Intro to Occlusion Exam 1 [Guidance and Dynamic Tooth Contacts]
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Maximal Intercuspal Position (MIP)
The complete intercuspation of the opposing teeth independent of condylar position, sometimes referred to as the best fit of the teeth regardless of the condylar position
MIP is independent of
condylar position
Centric relation
Dependent on condylar position and independent of tooth contacts
Centric cusps (Functional)
Maxillary lingual cusps
Mandibular buccal cusps
Non-centric cusps (non-functional)
Maxillary buccal cusps
Mandibular lingual cusps
Centric cusps functions
Mastication of food
Maintains fascial height
Non-centric cusps functions
Minimize tissue impingement
Maintain bolus on occlusal table
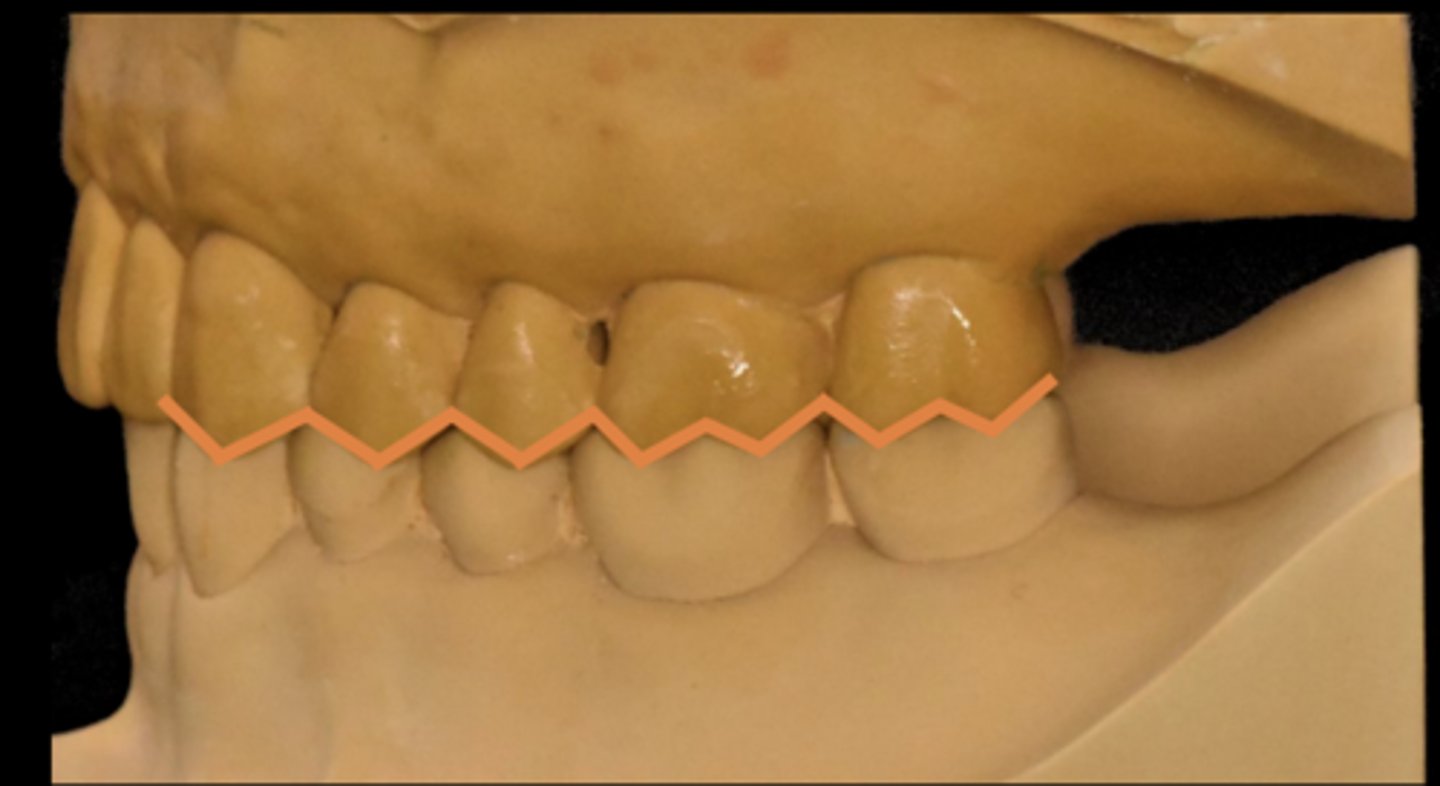
Guidance
The influence on mandibular movements by the contacting surfaces of the maxillary and mandibular anterior teeth
