
factors affecting population size/composition
- birth rates (less contraceptives)
- death rates (less healthcare/sanitation)
- migration rates (living standards)
dependency ratio
(population 0-14) + (population 65+) * 100 divided by population 15-64
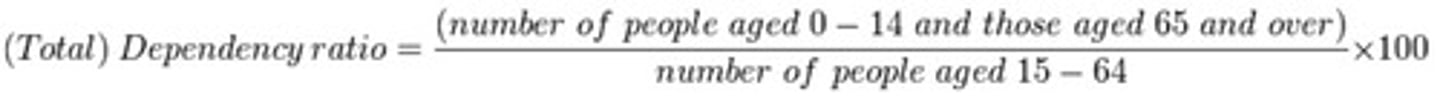
why HIC/LIC have diff pop pyramids
- sanitation/hygiene
- education for women
- contraceptives
- healthcare
- gender equality
- living standards
- early marriage
impacts of aging populations
- lower tax
- higher pension spending
- pressure on healthcare
- pressure to raise retirement age
strategies to manage a changing population
- education/opportunities for women
- pronatalist/antinatalist policies
- improved healthcare
- availablity/education contraception
lincoln index
n1 = 1st sample
n2 = 2nd sample
m = marked recpatured
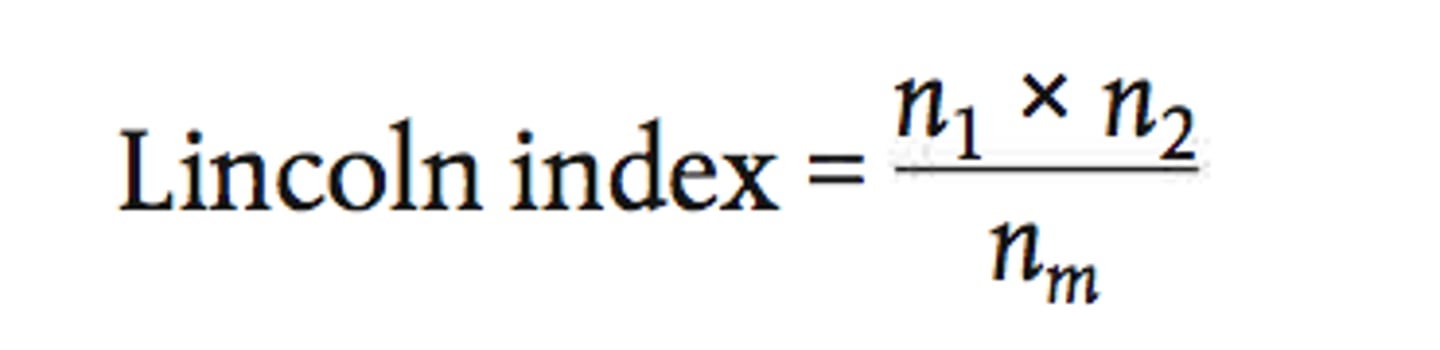
gross primary productivity
TOTAL gain in biomass/energy per unit time
