Perception and Object Recognition: Visual System, Gestalt Principles, and Models
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the first step in perception?
Sensation, which includes vision, hearing, touch, smell, taste, and kinesthetic senses.
What part of the brain is responsible for visual processing?
The visual cortex located in the occipital lobe.
What is the role of association areas in the brain?
They integrate sensory input into a cohesive whole, creating more complex perceptions.
What is the function of the retina?
It holds receptor cells that transduce light information into neural impulses.
What are the two types of receptor cells in the retina?
Rods, which are for dim light, and cones, which are for bright light, detail vision, and color vision.
What is the purpose of the optic nerve?
It transmits visual information from the retina to the brain.
What are the Gestalt Principles of Perceptual Organization?
Basic tendencies to perceive patterns as wholes rather than parts, including principles like closure and figure-ground.
What is the Template Matching Theory?
A theory that compares stimuli to stored templates in memory, though it requires many templates to account for variability.
What is the Feature-Analysis Theory?
A theory that compares features of stimuli to representations in memory, utilizing distinctive features.
What is Prototype Theory in object recognition?
A theory that compares stimuli to idealized patterns in memory, accounting for variation but questioning how prototypes are formed.
What are Feature Nets?
Models made of nodes and connections that activate with sensory input, where activation is influenced by recency and frequency.
What is the McClelland Rumelhart Model?
An updated feature net model that allows for excitatory and inhibitory connections and can learn to strengthen connections.
What is the Recognition by Components Model?
A structural theory by Beiderman that analyzes objects by comparing them to combinations of geons in memory.
What is the difference between Top-Down and Bottom-Up Processing?
Bottom-Up Processing takes sensory information from the environment, while Top-Down Processing uses prior knowledge to interpret sensory input.
What is the Fusiform Face Area?
A brain region specialized for face recognition, also activated by other significant objects.
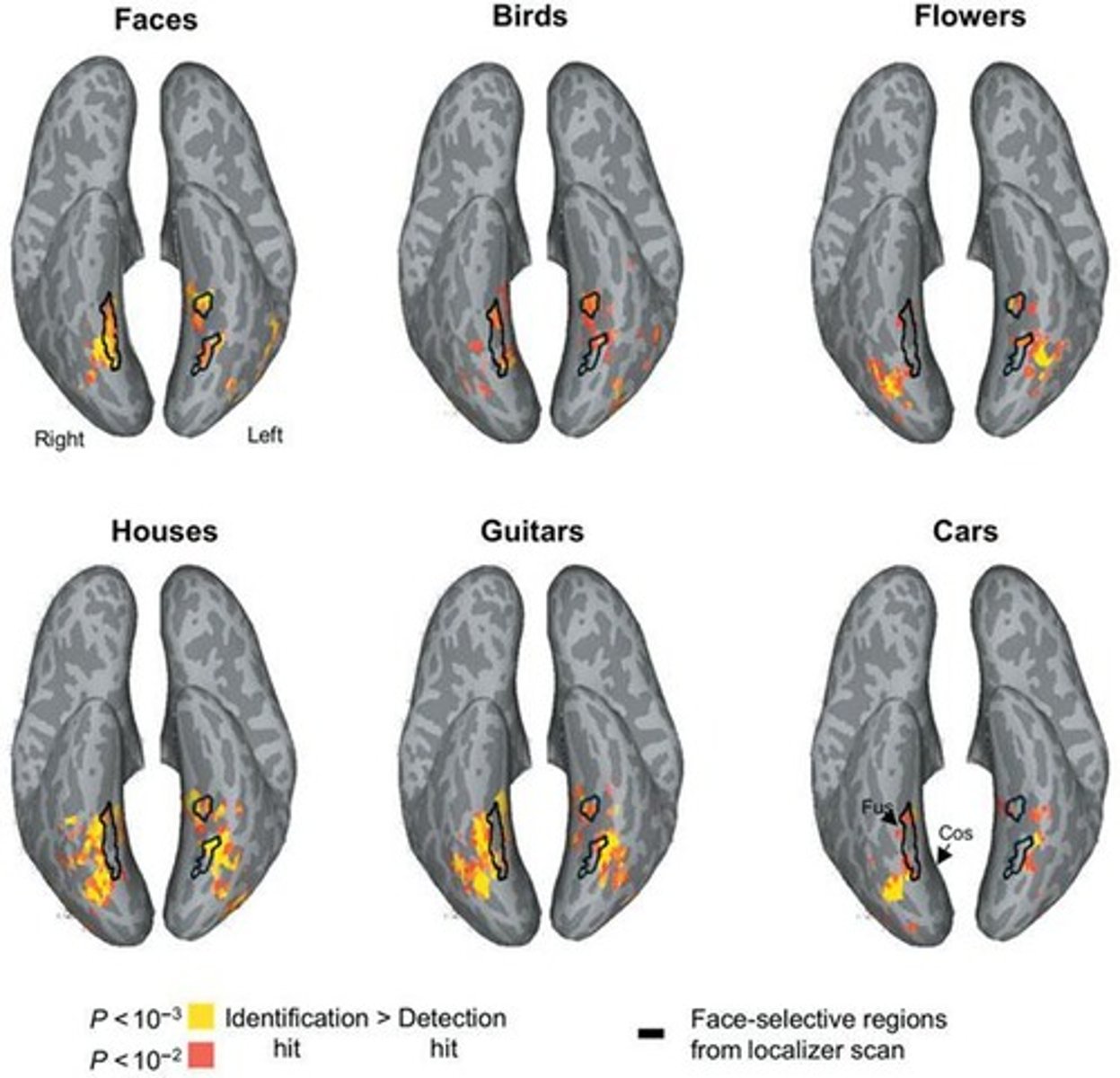
What is the Composite Face Effect?
