UCM Ecology Exam 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
ecology
the scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environment
Ernst Haeckel
termed the phrase ecology in 1866
importance of ecology (three)
improving the environment
natural resource management
public health
why ecology is important for improving the environment
reducing pollution
EX] phosphorus in soaps and fertilizers allow for algae to grow and result in fish death
non-native/introduced species
EX] feral pigs destroy acres of land and harm agricultural systems resulting in less food produced which leads to higher prices for us
why ecology is important for natural resource management
maintaining biodiversity
EX] protecting endangered species while highlighting the importance of the common creatures as well in the ecosystem
timber (role of fire)
EX] small prescribed burns can release nutrients into the soil and developed trees to promote quicker growth and encourages biodiversity, mimics the natural process
fisheries
EX] take care of estuaries (where a river and ocean meet) which are important for reproduction, build fish ladders to help fish get around dams
agriculture
EX] finding natural predators for pest to prevent crop destruction
why is ecology important for public health
disease/viruses
EX] Lyme disease and Zika virus are the results of pest-spread diseases that thrive in warmer climates
biomedical contribution
natural resources that have medicinal properties
EX] Taxol (tree) can be used for cancer treatments
natural services
EX] filtering by wetlands allows for cleaner water
levels in ecology from biggest to smallest
biosphere
region
landscape
ecosystem
community
interactions
populations
individuals
individuals
one organism
population
two or more individuals from the same species
interactions
two individuals interacting, species doesn’t matter
community
two or more species
ecosystem
all the organisms in a given area as well as the physical environment in which they live
nutrient flow
region
global processes
biotic factors
LIVING components of the ecosystem
EX] predators, prey, food, shelter (trees, etc.), competitors
abiotic factos
NON-LIVING components of the ecosystem
EX] wind, temp, soil, light, rain, climate
producer
produces own energy without eating other organisms
consumer
obtains its energy by eating other organisms
Net Primary Production (NPP)
amount of energy producers capture by photosynthesis - their metabolic heat (metabolism)
EX] plants will store extra energy by increasing biomass AKA growing bigger, producing roots, producing fruits, etc.
metabolism
chemical process that occurs within a living organism in order to maintain life (requires energy)
biomass
total mass of organisms in a particular area
evolution
change in allele frequencies (genetic characteristics) of a population over time
adaption
characteristic of an organism that improves its ability to survive or reproduce
natural selection
Process which individuals with certain characteristics tend to survive and reproduce at a higher rate because of those characteristics
natural selection can lead to evolution by changing allele frequencies in a population
observations and questions
make connection between unrelated observations using sight, sound, touch, taste and smell and using existing knowledge and experimental results
hypothesis characteristics
• Tentative explanation for observation(s) (cause-effect)
• Testable- must be able to collect data
• Cannot be proven true
• Accepted if enough evidence supports it
• Leads to predictions (if-then statements)
data collection
conclusions drawn from the data
two primary sources
observations (natural experiment)
controlled experiment
analysis
• Does evidence (data) support or falsify the hypothesis?
• Most interesting results are often unexpected
• Rethink hypothesis (feedback)
peer review
submit results to journal
reviewed by independent scientists
sample size
number of individuals in study/each treatment
independent variable
biologist manipulate this variable
dependent variable
may respond to independent variable
standardized variable
any variable held constant
controls
untreated group
important aspects of an experimental design
sample size
independent variable
dependent variable
