Choroid
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
the choroid begins anteriorly at _____
the choroid ends posteriorly at _____
begins at ora serrata
ends at optic nerve head
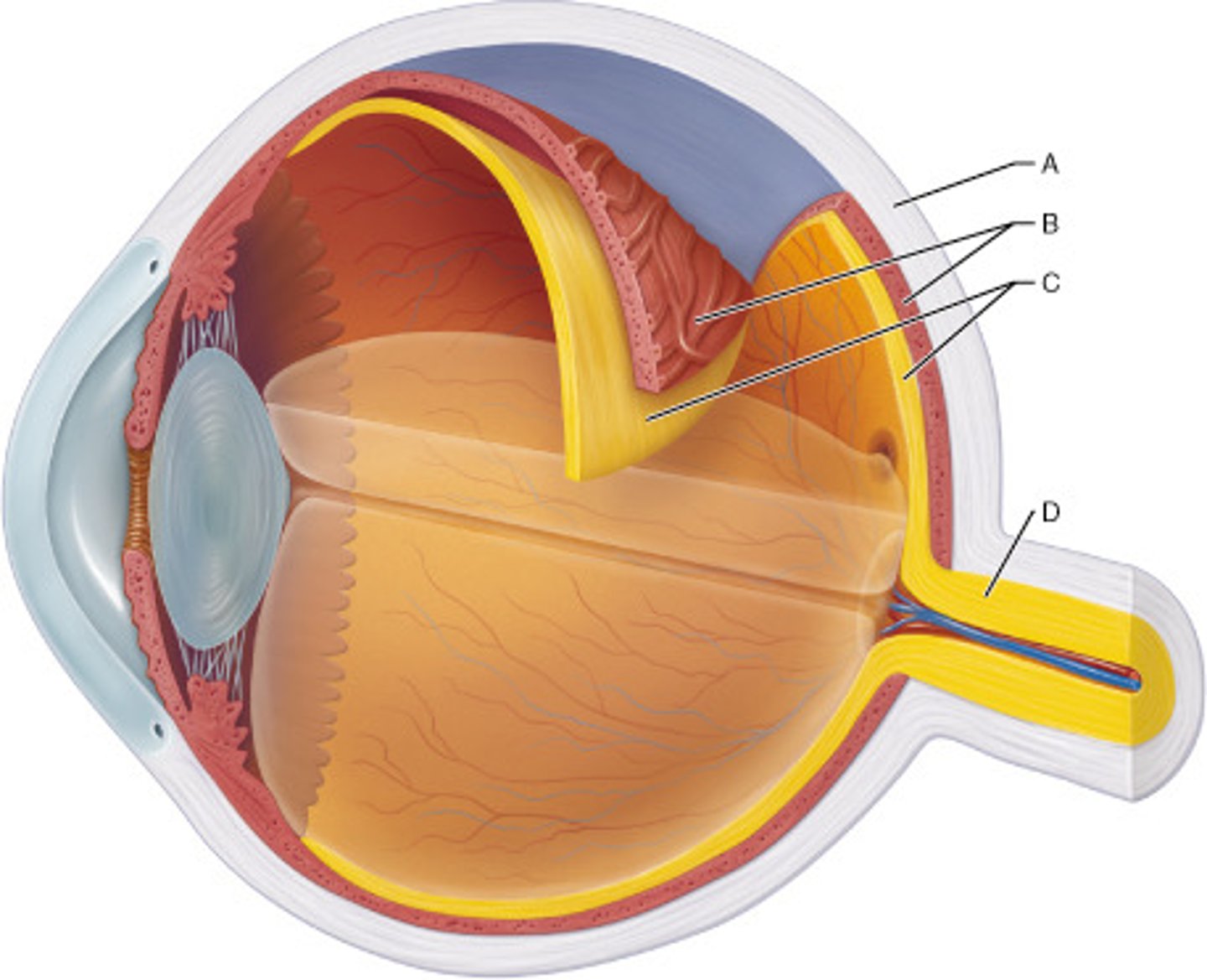
the choroid sits between the ____ & _____
