Human Anatomy & Physiology: The Eye
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
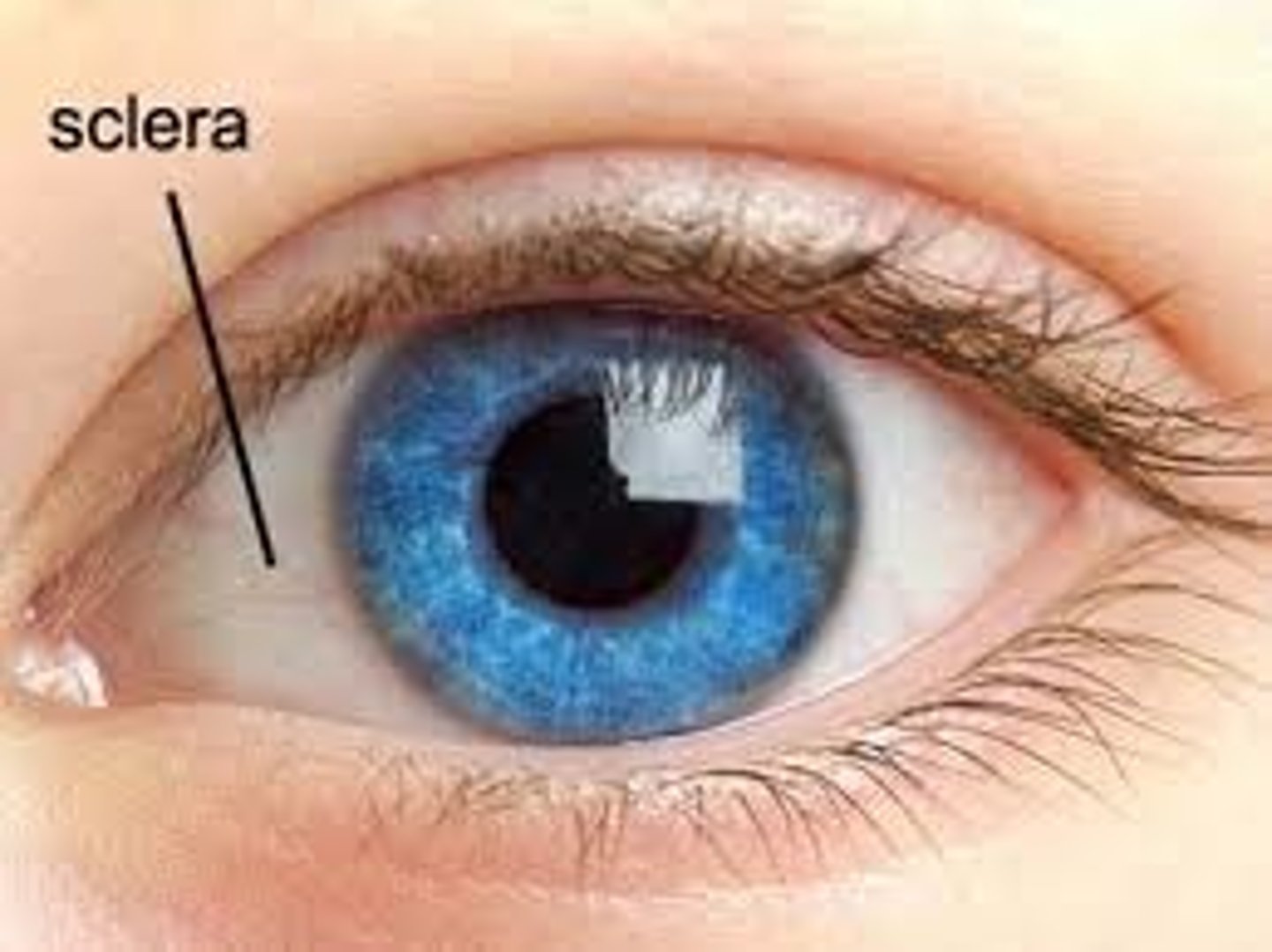
sclera
tough, fibrous, white outer coat extending