Chemistry 3.2- Alkanes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What order do the fractions come out, from top to bottom?
Gas, petrol, kerosene, diesel, fuel oil, bitumen
(These are mixtures of hydrocarbons with similar chain lengths)
What is a fraction?
A group of hydrocarbons with similar boiling points (because of similar chain lengths
Explain the trends in hydrocarbon fractions: boiling points, viscosity, flammability
The long chain hydrocarbons have high boiling points because they have greater Van der Waals forces between them and so they come out at the bottom of the column
The greater Van der Waals forces in longer chains means that they are held together more, so have a higher viscosity. Longer chains are also more likely to tangle
Hydrocarbons can only burn as vapours, so longer chain hydrocarbons with higher boiling points, that are less likely to be present as vapours, are less flammable
Why is cracking necessary?
The demand for short chain alkanes is greater than the supply in crude oil, and the products of cracking are more valuable than the reactants (branched and cyclic alkanes burn more cleanly than straight chains, so they are more desirable as fuels)
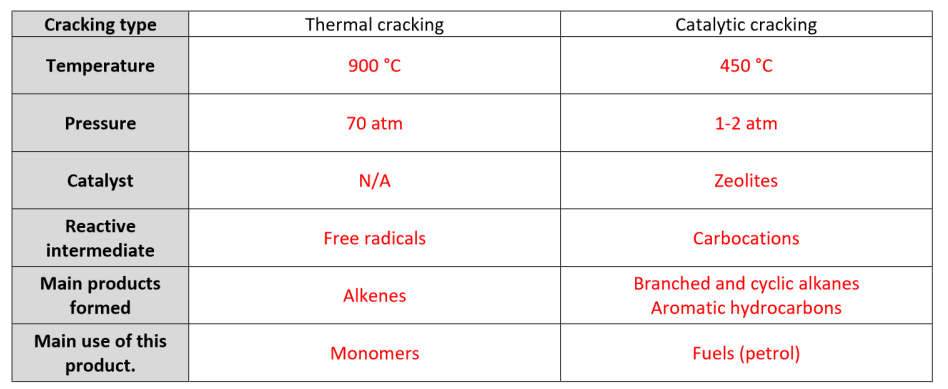
Compare the two kinds of cracking: temperature, pressure, catalysts, mechanisms, reactive intermediates, products + their uses
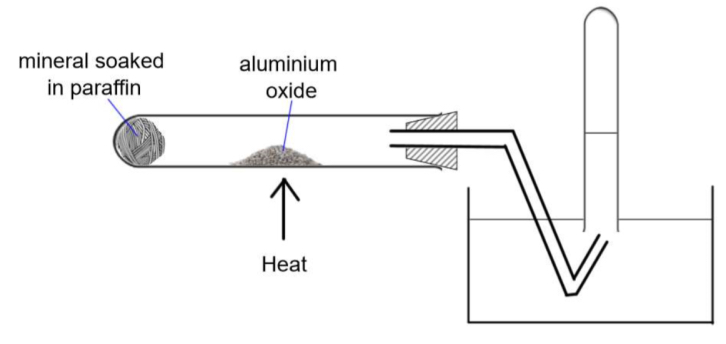
What is the set up for cracking paraffin in a lab? How could you confirm the product of the experiment?
This is catalytic cracking, so alkenes are produced and bromine water will turn from orange to colourless
What is the general equation for combustion?
Hydrocarbon + O2 —> CO2 + H2O
Give two general equations for incomplete combustion
Hydrocarbon + O2 —> CO + H2O
Hydrocarbon + O2 —> C + H2O
Why is incomplete combustion dangerous?
Produces carbon monoxide which is toxic as it binds to haemoglobin on blood cells and so reduces the blood’s capacity for oxygen (it is also highly flammable)
Produces soot which causes lung damage, can be a cause of asthma and lung cancer, and blackens buildings
How can nitrogen oxides be formed in an engine and why are they dangerous?