retina & sclera
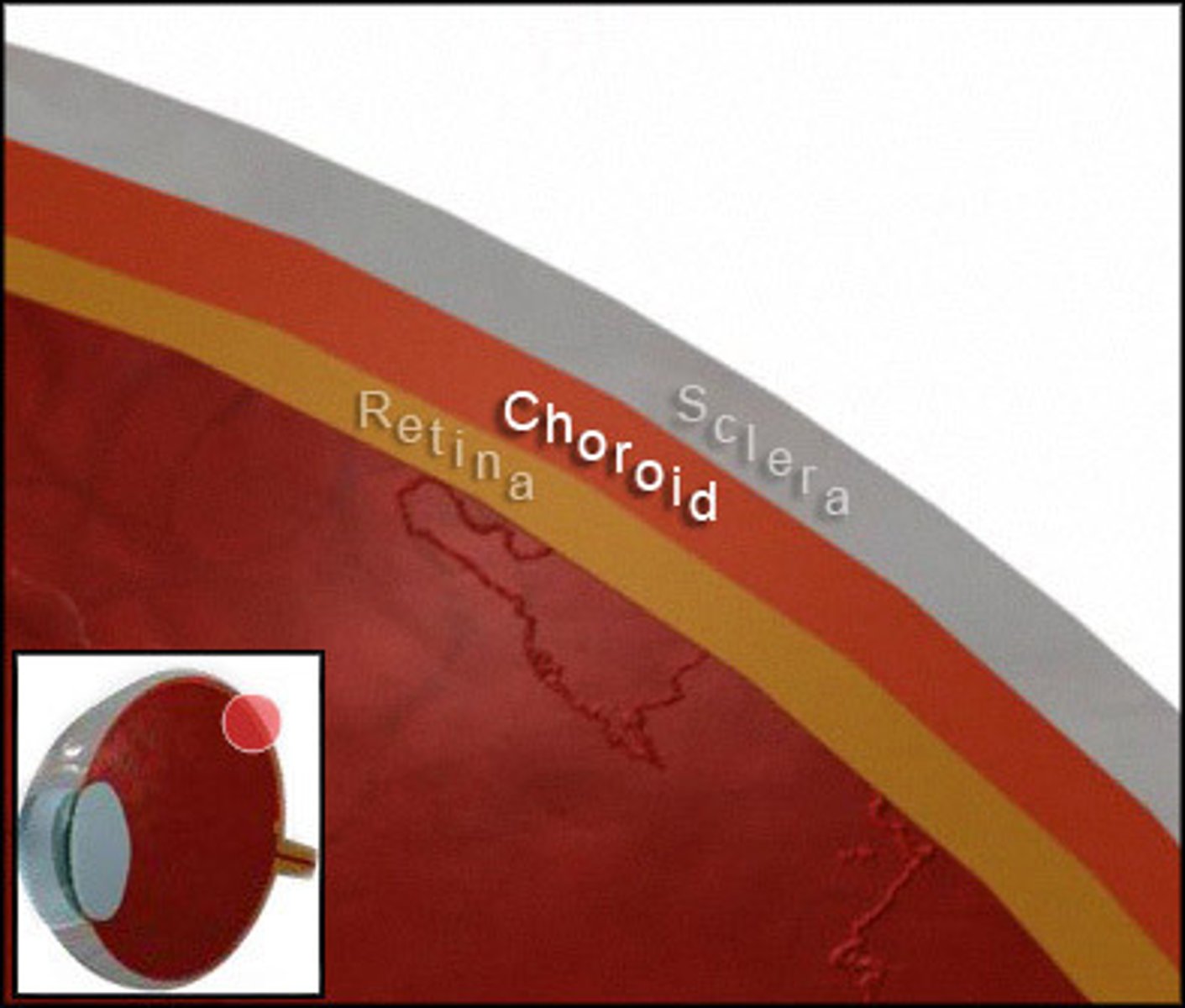
t or f: the choroid is a highly vascularized tissue
TRUE
3 layers of choroid (label external/internal)
(external) suprachoroid, stroma, choriocapillaris (internal)
the suprachoriod is continuous with...