from the cornea to the optic nerve
retina
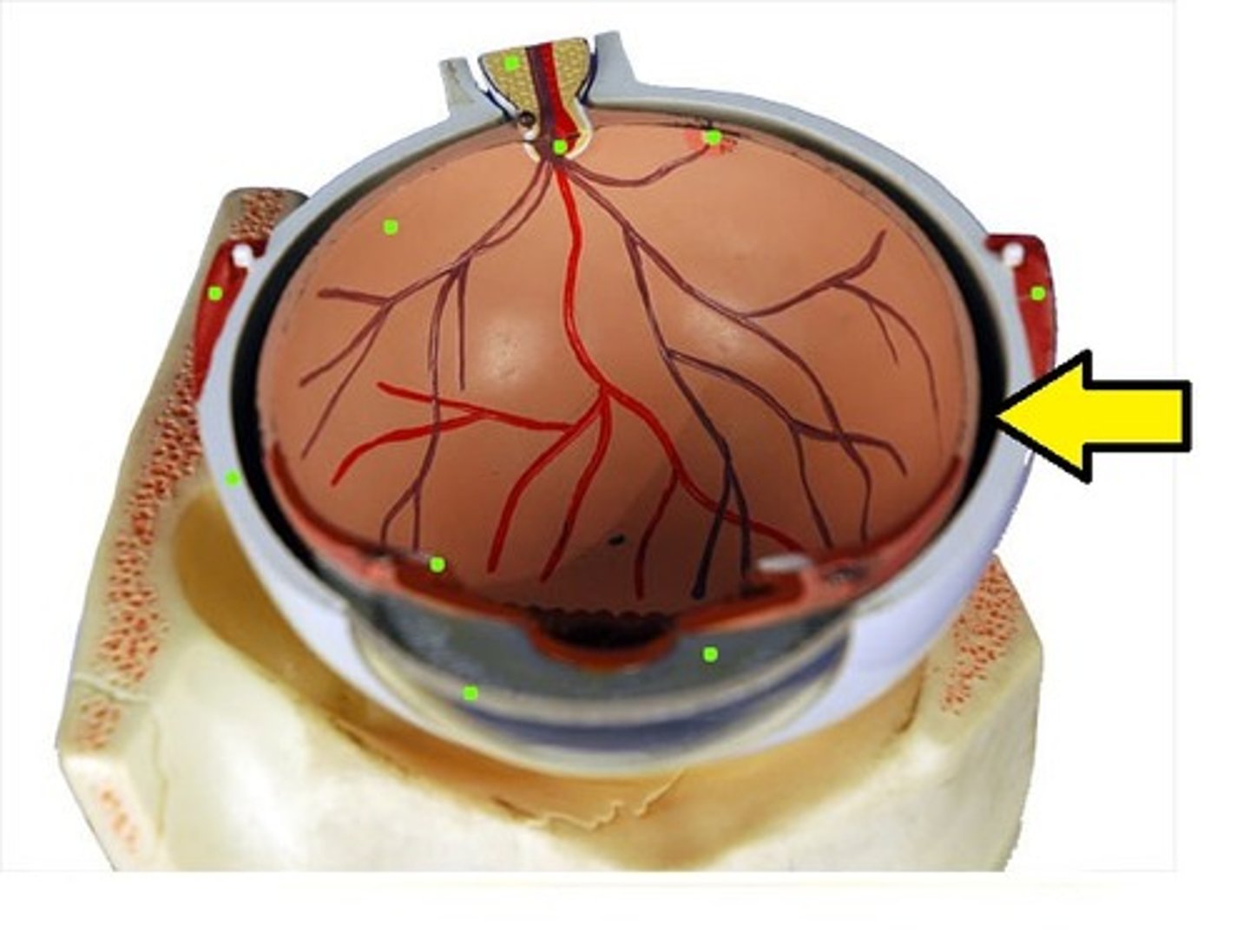
choroid
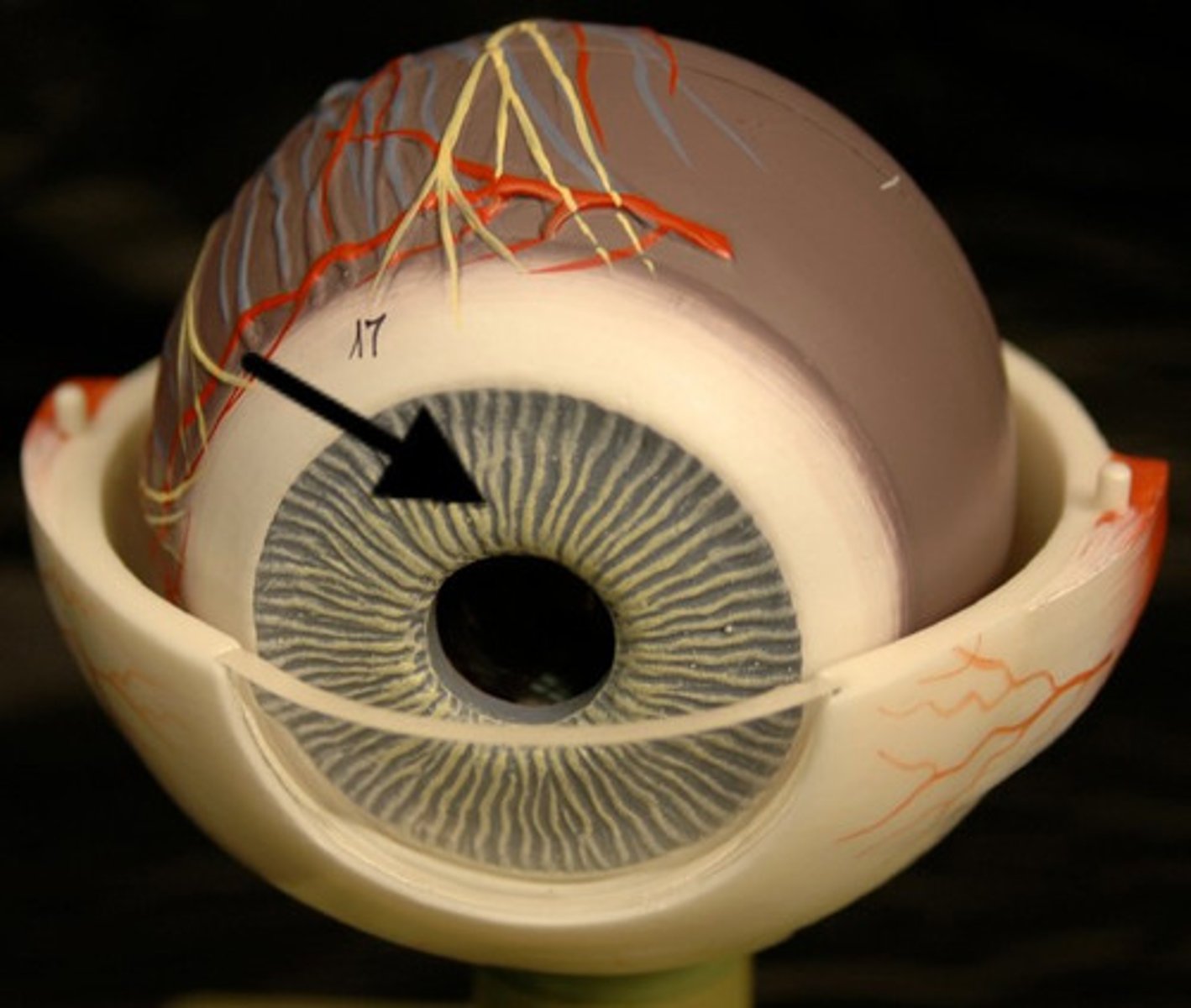
iris
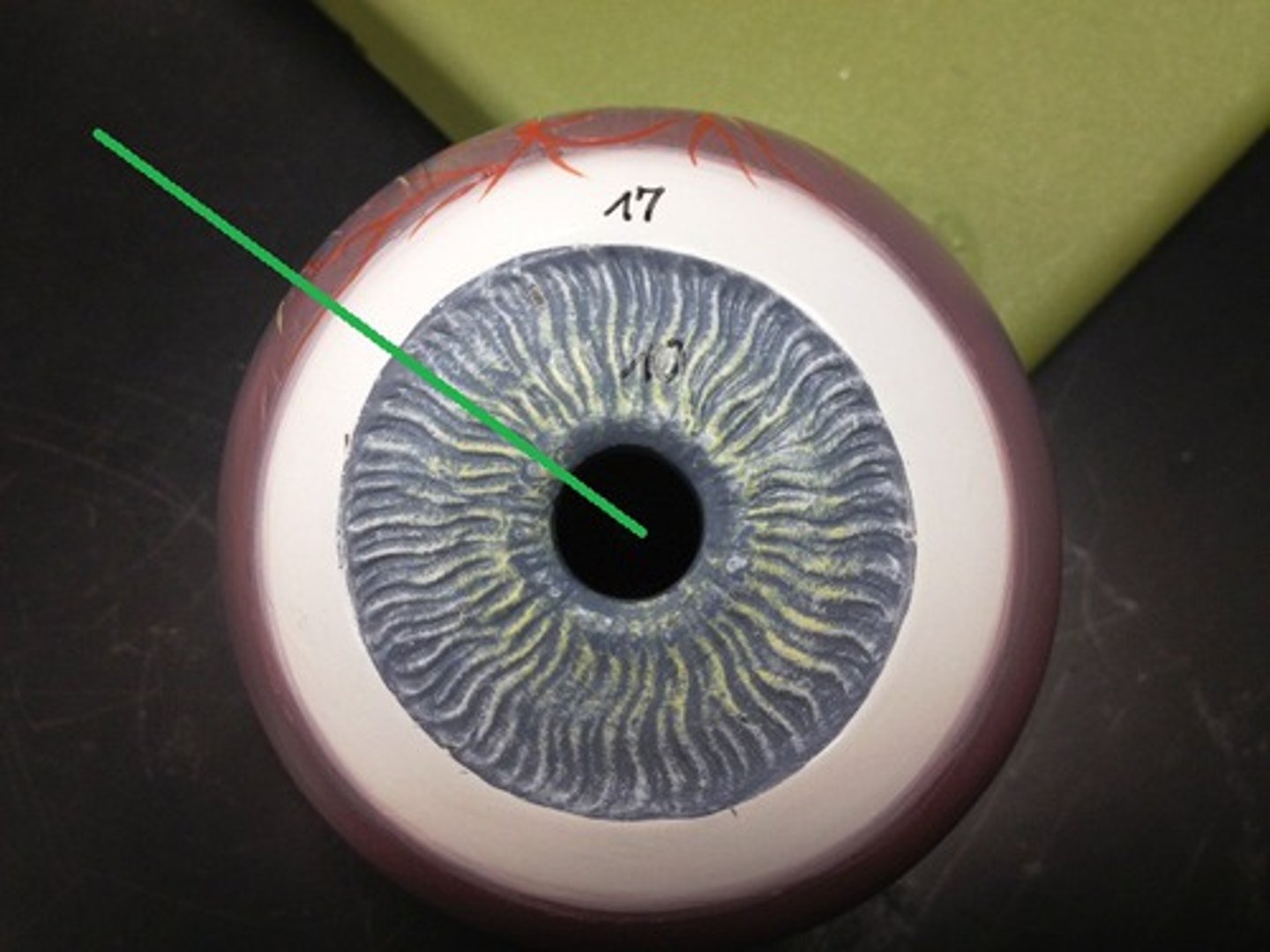
pupil
the adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
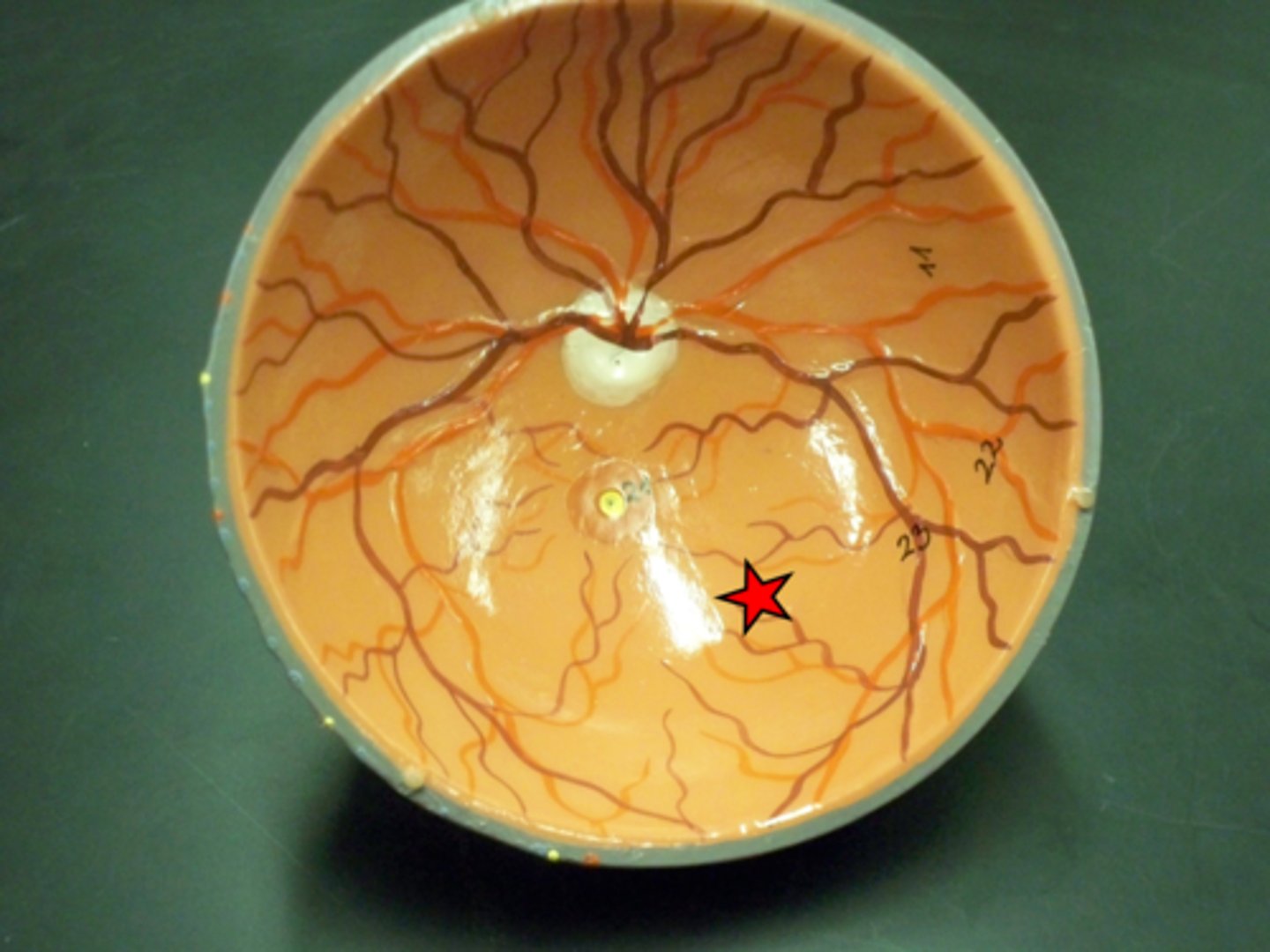
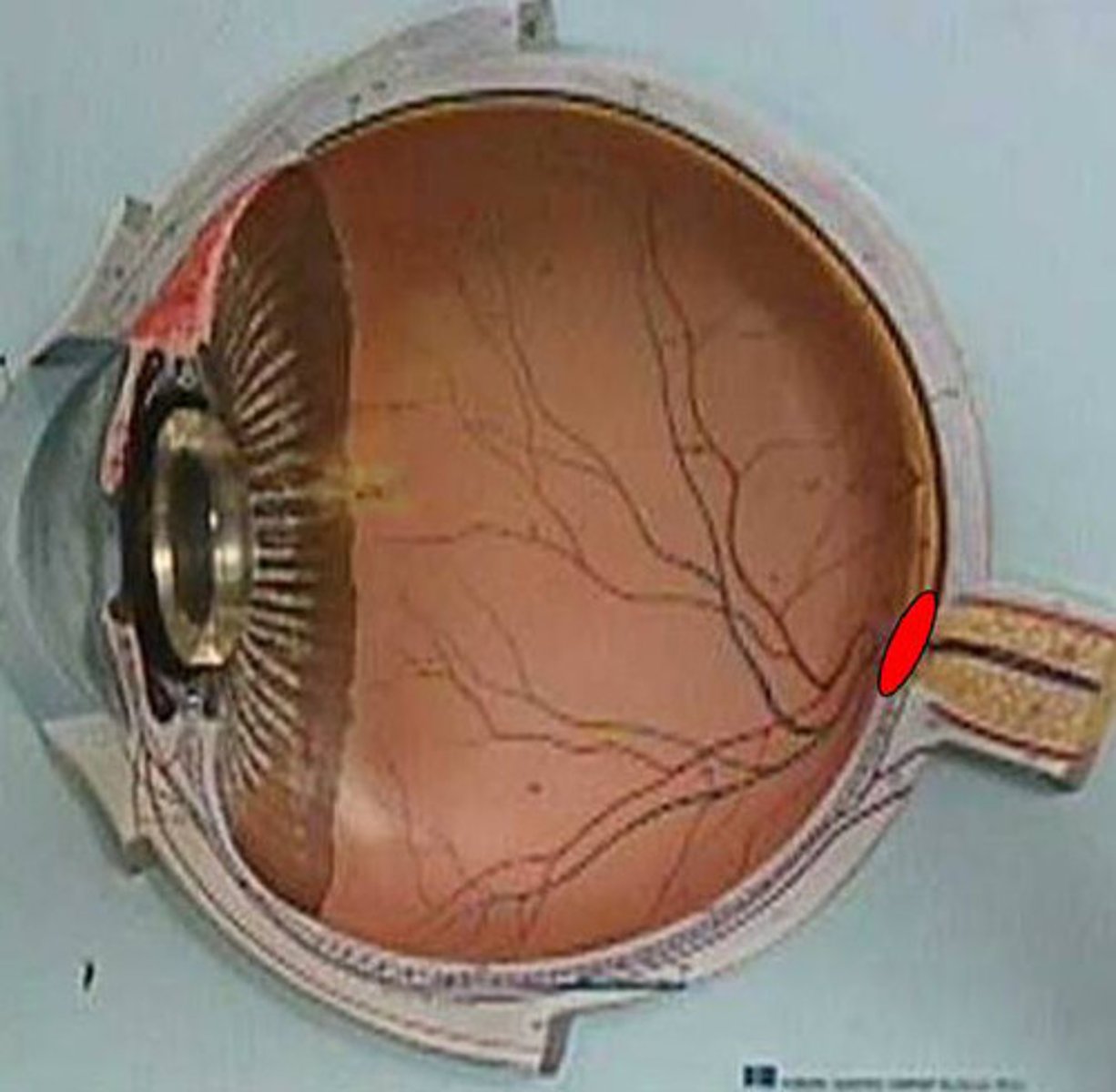
optic disc
Blind spot on the retina.
