362 final cardiac arrhythmias + EKG
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
intrinsic rate of sinus node
60 - 100 bpm
intrinsic rate of AV node
40 - 60 bpm
intrinsic rate of purkinje fibers
20 - 40 bpm
ways to assess rate of ventricular contractions
number of large squares between 2 R waves / 300
number of small squares between 2 R waves / 1500
number of Rs in a 6 sec period x 10
compensatory pause
pause in the beat occurring after a premature beat
description of normal sinus rhythm
60 - 100 bpm
normal R to R
p wave present
normal PR interval
description of sinus bradycardia
<60 bpm
normal R to R
p wave present
normal PR interval
interventions for sinus bradycardia
pacemaker
atropine
description for sinus tachycardia
100+ bpm
normal R to R
p wave present
normal PR interval
interventions for sinus tachycardia
treat underlying cause!
description of sinus arrhythmia
rate 60 - 100
irregular R to R
p wave present
normal PR interval
is sinus arrhythmia dangerous?
no, usually common in younger pt and benign
occurs when BPM increase with inhalation and decrease with exhalation
description of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
rate 150 - 200
cannot see P wave
interventions for SVT
vagal maneuvers
adenosine
ablation
lifestyle changes (caffeine, nicotine, etc.)
description of premature atrial contractions (PACs)
abnormal P wave that comes early + has a pause
causes of PACs
atrial muscle irritation
