OB First: Exam 2
1/325
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
326 Terms
What are the nutritional needs of the newborn?
105-108 kcal/kg/day
How do breastfed babies differ from formula fed babies?
Formula fed babies gain weight much faster than breastfed babies because breastmilk progresses with fat content and is digested more easily.
How does a baby's weight fluctuate during the first few days of life?
Babies lose weight during the first 3-4 days after birth.
They can lose up to 10% of their birth weight.
Pediatricians pay close attention when weight loss reaches 7%.
Increase in feedings or supplementation until milk production increases to ensure the baby gets adequate nutrition.
After initial weight loss, how much weight should baby be gaining?
10g/kg/day or 5-7oz/week
What are the signs of dehydration in a newborn?
Depressed Fontanelles
Rapid, Weak Pulse
Elevated Low Grade Temperture
Dark Concentrated Urine
Dry, Hard Stools
Dry Skin w/ Little Turgor
Elevated Specific Gravity (1.020)
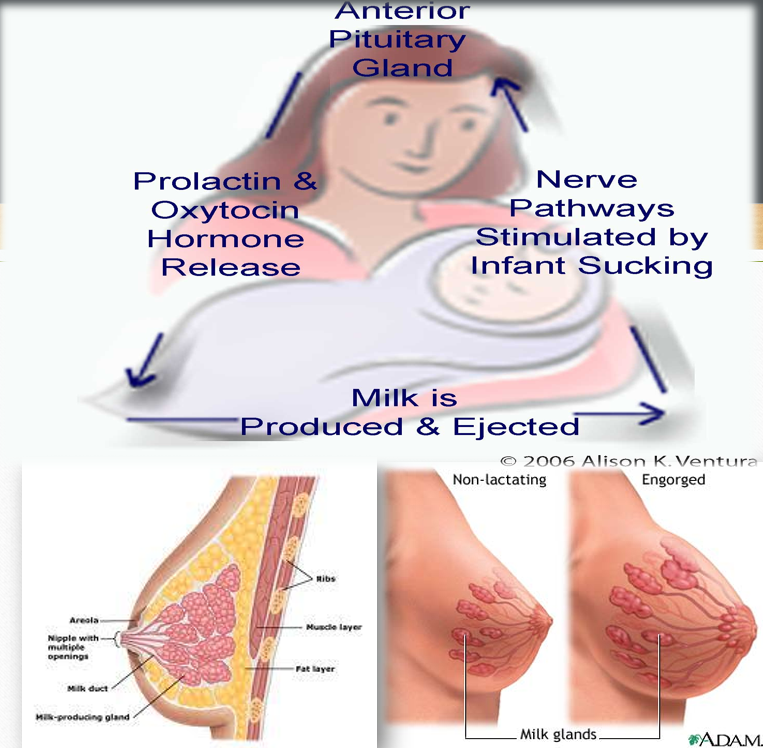
How does the breast make milk?
Ducts and alveoli grow during pregnancy under the influence of progesterone and estrogen.
Delivery of the placenta triggers the hormones prolactin and oxytocin.
Prolactin: produces milk.
Oxytocin: milk let down reflex (ejection of milk).
Stimulation of the breast.
The more often the breast is emptied, the more milk is made (Supply and Demand).
How much colostrum is present for 1 feed?
1-2 teaspoons
What factors interfere with milk supply?
Anything that interferes w/ the:
Growth of alveoli and ducts
Progesterone levels or other hormone levels
Breast stimulation
Breast reductions can interfere with milk production because of it cutting through nerve endings and the nipple. (a possibility)
Hx of breast cancer could cause issues w/ the milk supply.
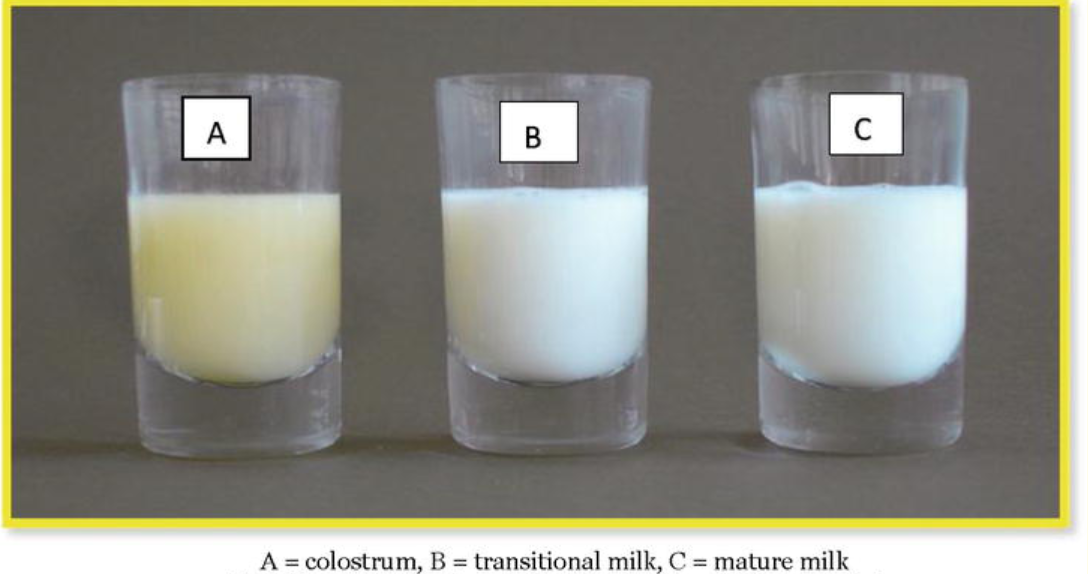
Colostrum
Yellow, creamy fluid.
Thicker than milk.
Contains: low fat, high protein, fat-soluble vitamins, and minerals.
Coats and protects the digestive tract.
Has a laxative effect that helps w/ meconium passage.
Provides passive immunity.
Develops during pregnancy and lasts several days (3-4) after delivery.

Transition Milk
Produced from the end of colostrum until two weeks postpartum.
Changes in appearance and composition.
Contains: more fat, sugar, vitamins, and calories.
Mature Milk
Looks thinner and more watery than cow’s milk.
White but can have a slight blue tint.