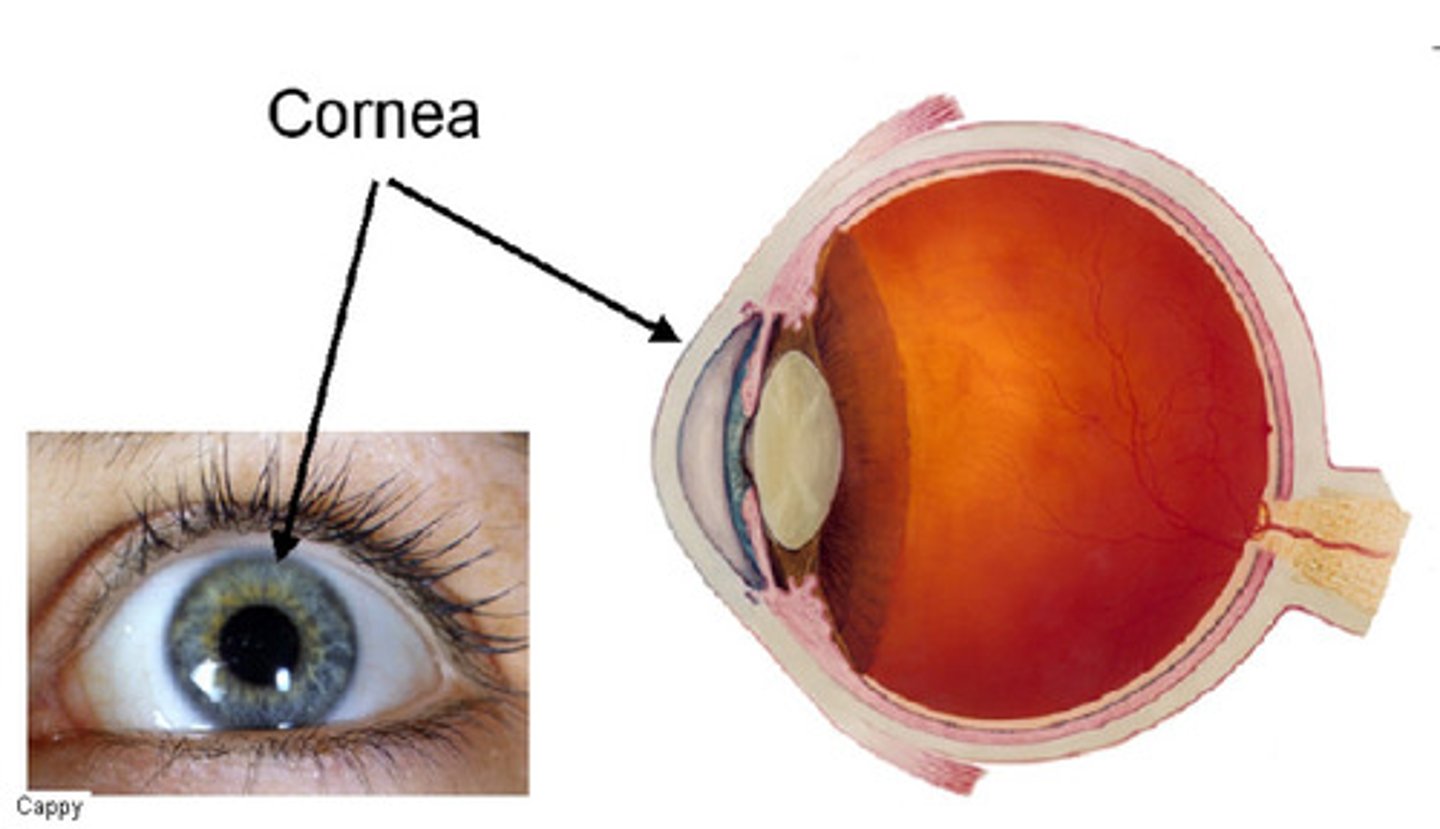
cornea
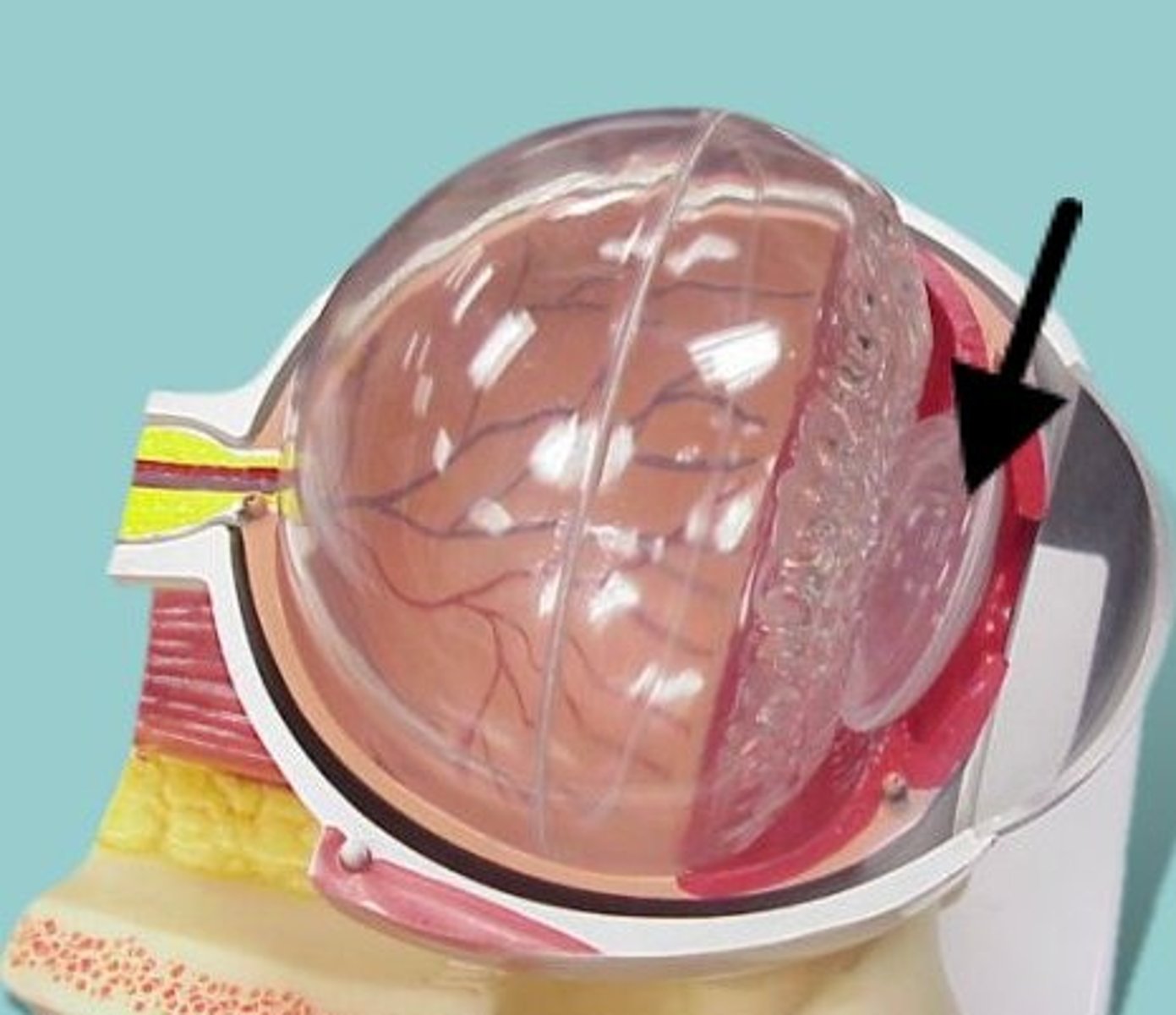
lens
The cornea is avascular.
Why can the cornea be easily transplanted into a person?
vascular
Consisting of blood vessels.
avascular
Lack of blood vessels.
The dark middle layer contains blood vessels that prevents scattering of light
What does the choroid contain?
Tears help to lubricate your eyes and they help to keep your eyes clean and protected from irritants.
Why are tears necessary for the eyes?
smooth muscle
The iris is composed of _____________.
regulate the size of the pupil
The function of the iris is to _____________.
aqueous humor
Fluid in the anterior chamber of the eye.
vitreous humor
Fluid in the posterior chamber of the eye.
rods and cones
Photoreceptors in the retina.
fovea centralis
This is the highest concentration of cones in the retina and provides the point of sharpest vision.