Posterior teeth protect anterior teeth in
MIP
Anterior teeth protect posterior teeth in
Excursion
Mutually protected occlusion
An occlusal scheme in which the posterior teeth prevent excessive contact of the anterior teeth in maximal intercuspal position, and the anterior teeth disengage the posterior teeth in all mandibular excursive movements
What is guidance influenced by
- Anterior teeth
- Posterior teeth
- Both
Both
Lateral movement
Lateral=away from the midline
Working side
always the side to which the mandible is moving
Canine guidance
Maxillary and mandibular canines only on the working side in contact as the mandible slides towards the working side
Group function
The simultaneous contact of multiple teeth on the working side as we make lateral movement
- Instead of the canine alone
Interferences
Antero-poterior movements
- Protrusion
- Retrusion
Lateral movement
- Mediotrusion
- Laterotrusion
Laterotrusion
Condylar movement on the working side in the horizontal plane
Mediotrusion
A movement of the condyle medially; syn, non-working-side movement
Laterotrusion always happens on the
Working side
Mediotrustion always happens on the
Non-working side
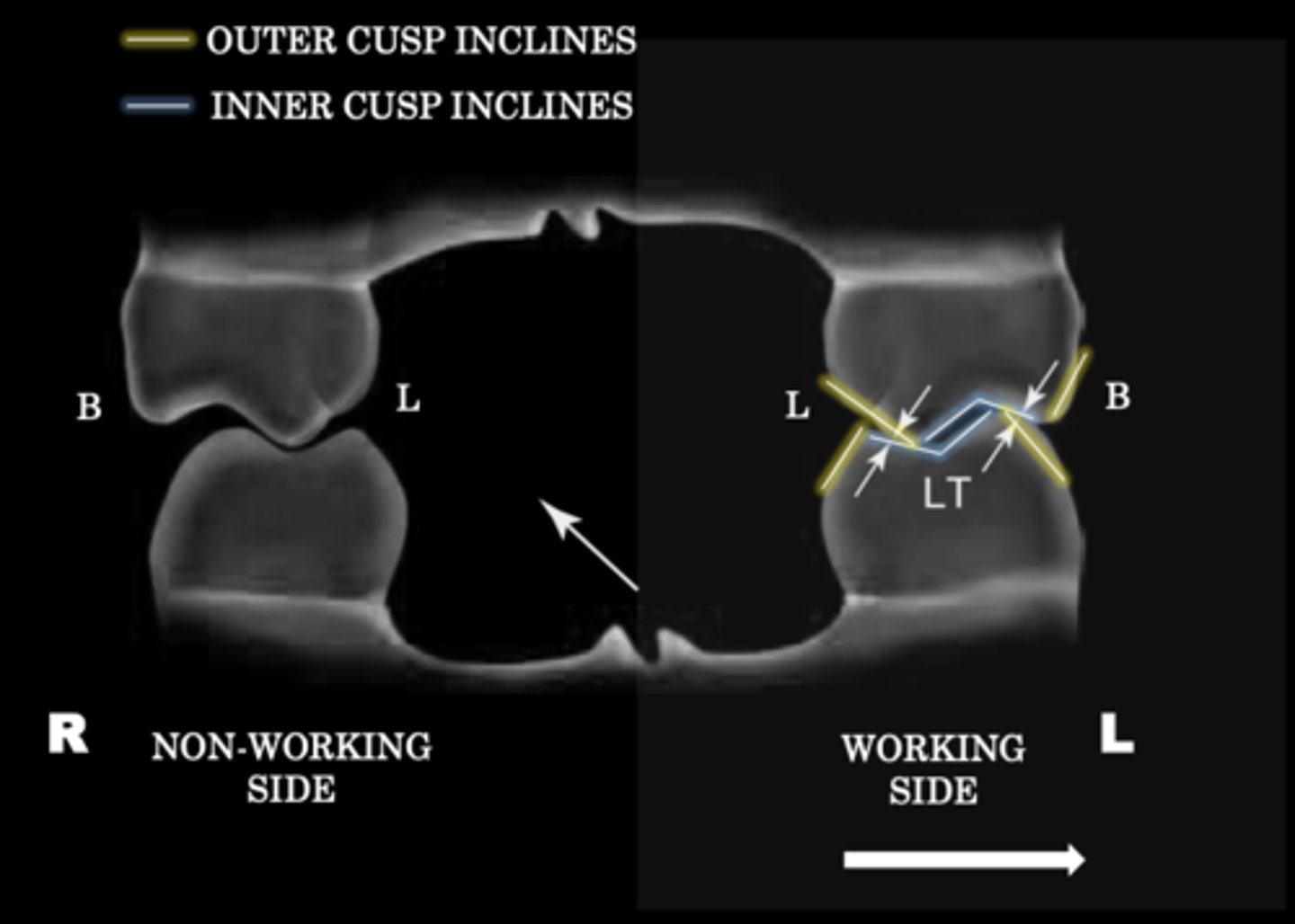
Laterotrusive interference
Outer inclines of our maxillary lingual cusps against inner incline mandibular lingual cusps
and/or
Inner incline of maxillary buccal cusps against outer incline of mandibular buccal cusps
Mediotrusive interference
Usually found at inner incline of maxillary lingual cusps against inner incline mandibular buccal cusp
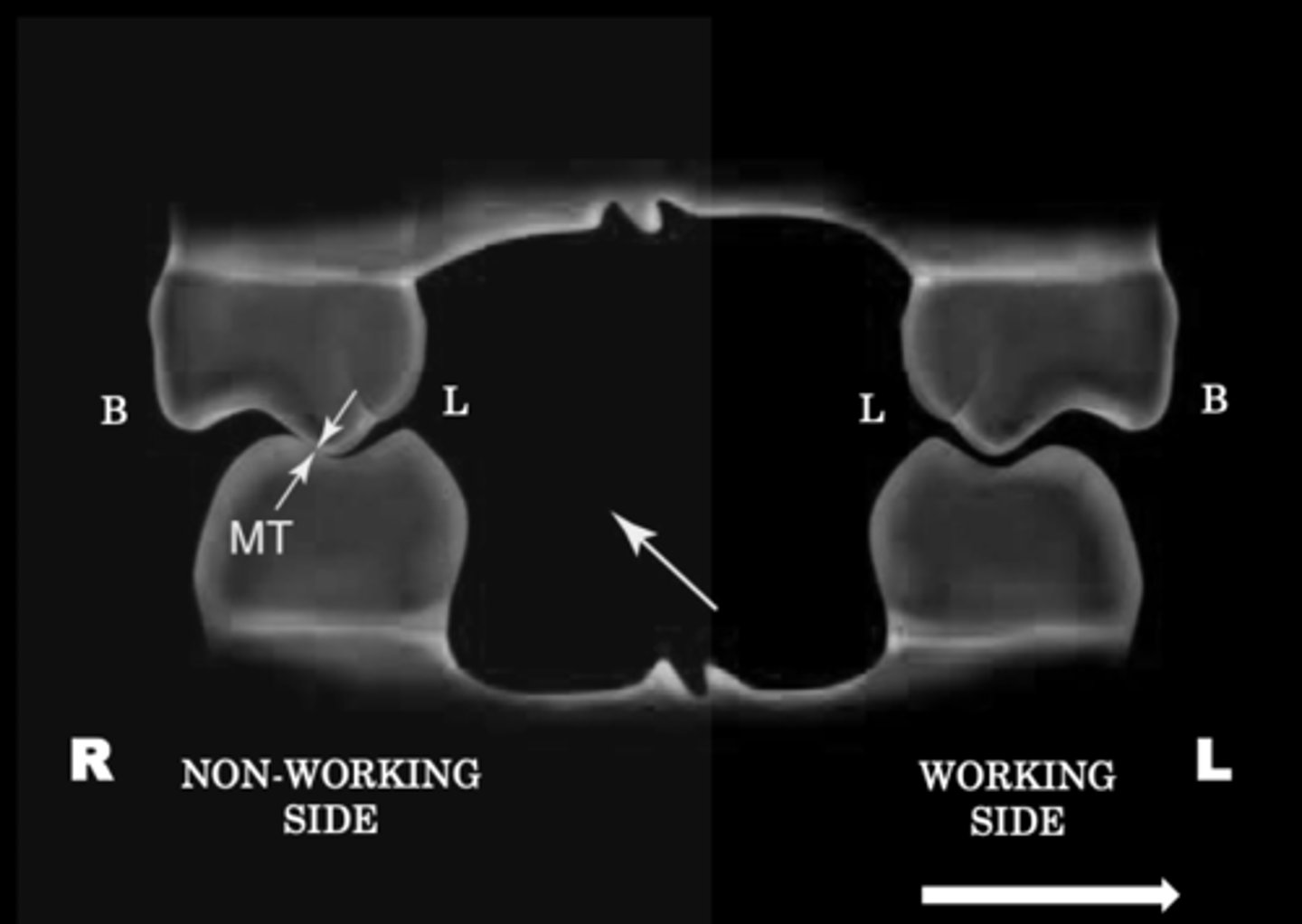
TIP if you find interferences of an inner incline against an inner incline that means its probably a
mediotrusive interference
TIP: If you have an outer incline against an inner incline, that means its probably a
Laterotrusive interference
Protrusive interference