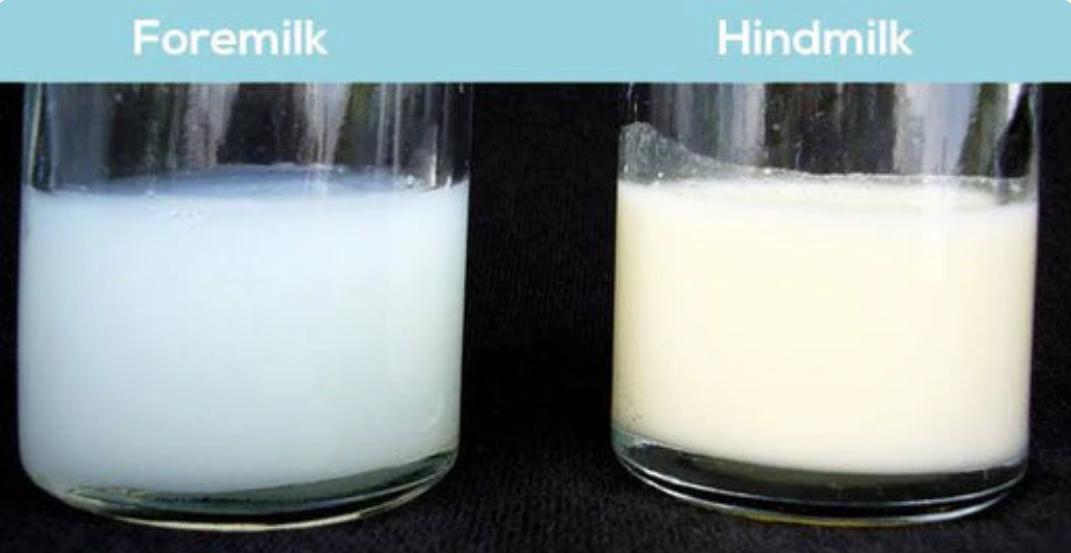
Foremilk: Found at the beginning of feeding; contains more water, less fat, and higher lactose (the appetizer).
Hindmilk: Found later in feeding; has a higher fat content (the entrée).
Important to let the baby complete feeding on one breast before switching to the other!
Provides 20kcal/oz.
Recommended for the first 6 to 12 months of life.

Breastfeeding Tips
Once the baby is done, gently take them off the breast and burp them.
Offer the other breast to see if they need a “topping off” or if they are truly full.
At the next feeding, start with the breast that was offered last to ensure both breasts are stimulated for sufficient milk production.
Types of Milk
Colostrum
Transition Milk
Mature Milk:
foremilk
hindmilk
The Golden Hour
Baby is alert and ready to feed within 1–2 hours after birth.
The optimal place for the baby to recover from birth is skin-to-skin on the mother’s chest.
Helps the baby de-stress, stabilize blood glucose, and regulate body functions.
Baby will instinctively root and seek out the breast.
Followed by recovery sleep (18-24 hours).
Might have to wake baby up to get their feed.
Educate momma.

What are the advantages of breastmilk?
Inhibits bacterial growth.
Easily digested—contains lactose, lipids, fatty acids, and amino acids.
Varies in content based on the newborn’s needs.
Promotes maternal-newborn attachment.
Convenient, safe, and free of cost.
What are the disadvantages of breastfeeding?
Medications can pass from mother to newborn through breastmilk.
Mother with HIV or AIDS should not breastfeed.
Excludes the father from direct feeding involvement.
Working mothers may need to pump during work to maintain milk supply.
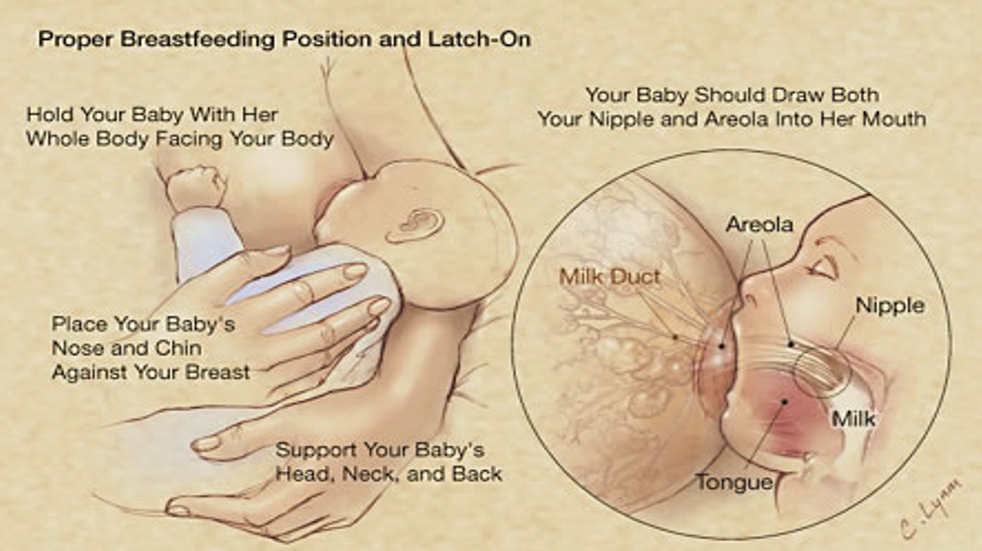
What is the best latch for baby and it doesn't hurt momma?
Hamburger Latch:
Prevents sore and cracked nipples.
Allows efficient milk transfer.
The baby must open really wide to latch onto the breast correctly.
If not, they will only latch onto the nipple, which can cause discomfort and ineffective feeding.
What are some breastfeeding positions?
Cradle hold
Cross-cradle hold
Football hold
Side-lying position
Laid-back nursing
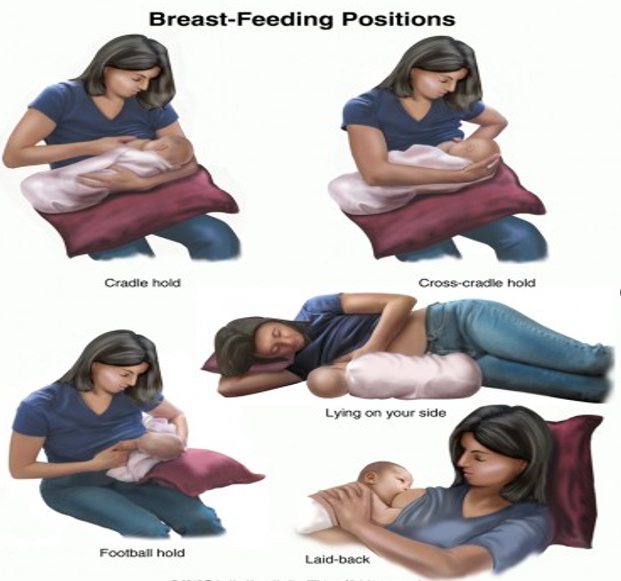

What is the most important factor when picking the best position for breastfeeding?
Momma needs to be comfortable!
Feeding Patterns
On demand
Usually every 2-3 hours
We don’t want the baby to go longer than 4 hours without feeding.
If this persists, call the pediatrician.

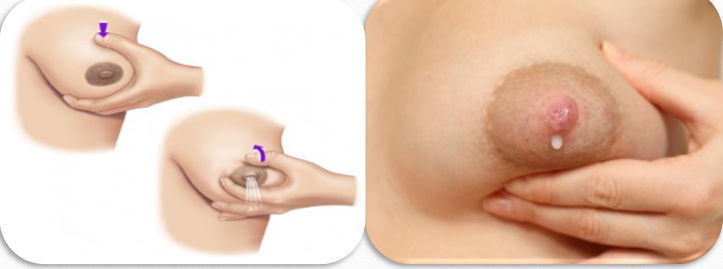
What is the technique for hand expression of milk?
Pull back on the breast, then push forward to expel milk.
15 to 30 drops of milk is considered a feeding for the baby
Typically done during baby’s recovery sleep when they are not interested in feeding.
