12.6 (4.1.1) The specific immune system
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
define antibody
Y-shaped glycoproteins called immunoglobulins which bind to a specific antigen on the pathogen or toxin that has triggered the immune response
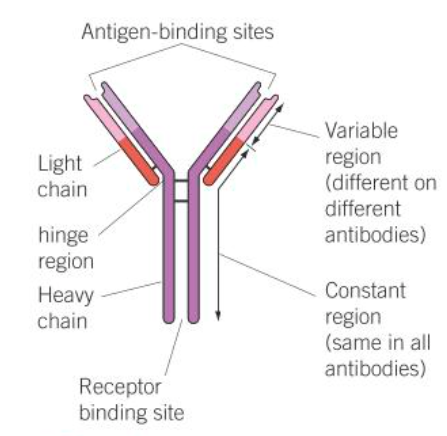
describe the structure of antibodies
made up of two identical long polypeptide chains called the heavy chains, and two shorter chains called the light chains
these are held together by disulphide bridges
disulphide bridges within the polypeptide chains hold them in shape
by what mechanism do antibodies bind to antigens
lock-and-key
define variable reigon
a binding site of 110 amino acids found on both the heavy and light chains which have a different shape on each antibody and gives the antibody specificity
define the constant reigon
the binding site on an antibody that allows phagocytes to bind to the antibody. this is the same on every antibody.
describe how antibodies defend the body
1) antibody on antigen-antibody complex acts as an opsonin, complex is easily engulfed and digested by phagocytes
2) most pathogens can no longer effectively invade the host cells once they are part of an a-a complex
3) act as agglutinins causing pathogens carrying a-a complexes to cluster together which prevents them spreading through the body and makes it easier for phagocytes to engulf a number of pathogens simultaneously
define agglutination
when one antibody binds to two pathogens causing them to clump together, making it easier for pathogens to be engulfed by phagocytosis
define neutralisation
when antibodies act as antitoxins, binding with toxins produced by pathogens which makes them harmless
diagram of antibody
define lymphocytes
a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) found in blood and lymph nodes
function of lymphocytes
recognise antigen molecules on the surface of pathogens and coordinate the immune response against that pathogen
where are B lymphocytes formed
bone marrow
where are T lymphocytes formed
thymus
T helper cells
produce interleukins which stimulate B cell and antibody production and attracts other T cells and antibodies
define cytokine
cell-signalling molecule
T killer cells
kill pathogens by producing perforin which makes holes in pathogen’s plasma membranes making them freely permeable
T memory cells
immunological memory as they remain the the blood for long periods of time. when a second infection occurs they divide rapidly to form many T killer cells
T regulator cells
prevent an autoimmune response by repressing the immune system after all pathogens have been destroyed. ensures body recognises self antigens
plasma cells
produce specific antibodies to an invading antigen
B effector cells
divide to form plasma cell clones
B memory cells
remain in the blood for long periods of time providing immunological memory
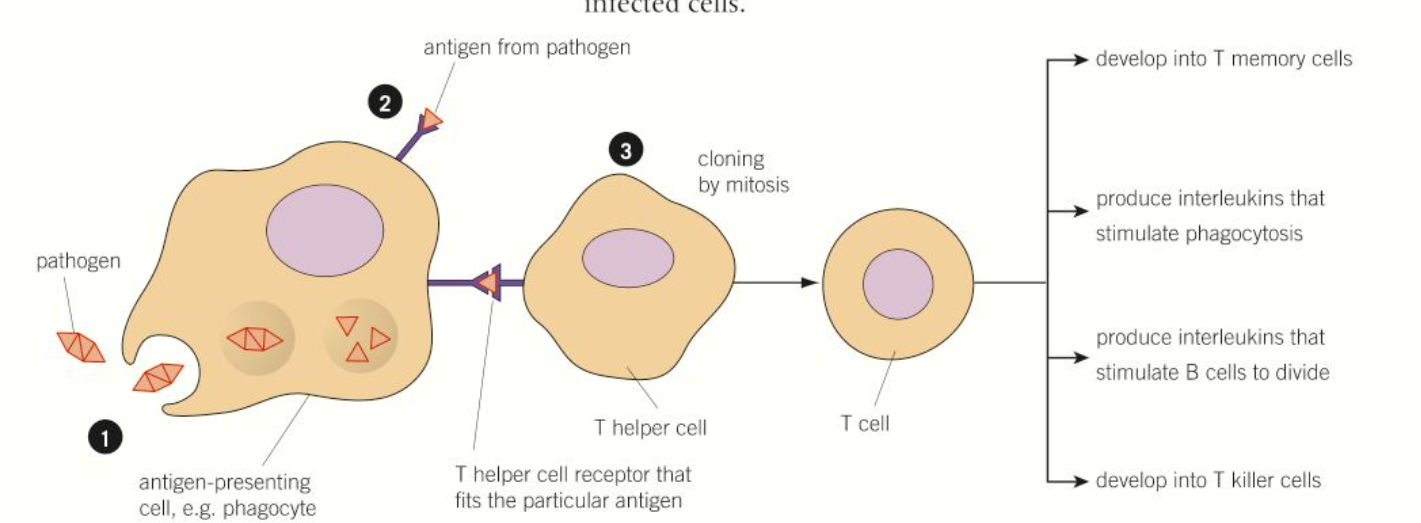
steps of cell mediated immunity
1) macrophages engulf and digest pathogens in phagocytosis. they present the antigens on their surface becoming APCs
2) specific T helper cells with receptors that fit the antigens will bind to the antigen on the APC and become activated and produce interleukins which stimulate more T cells to be produced by mitosis
3) T cells produced form clones of identical T helper cells that carry the right antibody to bind to a specific pathogen
4) cloned T cells may develop into T memory cells, produce interleukins that stimulate phagocytosis, produce interleukins that stimulate B cells to divide, produce clones of T killer cells
diagram of cell-mediated immunity
steps of humoral immunity
1) T helper cells bind to antigen on APC
2) APC releases interleukins to T helper cells (clonal selection)
3) T helper cell undergoes cell division + mitosis (clonal expansion)
4) activated T helper cell finds B cell with correct shaped receptor
5) T helper cell releases cytokines detected by B cell (cell signalling)
6) activated B cell undergoes clonal expansion
7) cloned B cells undergo differentiation
8) B effector cell becomes B memory cell or plasma cell (which secrete antibodies)
define autoimmune disease
immune system stops recognising ‘self‘ antigens and attacks healthy body tissue
type 1 diabetes
affects pancreas
insulin injections, pancreas transplants, immunosuppressants
rheumatoid arthritis
affects joints
no cure
anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, immunosuppressants, pain relief
lupus
affects skin and joins causing fatigue
can attack any organ
no cure
anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, immunosuppressants