Usually found at distal incline of maxillary cusps against mesial incline mandibular cusps
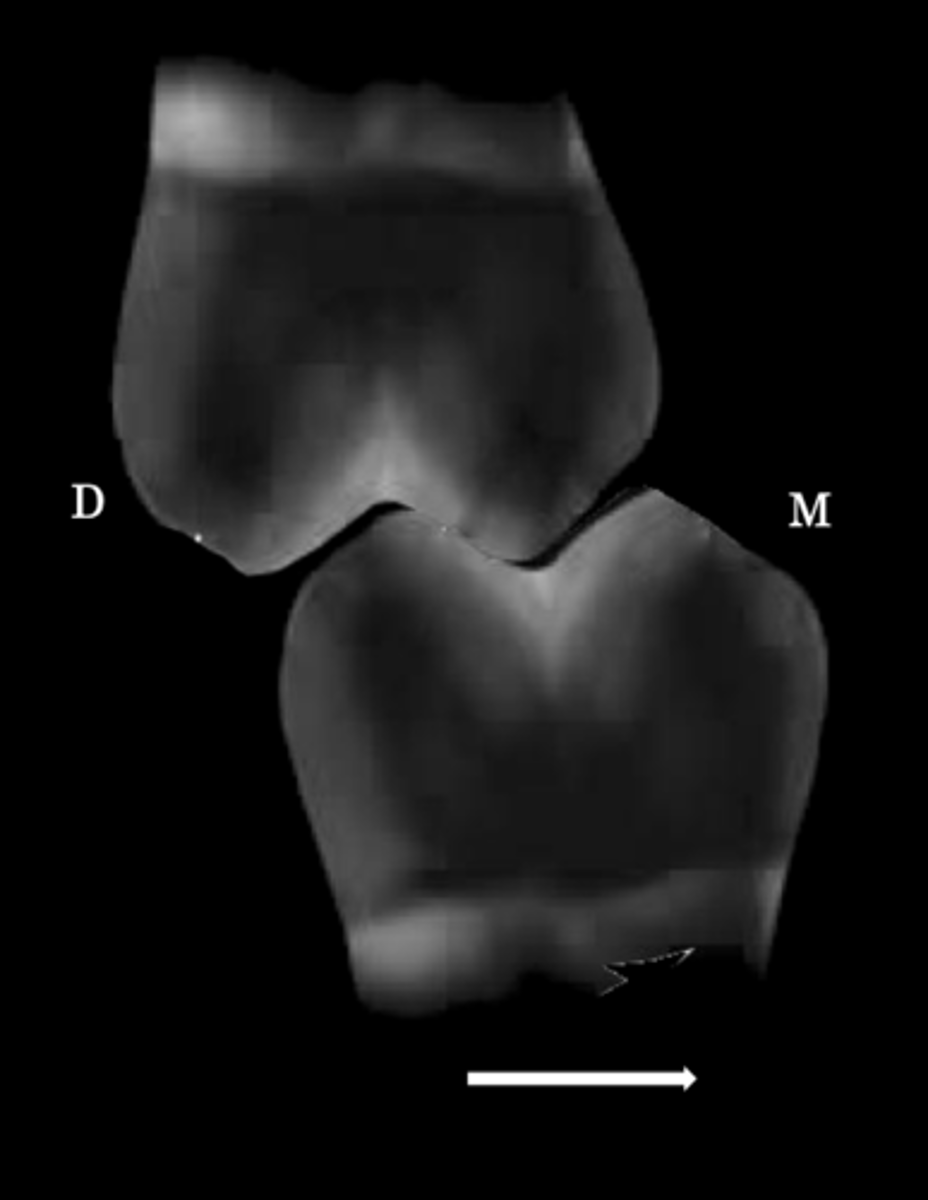
Retrusive interference
This type of interference you see when CR and MIP are not coincident
Usually found at mesial incline of maxillary cusps against distal incline mandibular cusps
Condylar guidance
The way in which the condyle slides down the slope at the base of the skull as the mandible slides forward
- Cannot be altered with restorations unlike lateral guidance and anterior guidance
- Measured with a protrusive record
- How shallow/steep it is can impact the occlusal morphology of restorations
The steeper the condylar guidance =
taller the posterior cusps can be
The shallower the condylar guidance =
shorter the cusps must be
Understand how the crows foot picture of cusp pathway works
I recommend going back through the video where we did the typodont exercise
Time: 1:06 on panapto