Bio Midterms ALL units 2a-6
1/680
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
681 Terms
carbon dioxide
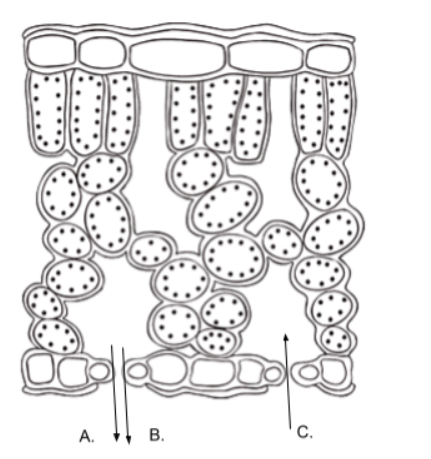
The image below represents a cross section of a leaf. The letters represent various substances entering and exiting the leaf during photosynthesis reactions. In the diagram, letter C is likely
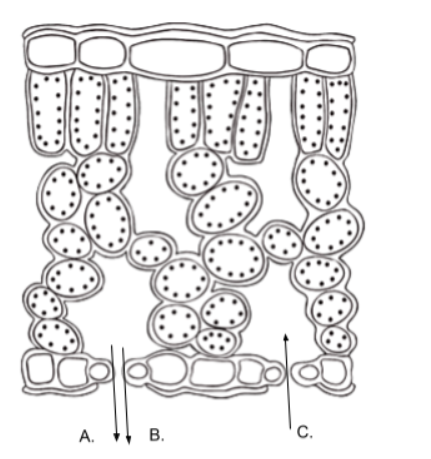
oxygen and water vapor
In the diagram above, letters A and B most likely represent what two substances?
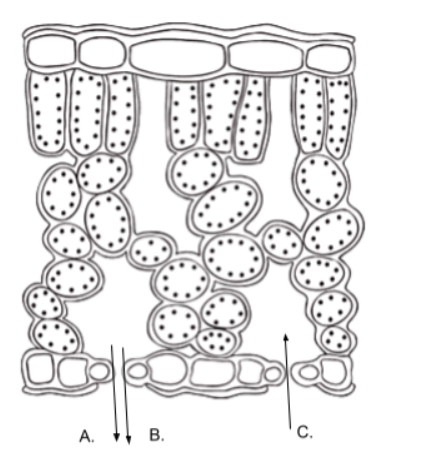
stomata
In the diagram above, the substances move through openings called
