ch 15 Jarvis Physical Examination & Health Assessment
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
eye anatomy
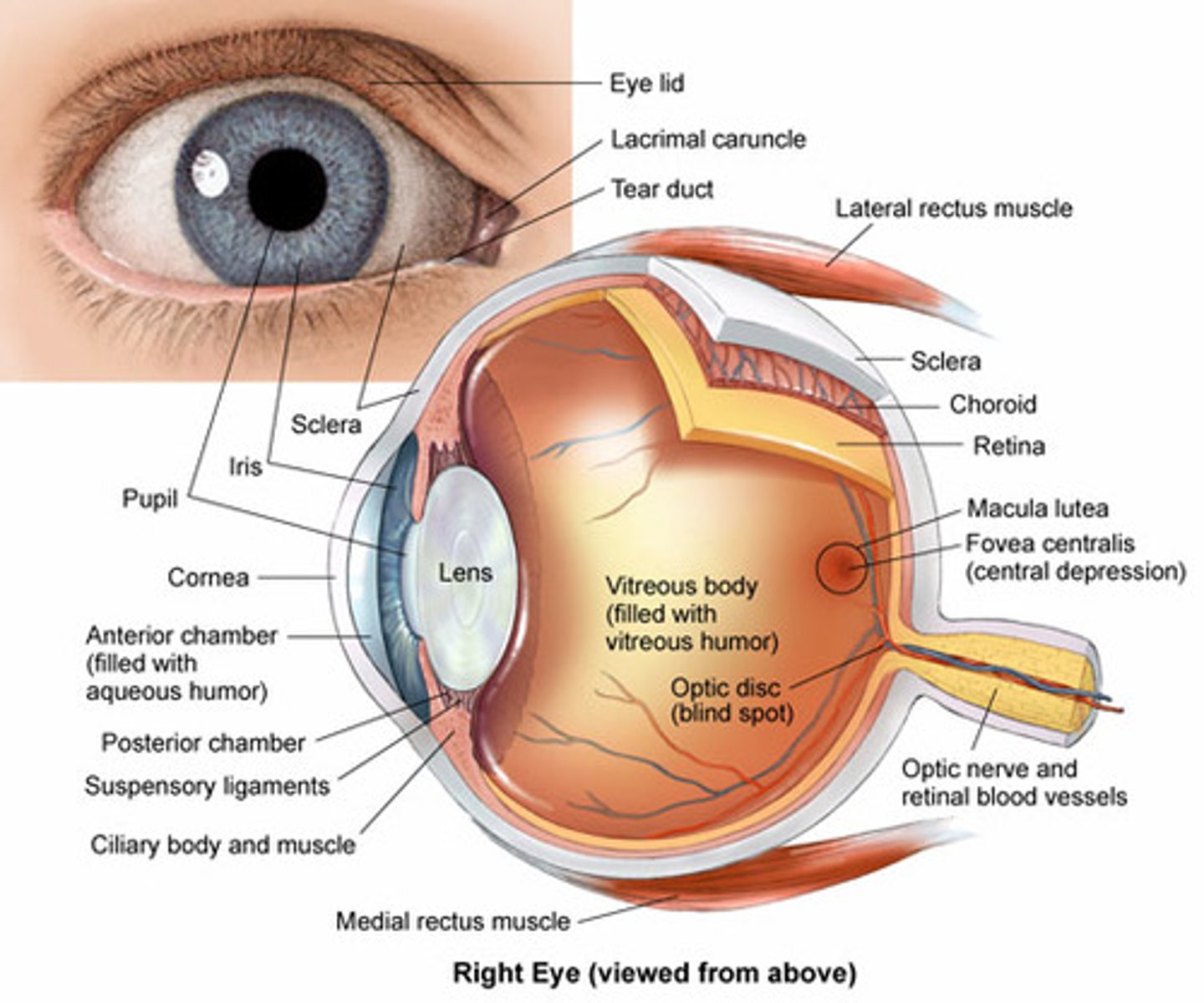
cornea: transparent, curved membrane on the front of the eye.
sclera: white out layer protective covering of eye.
aqueous humor: fills the cavity between the cornea and the lens.
iris: colored part of the eye, which covers the lens. Functions as a diaphragm, changing pupil size.
pupil: hole in center of iris that lets light through to fall on the lens. The iris opens and closes the pupil depending on the intensity of light.