usually benign but can precede more significant arrhythmias
caffeine, nicotine, stress, ischemia
description of junctional rhythm
SA node is not initiating or conducting properly, so initiation occurs above the ventricle at the AV node or bundle of his
rate 40 - 60 bpm
R to R regular
no P wave or inverted P wave
treatment of junctional rhythm
treat underlying cause (pacemaker malfunction, drug toxicity, etc.)
description of atrial fibrillation
atrial rate = 400 - 600 bpm
may have ventricular rate response, may not
R to R irregular
no pwave
QRS normal
atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response (AFib with RVR)
atrial fibrillation with ventricular rate as high as 110 - 160
patient will be tachy + hypotensive
primary complications of AFib
atrial kick is lost => CHF
thromboembolic events like stroke
tx for AFib
meds = cardizem, digoxin, Verapamil, beta blockers, ASA/anticoagulants, heparin drip
cardioversion or pacemaker if unstable
description of atrial flutter
atrial rate 200 - 300 with sawtooth pattern
R to R regular
mural thrombi
clot attached to a wall of the heart or blood vessel
associated with A Flutter
tx of AFlutter
meds = cardizem, digoxin, Verapamil, beta blockers, ASA/anticoagulants, heparin drip
cardioversion or pacemaker if unstable
description of preventricular contraction
irregular, wide/bizarre QRS complexes that come early + have a pause after
can be unifocal, bifocal, or multifocal
causes of PVCs
hypoxia