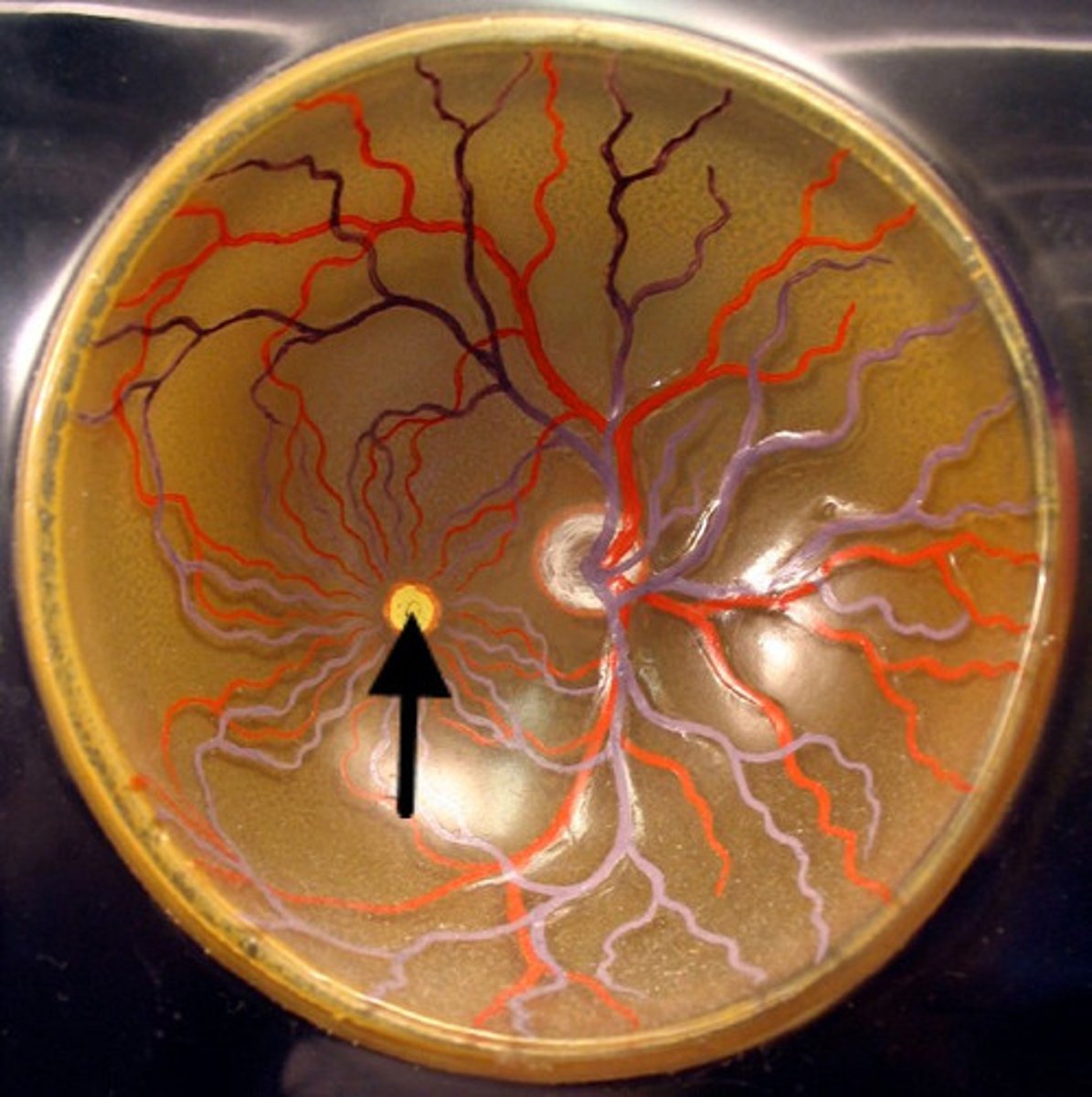
It is the area where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball.
What is the reason for the blind spot on the retina?
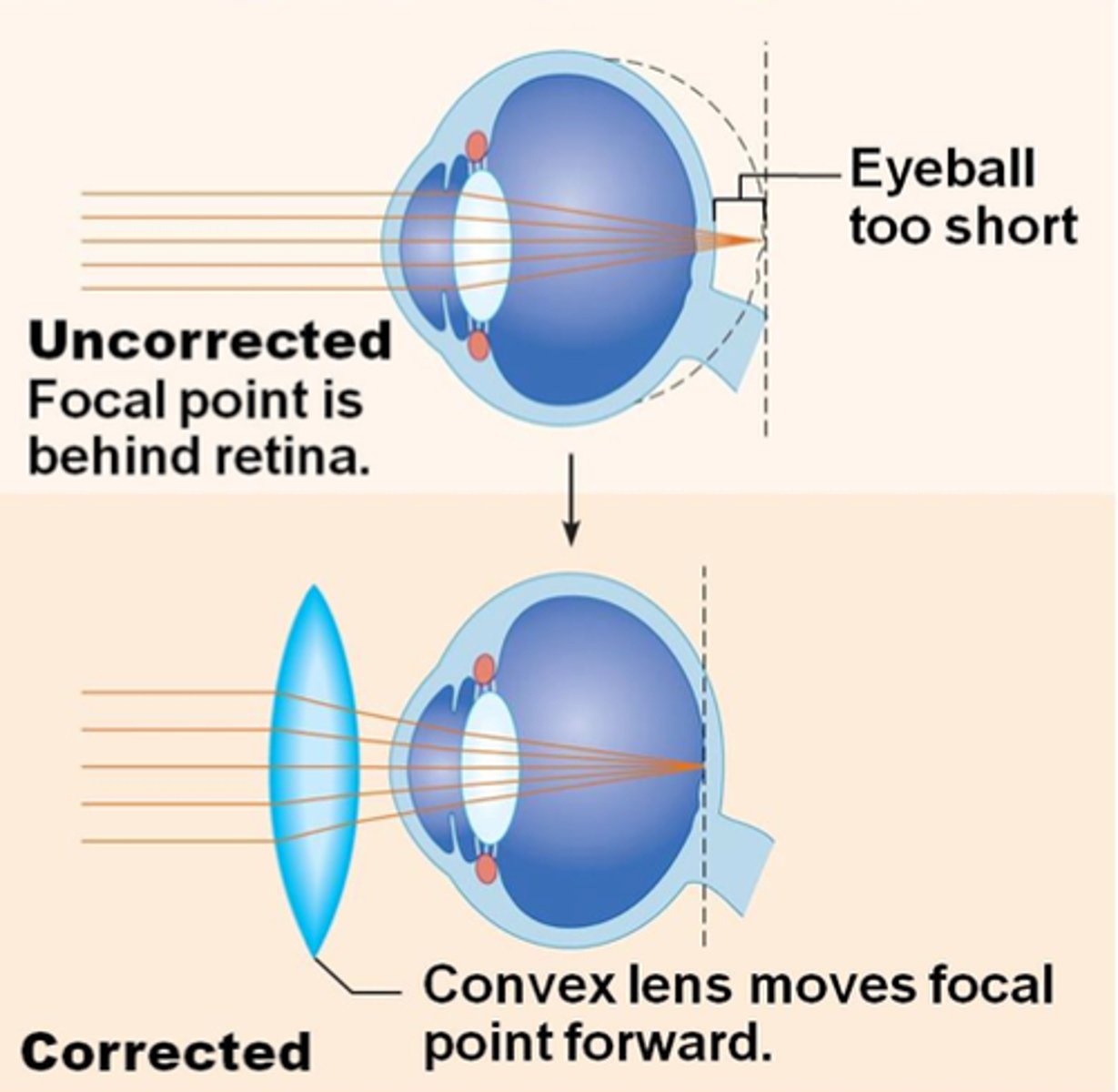
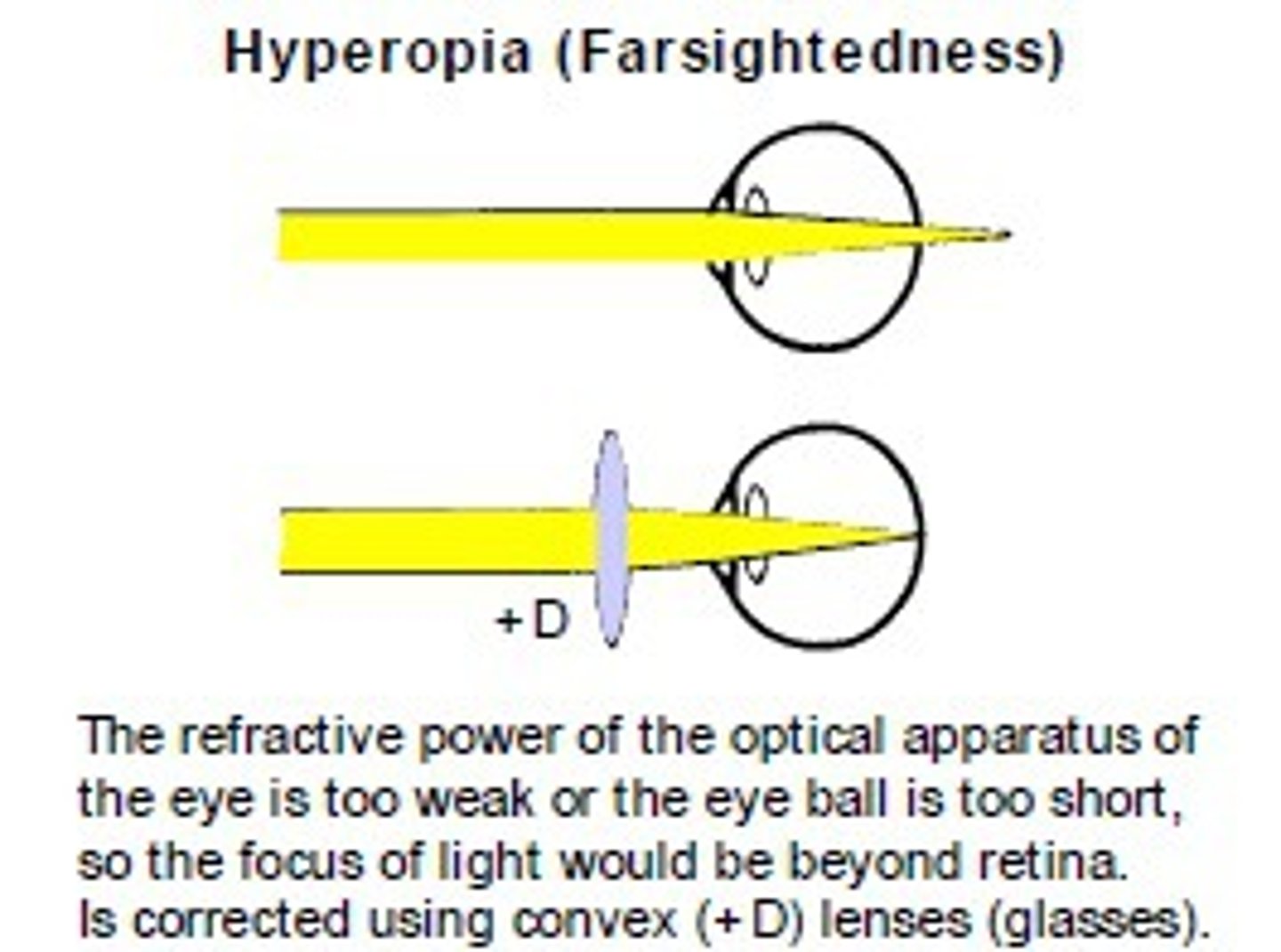
hyperopia