lens: focuses light. Under muscle control (ciliary body), it can move forward and backward, and also get thinner or fatter to change its focal length.
retina: surface of the inside of the eye, which is covered with light-sensitive receptor cells.
fovea: had highest density of photoreceptors can be found in the fovea; the fovea is the center of your visual field. Located at the center of the macula on the ocular fundus
accommodation
adaptation of the eye for near vision by increasing the curvature of the lens.
anisocoria
unequal pupil size
arcus senilis
gray-white arc or circle around the limbus of the iris that is common with aging
Argyll Robertson pupil
pupil does not react to light; does constrict with accommodation
astigmatism
refractive error of vision due to differences in curvature in refractive surfaces of the eye (cornea and lens)
A-V crossing
crossing paths of an artery and vein in the ocular fundus
bitemporal hemianopsia
loss of both temporal visual fields
blepharitis
inflammation of the glands and eyelash follicles along the margin of the eyelids
cataract
opacity of the lens of the eye that develops slowly with aging and gradually obstructs vision
chalazion
infection or retention cyst of a meibomian gland, showing as a beady nodule on the eyelid
conjunctivitis
inflammation of the conjunctiva (pink eye)
cotton wool area
abnormal soft exudates visible as gray-white areas on the ocular fundus
cup-to-disk ratio
ratio of the width of the physiologic cup to the width of the optic disc, normally half or less
diopter
unit of strength of the lens settings on the ophthalmoscope that changes focus on the eye structures
diplopia
double vision
drusen
benign deposits on the ocular fundus that show as round yellow dots and occur commonly with aging
ectropion
lower eyelid loose and rolling outward
entropoin
lower eyelid rolling inward
exophthalmos
protrusion of the eyeball
fixation
very rapid movements to put the target eye is "fixed" on back on the fovea when head is turning.
fovea
area of keenest vision at the center of the macula on the ocular fundus
consensual
both sides of the body respond equally to the stimulus (ex. both pupils dilate the same)
Glaucoma
a group of eye diseases characterized by increased intraocular pressure
hordeolum (stye)
red, painful pustule that is a localized infection of hair follicle at eyelid margin
lid lag
abnormal white rim of sclera visible between the upper eyelid and the iris when a person moves the eyes downward
macula
round darker area of the ocular fundus that mediates vision only from the central visual field
microaneurysm
abnormal finding of round red dots on the ocular fundus that are localized dilations of small vessels
miosis
constricted pupils
mydriasis
dilated pupils
myopia
nearsightedness, refractive error in which near vision is better than far vision
nystagmus
involuntary, rapid, rhythmic movement of the eyeball
optic atrophy
pallor of the optic disc due to partial or complete death of optic nerve
optic disk
area of ocular fundus in which blood vessels exit and enter
papilledema
stasis of blood flow out of the ocular fundus; sign of increased intracranial pressure
presbyopia
decrease in power of accommodation that occurs with aging
pterygium
triangular opaque tissue on the nasal side of the conjunctiva that grows toward the center of the cornea
ptosis
drooping of upper eyelid over the iris and possibly covering the pupil
red reflex
red glow that appears to fill the person's pupil when first visualized through the ophthalmoscope
strabismus
crossed eyes
xanthelasma
soft, raised yellow plaques occurring on the skin at the inner corners of the eyes
opthalmoscope
instrument used to examine the interior of the eye
PERRLA (CN II, CN III)
P - Pupils should be clear
E - Equal in size and between 3 to 5 cm
R - Round in shape
R - Reactive
L - to Light both directly and consensually when a light is directed into one pupil and then the other
A - Accommodation of the pupils when they dilate to look at an object far away and then CONVERGE and CONSTRICT to FOCUS on a near object.