Finger feeding: Expelling milk, placing it on a finger, and putting it into the baby's mouth.
Spoon feeding: Cleaner than finger feeding and allows visibility of milk intake.
Breast Pumps

Milk Storage
The Rule of 5
Room Temperature: 5 hours
Fridge: 5 days
Freezer: 5 weeks
Deep Freezer: 5 months
**After a feeding, only leave bottle out for an hour b/c of bacterial growth (for breast milk and formula)**
How do we prepare breastmilk?
Never use the microwave!
hot and cold spots.
Submerge in warm water.
How do we know if breastfeeding is successful?
Nursing at least 8 times in 24 hours
Infant swallowing
Breasts appear soft after feeding
Wet diapers*
Stools*
Weight gain*
**Tell mom and dad to log pees and poops**
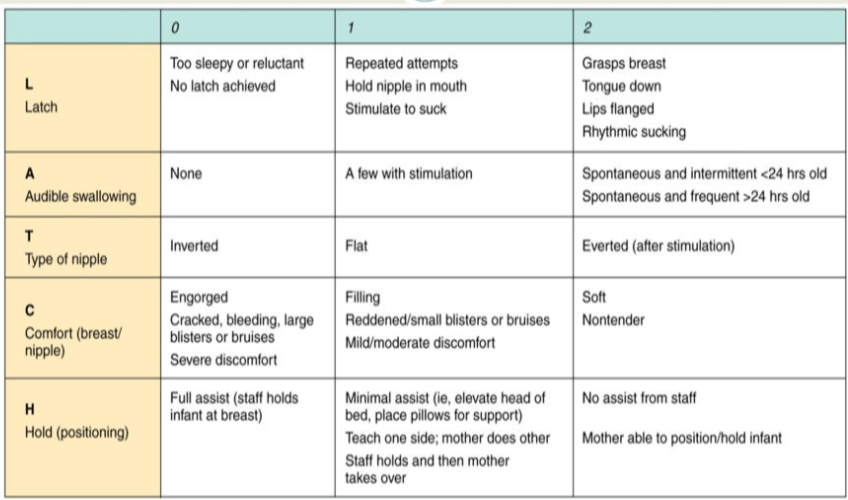
What is the LATCH Score?
It is a systematic method for breastfeeding assessment and charting.
L - Latch
A - Audible swallowing
T - Type of nipple
C - Comfort
H - Hold
Each category is worth up to 2 points, for a total of 10 points.
What are the 10 Steps to Successful Breastfeeding?
Have a written breastfeeding policy that is routinely communicated to all healthcare staff.
Train all healthcare staff in the skills necessary to implement this policy.
Inform all pregnant women about the benefits and management of breastfeeding.
Help mothers initiate breastfeeding within one hour of birth.
Show mothers how to breastfeed and maintain lactation, even if they are separated from their infants.
Provide infants no food or drink other than breast milk, unless medically indicated.
Practice rooming in—allow mothers and infants to remain together 24 hours a day.
Encourage breastfeeding on demand.
Give no pacifiers or artificial nipples to breastfeeding infants.
Foster the establishment of breastfeeding support groups and refer mothers to them on discharge from the hospital or birth center.
What is the benefit of milk donation?
If momma is unable to breastfeed or can't be there (nicu).
Formula feeding is…
Based on cow’s milk, soy protein, and other special formulas.
Must be prepared correctly with the right proportions, clean water, and bottles.
Potential allergic reactions.
Used up to one year of age.
Expensive.
**Once the bottle’s nipple is attached, you have 1 hour to use it. Do not reuse due to the risk of infection.**
What are the teaching guidelines for Formula feeding?
Wash your hands with soap and water before preparing formula.
Mix the formula and water in the exact proportions specified on the label.
Always hold the newborn and bottle during feedings; never prop the bottle.
Never freeze formula or warm it in the microwave.
Place refrigerated formula in a pan of hot water for a few minutes to warm.
Test the temperature of the formula by shaking a few drops on your wrist.
Hold the bottle like a pencil, keeping it tipped to prevent air from entering. Position the bottle so the nipple remains filled with milk.
Burp the infant after every few ounces to allow swallowed air to escape.
Move the nipple around in the infant’s mouth to stimulate sucking.
Always keep a bulb syringe close by in case choking occurs.
Avoid putting the infant to bed with a bottle to prevent "baby bottle tooth decay."
Feed the newborn approximately every 3 to 4 hours.
Use an iron-fortified formula for the first year.
Prepare enough formula for the next 24 hours.
Check nipples regularly and discard any that are sticky, cracked, or leaking.
Store unmixed, open liquid formula in the refrigerator for up to 48 hours.
Throw away any formula left in the bottle after each feeding.
What are the advantages of formula feeding?
Easy and ready to use
Father can feed
Helpful for working mothers

What are the disadvantages of formula feeding?
Less skin-to-skin contact.
Less immunity passed to baby.
Refrigeration system necessary.
Clean water and bottles needed.

What is high risk pregnancy?
A condition that jeopardizes the health of the mother, her fetus, or both.
This condition may result from pregnancy or may have been pre-existing before pregnancy.
1 in 4 pregnancies are considered high risk.
What are the 4 types of factors that place a woman at risk for a high risk pregnancy?
Biophysical
Environmental
Psychosocial
Sociodemographic
What are biophysical factors that place a woman at risk for a high risk pregnancy?
Genetic Conditions
Chromosomal Abnormalities
Inherited Disorders
Large Fetal Size
Preterm Labor and Birth
Cardiovascular Disease
Placental Abnormalities
Infection
Diabetes
Nutritional Status
Post-Term Pregnancy
What are environmental factors that place a woman at risk for a high risk pregnancy?
Infections
Radiation
Pesticides
Illicit drugs
What are psychosocial factors that place a woman at risk for a high risk pregnancy?
Smoking
Caffeine
Alcohol and Substance Abuse
Inadequate Support System
Maternal Obesity
Situational Crisis
History of Violence
Emotional Distress
Unsafe Cultural Practices
What are sociodemographic factors that place a woman at risk for a high risk pregnancy?
Poverty
Lack of Prenatal Care
Age Younger than 15 or Older than 35
Marital Status
Accessibility to Healthcare
Ethnicity
What are 2 types of antepartum bleeding?
Placenta Previa
Abruptio Placentae (aka placental abruption)
Placenta Previa
The placenta is improperly implanted in the lower uterine segment.
Placenta may cover the cervical os (opening of the cervix).
Diagnosed by ultrasound.
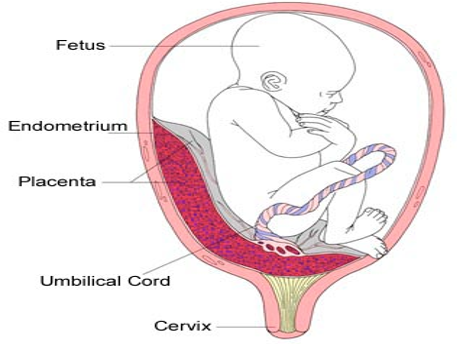
What is the classical presentation of a Placenta Previa?