The phenomenon where faces are processed holistically rather than feature-by-feature.
What is prosopagnosia?
A type of agnosia characterized by the inability to recognize faces.
What is the Inverted Face Effect?
The difficulty in recognizing faces when they are presented upside down compared to upright.
What is agnosia?
A condition where a person is unable to process sensory information, leading to difficulties in recognition.
What is the purpose of Top-Down Processing in vision?
To use memories and expectations to make sense of sensory information, especially in complex or ambiguous situations.
What is the role of the LGN in the visual system?
It provides correlations between spatial and temporal information from the eyes and ears and processes color and depth.
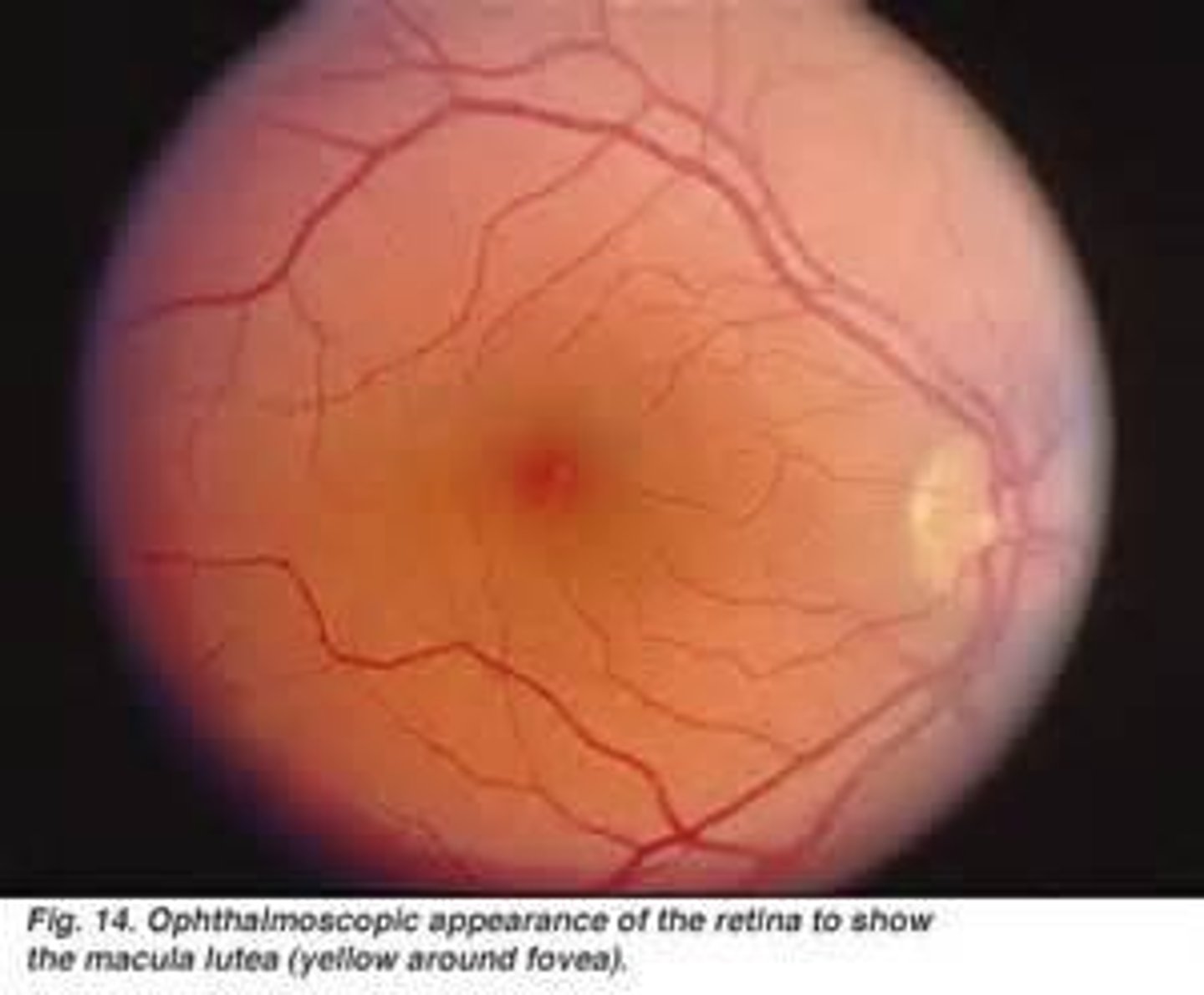
What is the significance of the fovea?
It is the area of the retina with the highest concentration of cones, responsible for sharp central vision.
What are illusory contours?
Perceptual phenomena where edges are perceived even when they are not physically present.
What is the purpose of the lens in the eye?
To focus light onto the retina.
What is the process of perception?
The rapid integration of sensory information into meaningful experiences, typically occurring in less than a second.