At the high temperatures of the spark plug in an engine, nitrogen form the air can react with oxygen:
N2 + O2 —> 2 NO
2 NO + O2 —> 2 NO2
Nitrogen dioxide reacts with water in clouds to form nitric acid, which contributes to acid rain
4 NO2 + O2 + 2 H2O —> 4 HNO3
Acid rain kills trees and fish and corrodes buildings
How can sulphur dioxide be formed in an engine and why is it dangerous?
Sulphur is an impurity found in crude oil- when fuels are burnt in an engine, it can react with oxygen to form sulphur dioxide
S + O2 —> SO2
Sulphur dioxide reacts with water in clouds to form sulphurous acid, which causes acid rain
H2O + SO2 —> H2SO3
Acid rain kills trees and fish and corrodes buildings
What is dangerous about unburnt hydrocarbons?
Not all fuel combusts in the engine, so unburnt hydrocarbons can be released, which contributes to chemical smog
How can pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and unburnt hydrocarbons be removed from exhaust gases?
In a catalytic converter, the precious metals platinum, palladium and rhodium are coated on a honeycomb (large surface area), which converts harmful pollutants into less dangerous forms:
2 CO + O2 —> 2 CO2
2 CO + 2 NO —> 2 CO2 + N2
C8H18 + 8.5 O2 —> 8 CO2 + 9 H2O
How can sulphur dioxides be removed from exhaust gases of power stations?
In flue gas desulphurisation, sulphur dioxide is reacted with calcium oxide or calcium carbonate to produce calcium sulphate
CaO + SO2 —> CaSO3
CaCO3 + SO2 —> CaSO3 + CO2
CaO and CaCO3 are used because they are bases, so they can form salts with acids, and because the product, calcium sulphate, can be used to produce plasterboard to offset the cost of the process
Why are some molecules greenhouse gases and others aren’t?
Molecules like carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour contain polar bonds, that can vibrate at the same frequency as infrared radiation, so can absorb and reemitt it
Gases like nitrogen and oxygen don’t contain polar bonds, so they can’t absorb Ir radiation
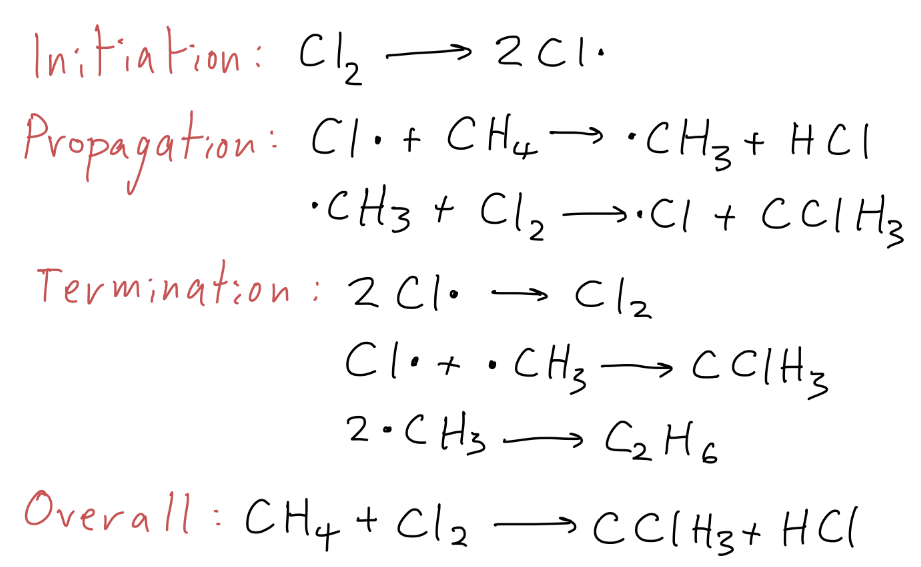
Give the initiation step, propagation steps, termination steps and overall equation for the substitution of chlorine into methane