Painless
Bright-red bleeding
Normal Placenta vs Placenta Previa
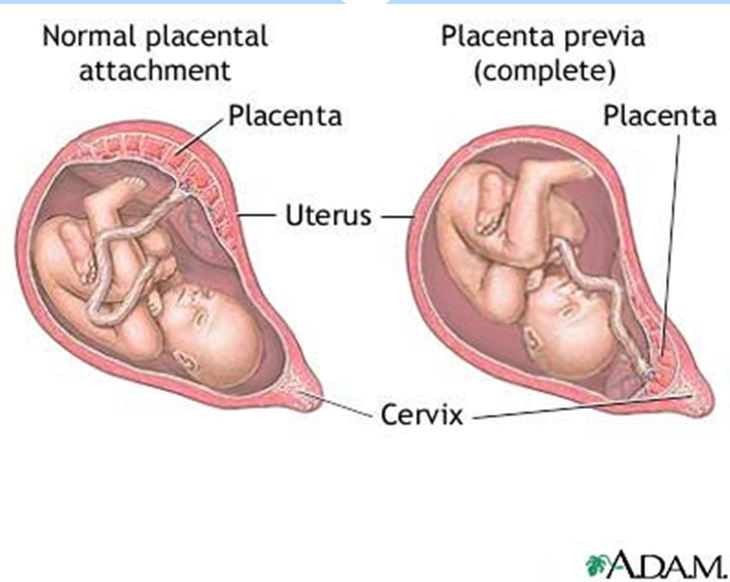
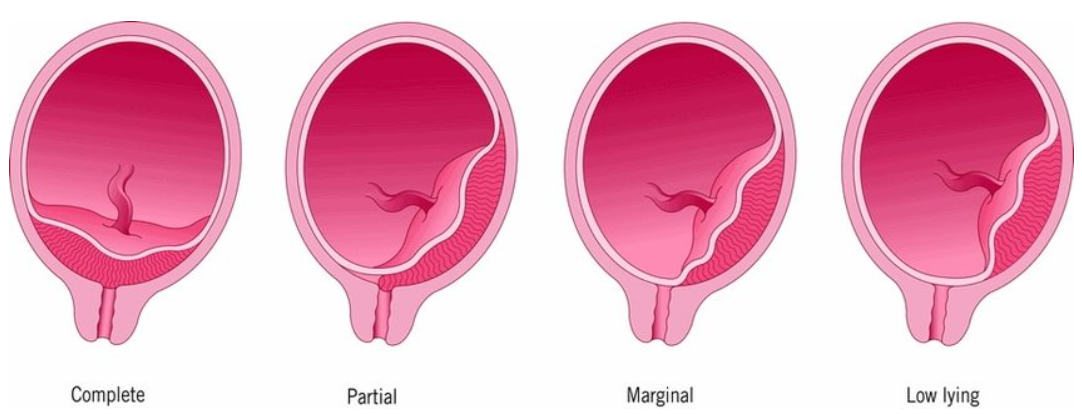
What are the classifications of Placenta Previa?
Total/Complete: Internal os is completely covered by the placenta.
Partial: Internal os is partially covered by the placenta.
Marginal: Edge of the placenta is at the margin of the internal os.
Low-lying placenta: Placenta is implanted in the lower segment but does not reach the os.
What is the management of a Placenta Previa?
Bed rest until 37 weeks (so until full-term)
No vaginal exams
Monitor blood loss
Monitor fetal heart tones
Betamethasone (medication given to mom for fetal lung development)
IV fluids and monitor mom’s vitals
Pelvic rest, including no intercourse
_______________________________________________________________
**So, it can resolve itself over the course of pregnancy → As the uterus grows, the placenta migrates/moves out of the way.**
**If previa does not resolve, a C-section will be required for safe delivery.**
Placenta Previa & Placental Abruption
For placenta previas, you do not need oxygen since it is just out of normal position.
When the placenta starts separating from the uterus (abruption), that’s when the baby needs oxygen.
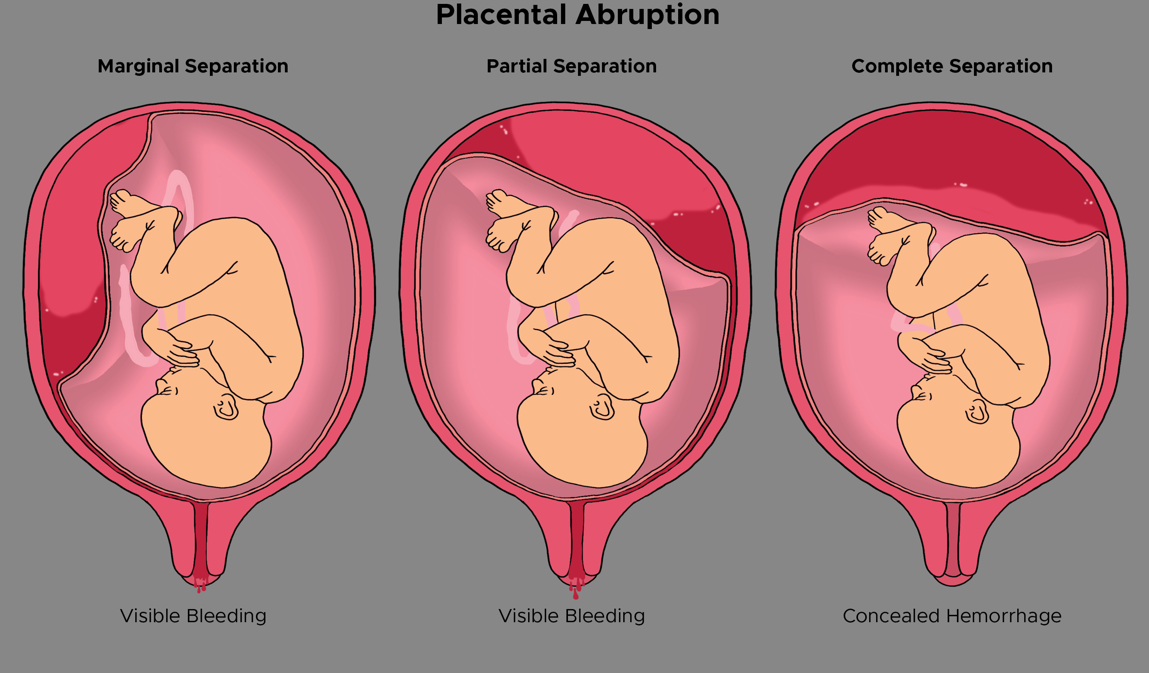
Abruptio Placenta (aka Placental Abruption) is the…
The premature separation of a normally implanted placenta from the uterine wall.
Mom is going to go in for an emergency C-Section
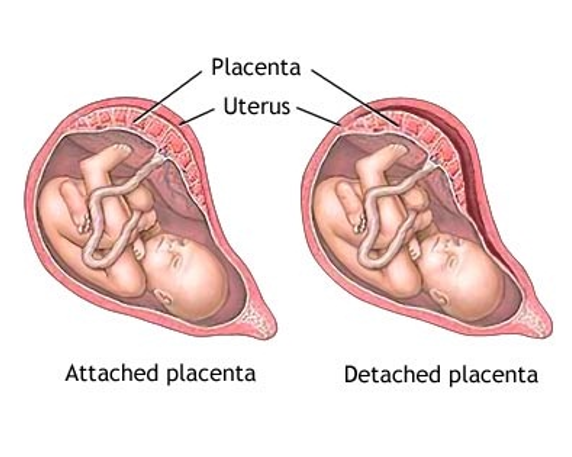
What is the classical presentation of a Placental Abruption?