net primary productivity
gain in biomass/energy per unit time AFTER respiratory loss
primary succession
on newly formed habitats w/ no existing community (glaciers/volcano), pioneer species form
secondary succession
on sites that previously supported communities (hurricane), climax species
ecosystem productivity
biomass production rate for ecosystem
tundra soil
thin w/ permafrost underneath
tundra climate
around 90 degrees latitude, extremely cold
tundra vegetation
herbs, lichens, mosses
grassland climate
around 40-50 degrees latitude, seasonal rainfall
grassland soil
rich in organic matter
grassland vegetation
tall/wet & short/dry grasses
tropical forest climate
around 0 degrees latitude, hot & humid
tropical forest soil
thin layer fertile
tropical forest vegetation
nuts, coffee, chocolate
desert climate
hot days & cold nights, around 30-60 degrees latitude
desert soil
thin, porous, alkaline
desert vegetation
scattered shrubs & lichen rocks
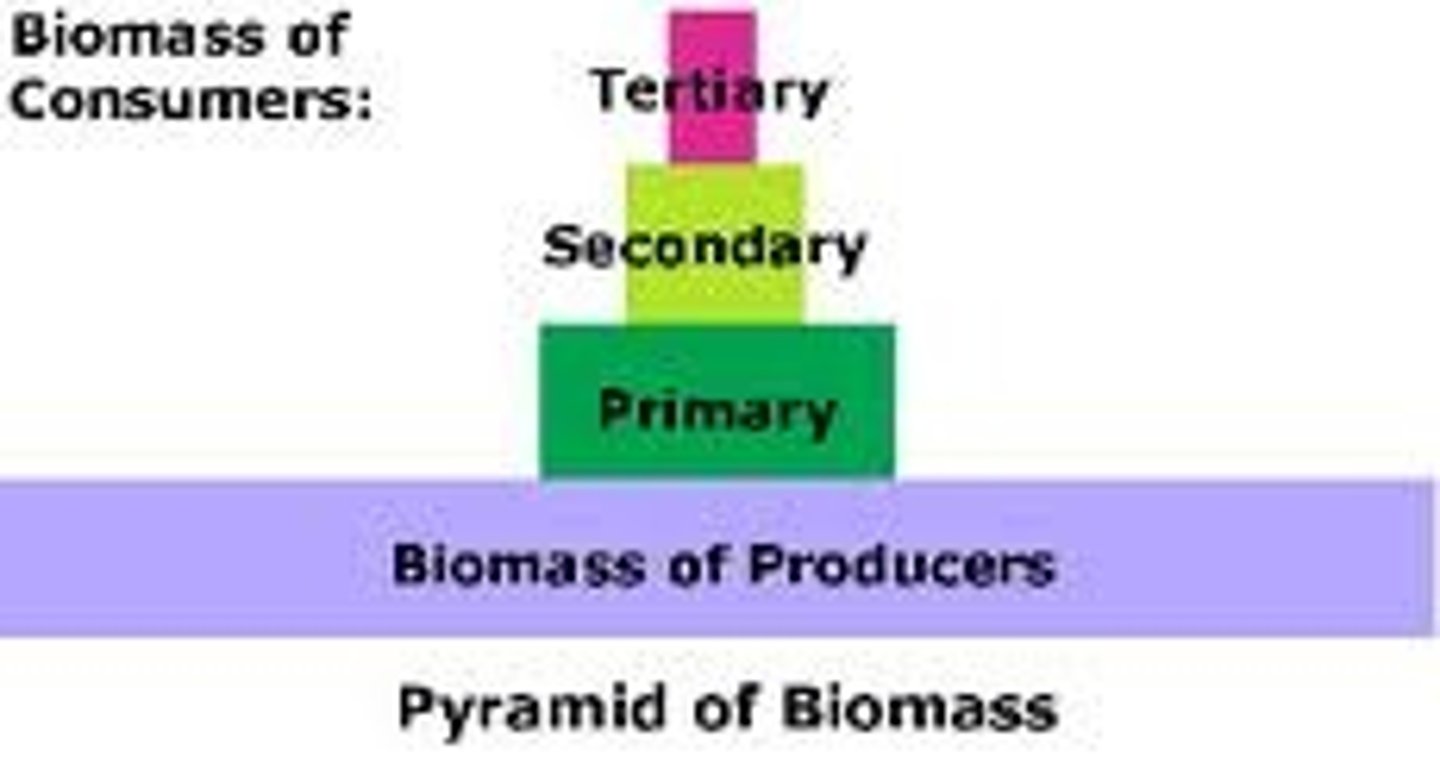
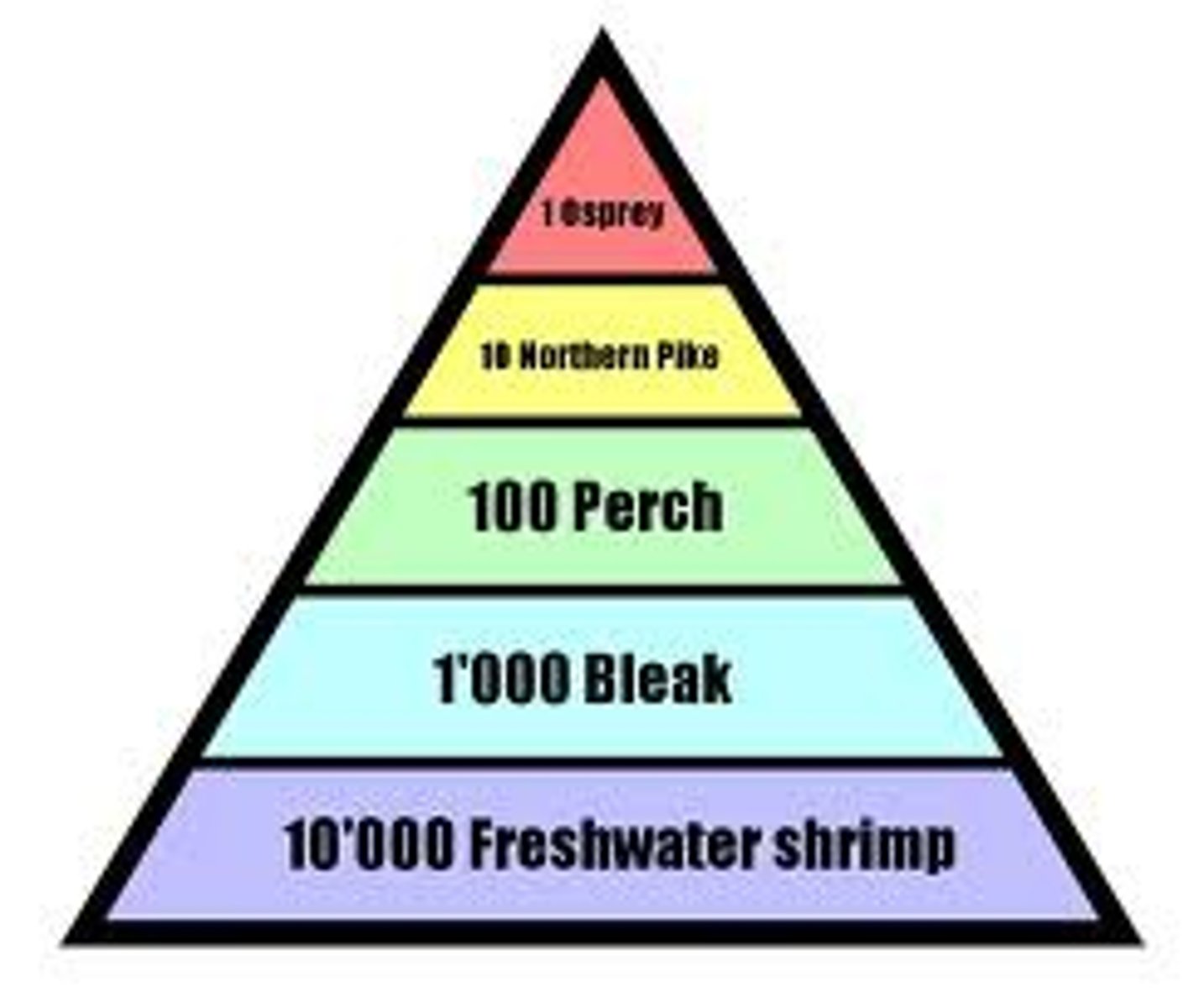
pyramid of biomass
pyramid of energy
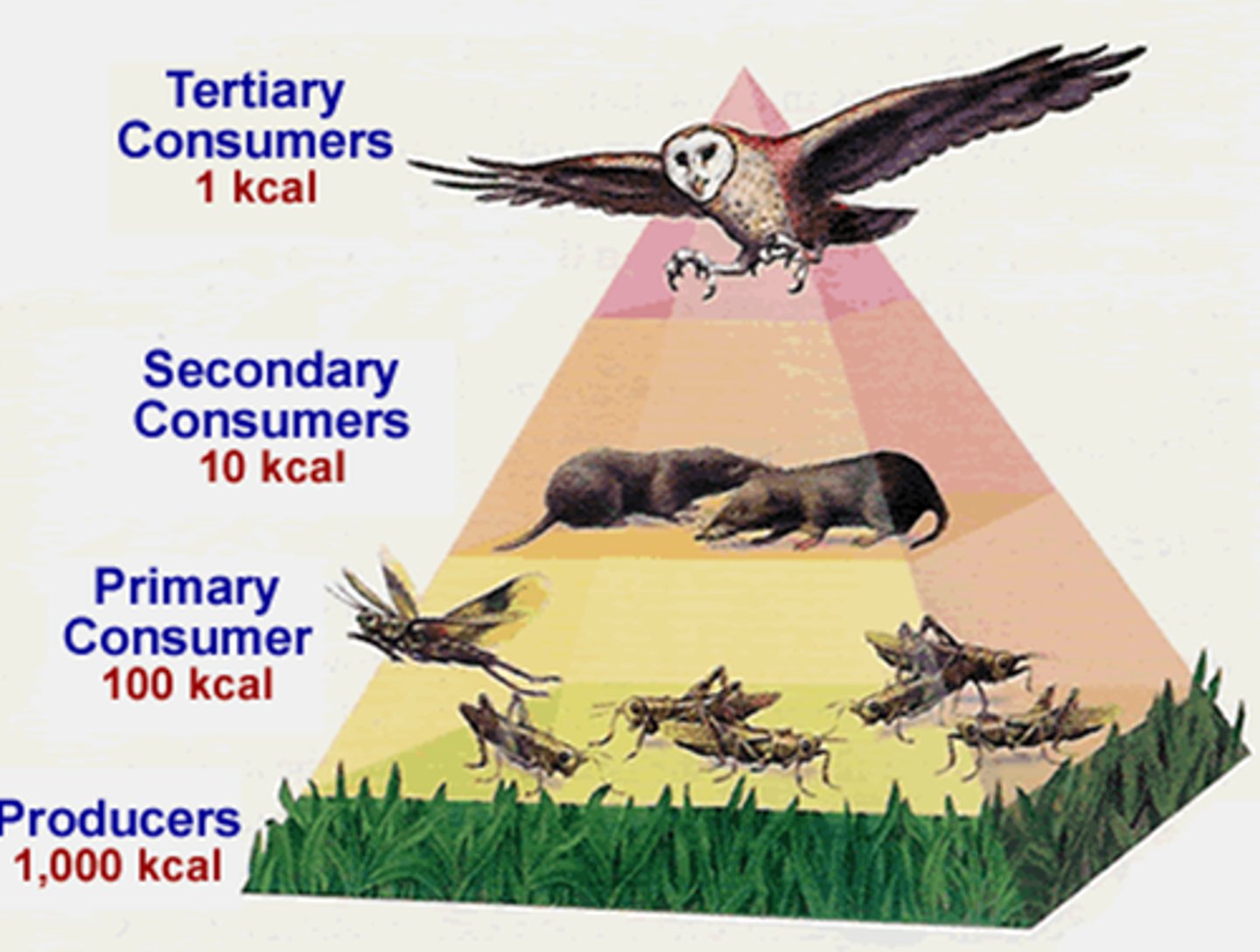
pyramid of numbers
chlorophyll
catches light energy for photosynthesis
producer
organism makes its own food
primary consumer
feeds directly on producers
secondary consumer
eats primary consumers
tertiary consumer
eats secondary consumers
decomposer
breaks down waste & obtains energy from dead organic matter
carbon cycle
photosynthesis: plants produce oxygen & glucose
respiration: oxygen & glucose is used to release CO2
feeding: moving carbon in form of biological molecules
decomposition: minerals decay in a dead body
fossilization: sediment fossilized to be used as fossil fuels
combustion: organic material burned in presence of oxygen to give off product of CO2, H2O, & energy.
scientific method
involves interplay between observations & formation/testing/evaluation of hypotheses
dependent variable
outcome/effect/response of the independent variable
independent variable
manipulated
hypothesis -> theory
with consistent support by investigation & observation
historical data development
in terms of climate change, there has been advancements in scientific theory, a previously limited amount of historical data, and advances in technology
how has bias led to the misuse of scientific data
creating false conclusions & misrepresentation from unreliable data
sampling strategies
used to collect representative data
random & systematic sampling
aim to ensure samples are well distributed with a low risk of bias due to standardization/randomization
simpson index of diversity
∑ = sum of (total)
n = the number of individuals of each type present in the sample (types may be species and/or higher taxa such as genera, families, etc.)