supraciliaris
what type of cell is found abundantly in the suprachoroid? what is its function?
melanocytes
create a dark chamber & reduce oxidative stress
is the suprachoroid located internally or externally? (compared to the other layers of the choroid)
externally
longitudinal fibers from the ciliary body insert into what layer of the choroid?
suprachoroid
which layer of the choroid is a potential space?
suprachoroid
the suprachoroid attaches the choroid to what layer?
scleral proper
function of the suprachoroid
allows for choroid remodelling without disrupting the retina or sclera
t or f: the suprachoroid is highly innervated
true
what type of tissue is the suprachoroid?
LCT
t or f: the direction of the collagen fibers in the suprachoroid is anterior-posterior
false, they run diagonally
what is the widest layer of the choroid?
stroma
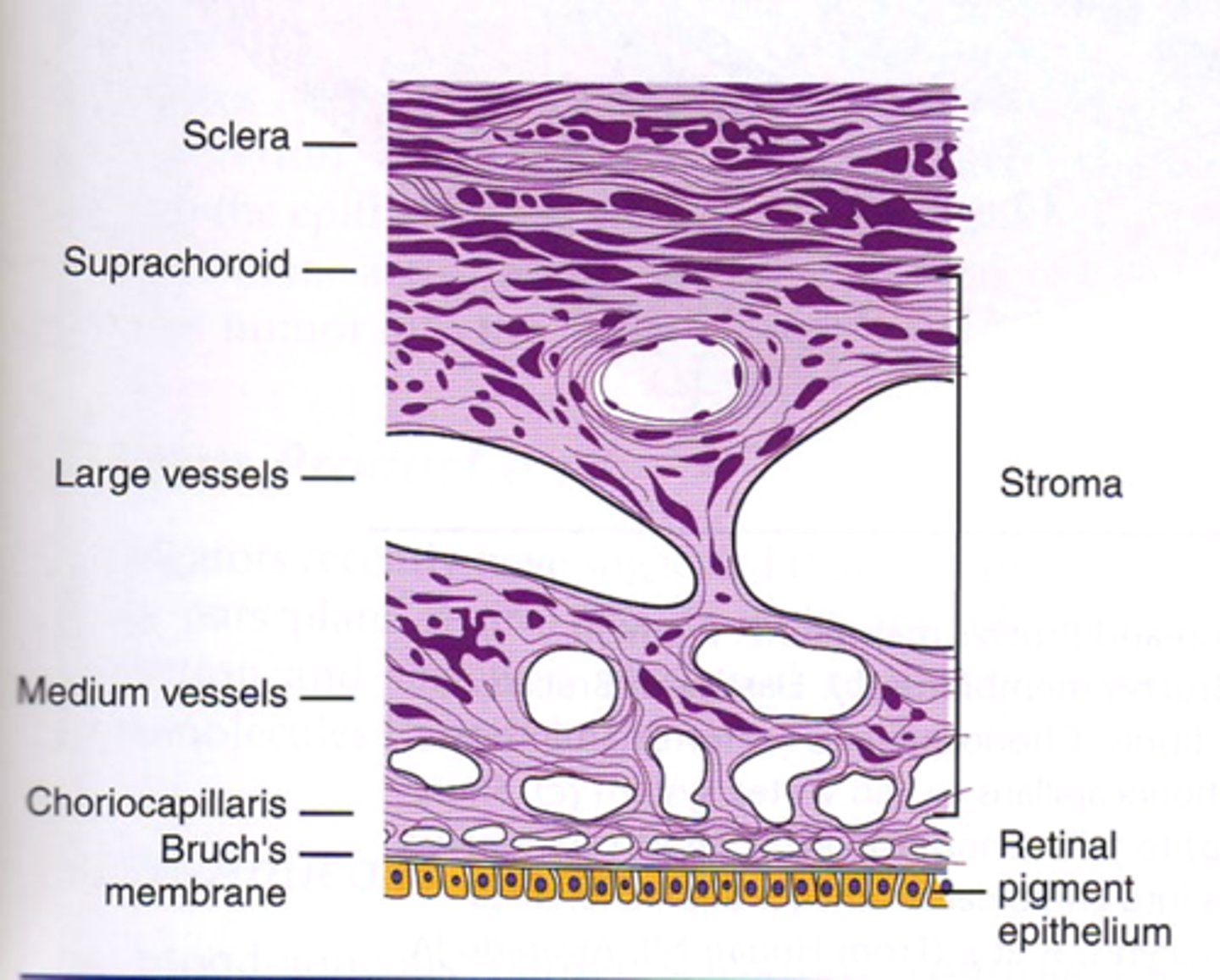
components of the choroid stroma
connective tissue, collagen, fibroblasts, APCs, melanocytes, blood vessels