farsightedness, focal point is BEHIND the retina
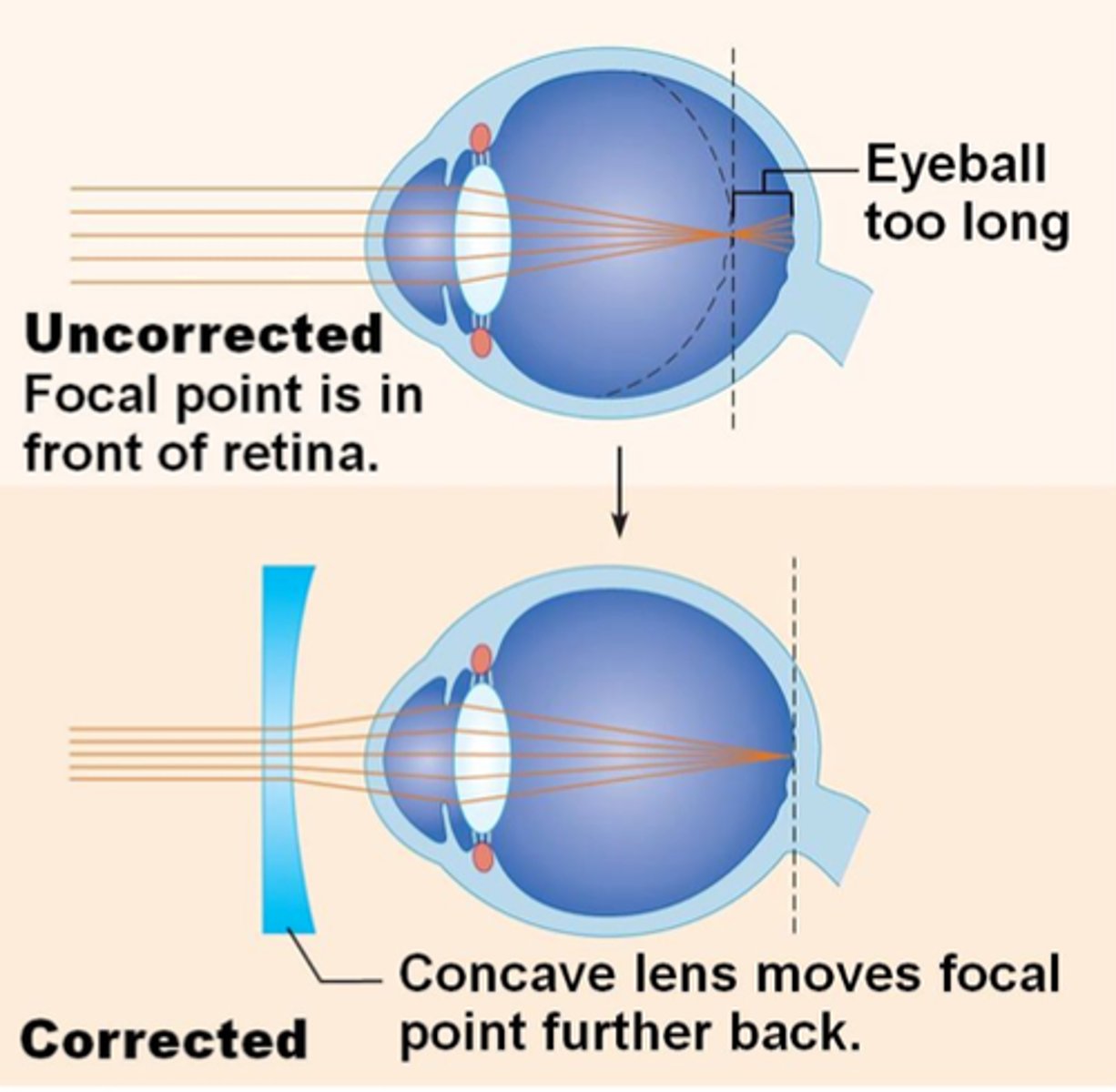
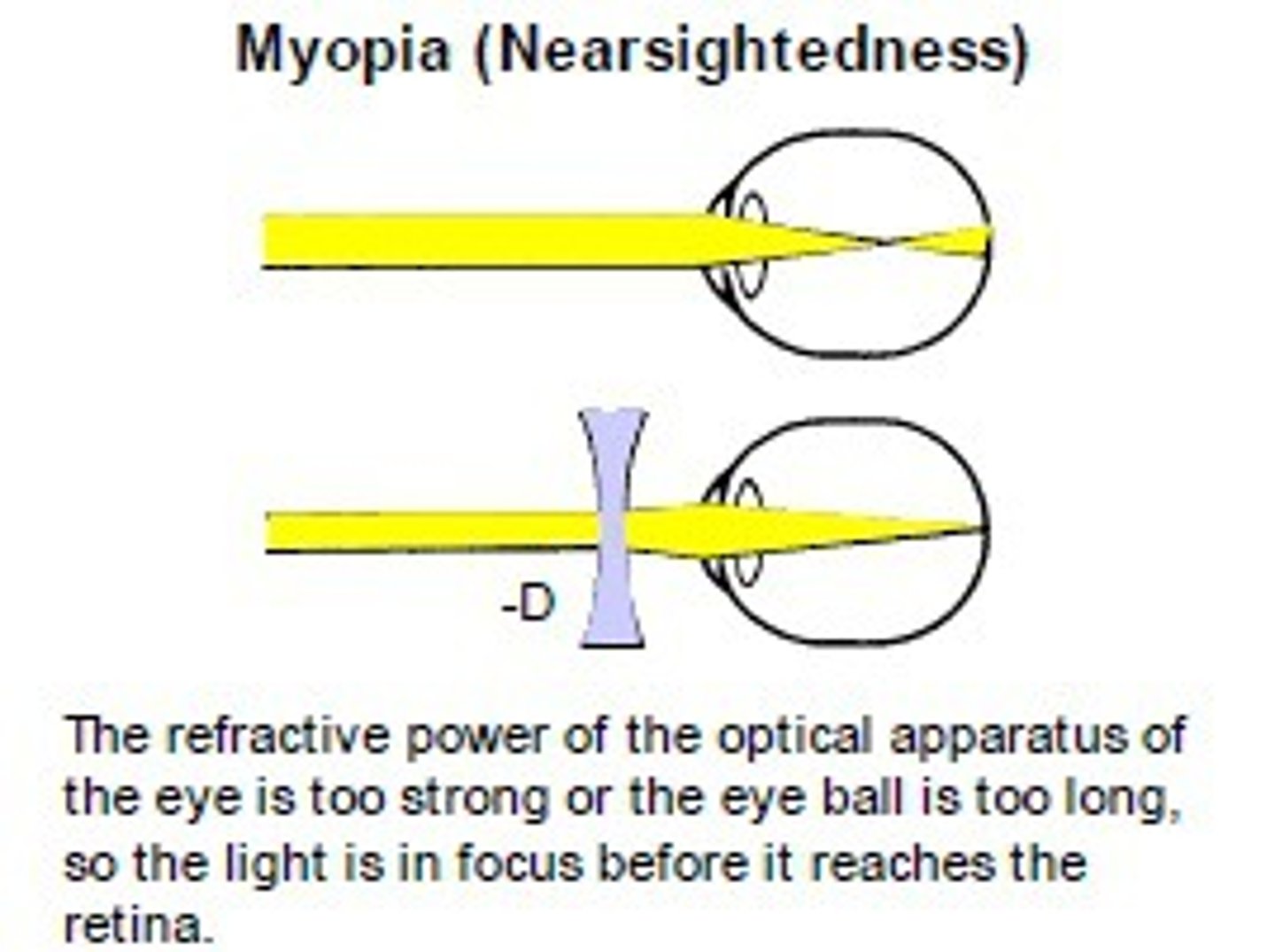
myopia
nearsightedness, focal point is in FRONT of the retina
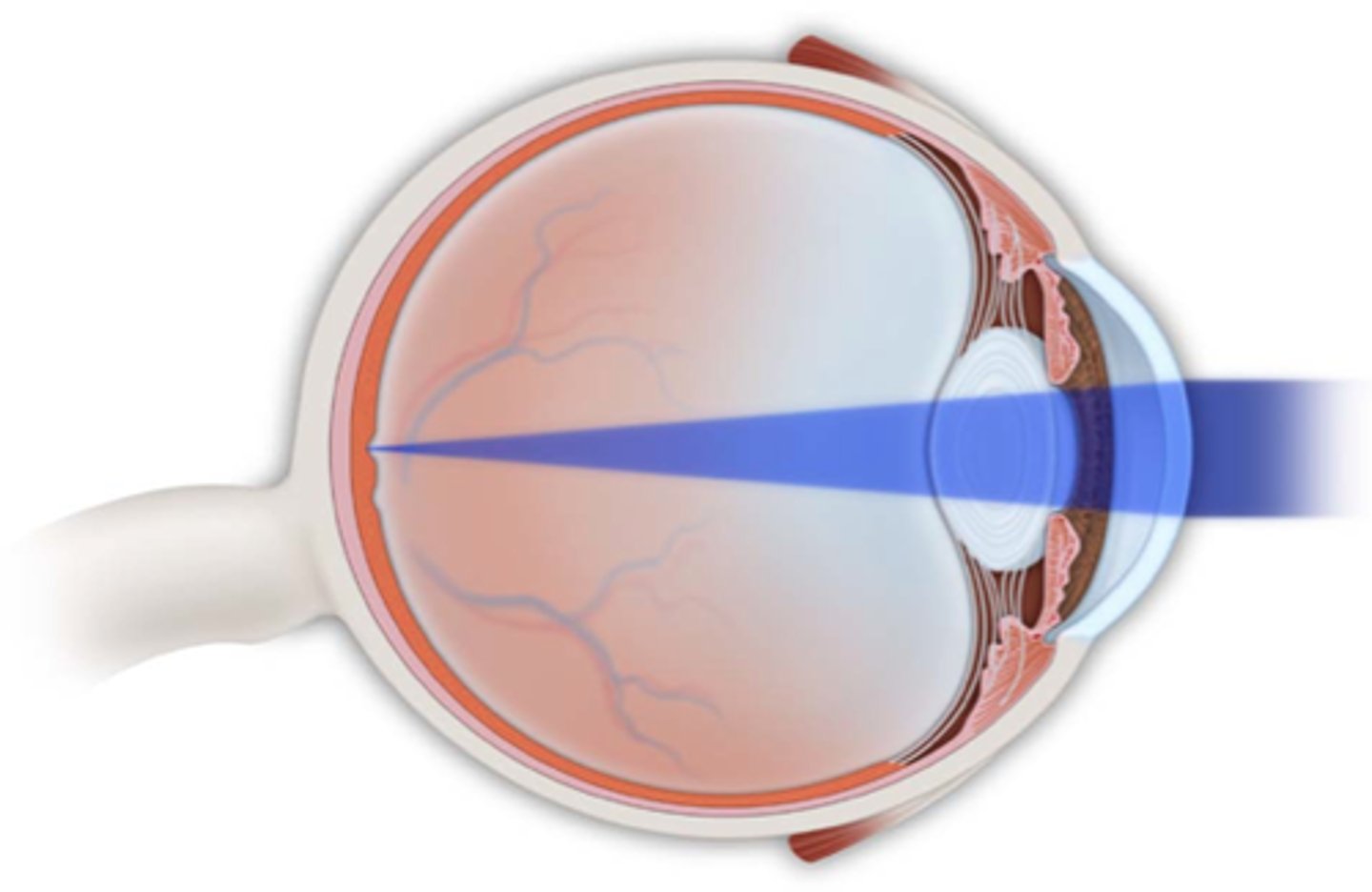
emmetropia
normal, focal point rests on the retina
concave lens
What lens is used to correct myopia?
convex lens
What lens is used to correct hyperopia?
Nasoloacrimal duct
nasolacrimal duct (sometimes called the tear duct) carries tears from the lacrimal sac of the eye into the nasal cavity.
