Unit 6 & 7 Gradesavers (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
1
New cards
site
the physical characteristics of place
2
New cards
situation
location of a place relative to its surroundings and connectivity to other places
3
New cards
urbanization
the process of developing towns and cities
4
New cards
suburbanization
the process of people moving, usually from cities to residential areas on the outskirts of cities
5
New cards
urban sprawl
the rapid expansion of the spatial extent of a city and occurs for numerous reasons
6
New cards
urban decentralization
the tendency of people or businesses and industries to locate outside the central city
7
New cards
edge cities
nodes of economic activity that have developed in the periphery of large cities
8
New cards
exurb
the prosperous residential districts beyond the suburbs
9
New cards
boomburg/boomburb
rapidly growing communities in the suburbs
10
New cards
megacities
cities that have a population of more than 10 million people
11
New cards
metacities
cities that have a population of more than 20 million people OR attributes of a network of urban areas that have grown together to form a large interconnected urban system
12
New cards
megalopolis
a chain of cities
13
New cards
world cities
cities that exert influence far beyond their national boundaries
14
New cards
urban hierarchy
a ranking of cities based on influence or population size
15
New cards
rank-size rule
describes one way in which the sizes of cities within a region may develop
16
New cards
primate cities
cities that are more developed than other cities in the system and are, consequently, more powerful
17
New cards
gravity model
states that larger and closer places will have more interactions than places that are smaller and farther away
18
New cards
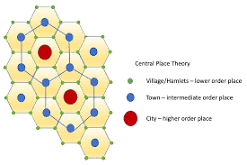
Christaller’s Central Place Theory
explains the distribution of cities of different sizes across a region
19
New cards
Central Business District (CBD)
the commercial heart of a city
20
New cards
periférico
the outer ring of a city that shows poverty, lack of infrastructure, and areas of poorly-built housing
21
New cards
infilling
when open space presents an economic opportunity for landowners to build small, multi-family housing units, placing more people into existing city blocks
22
New cards
urban planning
a process of promoting growth and controlling change in land use
23
New cards
filtering
a process of change in the use of a house, from single-family owner to abandonment
24
New cards
infrastructure
the facilities and systems that serve the population
25
New cards
municipality
the local entity that is all under the same jurisdiction
26
New cards
mixed land use
combines residential, commercial, cultural, or institutional functions into a building, block, or neighborhood
27
New cards
urban walkability
the extent to which the built environment is friendly to the presence of people living, shopping, visiting, enjoying or spending time in an area
28
New cards
transportation-oriented development
a mixed-use residential and commercial area designed to maximize access to public transport
29
New cards
smart-growth politics
governmental regulations that try to prevent sprawl and retain farmland
30
New cards
sustainable design initiatives
policies/approaches that take into account the human and environmental impacts of a growing city
31
New cards
sustainable design zoning
government allows local and national authorities to regulate and control land and the property markets to ensure complementary uses
32
New cards
greenbelts
areas of undeveloped land around an urban area
33
New cards
new urbanism
the urban design movement which promotes environmentally friendly habits by creating walkable neighborhoods containing a wide range of housing and jobs (including sustainable practices)
34
New cards
slow-growth cities
urban communities where the lanners have put into place smart growth initiatives to decrease the rate at which the city grows horizontally to avoid the adverse effects of sprawl
35
New cards
de facto segregation
racial segregation by the people, not by law
36
New cards
quantitative data
data that can be counted or measured (numbers)
37
New cards
qualitative data
data from surveys
38
New cards
census data
data from censuses
39
New cards
housing discrimination
discrimination of people trying to buy, sell, and/or finance a home based on certain characteristics
40
New cards
redlining
when banks refuse loans to those who want to purchase and improve properties in certain urban areas
41
New cards
blockbusting
A process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that black families will soon move into the neighborhood
42
New cards
housing affordability
the extent to which housing is affordable, relative to how much the buyer is willing to pay
43
New cards
environmental injustice
the disproportionate exposure of minorities and the poor to pollution and its impacts, plus the unequal protection of their rights under the law
44
New cards
disamenity zone
the very poorest parts of cities that in extreme cases are not even connected to city services (amenities) and are controlled by gangs and drugs
45
New cards
zone of abandonment
areas of a city that have been deserted by their owners for economic or environmental reasons
46
New cards
squatter settlement
any collection of buildings where people have no legal rights to the land their are built upon
47
New cards
land tenure
the legal protection of contracts to show ownership of the land or structures
48
New cards
inclusionary zoning
offers incentives for developers to set aside a percentage of housing for low-income owner-occupied area of a city
49
New cards
urban renewal
allows governments to clear out the blighted inner-city slums
50
New cards
gentrification
the process of converting an urban inner-city neighborhood from a mostly low-income, renter-occupied area to a predominantly wealthier, owner-occupied area of a city
51
New cards
urban sustainability
a city can be organized without reliance on the surrounding countryside and power itself with renewable energy
52
New cards
ecological footprint
the impact of human activity on the environment
53
New cards
suburban sprawl
the rapid spread of development outward from the inner-city
54
New cards
urban canyons
streets that are lined with tall buildings, can channel and intensify wind, and prevent natural sunlight from reaching the ground
55
New cards
urban heat island
an area of a city warmer than the surrounding areas
56
New cards
brownfields
consists of run down buildings, and polluted or contaminated soils