heterotrophs
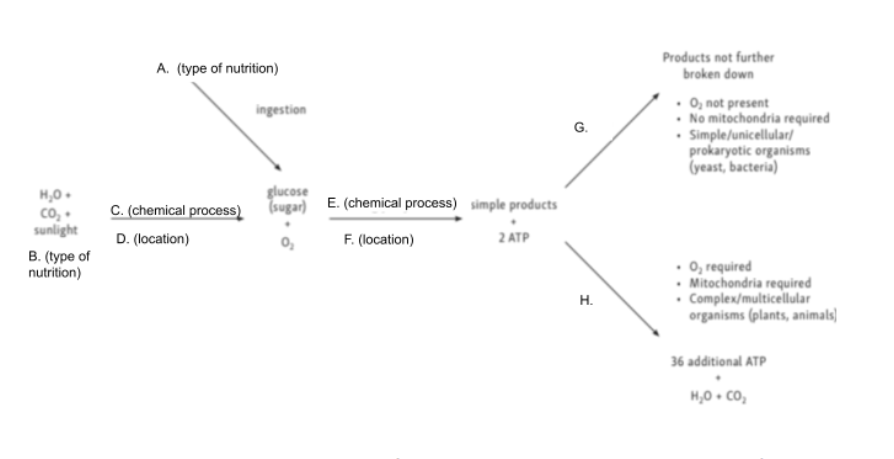
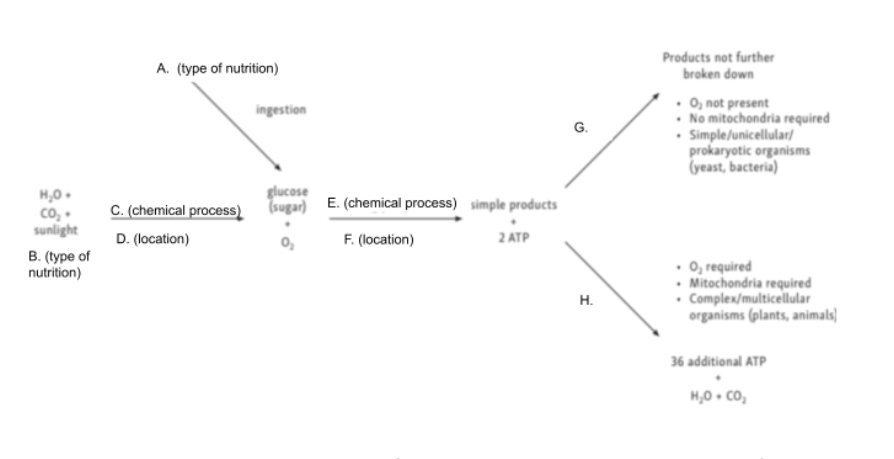
Given the following diagram, match A with the correct word

Autotrophs
Given the following diagram, match B with the correct word
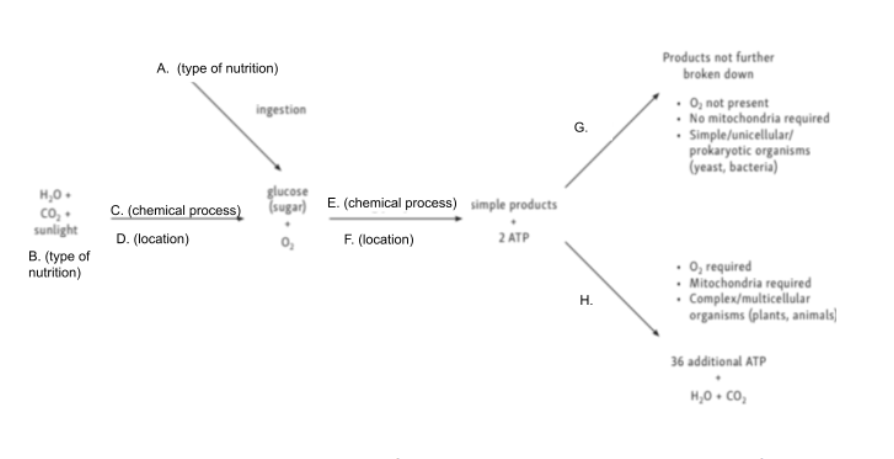
Photosynthesis
Given the following diagram, match C with the correct word
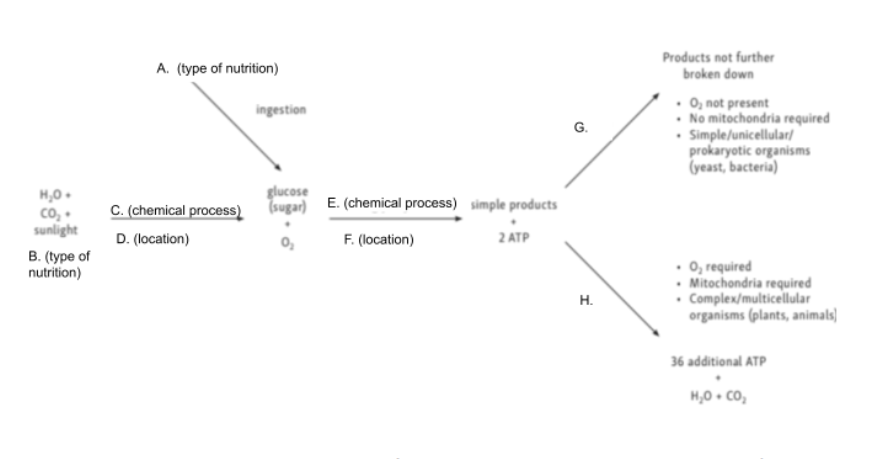
Chloroplast
Given the following diagram, match D with the correct word
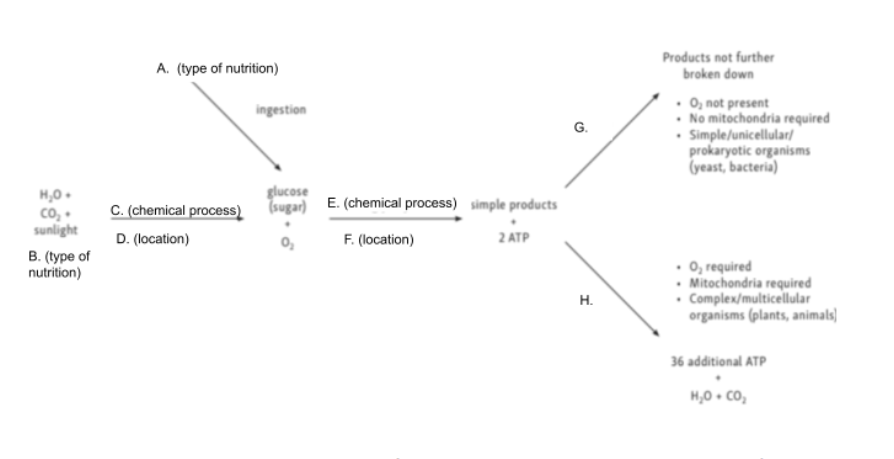
Glycolysis
Given the following diagram, match E with the correct word
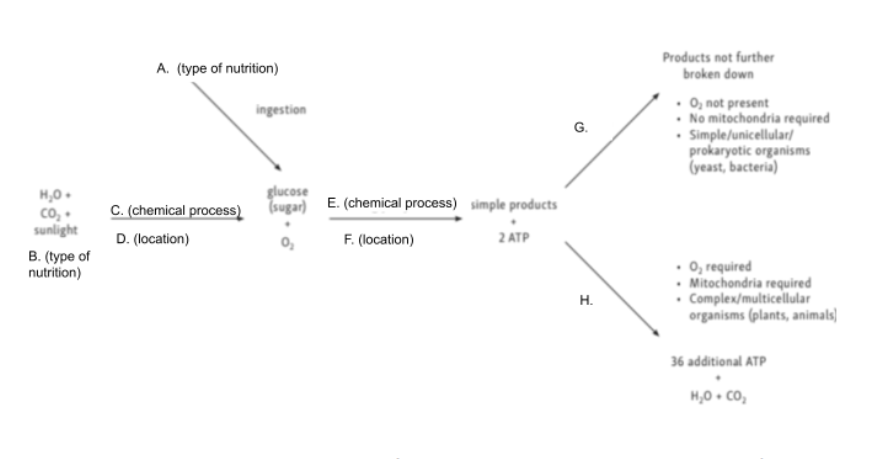