N = the total number of all individuals of all types present in the sample
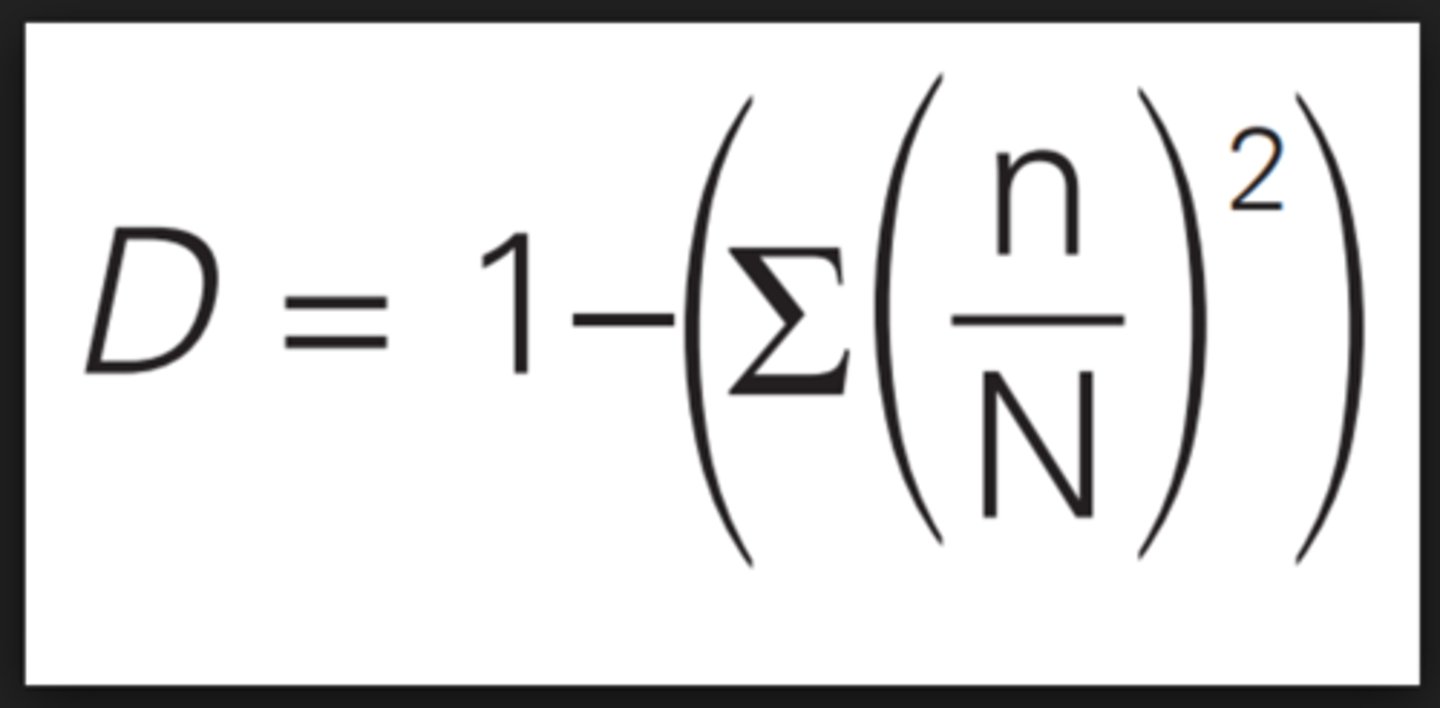
native species
naturally evolved in an area
invasive species
introduced by humans, not natural to area. harms biodiversity as they dont have natural predators or competition
benefits of conserving biodiversity
- potential medicine resources
- food/wood/fibers/oils/fuels
- diversity in genes
- ecological services
- cultural/recreational values
describe/evaluate legislation & protocols as methods of conserving biodiversity
- protection of species
- regulation of sustainable harvesting
- international trade in endangered species (CITES)
- international whaling commission (IWC)
- european union common fisheries policy (EU CFP)
- international tropical timber organization (ITTO)
- international union for conservation of nature (IUCN) red list
role of the EDGE program in the conservation of biodiversity
focuses specifically on unique threatened species w a scientific framework to identify them. aims to put species on map and use conservation action to secure their future