standardized variable
control
replication
randomization
biomes
major divisions of terrestrial environment
distinguished by their predominant plants
associated with particular climates
global climate patterns
a combination of temp, moisture, precipitation and winds
driven by solar radiation
greenhouse effect
sunlight penetrates atmosphere, warms Earth’s surface
solar radiation is absorbed by the surface, escapes back into space, or molecules or greenhouse gases absorb and warm the lower atmosphere
greenhouse gas increase = temp increase
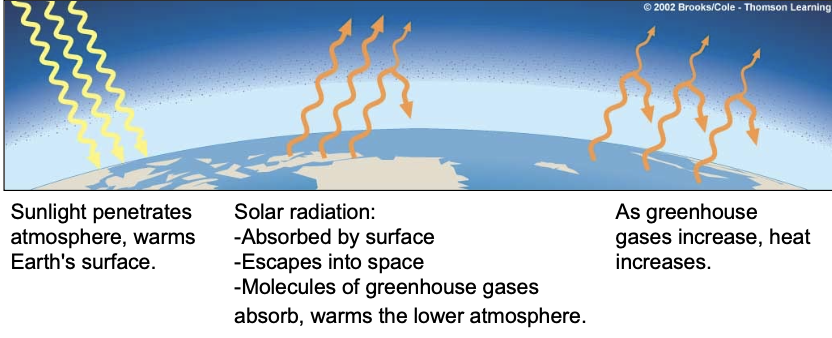
solar radiation
creates season relative to the position of the sun and the Earth’s tilt
average global temperature
hot at equator, cold at poles
Saturation Vapor Pressure
maximum amount of water the air can hold (temperate effects humidity)
solar-driven air circulation
hot air rises, cold air sinks causing dry conditions
average terrestrial precipitation
high precipitation at 0 and 60
low precipitation at 30
Coriolis effect
spin of Earth deflects win direction
wind functions
dispersal/migration
EX] can blow seeds, animals save energy flying with the wind
carries moisture
catastrophic
EX] tornado, hurricanes, wind storms
regional climate patterns determined by:
continental location (distance to water)
topographic features (mountains)
continental location
similar temperatures year round when by the water
east and west facing slopes (mountains)
mountains → rain-shadow
rain-shadow
one side is wet = windward
one side is dry = leeward
intercept air masses, cause them to rise
cooler atmosphereic temps cause vapor to condense
vapor becomes precipitation
north and south facing slopes (mountains)
south = more sunlight, less precipitate, high evaporation rates
north = less sun, more precipitation, low evaporation
urban climate
cities produce their own climate (heat dome/island)
man-made structures absorb more heat
releases heat at night
air pollution traps heat at surface
buildings alter air flow
lower humidity
albedo
amount of radiation reflected by a surface
EX] light surface = high albedo bc light reflects
dark surface = low albedo bc light is absorbed
climate diagrams
temperature on left, precipitation on right
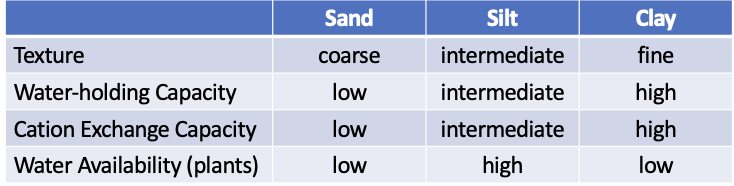
soil properties
texture (particle size) → water-holding capacity → cation exchange capacity (nutrients)
soil texture
relates to pore space between particle
movement of air and water
water storage capacity
nutrient exchange
penetration by roots
coarse soil water holding capacity
high permeability
fine soil water holding capacity
low permeability
saturated soil
amount of water that exceeds soil’s pore space
field capacity
water remaining in the pore spaces after gravity has drained the rest away (perfect conditions)
wilt point
point at which a plant can no longer withdraw water from the soil
available water capacity (AWC)
amount of water between field capacity and wilt point (water this is available to plants)
field property - wilt point = AWC
loam
best soil for crops, equal parts sand, clay and silt
function of soil
atmosphere composition
78% Nitrogen (N2)
21% Oxygen (O2)
1% others
mechanical weathering
increase surface area, roots can force their way through rocks
chemical weathering
release of soluble nutrients
leaching
movement of dissolved matter and minerals from upper to lower levels
decomposition
organic material broken down
EX] primarily plant matter, leaf litter
Humus
contains nutrients
increases water holding capacity
prevents compaction
climate influence on soils
processes most rapid in warm wet conditions
little decomposition in aquatic systems
most nutrients found in living biomass
processes slower in higher latitudes
soil abuse
poor agricultural practices
removal of vegetation
use of pesticides
use of fertilizers
bad fire
kills organisms
increases soil erosion and mudslides
exposes soil to sun
good fire
adds nutrient to soil
maintains community structure
“fire adapted” plants
can increase community diversity
tropical rainforest
soil = nutrient-poor
High temperatures, high precipitation
face deforestation/slash and burn
broadleaf evergreen trees
vertical dimension
epiphytes = plants growing on other plants
highest biodiversity
food (maize, rice, bananas, sugarcane)