Cytoplasm
Given the following diagram, match F with the correct word
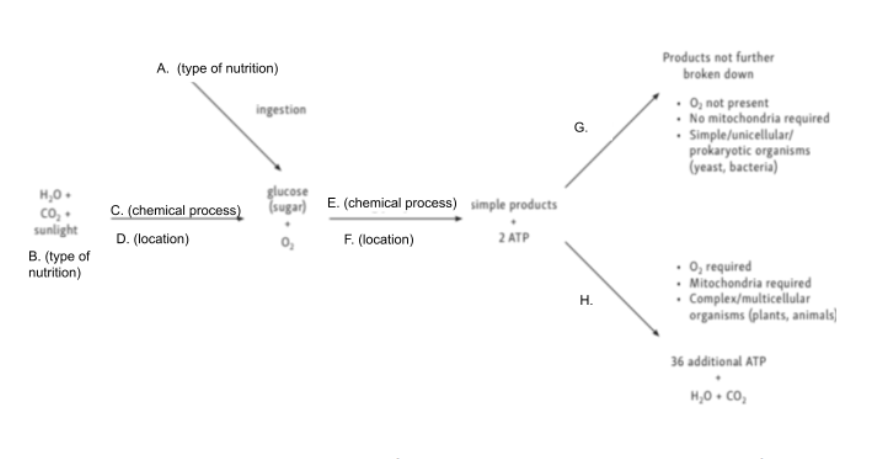
Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
Given the following diagram, match G with the correct word
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Given the following diagram, match H with the correct word
Light energy to chemical bond energy
Which energy conversion occurs during photosynthesis
green
A producer such as a plant would show the least growth when exposed to light of which color?*
starch
In most green plants, surplus glucose is stored as what chemical?