myocardial ischemia
hypokalemia
acidosis
exercise
increased digoxin levels
serious medical problems that can cause PVCs
MI
digoxin toxicity
hypoxia
electrolyte imbalances
PVCs are likely dangerous if:
they occur more than 6 per min
they are near a T wave
they occur in couplets, triplets, or more in a row
bigeminy
trigeminy
bigeminy = every other beat
trigeminy = every third beat
tx for PVCs
acute attack = IV lidocaine
treat cause
meds for long term control
amiodarone
beta blockers
calcium channel blockers
antiarrhythmics
if PVCs are related to ischemic problems
nitrates
oxygen
catheter ablation
catheter ablation
destroying part of the heart causing the PVC to stop them
description of ventricular tachycardia
ventricular rate 150 - 200+
wide/bizarre QRS
regular R to R
no P wave
sustained V tach
lasting longer than 30 sec
nonsustained V tach
lasting less than 30 sec
tx for Vtach
IV lidocaine
IV amiodarone
cardioversion
treat underlying cause
MI
potassium imbalance
chronic = may need implantable defibrillator
description of ventricular fibrillation
no QRS or P wave
rhythm is irregular / chaotic
rate is rapid + ineffective
tx for ventricular fibrillation
immediate defibrillation
CPR
ACLS protocol
antiarrhythmic drugs
tx for asystole
epi, atropine
pacemaker (external or temporary internal)
CPR
cardioversion
electrical shock synchronized with heart rhythm
less risk of putting someone in an even more lethal rhythm
turn synchronizer ON
