7. Principles of Exchange and Transport
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
examples of essential substances
Oxygen, glucose (respiration), plants need nitrates to make protein for growth
toxic products / waste
Carbon dioxide, urea
Where does this exchange take place in unicellular organisms?
Through the cell surface membrane
What do multicellular organisms have to facilitate this exchange?
Specialised exchange surfaces e.g. alveoli
What is meant by the surface area of an organism?
Total number of cells in direct contact with the environment
What is the volume?
3D space occupied by metabolically active tissues
What happens to this ratio as the cube gets larger?
Increasing size = decreases S.A:V
Small organisms can gain their metabolites directly across their surface due to large SA:V
Larger organisms require specialised exchange
surfaces to maximise efficiency due to small S.A:V
1. Increasing the surface area of the exchange surface
They have a large surface area and very small
volume = large S.A:V
Respiratory substances can diffuse through the body surface in sufficient quantities to meet their metabolic needs.
When are specialised exchange surfaces needed? What effect does this have on the surface area?
When the surface area to volume ratio is not large enough to enable enough respiratory gases to enter or leave
Specialised exchange surfaces significantly increase the surface area for exchange
example of external strucutre
folded external membranes of external gills of tadpoles = increase S.A for gases to diffuse
example Internal: structure
fish gills and alveoli of mammalian lungs increase surface area.
Thin separating surface
Exchange surfaces that are thin increase the rate of diffusion
Large concentration gradient diffusion occur
When there is a concentration gradient
How is this gradient created in respiring organisms?
Oxygen being used by respiring cells creates low levels of oxygen which enables oxygen to move into the lungs from the environment`
What additional feature do larger mammals require?
Ventilation system – to bring oxygen in and push carbon dioxide out.
What is the importance of mass flow?
Transport of substances within large organisms
Explain how mass flow works.
Brought about by pressure differences. Material moved from where the
pressure is generated (source) to where there is less pressure (sink)
To maximise the rate of exchange, gas exchange surfaces have:
Large surface area
Moist surface
Diffusion gradient
Permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide
Leaves are thin – short diffusion distance
flicks law

Where does photosynthesis take place in a leaf?
Chloroplasts in the palisade mesophyll layer
What does photosynthesis require and what does it produce?
Uses carbon dioxide and produces oxygen
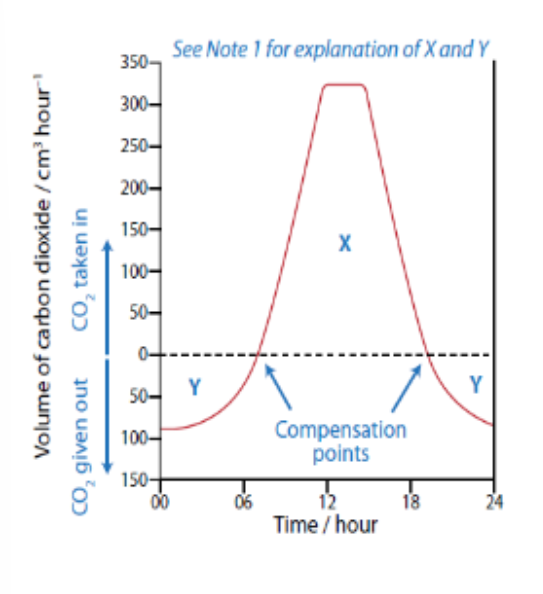
explain graph
Y – during these hours there is no light therefore no photosynthesis. Only respiration occurs = more carbon dioxide produced than used
X – more/bright light = Rate of photosynthesis > rate of respiration. More carbon dioxide used than produced
Compensation points = rate of photosynthesis = rate of respiration
No net gain or loss of carbon dioxide
Leaves are thin facilitates gas exchange
Short diffusion distance – higher S.A:V
All cells close to an exchange surface
Large surface area and moist gas exchange surface of SML facilitates gas exchange
Loose arrangement of the cells = large surface area
Gases involved in respiration and photosynthesis can easily diffuse between cells of SML and PML.
Intercellular air spaces of the SML facilitates gas exchange
Facilitate diffusion of gases within the leaf
Stomata (singular = stoma) facilitates gas exchange
Allow gases to enter or leave. Open during the day and close at night. Closing at night prevents water loss.
Controlled by guard cells – when turgid (guard cells) =stomata open, flaccid = stomata closed.
Very short diffusion distance in mammals
Squamous epithelial cells lining the alveoli = very thin
Alveoli surrounded by blood capillaries - which are one squamous endothelial cell thick
Capillaries are narrow which means RBC have the squeeze through and are in contact with the endothelial wall = further reduces diffusion distance.
Large surface area in mammals
Millions of saccular shaped alveoli and a large network of capillaries = increase S.A
A steep concentration gradient
Created by ventilation of the lungs (bringing oxygen in and releasing Carbon dioxide out). Flow of blood through capillaries maintains steep conc gradient as it is low in oxygen but rich in carbon dioxide when arriving
Surfactant is secreted in the alveolar wall.
What is its role?
Reduces surface tension in the moisture coating of alveoli – prevents their collapse (prevents the alveoli sticking together) which would reduce S.A.
What role do macrophages play?
Protect against infection by digesting microbes
through phagocytosis.
Inspiration (or inhalation) -
intercoastal muscles contact, ribs pulled up and out. Diaphragm contracts and move down. Volume increases, pressure decreases. This creates a difference in pressure between lungs and atmosphere – air enters the lungs (mass flow)
Expiration (exhalation) -
Intercostal muscles relax, ribs move down and in. Diaphragm relaxes and moves up. Volume decreases, pressure increases. Thorax has a higher pressure that the atmosphere, air forced out of lungs.
smoking causes cancer
Tar is carcinogenic (causes cancer). Can cause damage to DNA and cause cancer. Cancer cells divide to form a tumour which can block the airways and/or damage large sections of the lungs. This can reduce surface area.
Emphysema
Break down of the alveolar wall. Less alveoli which reduces the surface area = less diffusion of gases.
Cigarette smoke breaks down the elastic lining of the alveoli reducing their ability to stretch and recoil. If recoil is affected exhalation may not be efficient – residual air remains in the alveoli – less oxygen can enter.
Shortness of breath, tired due to less respiration.
Bronchitis
Inflammation of the bronchial tubes. Narrower bronchial tubes and mucus production = reduce air flow into and out of the lungs (harder to maintain a steep concentration gradient)
What does tar do to the cilia?
Shortens cilia. Paralyses them which makes it harder to remove mucus and microbes from respiratory tract – increasing risk of infection.