water
Which of the following is the molecular source of oxygen gas produced during photosynthesis?
chloroplasts
In green plants, carbohydrates are produced from inorganic substances within
photolysis of water
In the photosynthetic process, which of the following events occurs before the other three?
export of starch to the roots
oxygen release
photolysis of water
carbon dioxide absorption
oxygen gas is released
Which statement associated with the light dependent reaction is true?
cellular respiration ceases
carbon dioxide is absorbed
carbon fixation occurs
oxygen gas is released
stroma
The site of the Calvin Cycle is the ______
oxygen
Which of the substances below would not slow photosynthesis if it was in short supply?
Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide
Light
Chlorophyll
Are able to absorb parts of the light spectra chlorophyll a does not
Carotenoid pigments differ from Chlorophyll a in that
They are the same color visually
They absorb all wavelengths of light emitted by the sun
Are stored in plastids
Are able to absorb parts of the light spectra chlorophyll a does not
Carbon Dioxide
The continuous source of carbon in the Calvin Cycle is ____
carbon fixation
The removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and the formation of small carbon chain is known as
algae
The conversion of light energy into chemical bond energy occurs in which of the following:*
Algae
Grasshoppers
Heterotrophic bacteria
Yeast
synthesize glucose
In terms of nutrition, the significant difference between green plants and animals is that green plants alone are able to..
break down carbohydrates
synthesize glucose
carry on aerobic respiration
form ATP molecules
glucose
Which of the following is not a product of aerobic cellular respiration?
glucose
carbon dioxide
water
ATP
36
How many ATP molecules result from aerobic respiration?
2
How many ATP result from anaerobic respiration
glycolysis, cytoplasm
The initial stage of all forms of cellular respiration is __________ and occurs in the __________.
Potential chemical bond energy in glucose -------> ATP energy
The energy conversion that occurs during aerobic cellular respiration is best summarized as:
Potential chemical bond energy in glucose -------> ATP energy
Light energy ------> ATP energy
Light energy -------> Potential Chemical Bond Energy in glucose
ATP energy --------> Active Transport/cellular growth
all organisms
Phosphorylation of ATP promoted by the breakdown of glucose occurs in which organisms?
atp synthase
The enzyme responsible for the formation of adenosine triphosphate is primarily
christae
The inner folds of membrane where aerobic cellular respiration reactions occur are known as
Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation, Animal Muscle Cells, Ethyl Alcohol + Carbon Dioxide
Which of the lists below correctly identifies the form of fermentation with the organism who uses that strategy and the chemical(s) produced during the reaction.