*cannot check accommodation on unconscious patient
Snellen chart
used to measure visual acuity. (patient usually stand 20ft away from chart)
20/20 is normal
20/30-you can read at 20 ft what the normal eye can see at 30 ft
confrontation test
gross measure of peripheral vision. It compares the person's peripheral vision with your own (one eye covered, wiggling fingers)
Corneal Light Reflex (Hirschberg Test)
reflection of the light on the corneas, should be in the exactly same spot on each eye
assymetry indicates deviation in alignment from eye muscle weakness or paralysis
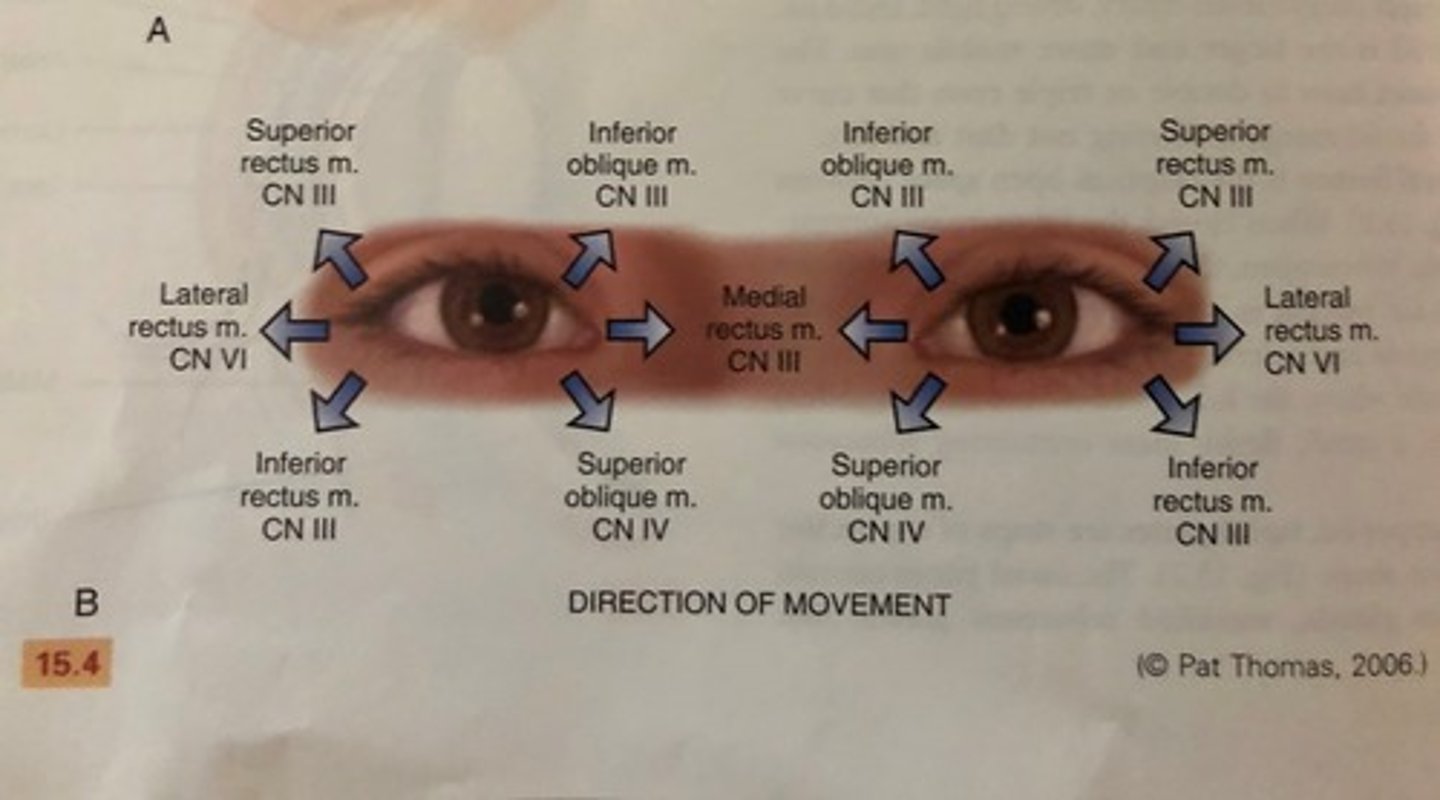
diagnostic positions test (CN III, CN IV, CN VI)
6 cardinal gazes: normal response is parallel tracking of the object with both eyes
when eye movement is not parallel: indicates weakness of an EOM or dysfunction of cranial nerve innervating it (CN III, IV, VI)
papillary light reflex (CN II, CN III)
dark room, patient looks into distance while light is shined from side of eye. Both pupils should constrict at same time (consensual)
accommodation test
patient looks at distant object (pupils dilate) patient looks at close object (pupils constrict)
lacramal apparatus
provides constant irrigation to keep the conjunctiva and cornea moist and lubricated.
lacrimal gland
gland located in the upper outer region above the eyeball that secretes tears
inner canthus
The corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet, tears drain into