what are the layers of blood vessels in the stroma named?
haller's & sattler's
what is Haller's layer?
external layer of LARGE lumened blood vessel in choroid stroma
what is Sattler's layer?
internal layer of NARROW lumened blood vessels in choroid stroma
choroid stroma is directly continuous with...
ciliary body stroma
the blood vessels in Haller's & Sattler's are... (fenestrated/non-fenestrated)
non-fenetrated (not leaky)
what is the choriocapillaris?
single layer of fenestrated (leaky), anastamosing (joined) capillaries
what is the function of the choriocapillaris?
deliver nutrients (especially to retina)
what layer lies directly external to the choriocapillaris? what lies internal?
external - choroid stroma/Sattler's
internal - Bruch's membrane/RPE
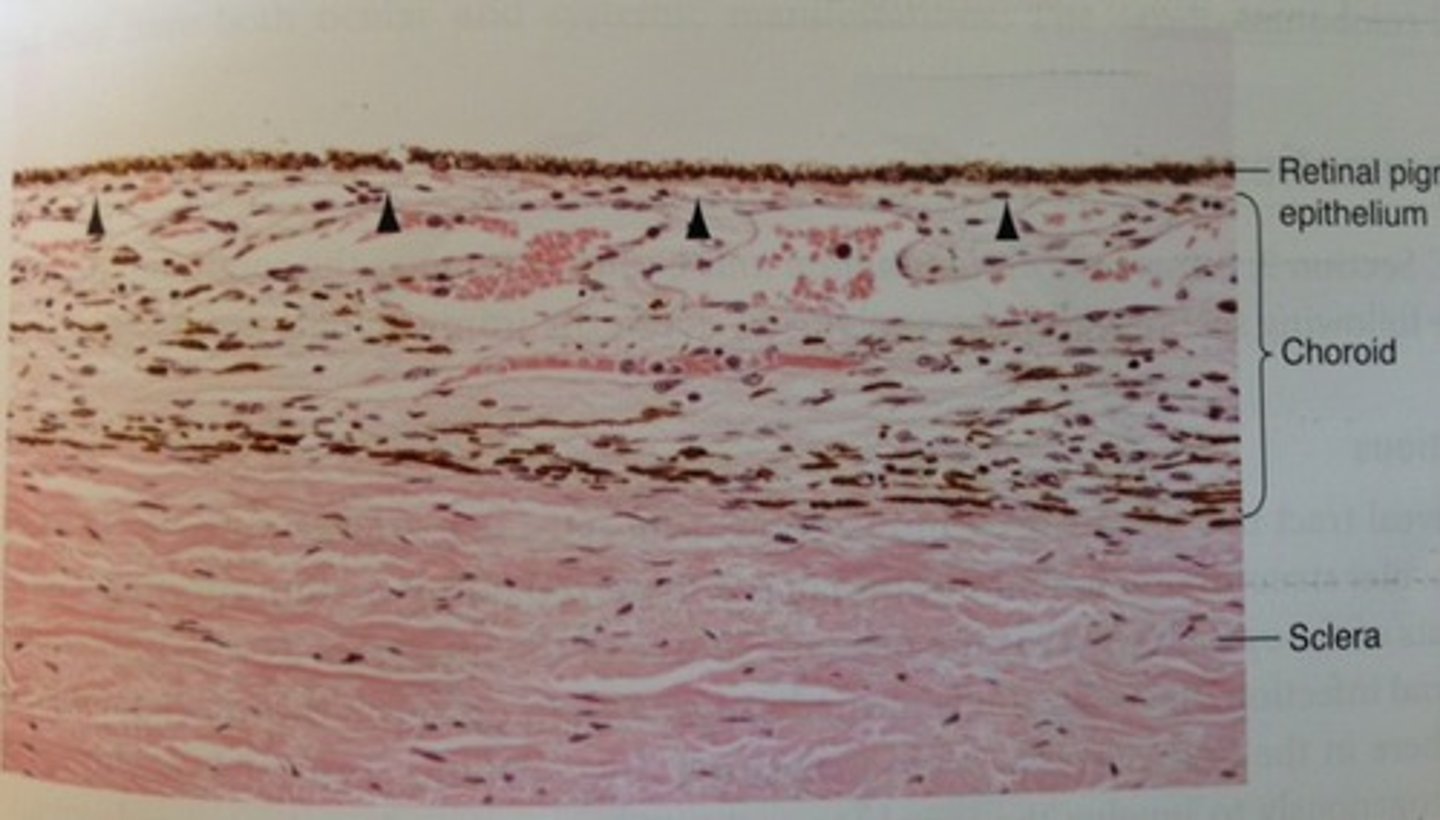
t or f: the choroid capillaries in the choriocapillaris have a narrow lumen
false, they have a wide lumen
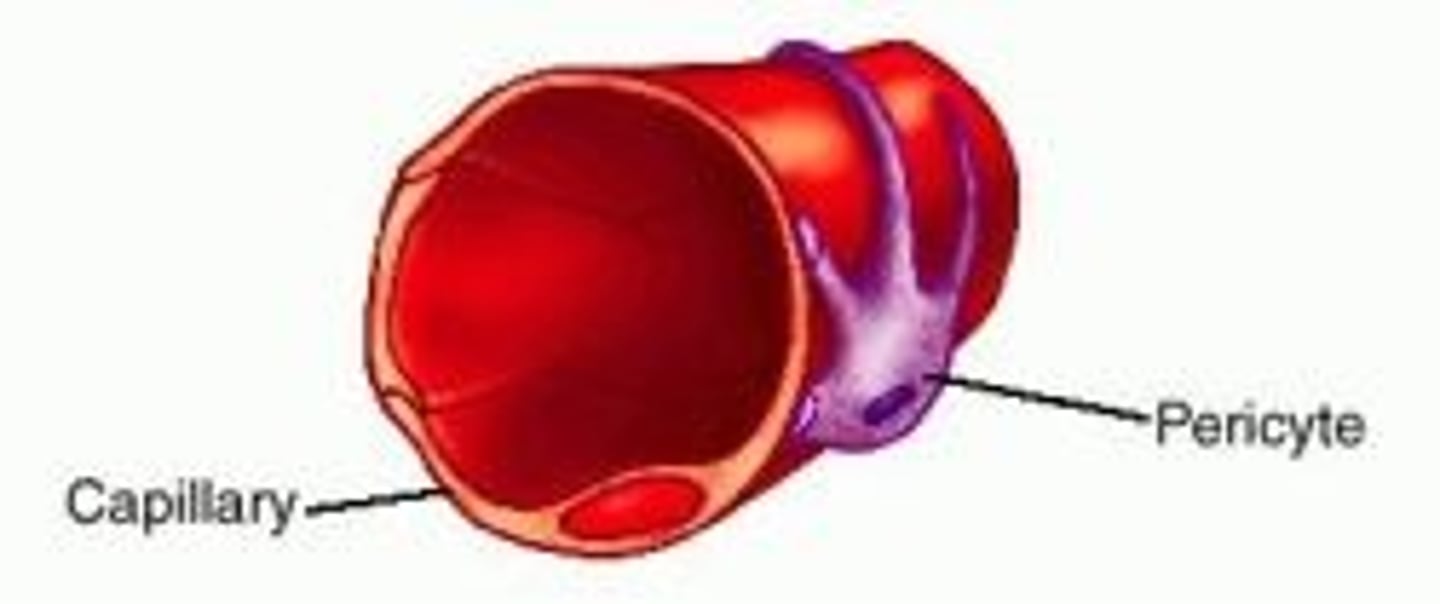