Sudden pain (stabbing)
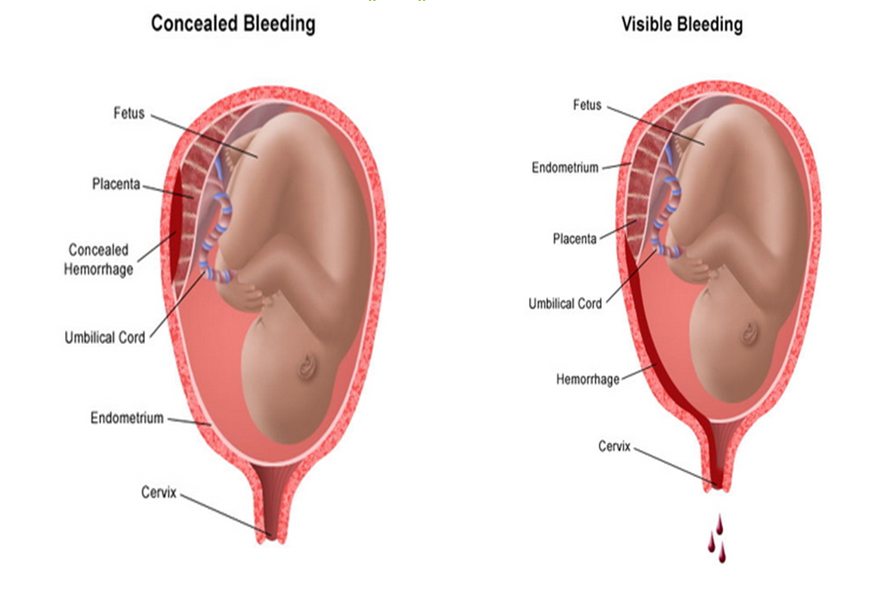
Blood can be visible or concealed
May have fetal distress
Uterus may be firm or rigid
Concealed Bleeding vs Visible Bleeding
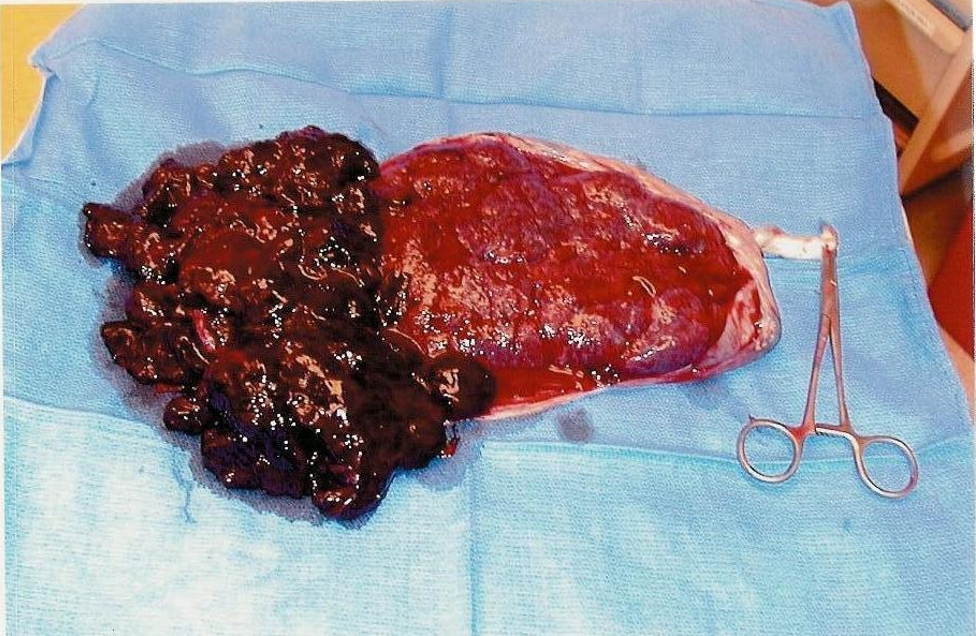
Abrupted Placenta Picture
Causes of a Placental Abruption are…
Cigarette Smoking
Increased Maternal Age
Alcohol
Cocaine
Short Umbilical Cord
Multiparity
Trauma
Hypertension (most common cause)
What are the classifications of Placental Abruption? (dont’t need to memorize)
Marginal: Blood passes between the fetal membranes and the uterine wall and escapes vaginally.
Central: Placenta separates centrally, and blood is trapped between the placenta and uterine wall (concealed bleeding).
Complete: Massive vaginal bleeding (almost total separation).
___________________________________________________________________
Class O = Asymptomatic
Class I = Mild; most common
Class II = Moderate; mom and fetus show distress
Class III = Severe; maternal shock and fetal death likely
What are the predisposing factors for a PPH?
Uterine Atony (the uterus is not contracting)
Lacerations
Retained Placental Fragments
Overdistended Bladder
Nursing Interventions of PPH
Uterine massage (fist/aggressive massage)
Frequent voiding (encouraging mom)
Assess H&H (see how much it dropped during episode)
Medications:
Oxytocin (causes uterine to contract)
Cytotec (causes uterine to contract)
Methergine (used IM)
Hematite (SE of diarrhea is common)
Assess urinary output
Encourage rest
Encourage foods high in Iron (Ex: red meats, poultry, fish, liver, spinach, tofu, etc)
Safety:
Rise slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Seated while holding the newborn.
Prenatal Loss
Loss of a fetus from the time of conception until the time of delivery.
Spontaneous Abortion/Miscarriage
Stillbirth
Ectopic Pregnancy
Death shortly after birth

Spontaneous Abortion
A naturally occurring abortion prior to 20 weeks.
Risk Factors:
AMA
Drug Use
Weakened Cervix
Placental Abnormalities
Chronic Maternal Disease
Classifications of Spontaneous Abortion
Threatened: unexplained bleeding; the fetus may be in danger or not; the cervix is usually closed.
Imminent/Inevitable: it is going to miscarry, nothing is going to stop it; more bleeding/cramping; cervix starts to dilate.
Complete: all products of conception are expelled from the body.
Incomplete: only parts of conception are expelled; usually the placenta remains.
Missed: fetus dies but not expelled; cervix closed; diagnosed via ultrasound.
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: 3 or more pregnancy losses.
Septic: presence of infection (like prolonged rupture of membrane)
Management of Spontaneous Abortion
Psychological Support
Reflective Listening
Pain Relief
Nursing Management

Postmortem Care After a Perinatal Loss
Place appropriate signage on the outside of the room so everyone in the hospital is aware of the loss.
Give parents the opportunity to spend time with their baby.
Bathe and swaddle the baby.
Allow parents to participate or do this independently as desired.
Support parents’ wishes regarding photography (professional or otherwise).