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Yeast, Lactic Acid
Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation, Yeast, Ethyl Alcohol + Carbon Dioxide
Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation, Yeast, Ethyl Alcohol
Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation, Animal Muscle Cells, Ethyl Alcohol + Carbon Dioxide
Both organelles can live independently from their host cell
Which of the following does not provide evidence that both the mitochondria and chloroplast evolved from independently living bacteria?*
Both organelles can live independently from their host cell
Both organelles contain Ribosomes
Both organelles contain double membranes
Both organelles contain circular rings of DNA
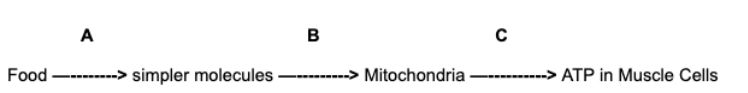
digestion, diffusion, cellular respiration
Arrows A, B, C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to transfer the energy stored in food available for muscle cell activity. The correct sequence of A, B, and C is:
diffusion, synthesis, active transport
digestion, diffusion, cellular respiration
digestion, excretion, cellular respiration
synthesis, active transport, excretion
glucose
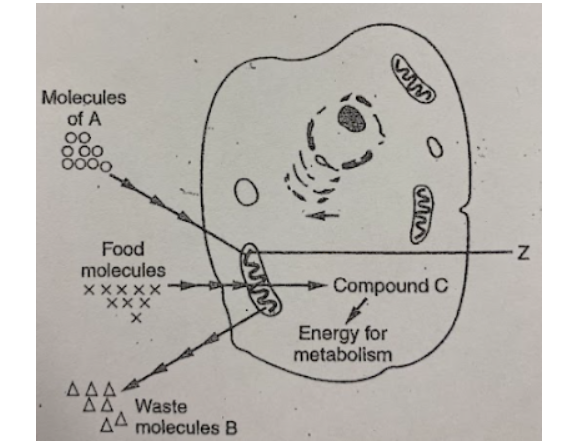
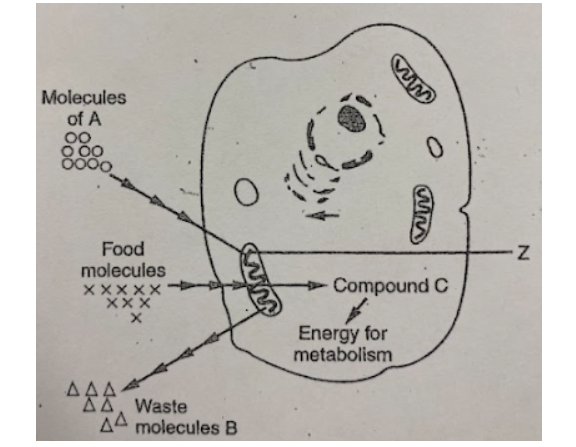
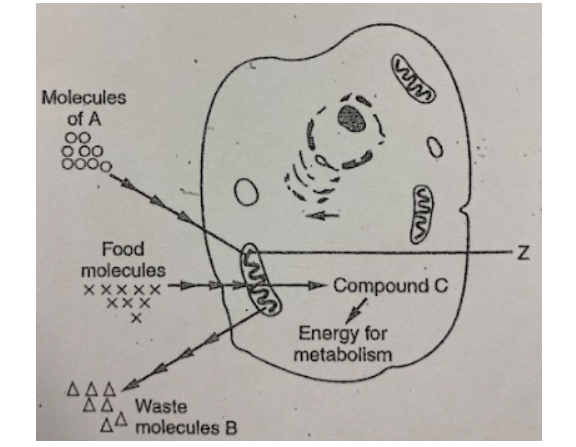
In the diagram below, the item labeled as food molecules most likely represent
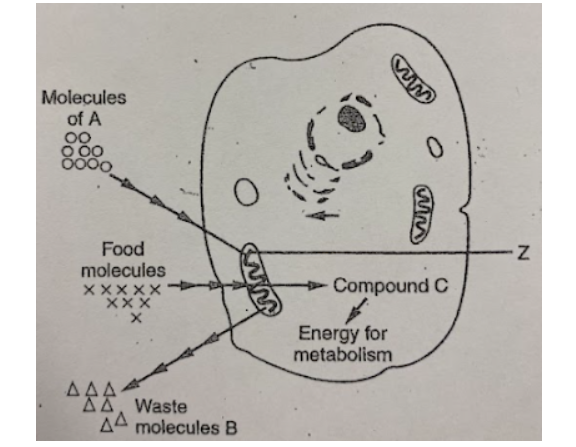
ATP
In the diagram, compound C most like represents some molecules of:
oxygen
glucose
ATP
DNA
carbon dioxide
If this cell is carrying on aerobic respiration, B would represent molecules of a waste product known as
oxygen
If this represents a cell from a human body, the molecules "A" are most likely
mitochondria
The cell organelle labeled "Z" is called

lactic acid fermentation, ethyl alcohol fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
Aerobic Cellular Respiration: A form of anaerobic respiration
aerobic Cellular respiration,
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Occurs in muscle cells of humans
aerobic Cellular respiration
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Requires mitochondria to occur
aerobic cellular respiration
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration: 19X more efficient than other forms
All
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration:Includes the process of glycolysis
aerobic cellular respiration
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration:Requires oxygen as a reactant
all
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration:Produce ATP as a product
Lactic acid fermentation, ethyl alcohol fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration: May be used by bacteria
ethyl alcohol fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration: may be used by yeast
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Lactic Acid Fermentation, Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation
or Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Performed by plants
Endosymbiont Theory
This theory explains the evolution of eukaryotic cells from the cooperation of ancient prokaryotic cells.
carbon fixation
The conversion of atmospheric carbon to usable organic molecules
Phosphorylation
The process that bonds a phosphate group to a molecule.
ATP synthase
