AP Music Theory Terms - Q2
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Picardy Thirdy
A major chord that occurs at the end of a piece in a minor key
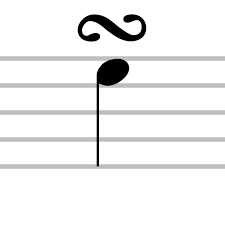
Turn
A musical ornament consisting of the notes above and below a principal note and returning to the original note
ex. e—» f —» e —» d —» e
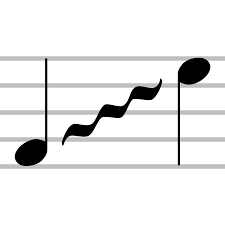
Mordent
A musical ornament that consists of a principal note, followed by the note immediately below or above it, and then returning to the principal note.

Glissando
A continuous slide from one pitch to another
Tremolo
A musical technique in which a performer plays an individual note or two alternating notes as fast as possible

Sentence
musical phrase; basic music idea
must have a cadence
Sentence Structure
[ x —» x1 —» series of fast runs —» cadence ]
A specific organization of musical ideas within a sentence, typically involving a musical idea (x), followed by a continuation (x1), a series of fast runs, and concluding with a cadence.
Period
A musical structure consisting of two phrases, the first ending in a weak cadence and the second in a strong cadence.
question followed by an answer
must have two cadences
Parallel Period
A type of period where the two phrases are similar in melody but differ in their endings, with the first ending in a weak cadence and the second in a strong cadence.
Contrasting Period
A type of period where the two phrases are contrasting in melody and differ in their endings, with the first ending in a weak cadence and the second in a strong cadence.
Double Period
a section of music that is made up of four phrases, with the first two phrases forming the antecedent group and the last two forming the consequent group
[phrase 1 (a)(weak Candace) —» phrase 2 (b)(strog cadance)]—» [phrase 3 (a’)(weak cadance) —» phrase 4 (b’) (strong cadance)]
Antecedent
A complete phrase that creates an expectation that is resolved by the subsequent consequent phrase
Consequent
A phrase that comes after an antecedent phrase and provides a conclusion or resolution