t or f: the choroid capillaries in the choriocapillaris have pericytes
true
what is the purpose of pericytes?
control movement of nutrients
the retina is supported by 2 blood supplies. what are they?
choroid & retinal vasculature
choroid vs. retinal vasculature: which is responsible for supporting the internal retina?
retinal vasculature
choroid vs. retinal vasculature: which is responsible for supporting the macula/fovea?
choroid vasculature
t or f: the high arteriole-to-venule ratio predisposes the choroid to hemorrhages
false, it has a predisposition to edema
high arteriole-to-venule ratio makes the tissue resistant to...
ischemia
where is the arteriole-to-venule ratio the highest?
macula & peripapillary area
where is the arteriole-to-venule ratio the lowest?
equatorial & periphery
t or f: the arteriole-to-venule ratio is inversely related to the number of photoreceptors in an area
false, they are directly proportional
increase ratio = increase number of photoreceptors
a low arteriole-to-venule ratio make a tissue suseptible to _____, but resistant to _____
suseptible to ischemia
resistant to edema
t or f: Haller's & Sattler's are only distinct in the periphery
false, they are distinct in the central region
which cell in the choriocapillaris controls the movement of nutrients?
pericytes
t or f: the absence of retinal vasculature in the fovea decreases light scatter
true
t or f: Bruch's membrane is a less efficient method of nutrient delivery, but it is used between the choroid/RPE to control the delivery of nutrients
false, Bruch's is more efficient
5 layers of Bruch's membrane
1. BM of the choriocapillaris
2. outer collagenous layer
3. elastic layer
4. inner collagenous layer
5. BM of the RPE
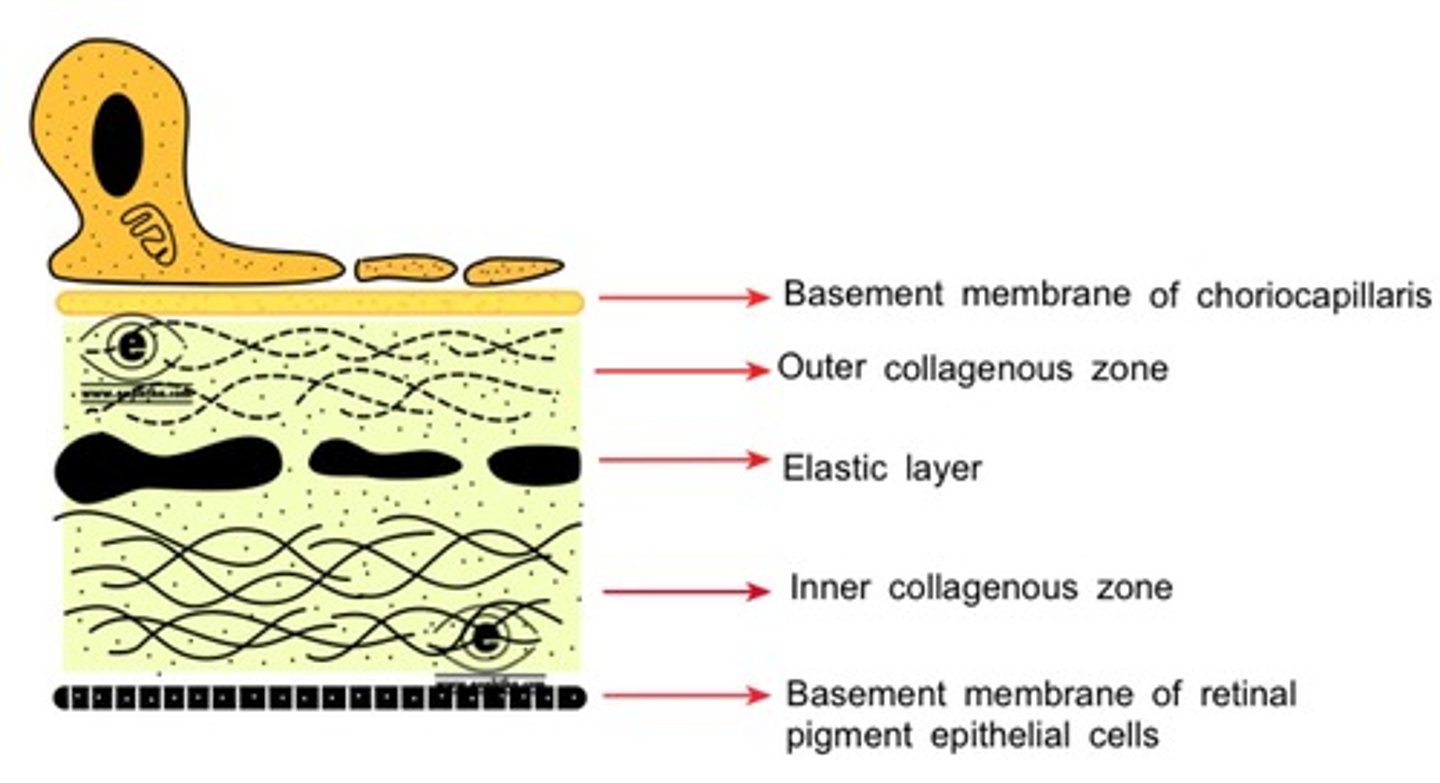
t or f: the BM of choriocapillaris is discontinuous
true
main type of collagen in the BM of the choriocapillaris
type IV
main type of collagen in the outer collagenous zone
type I
main type of collagen in the inner collagenous zone
type I
main type of collagen in the BM of the RPE
type IV
the outer & inner collagenous zones are held together by...
elastic layer
t or f: the outer collagenous zone is made during embryology
false, the inner collagenous is made during embryology
where does Bruch's membrane taper?
pars plana
as you approach the retina, the BM of the non-pigmented ciliary epithelium is continuous with...
the internal limiting membrane of the neural retina
as you approach the retina, the BM of the pigmented ciliary epithelium is continuous with...
the BM of the RPE (part of Bruch's)
t or f: Bruch's dead ends at the ora serrata
false, most of the components of Bruch's will end, but the RPE BM will be continuous with the pigmented ciliary epithelium BM
innervation of the choroid
sympathetic (directly stimulates vasocontriction)
parasympathetic (indirectly stimulates vasodilation)
functions of the choriod
absorb stray light
thermoregulation
remove waste
supply blood to retina
what is drusen?