defibrillation
shock that is not synchronized with heart rhythm
turn synchronizer OFF
uses for a pacemaker
sick sinus syndrome
heart blocks
post op cardiac surgery
post MI with heart block
use of an implantable defibrillator (ICD)
senses + converts vtach / vfib
complications of pacemaker or defibrillator use
infection
bleeding/hematoma
dislocation of lead
skeletal muscle / phrenic nerve stimulation
cardiac tamponade
malfunction of pacemaker / defibrillator

normal sinus rhythm
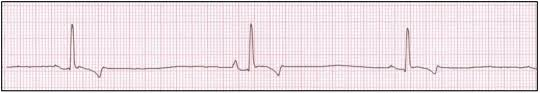
sinus bradycardia
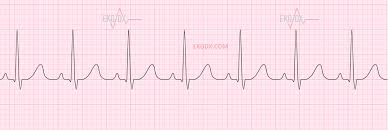
sinus tachycardia
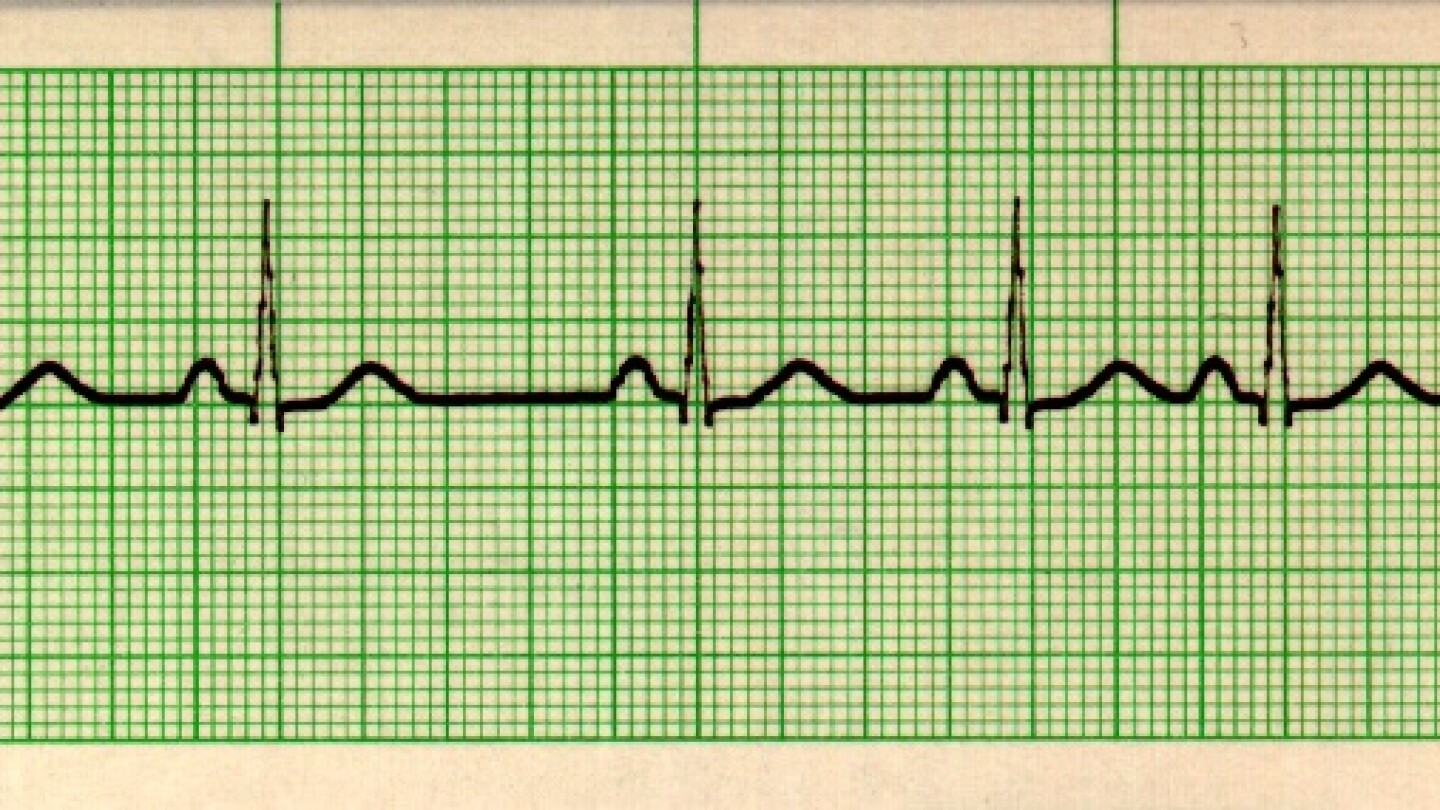
sinus arrhythmia
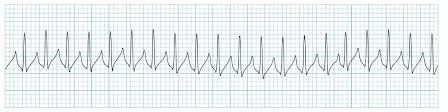
supraventricular tachycardia
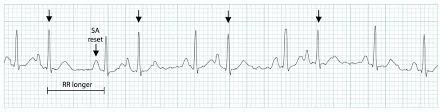
premature atrial contraction (PAC)
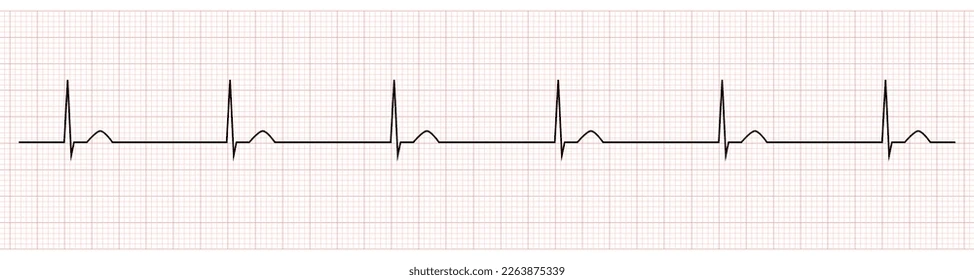
junctional rhythm
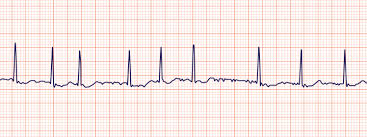
atrial fibrillation
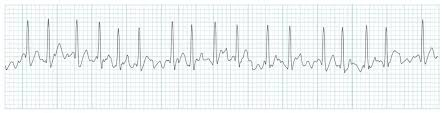
atrial fibrillation with RVR
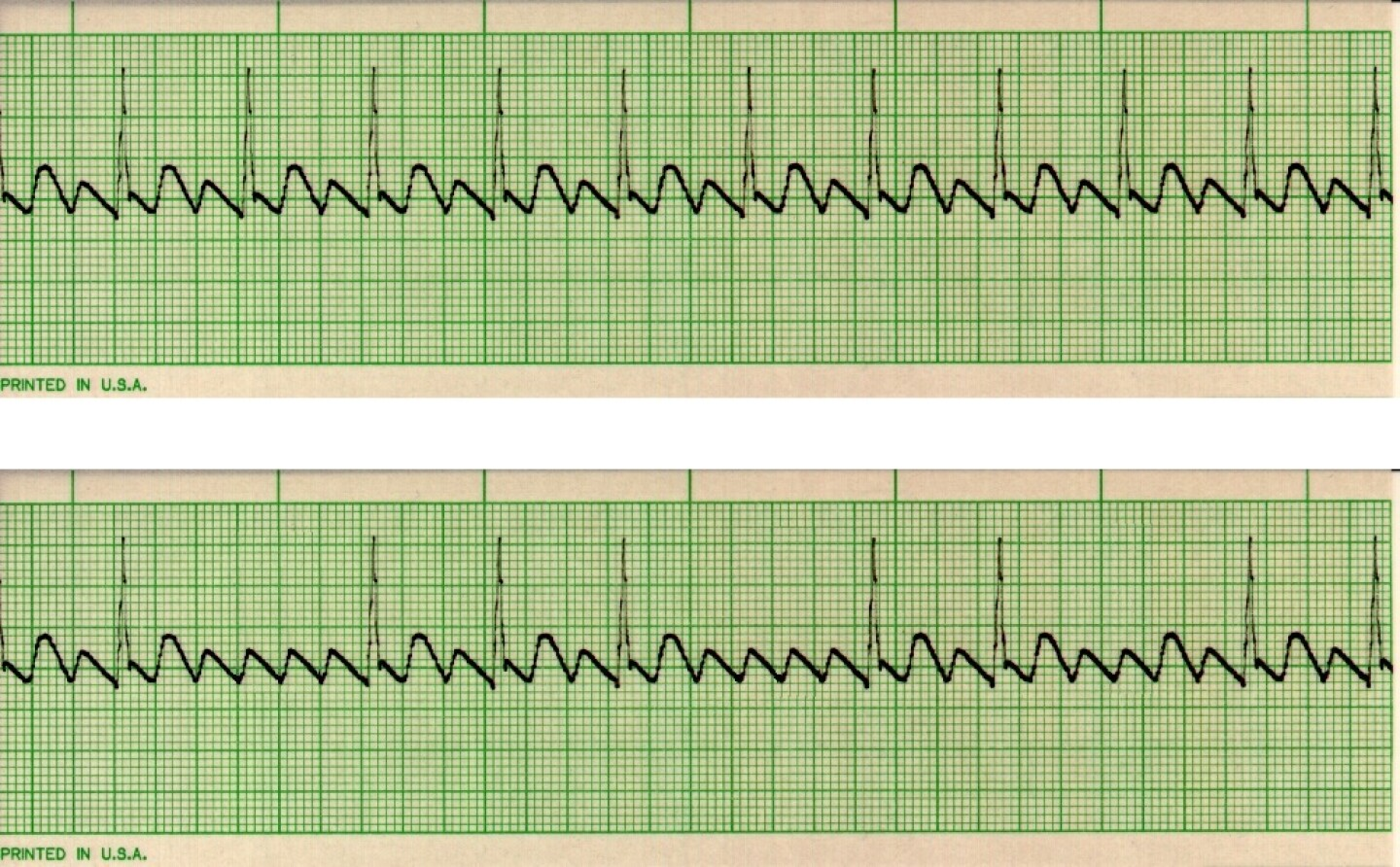
atrial flutter
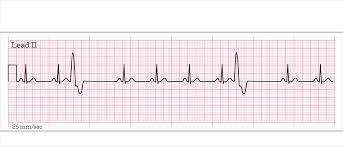
preventricular contraction
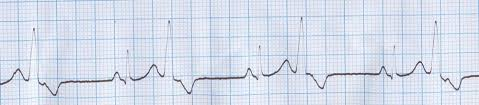
bigeminy
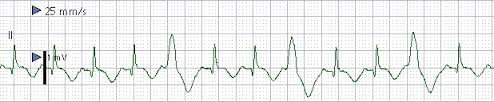
trigeminy
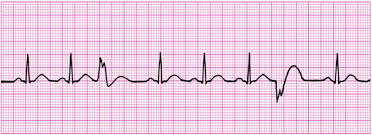
multifocal PVC
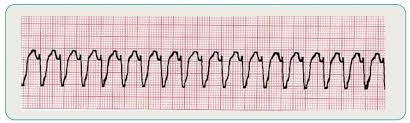
ventricular tachycardia
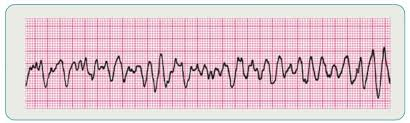
ventricular fibrillation
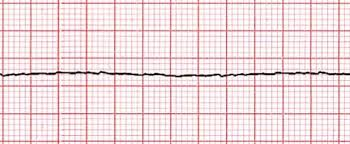
asystole