prescription drugs
produce 20% of the world’s oxygen
carbon sequestration
equator
ex) brazil, congo, Malaysia
tropical dry forest and savanna
strongly influenced by abiotic factors
dry season, fire
High temperatures, wet and dry season
seasonal migrations are common
termites = 10% biomass
soil good for agriculture
Mexico, India, Australia
desert
low in organic matter
higher salt content
space plant cover, succulent plants
low abundance, high diversity
fragile habitat
good for recreational areas and solar power
Arizona, chad, Mongolia
mediterranean woodland and shrubland
cryptogamic crust
Mild wet winters, hot dry summers
high biodiversity
plants are small evergreen and adapted to drought and fire
hugely impacted by humans
produces olive oil and wine + ppl love living here
San Diego, Italy, Australia
temperate grassland
Warm wet summers, cold drier winters
deep fertile soil
67% of biomass is underground
dominated by herbaceous vegetation (formally herds herbivores)
regular fires prevent growth of trees
less than 5% remains
Kansas, Russia, China
temperate forest
Warm wet summers, cold drier winters
largest organisms (high biomass)
fertile soils
1-2% remain
boreal forest
Cold winters, mild summers, more precipitation
permafrost
low biodiversity
breeding site for tropical wintering birds
evergreen conifers
no historic human impact until recent
tundra
Cold and dry (very short growing season in summer)
layer of permafrost
low temps = slow decomposition
14% of the Earth’s carbon
herbaceous plants
lots of insects but not diverse
effected by oil and pollution
mountain climate
as elevation increases, temperature drop sea precipitation increases
lotic system
moving water
higher oxygen content
terrestrial (leaves, woody debris, dead animals)
in-stream (rooted vegetation, algae, dead animals)
affected by dams (→ fish ladders) and bridges
lentic system
standing water
lower oxygen content
limiting factor for organisms
cold water = higher oxygen
river continuum concept
stream flows downslope and increases in size
nutrient input from adjacent vegetation decreases
stream bed particles size decrease (boulders→sand)
more aquatic plants downstream
shredders
process coarse organic matter AKA tear up leaves
EX] caddisflies
collectors
collect fine particles from the water (from shredders)
EX] fly larvae
grazers
feed on aquatic plants and detritus, found on rocks and woody debris
flood pulse concept
floodplain: seasonal river flooded areas
flooding is a natural/required process
important for nutrient exchange
how is oxygen lost in lentic systems
increased temp
respiration of organisms
aerobic decomposition
biological oxygen demand (BOD)
the amount of dissolved oxygen in an aquatic system that is required for respiration by decomposers
oligotrophic lakes
lentic systems - nutrient poor
few plants/algae
deeper
low turbidity (clear)
high oxygen levels
cooler
eutrophic lakes
lentic systems - nutrient rich
plant/algae growth
shallow
high turbidity (sediments)
low oxygen levels
warmer
marsh
wetland dominated by herbaceous plants
swamp
wetland dominated by woody plants
human impact of aquatic systems
introductions
pollution
macroinvertrbrates (index of biological integrity)
benefits of wetlands
recharges groundwater aquifers
holds and discharges water slowly into aquifers
reduce the intensity of flooding
5% of wetlands can reduce flood flows by 50%
water filtration systems
vegetation takes up excessive nutrients and heavy metals
people treat urban wastewater by running it into natural or specially-created wetlands
sources of economic gain (wood products, horticultural peat, cranberry production)
habitat for a rich diversity of wildlife
protection against mangroves
marine
more salt
more stable temp
oxygen available
very different organisms
oceans
cover 71% of Earth’s surface
more uniform than terrestrial
ocean garbage islands
floating material concentrates in area between currents
upwelling
areas with high nutrients
nutrients and light required for productivity
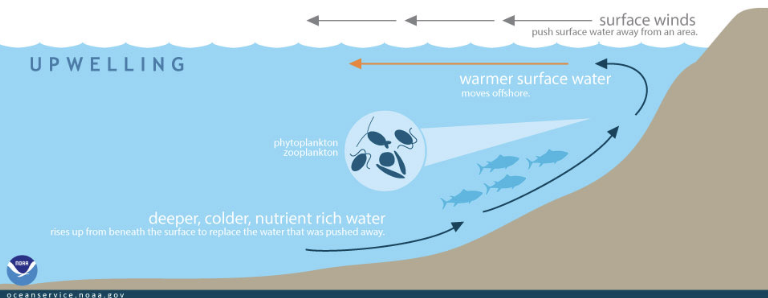
estuaries
junction of a river and the ocean where fresh water enters the ocean, freshwater flow + influx of salt water
important reproductive sites
crucial feeding areas for birds
threatened by sewage
MOST PRODUCTIVE AQUATIC SYSTEM