57
New cards
urban redevelopment
renovating a site within a city by removing the existing landscape and rebuilding from the ground up
58
New cards
Industrial Revolution
\
a series of technological advances starting in the 18th century
a series of technological advances starting in the 18th century
59
New cards
industrialization
transformation away from an agriculture resource-based economy, and towards an economy based on mechanized manufacturing
60
New cards
deindustrialize
a process of decreasing reliance on manufacturing jobs
61
New cards
cottage industry
small, home-based businesses that made goods
62
New cards
rust belt
regions that have large numbers of closed factories
63
New cards
primary sector
Extraction of raw materials and natural resources from the earth’s surface. (mining, fishing, agriculture, forestry)
64
New cards
secondary sector
Processing and manufacturing raw materials into a finished product. (factories & manufacturing)
65
New cards
tertiary sector
Service sector that focuses on moving, selling, and trading products in primary and secondary sectors. (retail, marketing, design, restaurants, shipping)
66
New cards
quaternary sector
Knowledge-based sector, focusing on research and information creation and transfer. (investment banking, real estate, college professors, education, software developers)
67
New cards
quinary sector
Highest levels of decision making that impact millions, includes top officials in government and business. (Congress, CEO)
68
New cards
break-of-bulk point
the procedure of transferring cargo from one mode of transportation to another
69
New cards
least cost theory
(Alfred Weber) explains the location of manufacturing industries based on three factors: transportation costs, labor cost, and the benefit of agglomeration
70
New cards
multiplier effect
the potential of a job to produce additional jobs
71
New cards
bulk-gaining industries
market-dependent industries, as production happens the weight and bulk of the product increases
72
New cards
bulk-reducing industries
raw material-dependent industries more likely to have their production be, as production happens the weight and bulk of the product reduces (likely located near the raw resources instead of near the market this is because it's cheaper to ship the final product)
73
New cards
core
tend to have the most advanced economies, typically have a higher standard of living, and have more of their job located in the tertiary
74
New cards
semi-periphery
countries that have an emerging economy that are experiencing an increase in their standard of living and have many jobs in the country located in the secondary sector as more industrialization continues to occur
75
New cards
periphery
lower standard of living since industrialization has not happened yet causing many of the jobs in the economy to be located in the primary sector (poor countries)
76
New cards
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
the amount of money, all goods and services produced within a country in a year
77
New cards
Gross National Product (GNP)/Gross National Income (GNI)
the amount of money all goods and services produced by a country’s citizens in a year
78
New cards
Gross National Income Per Capita
a measure of the total value of goods and services produced in a country divided by the country’s population
79
New cards
formal sector
the portion of the economy that is monitored by government, so people in it to follow regulations and pay taxes
80
New cards
informal sector
the portion of the economy that is not monitored by the government
81
New cards
GINI Coefficient
One measure of the distribution of income within a population. The values range from 0 to 1. The higher the number, the higher the degree of income inequality. If the number was zero, everyone would be getting paid the same.
82
New cards
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
A measure of several factors, including gender disparity. The higher the number, the more potential human development lost.
83
New cards
Human Development Index (HDI)
Combines the GNI per capita, with life expectancy, expected years of schooling, and average years of schooling. The higher the number, the greater levels of development.
84
New cards
income distribution
how income is distributed among different groups of individuals
85
New cards
fertility rate
an estimate of the average number of children born to each female in their childbearing years
86
New cards
infant mortality rate
the number of deaths per 1,000 live births of children under one year of age
87
New cards
access to healthcare
having access to healthcare
88
New cards
glass ceiling
a barrier to career advancement, usually in reference to women/minorities
89
New cards
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGO)
organizations that empower women to find jobs outside their homes, an organization that is not part of the local or state or federal government
90
New cards
micro loans
loans provided to woman by microcredit or micro finance programs to start or expand a business
91
New cards
Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth
\
1. Traditional Society
2. Preconditions of Take-Off
3. Take-Off
4. Drive to Maturity
5. High Mass Consumption
1. Traditional Society
2. Preconditions of Take-Off
3. Take-Off
4. Drive to Maturity
5. High Mass Consumption
92
New cards
Wallerstein’s World System Theory
divided the world into core, periphery, and semi-periphery
93
New cards
Dependency Theory
a dependency model that suggests all countries are dependent on each other
94
New cards
barter
a system of exchange in which no money changes hands
95
New cards
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good or service at a lower cost than others; says a country should specialize in certain products for export when they hold an advantage in producing those products, and import other products in which they do not have an advantage as compared to other countries
96
New cards
complementarity
when a country has good or services, another country desires
97
New cards
neoliberal policies
a set of reforms that reduced government regulations (less government control) and taxation
98
New cards
World Trade Organizations (WTO)
global organizations made to monitor the rules of international trade
99
New cards
mercosur
a trading bloc that includes several South American countries
100
New cards
The Organization of Petroleum Exchange Countries (OPEC)
an intergovernmental organization of 13 oil-producing countries that aim to coordinate and unify the petroleum policies of its members states