Lec 5: Hypothesis, data collection and error
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what does having a significance level or p value of 0.05 mean in words
willing to accept a 5% chance your results are due to random error
risk of type 1 error or alpha
how to calculate power with beta
1-beta
what does power represent
the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis when it is false
80% power implies a 20% chance of making a type 2 error
the higher the power…
the more sensitive the test is to detecting a true effect
if power is high, the chance of making a type 2 error…
goes down
when you increase the sample size…
you increase power, sensitivity
reduces alpha, beta
Link between Alpha and Beta
decrease alpha from 5% to 1% increases the beta
increasing the alpha from 5% to 10% decreases the beta but higher risk of a type 1 error
larger effect size easier to detect a difference
small effect size more difficult to detect a difference - so need to increase sample size or reduce beta
increasing sample size reduces alpha and beta as increase
precision
list the Basic Elements of Testing Hypothesis
state null and alternative hypothesis
choice of appropriate level of significance (α)
test statistic (formula): application of sample results in the formula to
calculate the value of test statistic use for decision purposerejection region (critical region): based on alternative hypothesis and
level of significance (α)decision: decide whether or not reject null hypothesis
Underlying Assumptions for Testing of Hypothesis for Population Mean
the sample has been randomly selected from the population or process
the underlying population is normally distributed (or if not normally
distributed, then n is large say greater than or equal to 30)population variance (σ²) either known or sample variance (s²)assumed to be approximately equal to population variance (σ²), when n is large
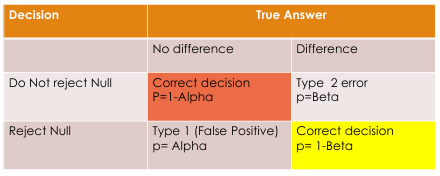
Potential Errors pic
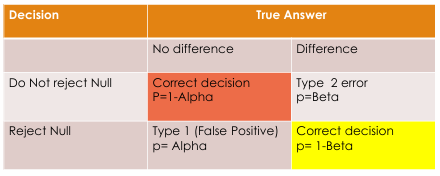
as type 1 error decreases…
type 2 error increases
what are alpha and beta also used to calculate
sample size
power of the test (probability of find an effect if one exists)
effect size
Statistical Testing purpose
used to determine the probability of error in the rejecting the null hypothesis
p value def
probability of finding an effect as large or larger than the observed effect
RESEARCH PROCESS steps
generating the idea
generating the hypothesis
deciding on risk of Type 1 and Type 2 errors
collecting the data
analysing the data
deciding whether the data supports us to reject the NULL HYPOTHESIS
dissemination
generating the idea for the next research project
which part of the hypothesis is the theory
conducts the study and puts forward an explanation for their predictions/findings
theory def/characteristics
interrelated set of constructs formed into propositions that specify the relationships among variables
describes how and why variables are related
can have a series of if-then statements
the p value is also rejected when..
its lower than the alpha