Allow visitation in accordance with the wishes of the parents.
Assist parents in the collection of keepsakes.
Stillbirth
Loss of a fetus after the 20th week of pregnancy.
1 out of 160 pregnancies
Can happen right up until time of delivery.
Causes:
Placental Abruption
Pre-Eclampsia
Growth Restriction and resulting Hypoxia
Infections
Chromosomal Disorder
Umbilical Cord Torsion
Nuchal Cord
Trauma
Risk Factors:
AMA
Smoking
Drug Use
Malnutrition
Lack of Prenatal Care
Women of African-American Ethnicity
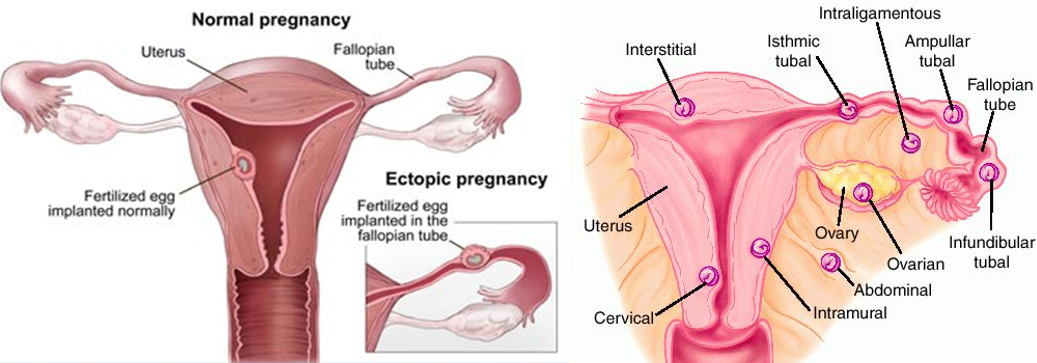
Ectopic Pregnancy
Implantation of a fertilized ovum in a site other than the endometrial lining of the uterus.
The egg can implant in the:
Fallopian tube
Ovary
Peritoneal cavity
Cervix
Risk Factors:
Tubal obstruction/damage
Delayed tubal transport
Congenital anomalies
Altered hormonal status
Smoking
AMA
Interventions for Ectopic Pregnancies
Methotrexate: terminates and expells the pregnancy.
lab work: have mom come in and watch beta hCG level go down to 0.
Surgery:
Salpingostomy (just the ectopic baby)
Salpingectomy (the whole tubes)
Rhogam: for moms that are Rh-negative.
**Folic acid is an antagonist to methotrexate, so they may need to stop prenatal vitamins**

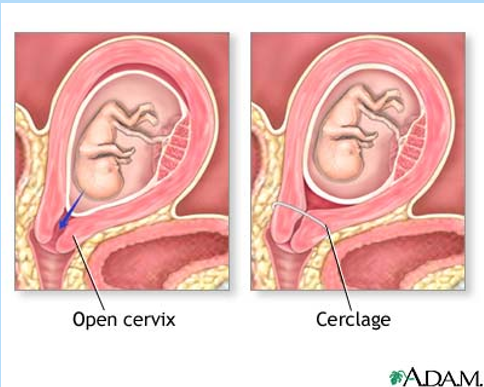
Incompetent Cervix (aka Cervical Insufficiency)
Painless dilation of the cervix without labor or uterine contractions.
Contributing Factors:
Congenital
Acquired
Biochemical
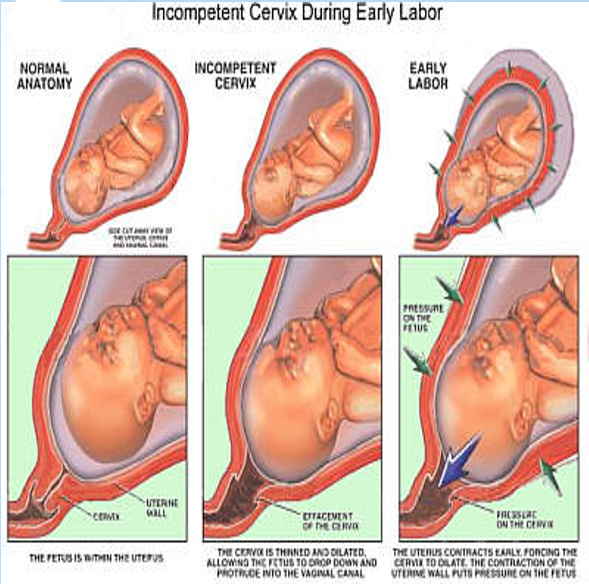
Interventions for Cervical Insufficiency
Close observation with ultrasound for cervical thinning
Cerclage:
Like tying a string early in pregnancy around the cervix to provide support so it doesn’t dilate too early; closer to delivery, around 37 to 38 weeks, the doctor will cut the string.
Tocolytics
Broad-spectrum antibiotics—due to mom being at increased risk for infection from cerclage.
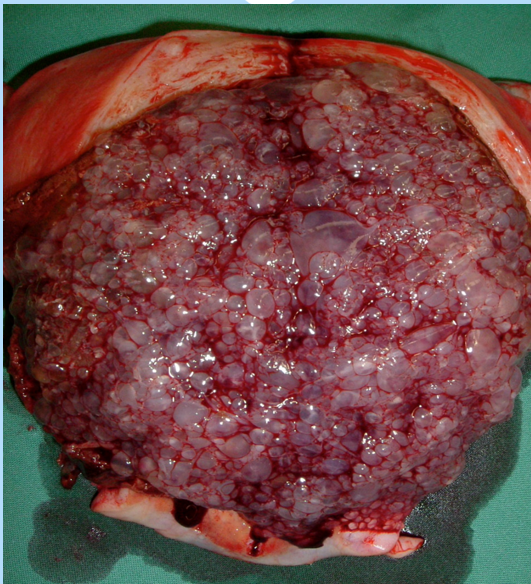
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (aka Molar Pregnancy)
A Condition in which a proliferation of trophoblastic cells (outermost layer of embryonic cells) results in the formation of a placenta characterized by hydropic (fluid-filled) grapelike clusters.
A fertilized egg that begins developing into a pregnancy but, instead of forming a viable baby, remains as pre-cancerous cells.
Signs and Symptoms of a Molar Pregnancy
Dark Brown Vaginal Bleeding (like prune juice—biggest sign)
Anemia
Hydropic Vesicles
Abnormal Uterine Enlargement
Absence of FHTs (fetal heart tones)
Marked hCG Elevation (b/c mom has that fertilized egg; positive pregnancy test)
Hyperemesis Gravidarum (pregnancy symptoms)
Interventions for a Molar Pregnancy
Surgery
Rhogam if indicated (negative blood type)
Methotrexate:
Due to possible development of choriocarcinoma
Following up by checking beta hCG levels to go down to 0.
No new pregnancies for 1 year:
Studies show that attempting pregnancy before waiting the full year significantly increases the risk of cancer recurrence and experiencing this condition again.
Preterm Labor (PTL)
Labor that occurs between 20 and 37 weeks completed of pregnancy.
