anatomy 2020: chapter 14 somatic nervous system
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1
New cards
special senses
complex anatomical structures, has a specialized receptor cell, includes olfaction, gustation, vision, hearing, linear acceleration, gravity, rotation
2
New cards
general senses
no complicated anatomical structures, uses free nerve endings or encapsulated endings, includes touch, pain, temperature, pressure, vibration, proprioception
3
New cards
chemoreceptors
respond to chemicals
4
New cards
mechanoreceptors
Sensory receptors stimulated by movement
5
New cards
photoreceptors
respond to light
6
New cards
olfaction
sense of smell or detection of odorants
7
New cards
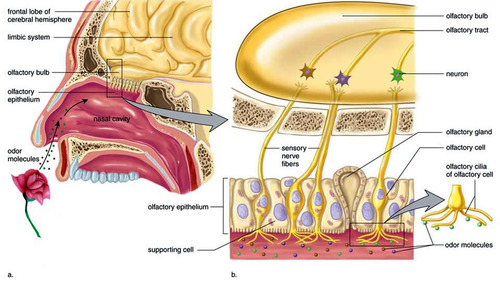
olfactory organ
olfactory epithelium lining the superior portion of nasal cavity
8
New cards
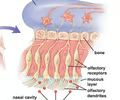
olfactory sensory neurons
highly modified neurons that contain odorant binding receptors on their dendrites, extend into the nasal cavity, their axons form olfactory nerve (I), can regenerate
9
New cards
olfactory epithelium
supports the olfactory sensory neurons, produces mucus to help trap odorants
10
New cards
odorants
airborne chemicals that are detected as odors
11
New cards
processing centers for olfaction include
olfactory cortex, hypothalamus, and limbic system
12
New cards
olfactory nerve (I)
sensory neuron, transmits olfaction to olfactory cortex, hypothalamus, and limbic system
13
New cards
G-protein coupled receptors
A signal receptor protein in the plasma membrane that responds to the binding of a signaling molecule by activating a G protein. Also called a G protein-linked receptor.
14
New cards
G protein
a protein coupled to a receptors, acts as a bridge between the 1st messenger and 2nd messenger
15
New cards
second messenger
acts as a signal molecule in the cytoplasm, often cAMP or calcium ion
16
New cards
first messenger
the chemical messenger that binds to the receptor
17
New cards
gustation
sense of taste (sour, salty, bitter, sweet, umami, and oleogustus) or detection of tastants
18
New cards
sour
hydrogen ions enter ion channels and depolarize gustatory sensory neurons
19
New cards
salty
sodium ions enter ion channels and depolarize gustatory sensory neurons
20
New cards
sweet
monosaccharides bind to G-protein coupled receptors on gustatory sensory neurons
21
New cards
bitter
alkaloids bind to G-protein coupled receptors on gustatory sensory neurons and can depolarize or hyperpolarize the cell
22
New cards
umami
"savory" the amino acid L-glutamate binds to G-protein coupled receptors on gustatory sensory neurons
23
New cards
Oleogustus
the taste of rancid fats
24
New cards
lingual papillae
rough projections that provide friction and can be involved in taste reception (if they contain taste buds)
25
New cards
filiform papillae
located on the tip of the tongue, provides friction (gets food into the mouth)
26
New cards
fungiform papillae
located middle of the tongue, contain 5 taste buds, has dual function of friction and taste
27
New cards
Vallate papillae (circumvallate)
located at the back of the tongue, contain 100 taste buds - taste is primary function
28
New cards
foliate papillae
on side walls of tongue and contain taste buds
29
New cards
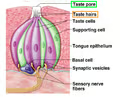
taste buds
located on fungiform, foliate, and circumvallate papillae, contain gustatory receptor cells, transitional cells, and basal (stem) cells
30
New cards
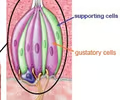
gustatory cells
located on taste buds, have microvilli to increase contact with tastants, synapse onto sensory neurons, replaced about every 10 days
31
New cards
salt and sour receptors
chemically-gated ion channels
32
New cards
sweet, bitter, and umami
G protein coupled receptors sensitive to certain molecules
33
New cards
cranial nerves involved in gustation
VII, IX, and X
34
New cards
processing center for gustation
gustatory cortex (insula lobe)
35
New cards
ceruminous glands
located lining the external auditory canal, produce cerumen (ear wax)
36
New cards
Perilymph
fluid around bony labyrinth, stimulates auditory hair cells (hearing)
37
New cards
endolymph
