AP Statistics Unit 3
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Population
group being observed
Sample
Part of said group to gain information about the population
Statistic
A value that describes a sample
Parameter
A value that describes a population (-estimated from the statistic)
Observational Study
no treatments
studies correlation, but cannot imply causation
lurking variables make it difficult to establish causal links
measured in a natural setting
Sample Surveys
research use questionnaires or interviews to collect information from a sample to learn about the entire population
Census - A type of survey meant to collect data for ALL individuals in the population.
Difficulties — Collecting responses cost resources, and time consuming.
Best used when it sample is randomly selected.
Bias can be introduced if sample is not randomly selected.
3 points to a good survey
Speak the audience’s language
Keep it simple
Stay unbiased
Advantages of Surveys
Various forms of collecting data:
Efficient for collecting data from a large population in a timely manner
Can be designed to focus only on needed response questions
Applicable to wide range of topics.
Disadvantages of Surveys
Dependent on respondents’ honesty and motivation when answering
Can be flawed by bias
Experiments
Purpose is to study whether a treatment causes a change in the response of an experimental unit.
Human experimental units are called subjects.
All experimental units need to believe they are experiencing the same condition.
The best experiments use random assignment into treatments, are comparative, double—blind, placebo controlled.
Confounding Variable
Lurking Variable
Placebo
“fake” treatment that appears to be the actual treatment, but has no effect.
Placebo Effect — Favorable response to the placebo.
Single-Blind Study
Double-Blind Study
SB — Researchers are aware which group has placebo. Subj don’t
DB — Both researchers and subjects are not aware which group has the placebo.
Simple Random Sample
Sample needs to be representative of the population
SRS allows every member to have an equal chance.
technology or table of rand digits.
Systematic Random Sampling
Is a form of SRS, but you pick units by increments.
Stratified Random Sampling
Divide the population into homogeneous groups; by characteristic
SRS from each strata
Cluster Random Sampling
Divide the population into heterogeneous groups; random grouping/not by characteristic
SRS from each cluster
Multistage Sampling
Combination of Cluster and Stratified
Stratified comes first.
The bigger the sample…
The better the estimate
Bias
Producing inaccurate information that systematically favors one outcome over other outcomes.
Coverage Bias
Over or under representation
i.e. Only seniors responded
Non-response Bias
Can’t be contacted or don’t participate.
i.e. Don’t fill out Google form on classroom
Response Bias
Underestimate or exaggerate
Hidden Bias (Implicit Bias)
Unconscious or automatic attitudes towards something or someone
Voluntary-response bias
Members of the population volunteer to be in the sample.
Individuals with strong pro/anti opinions are willing to participate
Convenience Sample
Easy-to-reach members of a population — Often does not question the entire population
i.e. Dr. Williams only sample her AP Calc students to represent all math students at our school.
Leading Question
Prompts or encourages you to answer in a certain way.
Loaded Question
Controversial or unjustified assumption and normally requires more information
Double-Barreled Question
Asking more than one question but looking for one response
Choice Bias
Repeated — Intervals overlap
Limited — Only a few choices.
3 types of experimental designs
Completely Randomized Design
Randomized Block Design
Matched Pairs Design
Principles of Experimental Design; how many are there?
4
Comparison
Groups don’t differ greatly before experiment begins
Factor — Explanatory variable; is manipulated
Levels — Various groups factors can take
Treatment — Combination of levels from all the factors an experimental unit receives.
Randomization
Must be incorporated in the selection process or distribution of experimental units into treatment and control groups
Minimizing differences allows measured differences to be correlated to treatment or by chance of RA.
Control
A group that is treated the same as the treatment groups, but doesn’t receive the treatment.
Control Group — Baseline
Reduces variability in the response variable.
Replication
Using enough experimental units so that differences in the effects of treatments can be distinguished from chance between groups
Natural variability can still occur
Experimental Units
Individuals or objects that are assigned treatments
Completely Randomized Design
→ Identify sample
→ Randomly Assign Subjects
→ Identify the treatments
→ Compare results
Randomized Blocked Design
→ Identify the sample
→ Block the subjects/units
→ Randomly Assign Subjects
→ Identify the treatments
→ Compare results
→ Combine results
Matched Pairs Design
Subjects receive both the control and the treatment
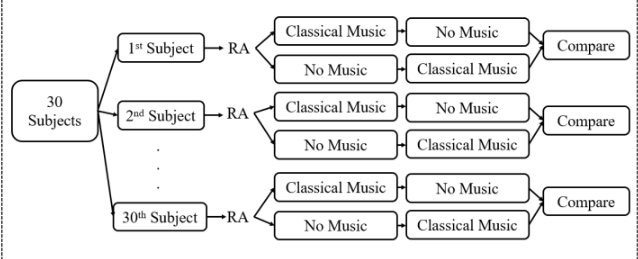
Selection Bias
When a sample doesn’t accurately represent a population from which it was drawn.
Explanatory Variable
The variable that is being manipulated; independent variable
Response Variable
The variable that changes in response to the explanatory variable; dependent variable
Why are control groups used in experiments?
Inference
Drawing conclusions beyond the data at hand
A Confounding/Lurking Variable
A variable that is present in an experiment that is
Tied to the explanatory variable in some way
Has an effect on the response variable
Difficult to seperate from the explanatory so we don’t know if it was the explanatory or confounding variable that caused the observed response.
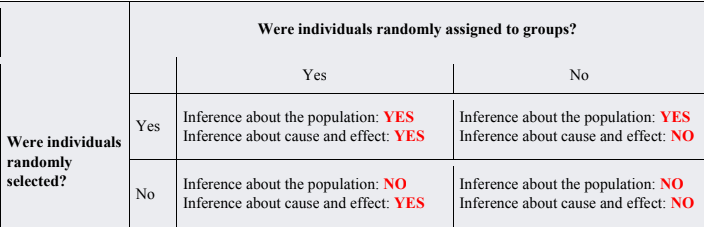
Were individuals randomly selected — Were individuals randomly assigned?
Inference about the population
Inference about cause and effect
Laws when dealing with human subjects
Revied by the IRB
Informed consent
Confidentiality
Replacement
the practice of returning a selected item back into the pool of possible selections before making another choice