#1 cause of neonatal morbidity
1 in 10 babies born prematurely
Infant may experience long-term health problems.
Estimated cost in the U.S: $30 billion annually spent on maternal and infant care related to prematurity.
Risk factors for PTL
African-American Race (double the risk)
Maternal Age Extremes (< 16 or > 40)
Low Socioeconomic Status
Alcohol, Smoking, or Drug Use
History of Previous Preterm Birth (triple the risk)
Multiple Gestations
Short Cervical Length
Infection (UTI, STI, Bacterial Vaginosis)
Stress
Signs & Symptoms of PTL
Spontaneous rupture of membranes (SROM)
Abdominal Pain
Low, Dull Back Pain
Pelvic Pain
Menstrual-like cramps
Vaginal Bleeding
Increased Vaginal Discharge
Urinary Frequency
Diarrhea
Pelvic Pressure
(Looks like normal labor pains)
What is the Criteria for Diagnosis of PTL
Cervical Dilation and Effacement
+
4 uterine contractions in 20 minutes or 8 uterine contractions in 1 hour
Management of PTL
Bedrest
Tocolytic Therapy—(to delay birth)
Corticosteriods—(to prevent or reduce respiratory distress on the infant in case of delivery)
Tocolytic Therapy
Goal: To arrest labor and delay birth long enough to initiate prophylactic corticosteroid therapy.
These drugs are used “off-label,” meaning that they must be effective for slowing down labor but have not been tested by the FDA for this purpose.
Procardia (Nifedipine)
Indomethacin (indocin)
Atosiban (Tractocile, Antocin)
Magnesium Sulfate
**Close monitoring of momma is necessary because of potential for serious side effects.**

Tocolytic Therapy: Magnesium Sulfate
Calcium antagonist and CNS depressant.
Prevents seizures; lowers blood pressure.
Relaxes smooth muscle of the uterus through calcium displacement.
Crosses the placenta.
Excreted by the kidneys.
Side Effects:
Headache
Visual Disturbance
Lethargy
Nausea/Vomiting
Toxicity:
Absence of Reflexes
Respiratory Depression
Oliguria
Confusion
Cardiac Arrest
**Use w/ caution in women w/ renal insufficiency and Myasthenia Gravis**
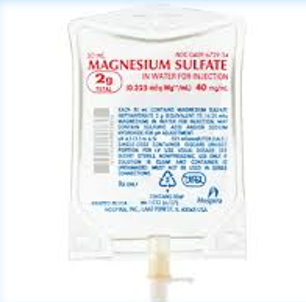
Nursing Considerations for a Patient on Magnesium Sulfate
Blood Pressure
Magnesium Levels (every 6-8 hours)
Respirations
Reflexes
Urinary Output
Fetus
Calcium Gluconate at bedside (reversal agent for magnesium toxicity)
**After birth, the neonate should be monitored and observed for magnesium toxicity for 24-48 hours.**
Corticosteroids: Betamethasone (Celestone)
Helps prevent or reduce the frequency and severity of respiratory distress syndrome and intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature infant.
Stimulates surfactant production in the unborn baby.
Administered 2 doses IM 24 hours apart.
Effects seen as soon as 48 hours after initial administration.
Nursing Implications:
Monitor maternal lung sounds and signs of infection.
Hypertension in Pregnancy
Most commonly encountered medical condition in pregnant women (up to 15% of all pregnancies).
Results in frequent hospital readmissions, maternal mortality, preterm births, and infant mortality.
Hypertension disorders include:
Gestational Hypertension (pregnancy-induced hypertension, PIH)
Pre-Eclampsia
Eclampsia
HELLP
Chronic Hypertension
Blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg before pregnancy or before 20 weeks gestation.
25% of women with this develop pre-eclampsia during pregnancy.
Management:
If BP exceeds 160/100, then drug treatment is recommended.
Gestational Hypertension (aka Pregnancy Induced Hypertension—PIH)
Hypertension that begins after the 20th week of pregnancy.
Blood pressure of 140/90 or greater without Proteinuria.
Must have an elevated blood pressure on 2 occasions, six hours apart.
Usually resolves by 12 weeks PP.
Pre-Eclampsia
Worldwide: 50,000 to 60,000 women die each year.
The most common hypertensive disorder in pregnancy.
A multisystem, vasopressive disorder that targets the cardiac, hepatic, renal, and central nervous system.
Pathophysiology:
Vasospasm which results in elevated BP, reducing blood flow to the brain, liver, kidneys, placenta, and lungs.
Decreased liver perfusion presents as epigastric pain and increased liver enzymes.
Decreased brain perfusion leads to headaches, visual disturbances, and hyperactive deep tendon reflexes (DTRs).
Decreased kidney perfusion leads to decreased urine output.
Proteinuria of 300 mg or greater in a 24-hour urine specimen.
Management of Mild Pre-Eclampsia
Mild: No signs of renal or hepatic dysfunction.
Bed rest (lateral recumbent position)
Diet (encourage mom to eat more protein!)
Monitor fetal status
Frequent evaluation of CBC, liver enzymes, platelet levels, and clotting factors.
Monitor protein in urine
Management of Severe Pre-Eclampsia
Bed rest (dark and quiet room to decrease stimulation)
Diet (encourage mom to eat more protein!)
Anticonvulsants (magnesium sulfate)
Corticosteroids (betamethasone)
Fluid and electrolyte replacement
Antihypertensives
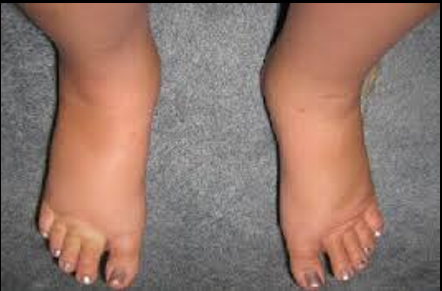
Signs that Pre-Eclampsia is Worsening
Increasing Edema
Worsening Headache
Epigastric Pain
Visual Disturbances
Decreasing Urinary Output
Nausea/Vomiting
Bleeding Gums
Disorientation
Generalized complaint of not feeling well
Hyperactive reflexes
Eclampsia
Blood pressure of 160/110 mm Hg
Marked Proteinuria
Seizures
Hyperreflexia
Other symptoms may include:
Severe Headache
Generalized Edema
Epigastric Pain
Visual Disturbances
Cerebral Hemorrhage
Renal Failure
HELLP
**Time for a C-Section!**
Management of Eclampsia
Assessment
Maintain Airways
Prevent Injury (seizure precautions—cushions on rails of bed)
Magnesium Sulfate
Dilantin or other anti-convulsants
Prepare for birth (C-Section)
What is the cure for Pre-Eclampsia and Eclampsia?
DELIVERY OF THE PLACENTA
HELLP acronym
H: Hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells)
EL: Elevated Liver Enzymes
LP: Low Platelet Count
HELLP is…
A variant (a relative) of preeclampsia and eclampsia.
Increased risk for:
Cerebral Hemorrhage
Retinal Detachment
Hematoma/Liver Rupture
Acute Renal Failure
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Placental Abruption
Maternal Death
Facts about HELLP
Hypertension is absent in 10-15% of women with HELLP.