fluid inside membranous labyrinth, stimulates hair cells in the ampulla (rotation)
38
New cards
hair cells
mechanoreceptor cells of the inner ear involved in sensing hearing, rotation, linear acceleration, and gravity
39
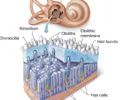
New cards
spiral organ (organ of corti)
located in the cochlear duct, contains hearing receptor cells
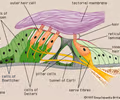
40
New cards
tectorial membrane
part of the spiral organ, hair cells bump up against the tectorial membrane when pressure waves move through the perilymph
41
New cards
basilar membrane
part of the spiral organ, moves in response to pressure waves in the perilymph, bumps hair cells against the tectorial membrane causing a signal to be sent to the sensory neurons
42
New cards
tympanic membrane
eardrum

43
New cards
round window
located just below the oval window; equalize pressure in the inner ear
44
New cards
auditory ossicles
malleus, incus, stapes - transmit vibrations and amplify the signal from tympanic membrane to inner ear
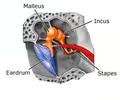
45
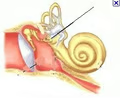
New cards
oval window
stapes of the auditory ossicles bump against the oval window which then converts sound waves into pressure waves in the perilymph
46
New cards
frequency
or pitch, determined by where the cochlear duct is stimulated
47
New cards
intensity
or volume, determined by how many hair cells are stimulated
48
New cards
semicircular canals
contains the ampullae, detects rotation
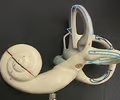
49
New cards
ampulla
located in the semicircular canals, contains hair cells that are displaced by endolymph triggering rotation information to be sent to sensory neuron
50
New cards
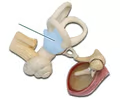
vestibule
contains maculae, detects linear acceleration and gravity
51
New cards
maculae
located in the vestibule, contains hair cells that are displaced by the otolith triggering linear acceleration and gravity information to be sent to the sensory neuron
52
New cards
vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
sends auditory, linear acceleration, gravity, and rotation information to the brain for processing
53
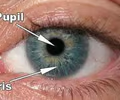
New cards
iris
pupillary muscle, controls the amount of light entering the eye
54
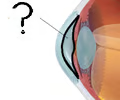
New cards
aqueous humor
circulates within the chambers of the eye providing nutrients, oxygen, and waste removal
55
New cards
ciliary body
circular muscle that controls the shape of the lens for focusing

56
New cards
ciliary zonule (suspensory ligament)
connect the ciliary body to the lens
57
New cards
lens
focuses photons (light) onto retina
58
New cards
vitreous humor
gelatinous mass located in the posterior cavity, stabilizes the shape of the eye and holds the retina in place
59
New cards
accommodation
changing the shape of the lens in order to focus the image
60
New cards
for close vision
ciliary muscle contracts > ciliary zonule are loose > lens has round shape > more refractive power (bend light)
61
New cards
for distance vision
ciliary muscle relaxes > ciliary zonule are tight > lens has flat shape > less refractive power
62
New cards
retina
neural tunic, contains photoreceptor cells, and neurons
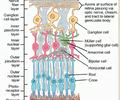
63
New cards
photoreceptor cells
rod and cone cells that respond to photons of different wavelengths based on different opsin pigments
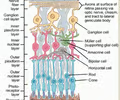
64
New cards
rod cells
black and white vision, peripheral vision, contain rhodopsin
65
New cards
cone cells
color vision, most accurate vision, concentrated in the fovea centralis
66
New cards
cranial nerve involved in vision
optic nerve (II)
67
New cards
processing center for vision
visual cortex in the occipital lobe
68
New cards
steps of "vision" in a rod cell
1. photon triggers retinal to be linear and opsin to activate
2. opsin activation triggers influx of Na+, causing the rod cell to stimulate the sensory neurons
3. bleaching occurs
69
New cards
bleaching
1. opsin and retinal separate (rod can't be stimulated again)
2. retinal converts back to bent shape
3. retinal is recombines with opsin and rhodopsin (the rod cell) is ready to be stimulated