degeneration of Bruch's membrane
collection of lipid & BM-like material in the inner collagenous zone
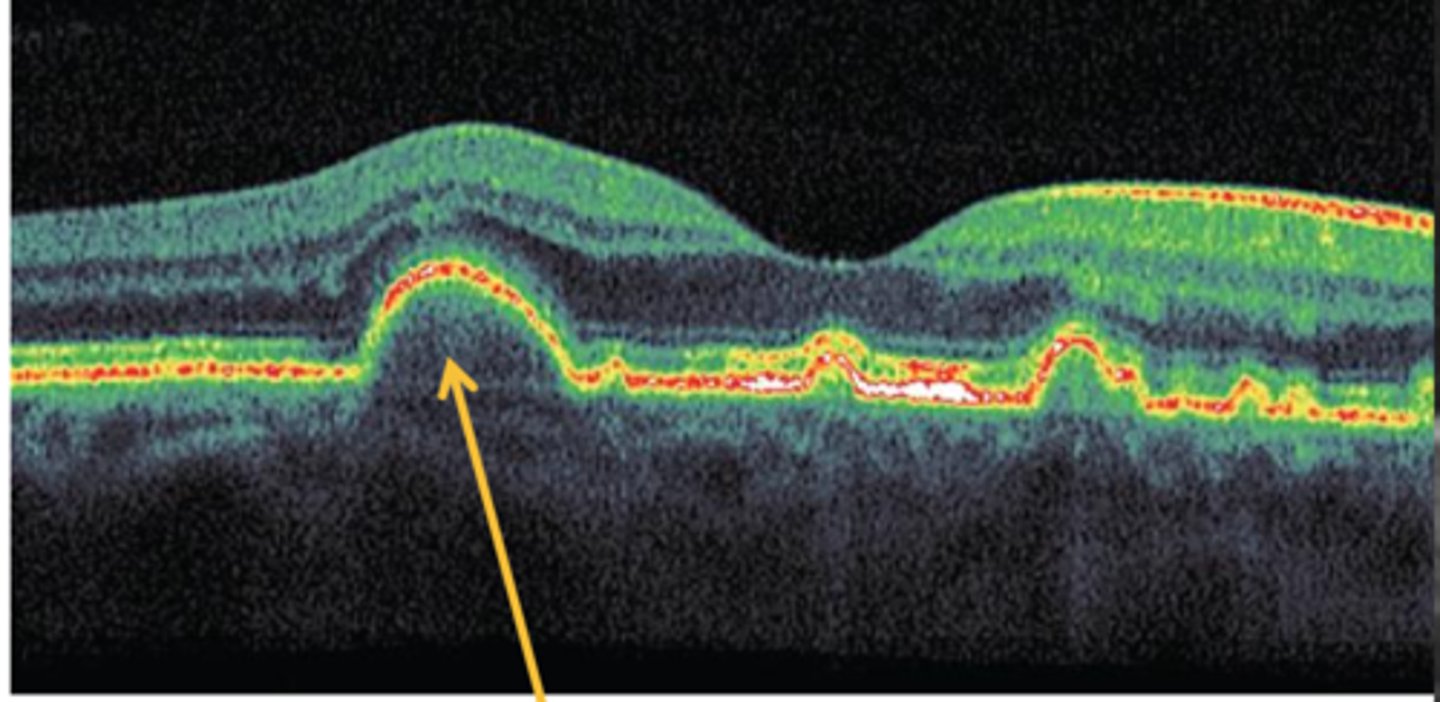
drusen increases your risk for developing...
age-related macular degeneration
what are the 2 types of AMD?
geographic atrophy/dry
wet
dry AMD is characterized by _____
wet AMD is characterized by ____
dry - RPE loss
wet - neovascularization
t or f: humans have a tapetum lucidum
false :(
which layer is the tapetum lucidum present in?
Sattler's layer
what is the purpose of the tapetum lucidum?
increase light scatter to improve light sensitivity/night vision