Symptoms include:
N/V
Flu-like symptoms
Epigastric pain
Common Misdiagnoses:
Gastroenteritis
Hepatitis
Gallbladder disease
Perinatal morbidity and mortality are high.
All women with HELLP give birth regardless of gestational age.
Doesn’t matter if momma is 20 or 35 weeks, we deliver that baby, or else momma isn’t going to make it!

HELLP lab work reveals…
Anemia: Low hemoglobin (<10)
Thrombocytopenia: Low platelets (<100,000)
Elevated liver enzymes:
AST: Exits with liver cells; when liver cells are damaged, AST levels rise to >20 u/L.
LDH: When liver cells are lysed, LDH spills into the bloodstream, increasing serum levels to >90 u/L.
Rh Sensitivity
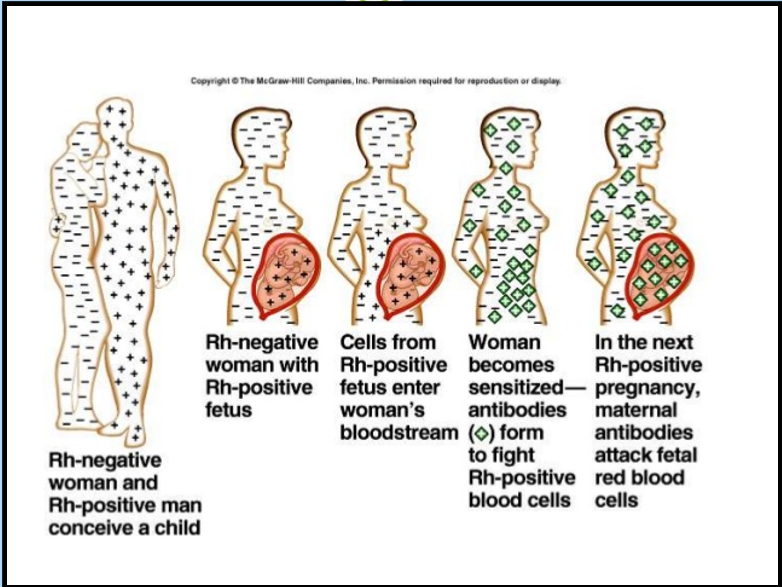
Rh-negative woman conceives with an Rh-positive man.
Rh-negative woman carries an Rh-positive fetus.
Fetal Rh-positive cells enter the mother’s bloodstream.
Mother becomes sensitized—her immune system forms antibodies against Rh-positive blood cells (mom’s body looks at it as an invader).
In the next Rh-positive pregnancy, maternal antibodies attack fetal red blood cells (so its a problem for the next pregnancy)
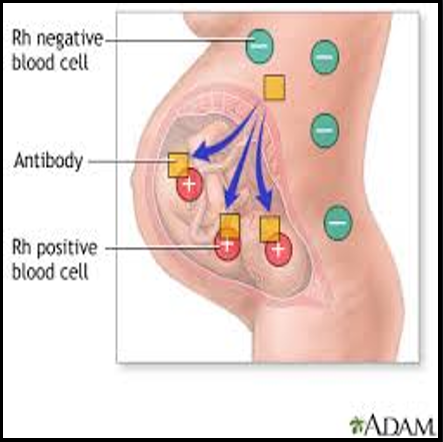
When Rh antibodies enter fetal circulation you’ll expect to see…
Hemolysis
Generalized Edema
CHF
Jaundice
Indirect Coombs Test
Measures the number of Rh+ antibodies in maternal blood (indirect antiglobulin test).
Screens pregnant women for antibodies that may cause hemolytic disease in the newborn.
Negative = fetus at no risk
Positive = fetus at risk
Direct Coombs Test
A test on the infant to detect antibody-coated Rh+ blood cells (direct antiglobulin test).
A positive result indicates an immune mechanism is attacking the baby’s own RBCs.
Rh incompatibility.
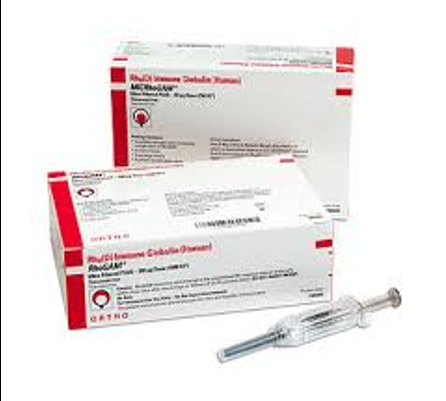
Rhogam
Given to Rh (-) women.
Given @ 28 weeks gestation.
Given within 72 hours after birth.
Also given after abortion, chorionic villus sampling, ectopic pregnancy, and amniocentesis.
Administered IV or IM.
Indication:
To prevent Rh (-) women from developing Rh antibodies.
Why do all Rh-negative women, even if it is their first pregnancy, receive Rhogam at 28 weeks?
Also, if the mother has a negative blood type and the father has a negative blood type, why would we still give the mother Rhogam?
Possible miscarriages that they were unaware of.
Maybe the baby is not the father's (infidelity).
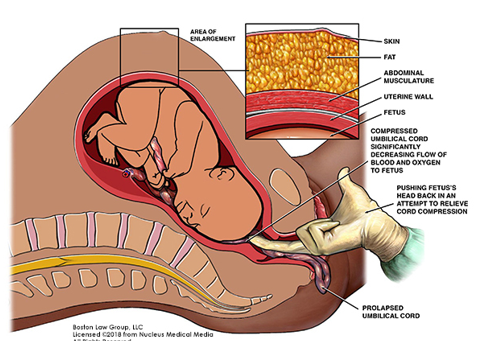
Cord Prolapse
Membranes must be ruptured.
Part of the cord drops through the opening of the cervix.
Part of the baby’s body pushes on the cord.
Interventions:
Must hold the presenting part of the infant off the cord until the baby is delivered by C-section.
Hyperemesis Gravidarium
It is so severe that it affects hydration and nutritional value.
The cause is unknown.
Frequent in:
Adolescents
Multiple gestation
Women with a mother or sister with a history of previous pregnancy.
Diagnosis Criteria:
History of intractable vomiting in the first half of pregnancy.
Dehydration
Ketonuria
Weight loss of 5% of pre-pregnancy weight.
Clinical Therapy for Hyperemesis Gravidarium
Goals:
Control Vomiting
Correct Dehydration
Restore Electrolyte Balance
Maintain Adequate Nutrition
Initial treatment (home care):
Start small with environmental triggers, small frequent meals, anti-emetics.
**If no improvement, hospitalization may be necessary.**
What are the effects of diabetes on momma?
Hydramnios—excessive fluid
Dystocia—baby’s head is too big to fit in the pelvis.
Infections
PIH (Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension)
Retinopathy
Diabetes Effects on the Baby
LGA—Hyperinsulinism (as a response to mother) acts as a growth hormone.
IUGR—Poorly controlled insulin-dependent mothers. (baby too small)
Congenital Anomalies—during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy b/c of fluctuation of blood sugar.
Hypoglycemia (after birth)
Hyperbilirubinemia