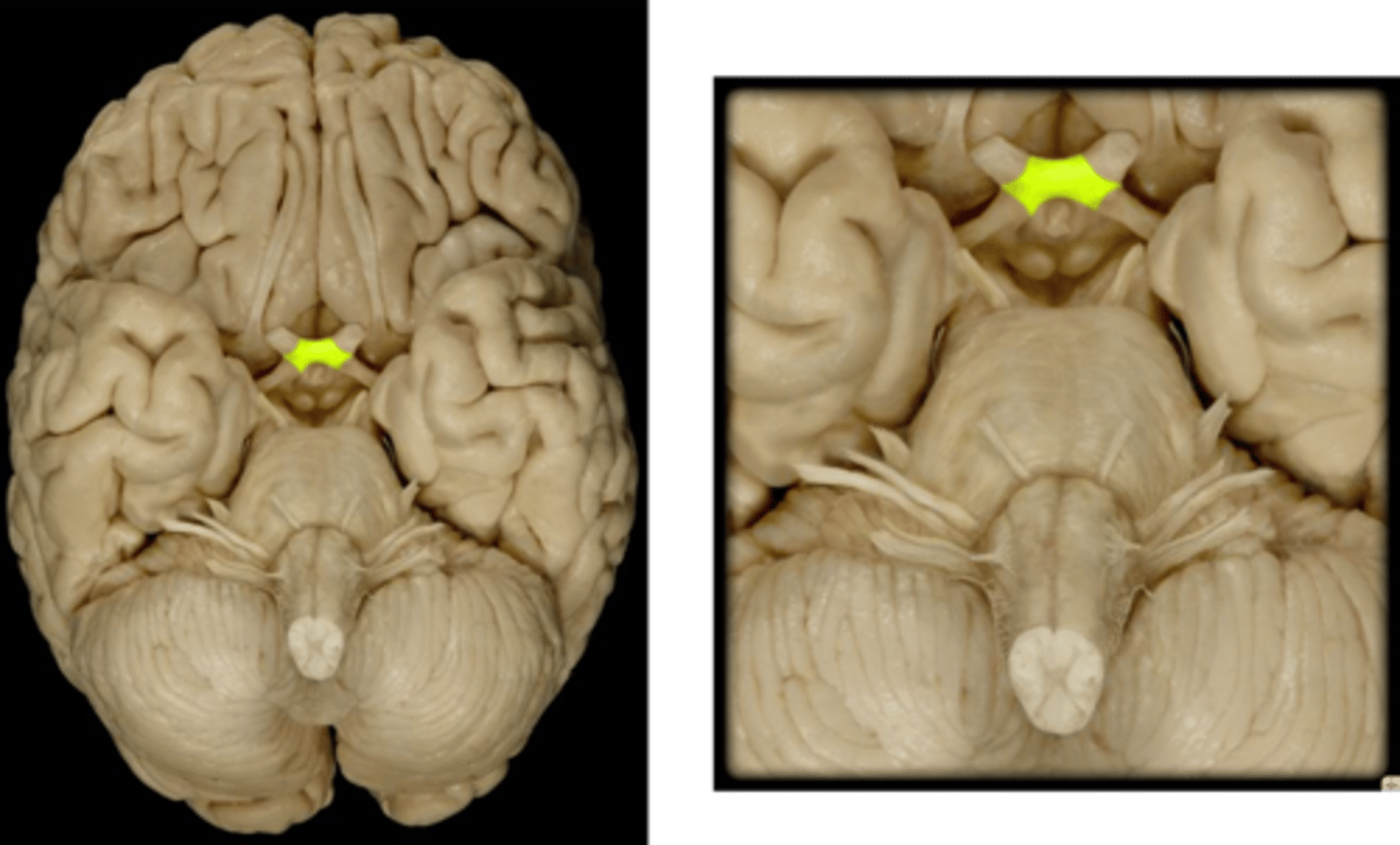
optic chiasma
The point at which nerve fibers from the medial side of each eyeball cross and go to the opposite side of the brain.
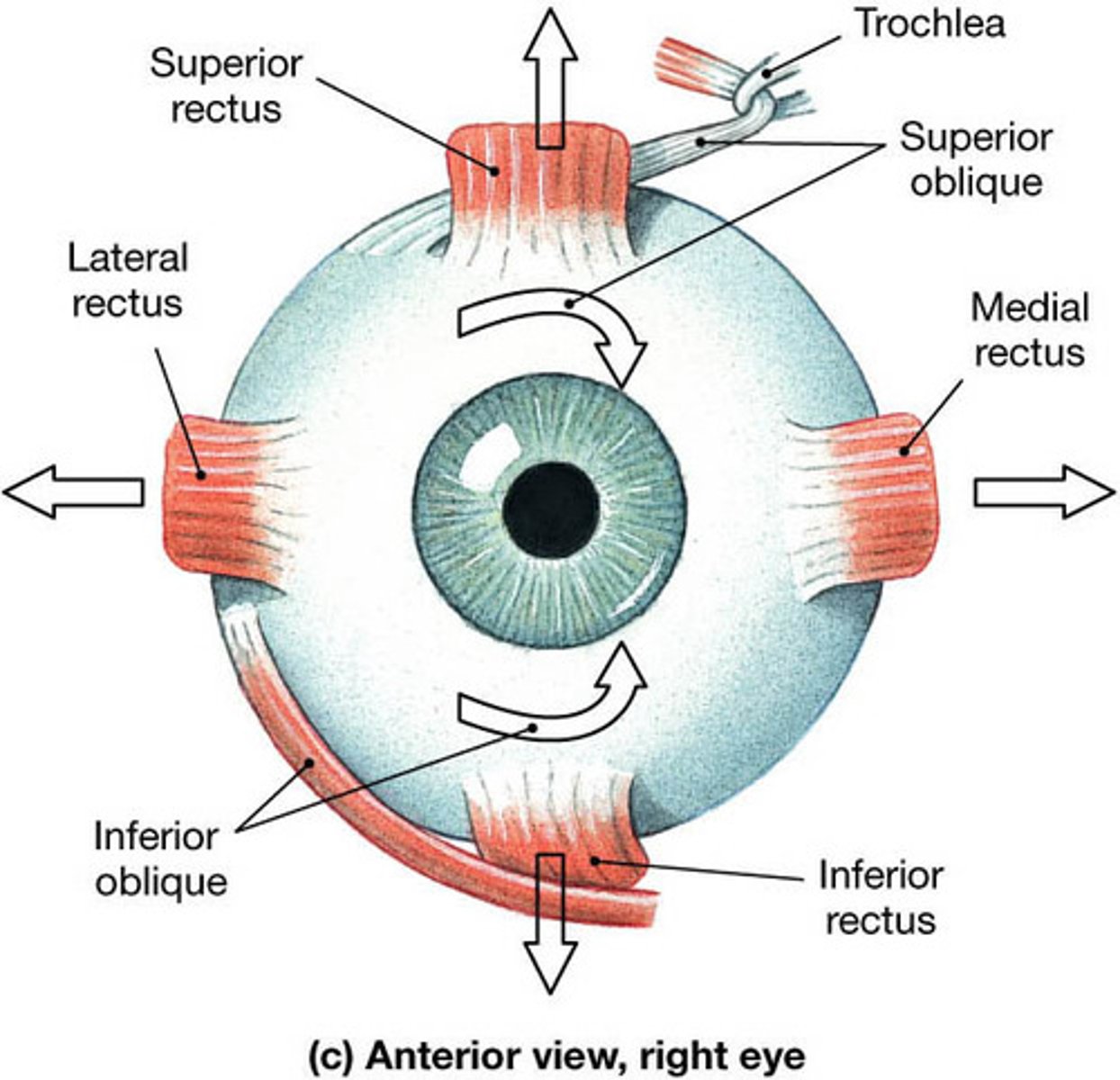
What are the Six Eye muscles ?
Cornea
the transparent layer forming the front of the eye.
Iris
Colored portion of the eye which is a muscle that Controls the amount of light entering the eye
Ciliary Body
Contains muscle that controls the shape of the lens
Lens
The lens is a transparent, biconvex structure in the eye that, along with the cornea, helps to refract light to be focused on the retina
Retina
Contains sensory receptors that process visual information and sends it to the brain