The name of the enzyme required to produce ATP.
thylakoid membrane
Location of light dependent reactions within the chloroplast
carotenoid
Orange-yellow accessory pigment found in plant leaves
photosystems
A collection of chlorophyll pigment and enzymes located within thylakoid membranes.
light dependent reaction
Stage of photosynthesis involving photolysis.
Calvin Cycle, Light independent reaction
Stage of photosynthesis that uses stored energy in NADPH and ATP as reactants, two answers..
stomata
Entry and exit point for gases required or produced during photosynthesis.
both
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contain a mitochondria
plant
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contains a cell wall
plant
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contain 1 large vacuole
plant
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contains chloroplasts
both
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contains a membrane
both
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contains a nucleus
animal
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contains centrioles
both
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contains ribosomes
both
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contain exoskeletons?
animal
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contain lysosomes?
animal
plant cell, animal cell, or both; have two vacuoles?
both
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contain cytoplasm
eukaryotic
Eukaryotic Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, or Both; contains a nucleus
both
Eukaryotic Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, or Both; contains genetic material
both
Eukaryotic Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, or Both; contains a cell membrane
prokaryotic
Eukaryotic Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, or Both, contains a DNA plasmid
both
Eukaryotic Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, or Both, contains ribosomes
eukaryotic
Eukaryotic Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, or Both, contains membrane bound organelles
prokaryotic
Eukaryotic Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, or Both; found ONLY in bacteria
eukaryotic
Eukaryotic Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, or Both, found in animals, animals, protests, fungi
golgi body
Packages and modifies proteins?
leukoplasts
Stores starch? what organelle.
cell membrane
Regulates movement of materials in or out of a cell
lysosomes
Contain digestive enzymes, breaks down cell parts
vacuole
Storage of materials
mitochondria
Produces cellular energy (ATP)
chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis
cell wall
Structural boundary of a plant cell
ribosomes
Site where proteins are made
chromoplasts
Store accessory pigments
cytoskeleton
Microtubules/ microfilaments
nucleolus
Site where ribosomes are made
both
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contain peroxisome?
both
plant cell, animal cell, or both; contains nucleolus?
Lysosomes, 2 Vacuoles, Centroids
what 3 are in animal cells but not plant cells?? (LVC)
Cell walls, chloroplasts, leukoplast, vacuole
what 4 are in plant cells but not animal cells?? (CCLV)
prokaryotic
eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell; old